Psychology - Social Influence
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AQA Social Influence
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
conformity definition
a change in a person's behaviour or opinions as a result of real or imagined pressure from a person or group of people
Compliance
‘going along with others’ in public but privately not changing personal opinions and/or behaviour - e.g. putting on an accent
Identification
The attitude, behaviours and norms associated with a particular social role are adopted e.g. teachers and students
Internalisation
occurs when a person genuinely accepts the group norm e.g. converting religion
informational social influence
believe other people to be right (Sherif - dot in a dark room estimation of movement - individual, group then individual)
normative social influence
to be liked or accepted by the group since public approval is more important than the issue itself (Asch - stimulus line and 3 other lines)
% of conformity for Asch’s experiment
37% of the time the real participant gave the wrong answer with 75% conforming at least once
Jenness (evaluation of conformity - STRENGTH)
estimate number of jellybeans in a jar - individual estimates moved towards estimates of groups (ISI)
Perrin + Spencer (evaluation of conformity - LIMITATION)
reproduced Asch’s study with British students from engineering, maths and chemistry courses - 0.25% compared to 37% (+ lacks time validity - McCarthyism)
Smith + Bond (evaluation of conformity - LIMITATION)
reviewed 31 studies of conformity in different cultures using Asch’s procedure - 14% in Belgium with 51% in Zimbabwe (culture differences - collectivist = more likely to conform)
group size affecting conformity data (ASCH)
1 participant + 1 confederate = 3%
1 participant + 3 confederates = 32%
1 participant + 6 confederates = 37%
unanimity affecting conformity data (ASCH + social support)
if one confederate disagreed = 32% → 5.5%
if one confederate gave a diff wrong answer = 9%
task difficulty affecting conformity data (ASCH)
conformity increases suggesting ISI
Bond (evaluation into variables affecting conformity - LIMITATION)
quick to accept Asch’s findings about size so majority used 3 as max
Zimbardo’s research
converted a basement of Stanford university into a mock prison
used volunteer sampling to get 14 participants that were then randomly assigned to either a guard or prisoner role
prisoners = regulated daily routines, follow all rules enforced by the guards, no names used (only numbers) and wore the same dress
guards = had own uniform with a wooden bat, handcuffs, keys mirror shades + complete control over prisoners
STOPPED AFTER 6 DAYS INSTEAD OF 14
Results of Zimbardo’s research
both guards and prisoners conformed to their roles
within hours the guards began to harass prisoners, behaving in a brutal and sadistic manner
prisoners rebelled against the harsh treatment but was quashed and soon become subdued, depressed and anxious
Abu Ghraib (evaluation of Zimbardo’s research - STRENGTH)
real life application - notorious for the torture and abuse of Iraqi prisoners
Reicher + Haslam (BBC prison study - evaluation of Zimbardo’s research - LIMITATION)
participants didn’t conform automatically as guards failed to identify with their role
individual differences (evaluation of Zimbardo’s research - LIMITATION)
1/3 behaved brutally
1/3 applied rules fairly
1/3 sympathised with prisoners
Banuazizi + Mohavedi (evaluation of Zimbardo’s research - LIMITATION)
merely play acting as was a simulation - demand characteristics - based off character in ‘Cool hand Luke’
lack of realism
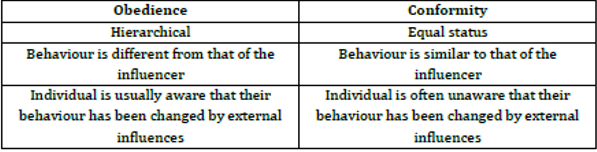
obedience vs conformity
findings of Milgram’s experiment
(learner + teacher + electric shocks)
no one stopped before 300V
65% gave max shock of 450V
dissented verbally but when prodded by experimenter carried on
location affecting obedience (MILGRAM)
Yale = prestigious setting, 65%
run-down office block = 47.5%
proximity affecting conformity (MILGRAM)
in different rooms = 65%
in same room = 40%
push hand down = 30%
instructions over phone = 20.5%
uniform affecting conformity (MILGRAM)
lab coat = 65%
everyday clothes = 20%
Bickman’s study (evaluation of situational variables - STRENGTH)
(made requests on street e.g. pick up rubbish)
guard = 38%
civilian = 19%
Bushman (evaluation of situational variables - STRENGTH)
(give change to motorist)
woman in uniform = 70%
smart clothes = 58%
Miranda (evaluation of situational variables - STRENGTH)
(cultural research + high control as limited extraneous variables = causality)
90% of Spanish students obey
ethical issues (evaluation of situational variables - LIMITATION)
deception, no right to withdraw, no protection from harm (stressed - biting nails, sweating)
BUT had debrief and 84% glad taken part a year later
Hofling’s study
unknown doctor instructed 22 nurses by phone to give 20mg of Astrofen (max 10mg on box + no signature from doctor) - 21 of 22 obeyed
legitimacy of authority
people perceived to be in a position of power so feel obligated to obey e.g. teachers
agentic state
acting as an agent for authority so don’t feel responsible for their actions (authoritative figure is responsible)
Milgram study supporting agentic state
participants could instruct a confederate to press the switches (65% → 92.5% going to max 450V)
authoritarian personality
Adorno - concluded people with this personality have a tendency to be especially obedient as have extreme respect for it (conventional attitudes to sex, race, gender etc.)
