Leukemia and Immunology
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is the most common cause of spontaneous tumor lysis syndrome in leukemia?
High tumor burden outgrowing vascular supply → hypoxia → Na⁺/K⁺ ATPase failure → cell swells and eventually lysis
What are the hallmark metabolic derangements in tumor lysis syndrome?
Hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, hyperuricemia, elevated LDH


Why does tumor lysis cause hyperkalemia?
Intracellular K⁺ is released from lysed tumor cells (bc of Na?K pump the cells have lots of K inside them)


Why does tumor lysis cause hyperphosphatemia?
Tumor cells are rich in phosphate from nucleotides and phospholipids


Why does tumor lysis cause hypocalcemia?
Phosphate binds calcium → calcium phosphate precipitation (Ca2+ sticks with phosphate and becomes calcium phosphate so less free Ca2+)


Why does tumor lysis cause hyperuricemia?
Cell lysis=>Nucleotide breakdown and spread → purines → xanthine → uric acid via xanthine oxidase


Why is LDH elevated in tumor lysis syndrome?
Tumor cells rely on glycolysis → LDH converts pyruvate to lactate to regenerate NAD⁺ for glycolysis (tumor cells hoard LDH)


What is the mechanism of urate nephropathy in Tumor Lysis Syndrome?
Uric acid precipitates in acidic renal tubules → obstructive nephropathy
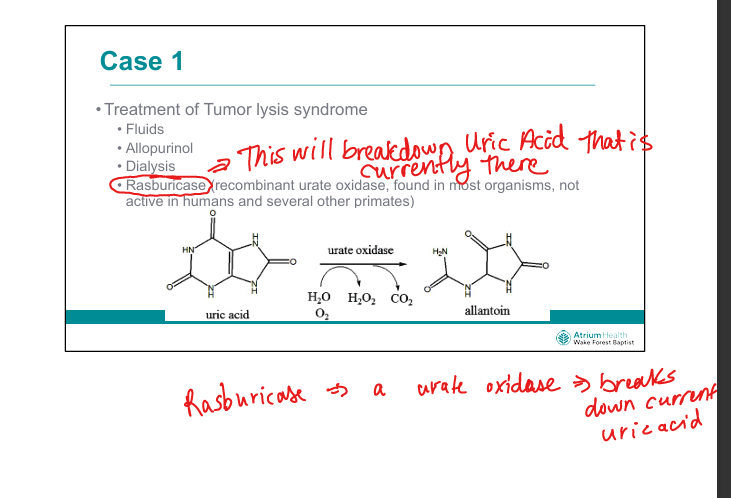
What is the role of allopurinol in TLS?
Xanthine oxidase inhibitor → prevents new uric acid formation (but doesn’t reduce existing urate)
What is the role of rasburicase in TLS?
Recombinant urate oxidase → converts uric acid to allantoin (soluble)

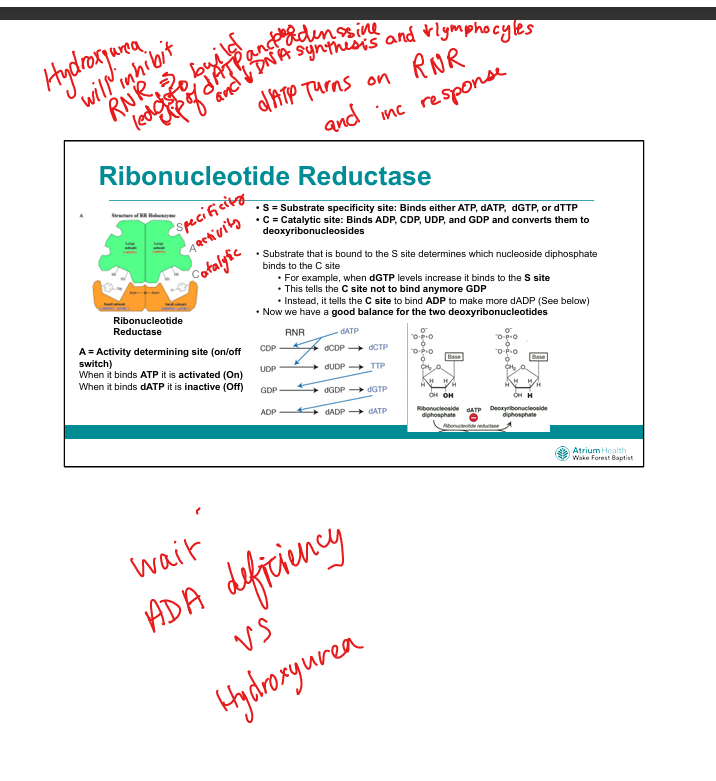
What is the mechanism of hydroxyurea in Acute Myeloid Leukemia?
Inhibits ribonucleotide reductase → blocks dNTP synthesis → S-phase arrest and no DNA synthesis

