Unit 3 Exam
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
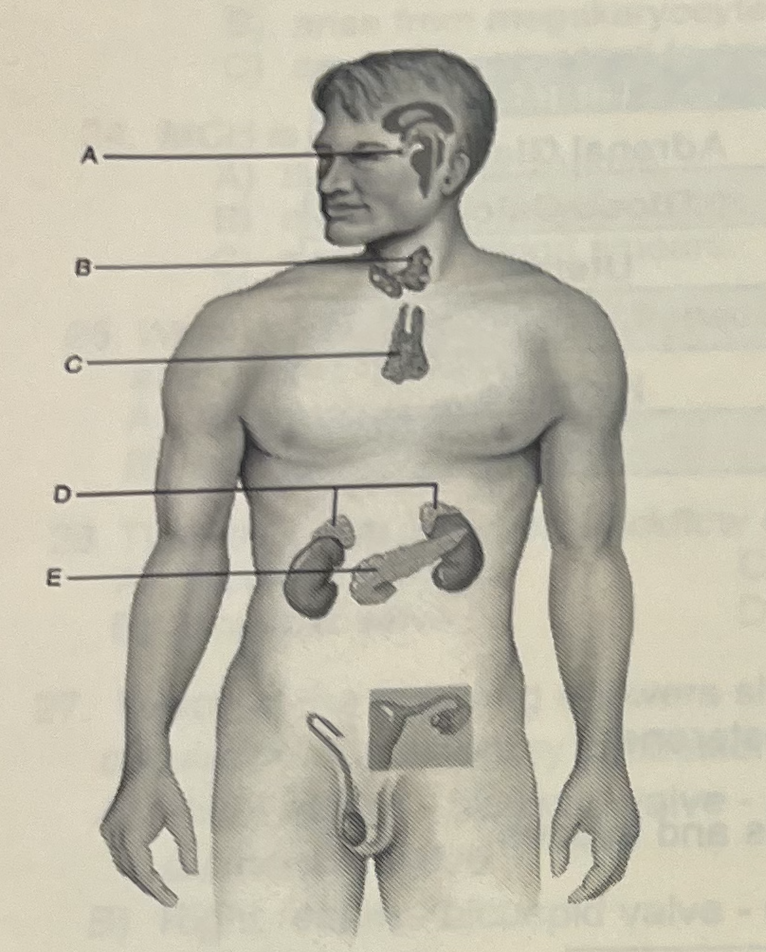
Identify the letter that indicates a gland that secretes horomones that control blood glucose levels
C (pancreas)
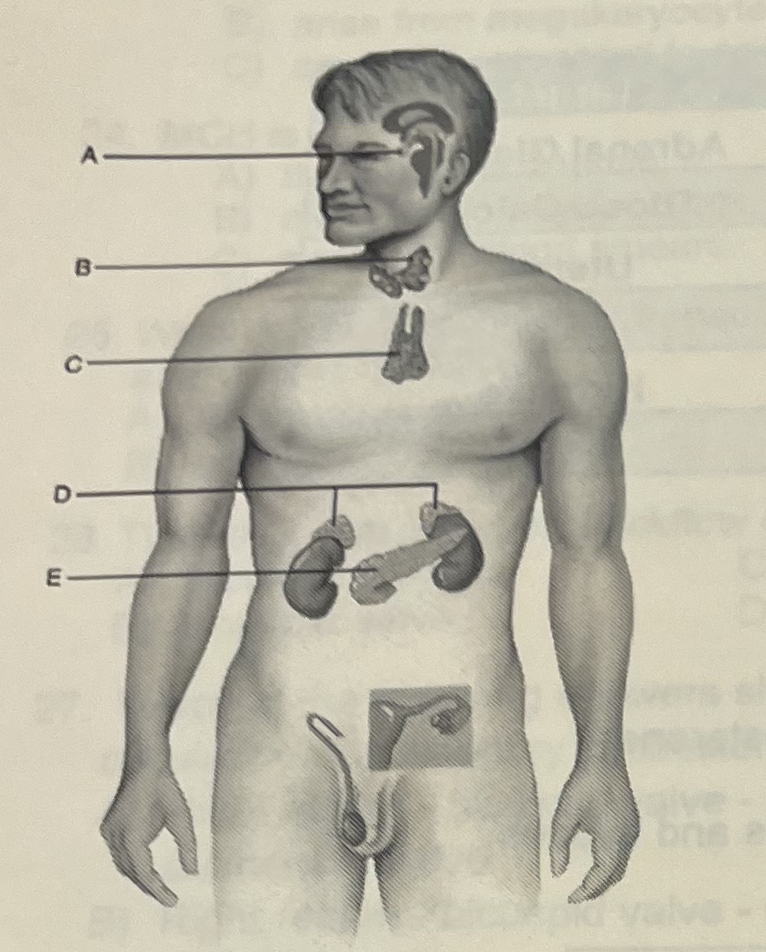
Identify the letter that indicates a “master gland” that secretes nine horomones
A (pituitary)