Elms + Milgram (supporting authoritarian personalities)
interviewed 20 of the obedient participants and 20 defiant ones - obedient ones have high levels of authoritarianism and saw experimenter admirably
Altemeyer (supporting studies of authoritarian personalities)
those with this personality type gave themselves higher shocks
Pre-war Germany (limitation to authoritarian personality)
millions obeyed but unlikely all possess authoritarian personality
internal locus of control
they are in control of their destiny and their actions make a difference - higher resistance as less need for social approval
Shute (evaluation of internal locus of control - STRENGTH)
exposed undergraduates to peers who expressed their attitudes to drug taking - those with internal locus of control conformed less to expressing pro-drug attitudes
Spector (evaluation of internal locus of control - STRENGTH)
Measured LoC and predisposition to NSI and ISI in 157 undergraduates and found a significant correlation with internal LoC and NSI as lower need for social approval
Holland (evaluation of internal locus of control - STRENGTH)
repeated Milgrim’s study and measured if internal or external
37% internals didn’t continue to 450V
23% externals didn’t continue to 450V
Oliner + Oliner (evaluation of internal locus of control - STRENGTH)
interviewed 406 German people who had sheltered Jewish people from Nazis and majority internal LoC
Twenge et al (evaluation of internal locus of control - LIMITATION)
analysed data from American obedience studies showed people have become more resistant but also more external LoC
social support
the presence of people who resist pressures to conform or obey can help others do the same
obedience in Milgram’s experiment for social support
65% → 10% when genuine participant joined by a disobedient confederate
Allen + Levine (evaluation of social support - STRENGTH)
conformity reduced on a task involving visual judgements if with a dissenter even if admit to sight problems
Mullen et al (evaluation of social support - STRENGTH)
disobedient models broke the law by jay walking which caused increase in jay walking even when not around
Rosentrasse protest (evaluation of social support - STRENGTH)
1943 - group of German women protested and demanded for the release of their Jewish husbands + sons
Gamson et al (evaluation of social support - STRENGTH)
discuss fake scenario about an oil company firing an employee for immoral behaviour + filmed + cameraman told participants to argue from one point of view - 29 of the 33 groups didn’t let video be used
minority influence
a minority of people persuade others to adopt their beliefs, attitudes or behaviours leading to internalisation
consistency affecting minority influence
maintain the same belief over time as draws attention to the minority view
commitment affecting minority influence
demonstrate dedication to their position by making personal sacrifices to show not acting out of self-interest
flexibility affecting minority influence
must show you accept the possibility of compromise and be prepared to accept reasonable and valid counter arguments
Moscovici et al (evaluation of minority influence - STRENGTH)
‘calling a blue slide green’ - 23 groups of six women with 2 confederates to say green
consistent minority - 8.2% convinced
inconsistent minority - 1.23% convinced
Wood et al (evaluation of minority influence - STRENGTH)
meta-analysis of almost 100 studies found minorities who were consistent = influential
Nemeth + Brilmayer (evaluation of minority influence - STRENGTH)
studied role of flexibility when discussing amount of compensation to someone in a ski lift accident - the confederate that was open to compromise influenced the group
Papastamou (evaluation of minority influence - STRENGTH)
questionnaire about responsibility for pollution and when the extreme minority view was flexible by compromising they were seen as cooperative and more persuasive
social change
process by which society as a whole adopts a new belief or way of behaving which then becomes widely accept as the ‘norm’
stages of social change
attention of majority drawn to an issue
cognitive conflict - start to rethink
consistency
the augmentation principle - minority must be open to suffering
the snowball effect - more and more people are persuaded
African American civil rights movement
marches drew attention to issue
other people began to rethink issue
many marches with lots of people
walk to work + ‘freedom fighters’ beaten
more and more people persuaded until civil rights act passed
Nemeth (evaluation of social change - STRENGTH)
the ‘dissent’ of minorities leads to individuals opening their mind to information and consider other options
Nolan (evaluation of social change - STRENGTH)
messages were hung on the front doors and houses every week for a month about reducing energy usage - caused less energy usage