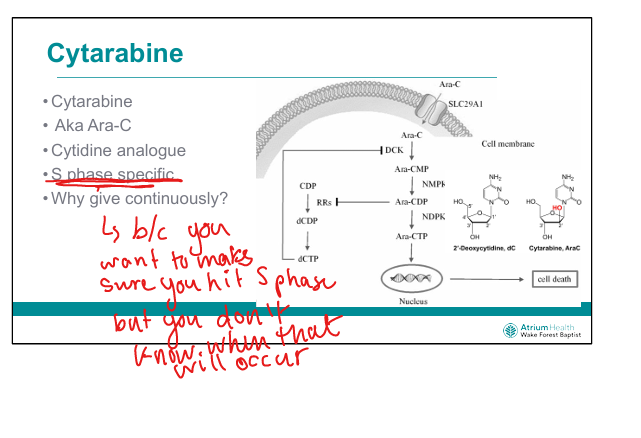
What is the mechanism of cytarabine (Ara-C)? (C makes an S sound)
Cytidine analog → incorporated into DNA → chain termination during S-phase
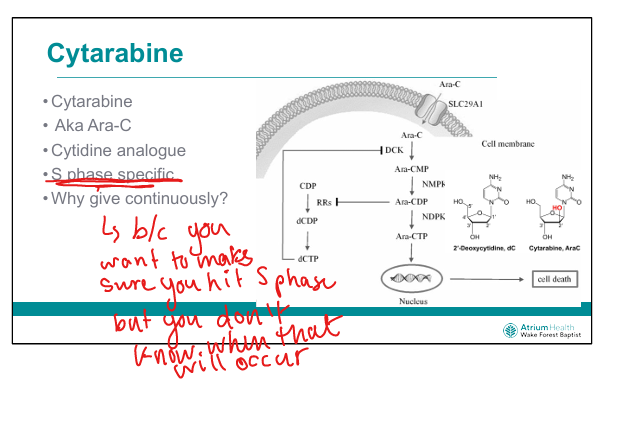

Why is cytarabine given by continuous infusion?
To ensure exposure during S-phase, which varies across tumor cells

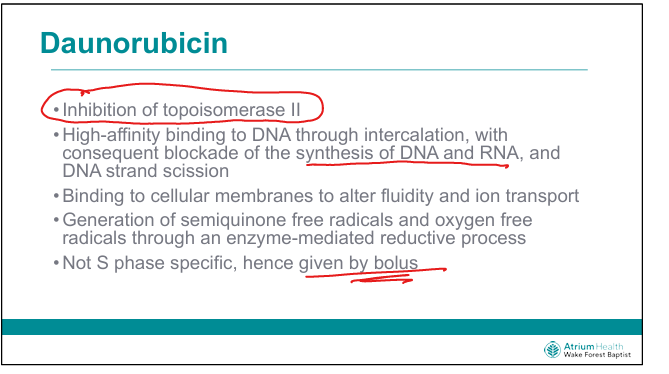
What is the mechanism of daunorubicin?
Intercalates DNA, inhibits topoisomerase II, generates free radicals → DNA damage (Think RUBs help me unwind)