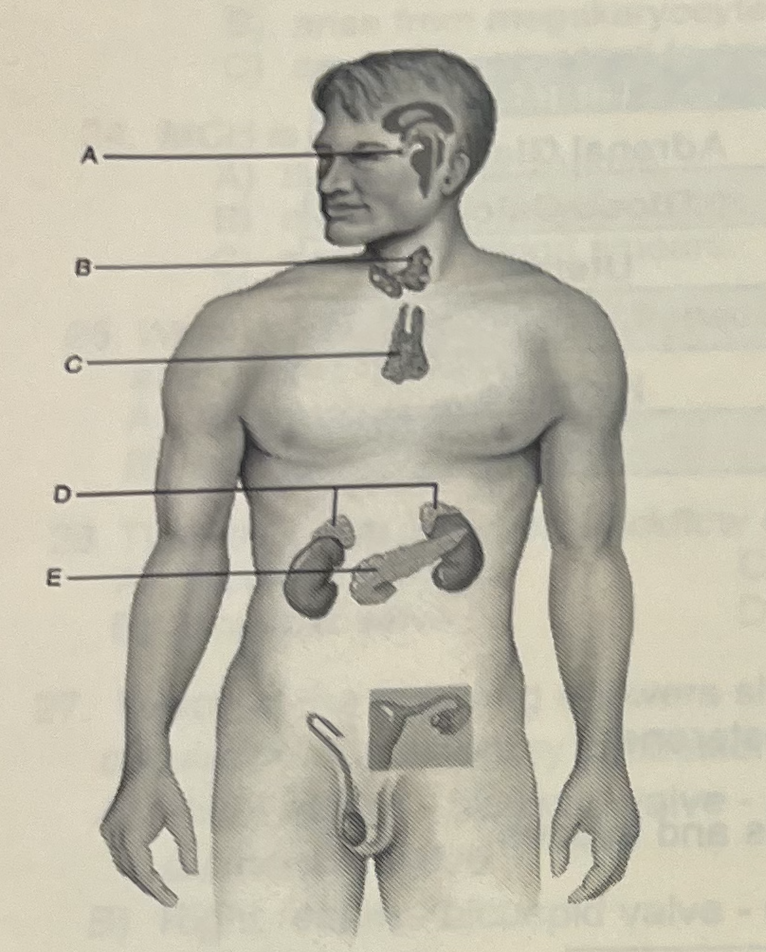
Which gland secretes horomones that control metabolic rates
B (thyroid)
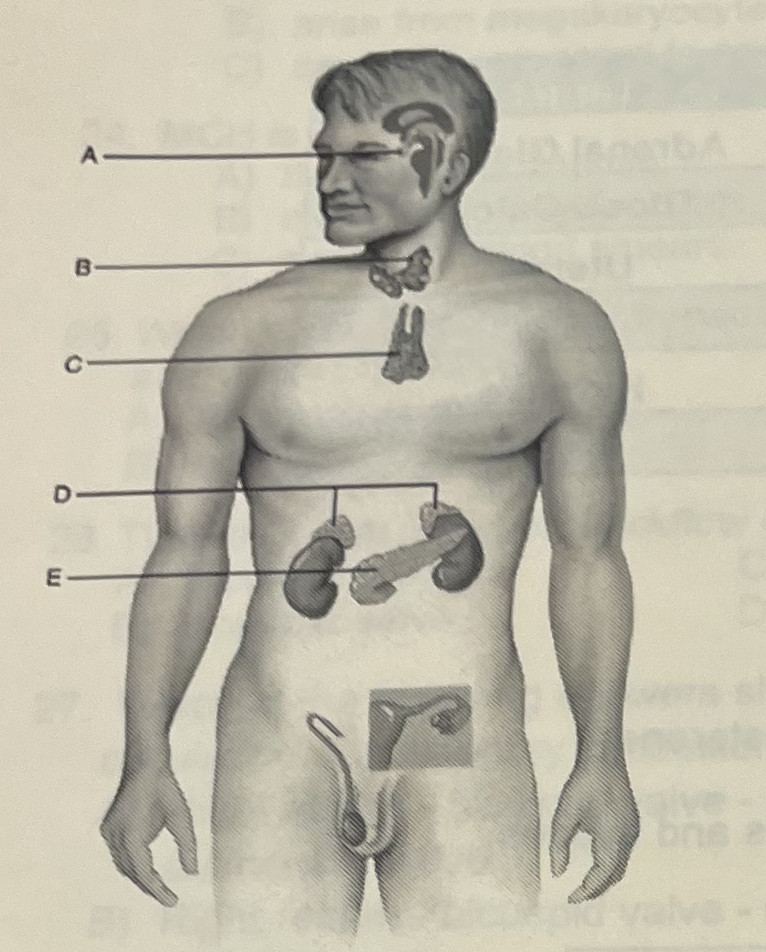
Stress (either real or imagines) would likely cause this organ to release horomones
D (Adrenal Glands)
Which of the following horomones triggers ovarian follicles to begin maturation in the female cycle?
