2.01, 2.04, 2.05, 2.07-2.21 Fundamentals of circuits
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is the formula between power, current and voltage
Power = current x voltage
Formula between energy transferred, current, voltage and time
Energy transferred = current x voltage x time
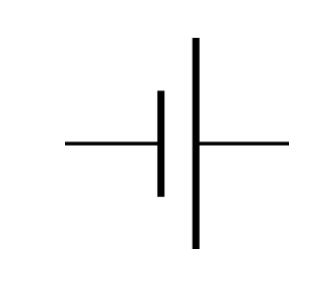
Cell
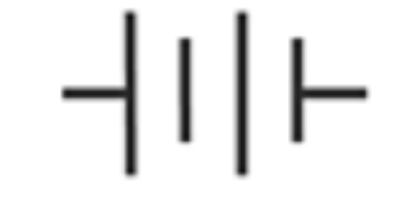
Battery
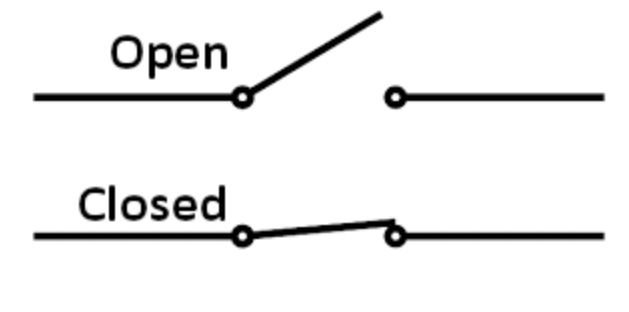
Switch

Fixed resistor
What does a resistor do
Limits or resists the current flow
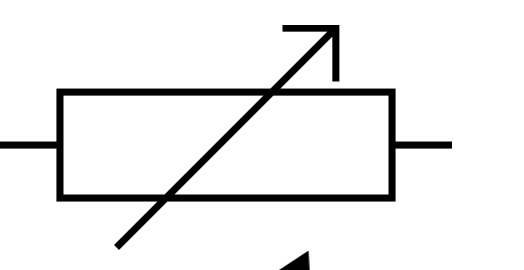
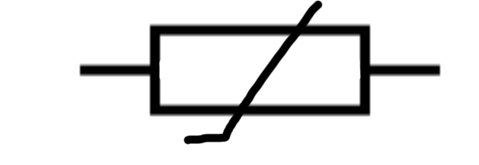
Variable resistor
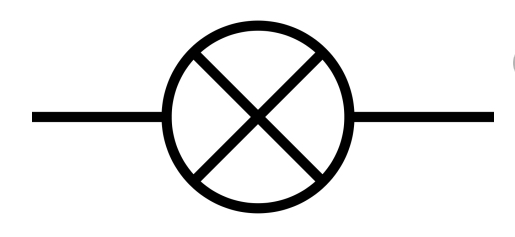
Lamp
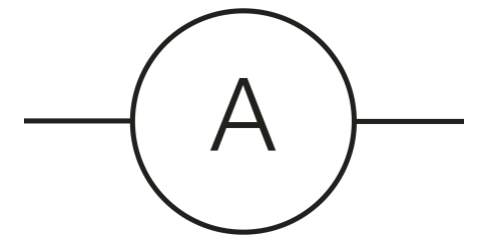
Ammeter