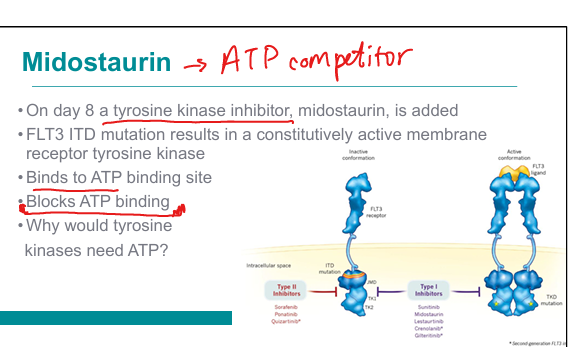
What is the mechanism of midostaurin in FLT3-mutated AML?
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor → blocks ATP binding to FLT3 receptor → inhibits signaling
Brute memorization as of now

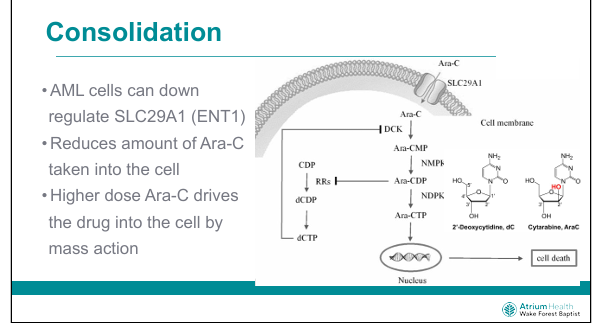
Why does high-dose cytarabine overcome resistance?
Overcomes downregulation of ENT1 (SLC29A1) by mass action

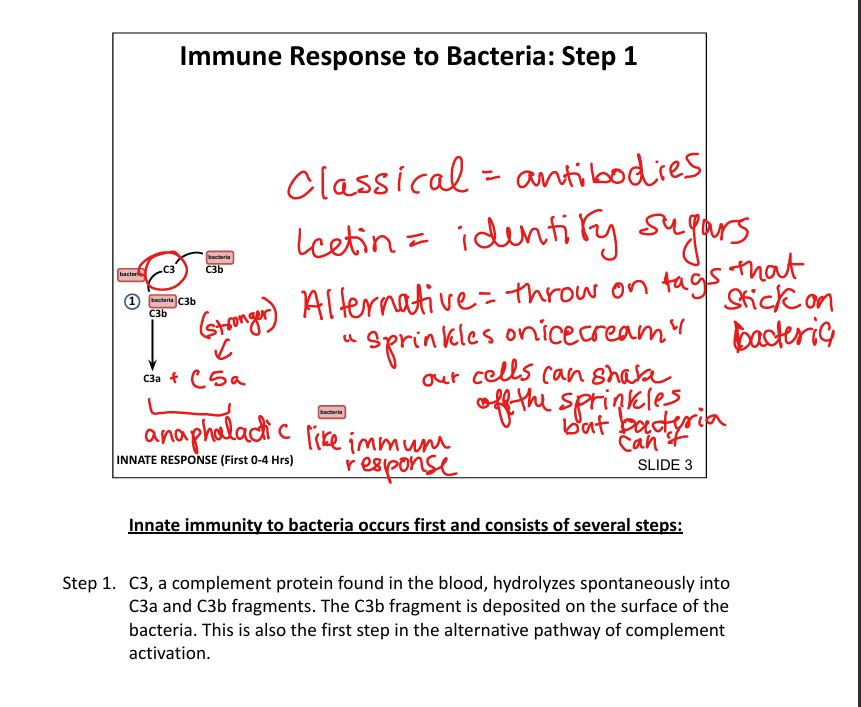
What is the first step in the innate immune response to bacteria?
Spontaneous hydrolysis of C3 → C3b binds bacterial surface (alternative pathway»sprinkles on icecream)