A (FSH)
Which of the following is defined as “plasma minus clotting factors”
C (serum)
Which is the most abundant formed element
A (Erythrocyte)
Which leukocyte is primarily responsible for destroying bacteria
D (neutrophil)
Which cell transforms into a macrophage
E (Monocyte)
B (anterior pituitary)
D (progesterone)
12.
e (PTH)
A (kidneys)
14.
C (posterior pituitary)
15.
a (Kidneys)
A hematocrit measures the percentage of blood volume that consists of:
E (hemoglobin)
Which of the following organs does not form blood cells in the fetus?
B (kidneys)
Yellow bone marrow gets its color from:
D (fat)
An average female has approximately ________ of blood:
A (5.5)
Fibrinogen and albumin are examples of blood:
D (proteins)
Which answer lists the leukocytes from most to least abundant?
B (neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes…)
Which type of connective tissue mostly occurs in dormant bone marrow cavities?
D (reticular)
Thrombocytes
E
MCH is:
E
Which of the following are threadlike structures of the endocardium that prevent prolapse of the atrioventricular valves?
D
The valve that prevents backflow of blood from the systemic circuit into the heart:
C
Which answer shows the correct route of blood through the heart (systemic → pulmonary → systemic)?
D
The right atrium receives blood directly from all of the following except:
D
Large cardiac cells of the conducting system embedded in the ventricular walls between the endocardium and myocardium:
D
The “pacemaker” of the conducting system is the:
D
Which of the following vessels does not carry oxygen-rich blood?
B
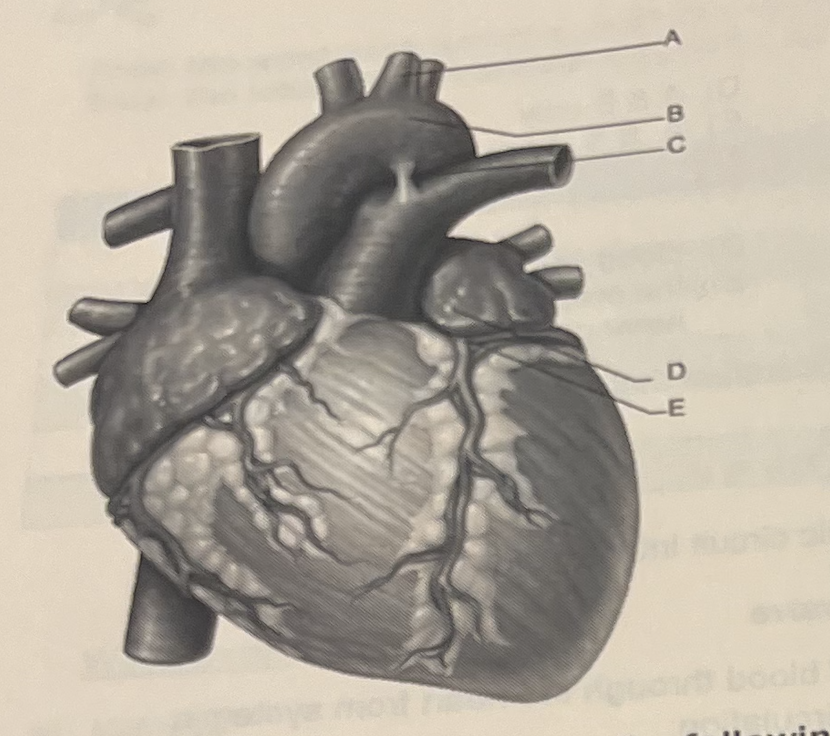
Identify the letter that indicates one of the forst tqo arteries to branch from the aorta after blood leaves the left ventricle.