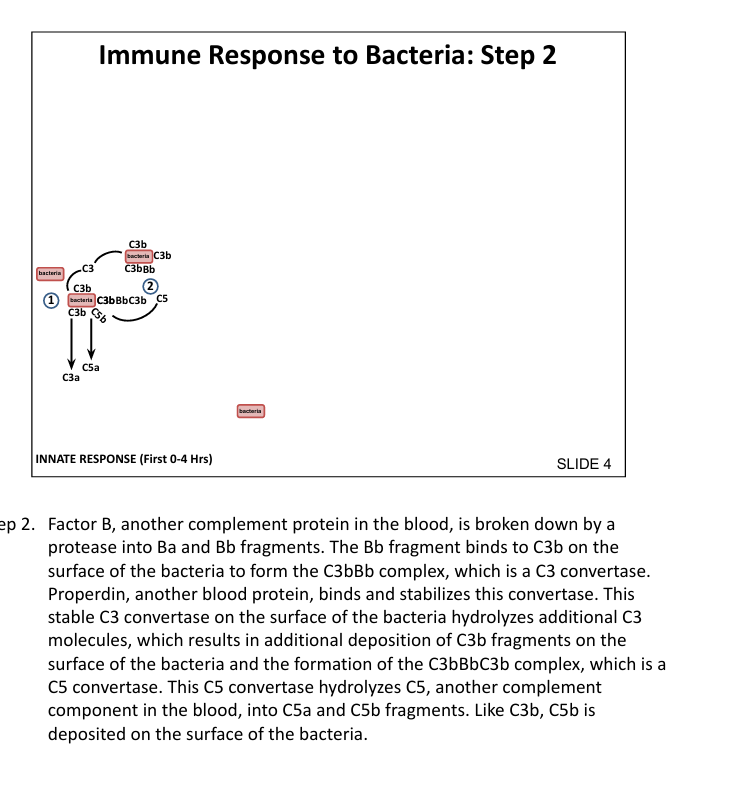
What stabilizes the C3 convertase on bacterial surfaces?
Properdin binds C3bBb complex
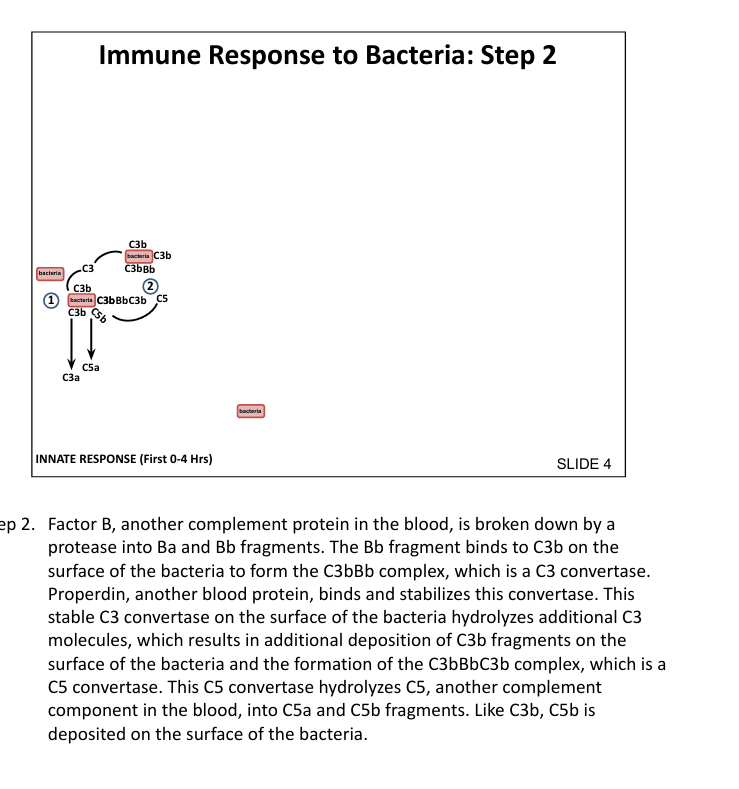

What is the function of C5 convertase?
Cleaves C5 → C5a (inflammatory) and C5b (initiates MAC)