E
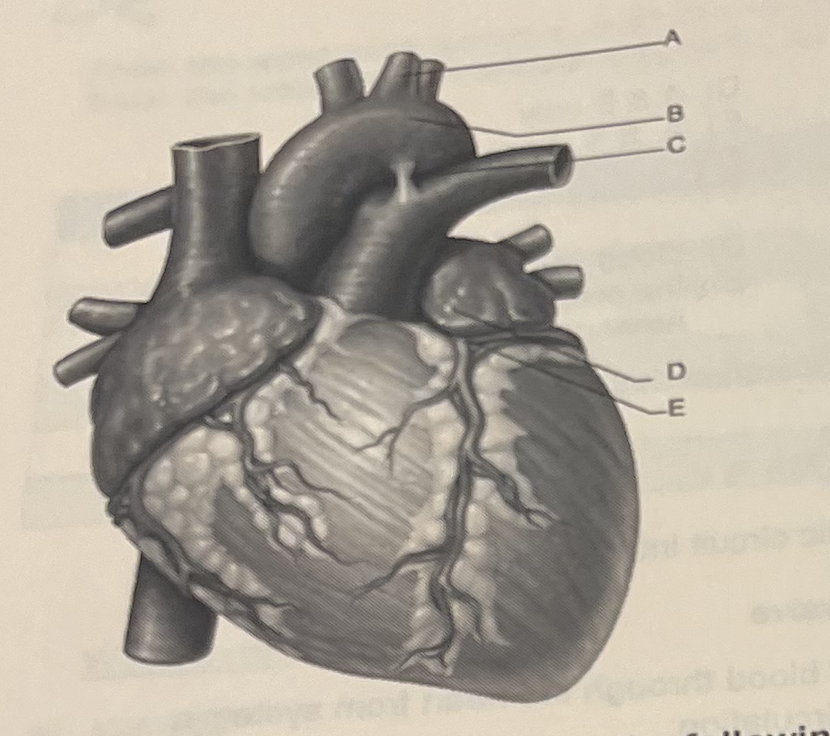
Identify the letter that indicates the largest artery of the body
A
The inner endothelial layer that lines the heart is the
D (endocardium)
Blood returning to the heart from the left lower extremity would enter the heart through which vessel?
B (inferior vena cava)
Semilunar valves are located:
A (between the ventricles and the great arteries)
An occaisionally lethal condition in which the atria are unable to pump the last of their blood becasue of rapid, “quivering” of cardiac muscle fibers is because
A (atrial fibrilation)
What is the effect of parasymphatetic stimulation on the heart?
C (it slows the heartbeat)
If the beating heart makes a “lub-dup” sound, the “dup” second heart sound is caused by
D (vibrations)
In the heart wall, the layer that contains the cardiac muscle is the
B (myocardium)
The foramen ovale in the fetal heart gives rise to which structure in the fully formed heart?
C (fossa ovalis)
The tricupsid valve is closed
D (when the ventricle is in systole)
A “coming together” of alternate pathways of blood vessels
D
Blood pressure is under greatest control in the
B
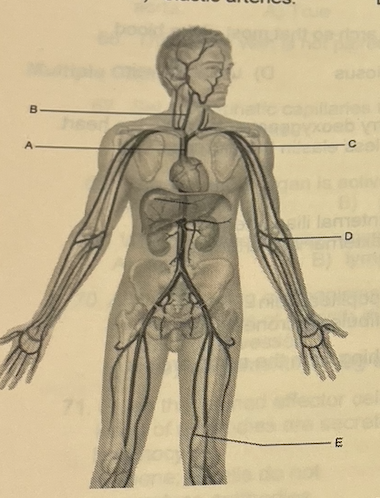
The vessel indicated by letter “A” is the
C (great)
Letter “B” supplies most of the oxygen to the right half of the brain
A
Identify the letter that indicates the longest vessel in the body
C
Most of the capillaries that are found in body
C
Present in most capillaries, these structures are absent in those of the blood-brain barrier.
C
Functionally, there are no valves in arteries (as opposed to in veins) because:
A (blood pressure)
The hepatic portal system has two distinct capillary beds separated by a portal vein. What are the functions of these two capillary beds?
B
What vessel in the fetus connects the pulmonary trunk to the aortic arch so that most of the blood bypasses the immature lungs?
C
Which of the following statements about veins is false?
C
The abdominal aorta divides at its distal end into which arteries?
B
Which of the follwoing is most likely to become a varicose vein?
D (great saphenous)
The correct proximal to distal sequence of the three vessels branching from the aortic arch is
B
What prevents the backflow of blood in veins
A
The diameter of a typical capillary is equal to or just slightly larger than”
C (erythrocyte)
Which artery arises from the inferior part of the abdominal aorta and supplies the proximal half of the large intestine?
C
The right gonadal vein drains into the inferior vena cava, but the left gonadal vein drains into the
D
Which arteries unite to form the basilar artery which in turn goes on to contribute to the posterior aspect of the cerebral anterial cirlce?
C
The circulatory route responsible for reoxygenation of blood is called:
A
Systemic blood pressure is regulated by adjusting the diameter of the aorta
B
The pulse of the popliteal artery is palpated behind the knee
A )True)
The inferior vena cava ascends to the left of the vetebral bodies and to the left of the abdominal aorta
B false
The basilar vein is not paired with an artery of the same name
A (true)
Lymphatic capillaries that collect fat-laden fluids are
C (intestinal trunk)
This lymphoid organ Is active from childhood into the twenties, and greatly diminished afterward.
C
Which lymphoid organ recycles red blood cells and initiates immune response
D spleen
All the following mechanisms help move lymph through the lymphatic vessels except
C
Given that cloned effector cells arise from a single activated lymphocyte
E (one)
Structures comprised of endothelial cells spearated ny flap like mimi valves that are opened as fluid accumulates in peripheal tissue describes
C (lymph capillaries)
Which of the following lymphoid organs is not directly involved in fighting immune battles
B (thymus)
Lymphoid tissue associated with the mucosa of digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts
A (MALT)
The immune system cell type that is targeted by infectious mononucleosis is the
A (B lymphocyte)
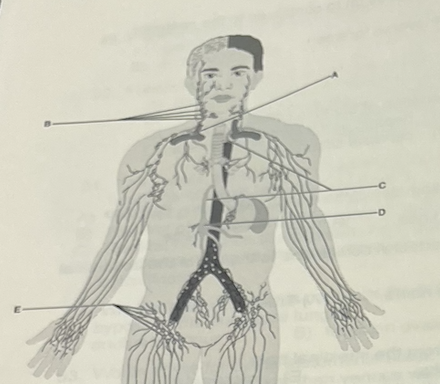
The largest kins of lymphatic vessel is a lymphatic
A (duct)
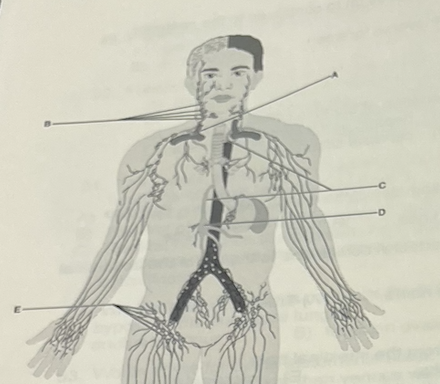
Identify the letter that indicated the large lymph vessel that drains three-quarters of the body
B
The likely area to check lymph nodes to see if breast cancer has spread would be the
D. axillary
Which of the following cells are the largest producers of antibodies?
A (plasma cells)
Which cell listed here has the responsibility of presenting antigens to lymphocytes
B (dendritic cell)
The serous membrane closest to the lung in the thoracic cavity
A (visceral pluera)
The —— flaps over the glottis during deglutition
B (epiglottis)
Fluid that reduces surface tension of the alveolar walls
C (surfactant)
Which structure is not located within the nasopharynx
B (palatine tonsil)
Which of the following is not a function of the nasal conchae?
D
When the diaphragm contracts, the size of the thoracic cavity increases, the pressure inside the thoracic cavity drops, and air flows into the lungs.
D (increases: drops: out of)
Sympathetic stimulation of terminal bronchioles causes
B
The right lung
A (has three lobes)
What epithelium occurs in the respiratory membrane?
B (simple squamous)
Most foreign substances in inspired air fail to reach the lungs because of the
D
The ability to vary the pitch of the voice results from varying
B
An aortic aneurysm or upper lung tumor that presses on the left recurrent laryngeal nerve could lead to
C
The vocal ligaments attach between the thyroid cartilage and the
A
At birth we only possess what fraction of alveoli that our lungs will have at maturity?
B
The ventral respiratory group (VRG) is a group of neuron cell bodies located within the
B
Identify one element of innate (inborn) immunity.
Skin (mucous membranes)
Where does external respiration take place?
Alveoli of the lungs
Name the organ that releases hormones that help us cope with both short and long-term effects of stress and name one of the “stress” hormones that it secretes.
Adrenal gland; Cortisol (epinephrine)
What mineral “unlocks” thyroid hormone and what organ malformation occurs if a person has a prolonged dietary deficiency in this mineral?
Iodine; Goiter
What two systems did we discuss where deoxygenated (blue) blood is carried by arteries?
Pulmonary System and fetal circulatory system