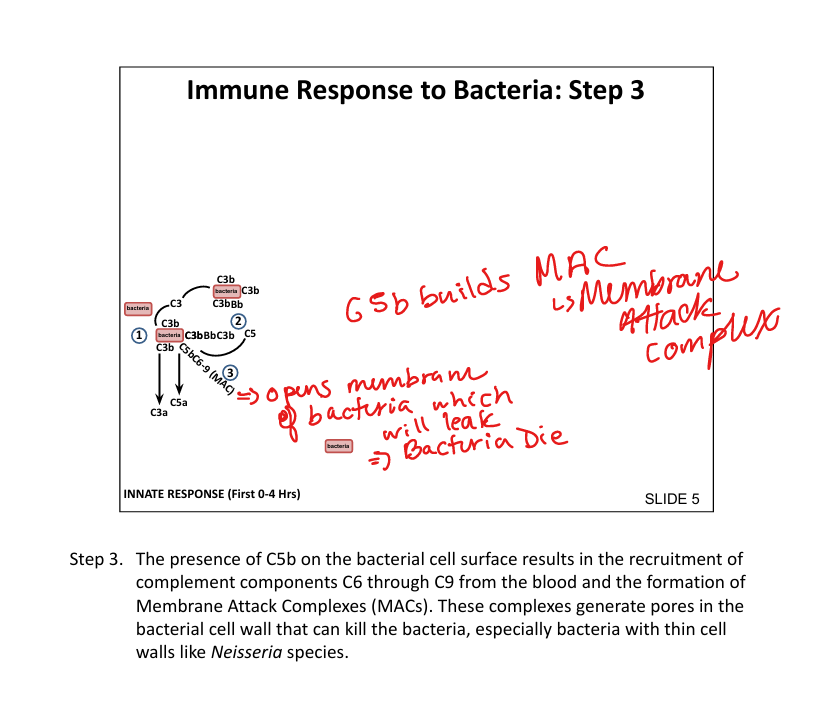
What is the membrane attack complex (MAC)?
C5b + C6throughC9 → forms pore(drills a hole) in bacterial membrane → lysis (bacterial cell leaks out and dies (especially Neisseria)

What are the roles of C3a and C5a?
Anaphylatoxins → recruit and activate neutrophils, increase vascular permeability, inflammation
How does C3b enhance phagocytosis?
Opsonizes bacteria → binds CR1 on neutrophils/macrophages
What cytokine is produced by macrophages upon PRR activation?
IL-12
What does IL-12 do?
Activates NK cells → secrete IFN-γ → activates macrophages
What cytokines are secreted by activated macrophages? (think inflammation)
TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-12 → promote inflammation
What signals are required for CD4⁺ T cell activation?
TCR:MHC II + CD28:CD80/86 (costimulation)
What cytokine drives TH1 differentiation?
IL-12 (from DCs/macrophages) and IFN-γ (from NK cells)
What is the function of TH1 cells?
Secrete IFN-γ → activate macrophages to kill intracellular bacteria
How do B cells recognize bacterial antigens?
BCR binds antigen + CR2 binds C3d → strong activation

What is the role of Helper T cells?
Provide help to B cells in germinal centers → class switching and affinity maturation
How do antibodies enhance phagocytosis?
Fc receptors on phagocytes bind Fc region of IgG-coated bacteria
How does the classical complement pathway get activated?
C1q binds Fc region of antibody on bacteria → activates C3 convertase (Classic= C1 binds Fc of antiBody)

How does the Lectin pathway get activated
identifies sugars(ex: mannose); eventually forms C3 convertase
How does the alternative pathway get activated?
Spontaneous hydrolysis of C3»c3 convertase

CD19 is a marker for____. Low CD19 with normal CD3 incidates:
B-cells. Indicates X-linked agammaglobulinemia or Bruton’s/BTK where B cells are missing but T cells are normal
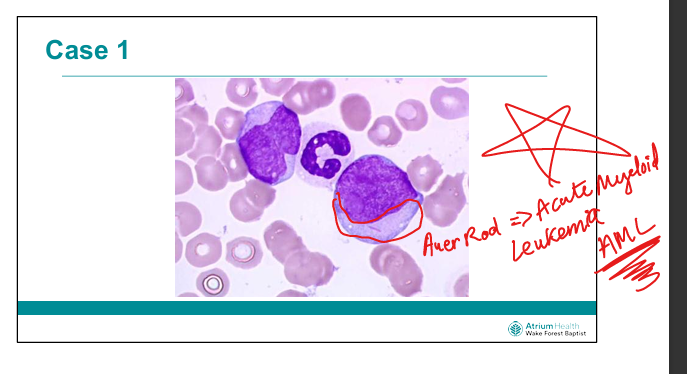
What histological feature is pathomneumonic to Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Auer Rod