Voltmeter

Fuse
What does a fuse do
It is a wire that melts when a high current flows through it, breaking the circuit so that it prevents electrical damage or injury
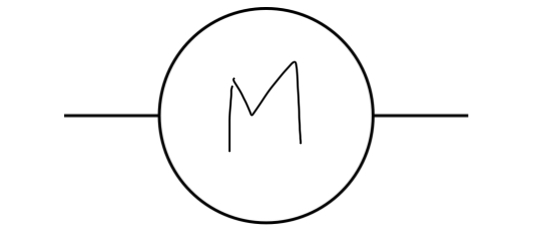
Motor
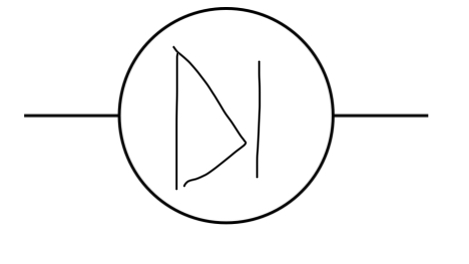
Diode
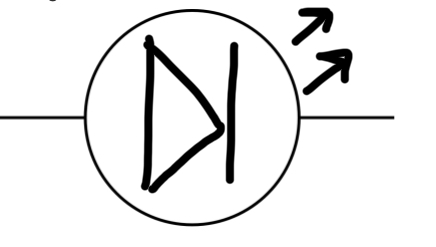
LED
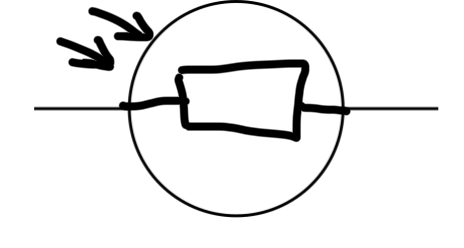
Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)
Thermistor
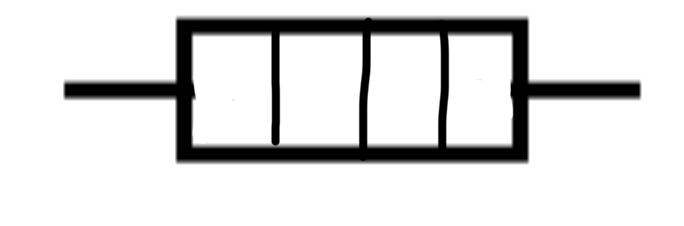
Heater
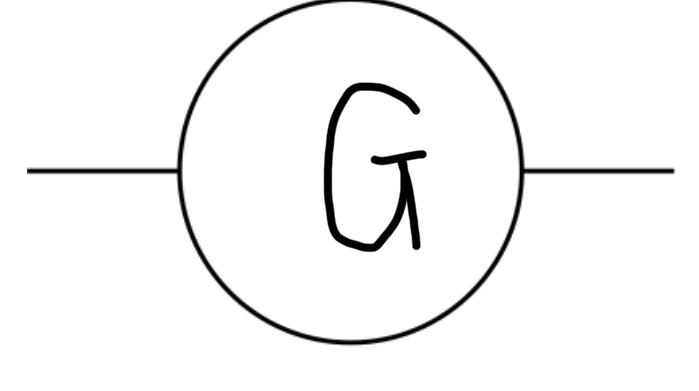
Generator
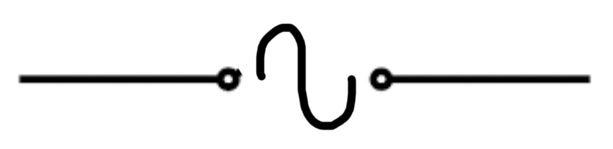
Power supply (AC) Alternating Current
What way does flow charge?
From positive to negative
What is current?
The rate of flow of charge (electrons) through a circuit per second
What does an ammeter do
Measures current
Describe the current in a series circuit
The current in the same anywhere in the circuit
Where can you connect an ammeter on a series circuit
Anywhere
Describe the current in a parallel circuit
The current splits at the junction and the current of each branch equals the current from the power source
Advantages of parallel circuit
If one branch of the series breaks the others are still intact and work, all bulbs will end up the same brightness and brighter
What is voltage
Amount of energy per unit charge
Where to put a voltmeter
Across a component
Explain the voltage in a series circuit
It is shared equally amongst each component
Explain the voltage in a parallel circuit
Voltage is the same across every branch of the parallel circuit
What is resistance
It is how hard it is to produce a big current in a circuit.
What is ohms law?
Voltage = current x resistance
How to draw diode in circuit
The arrow points to the negative side from the positive side
What does an IV graph measure?
Current (y axis) against voltage (x axis)
What does a linear line mean on an IV graph?
The resistance is constant
Components with a linear IV graph
Fixed resistor (at constant temp), wires (at constant temp)
Components with a non linear IV graph
Filament lamps, diodes, LDRs, thermistors
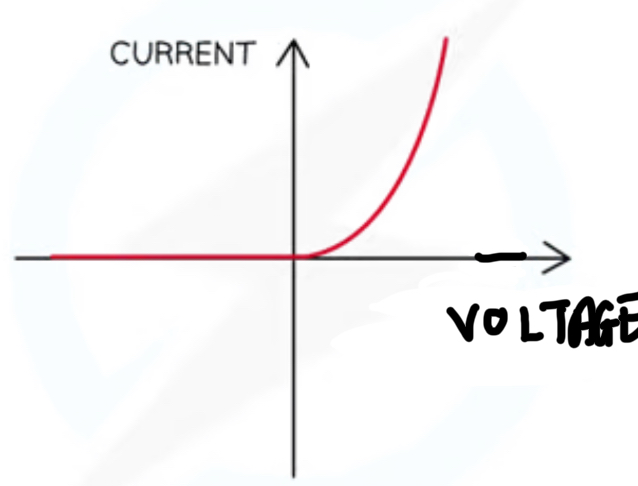
What component is this IV graph for
Diode
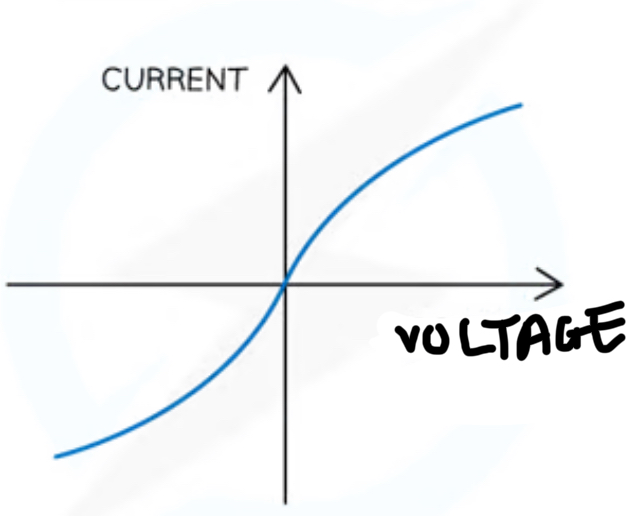
What component is this IV graph for
Lamp
Why does the resistance of the lamp increase as the current of the lamp increase
Higher current causes higher temperature, causing atoms to vibrate more, causing increase in resistance as it becomes more difficult for free electrons to pass through, causing more resistance
Describe relationship between voltage and current in lamp
As the voltage increases, the current increases but at a proportionately slower rate
How can you read resistance on an IV graph
The flatter the slope, the higher the resistance
Describe the relationship between resistance and light intensity in an LDR
As the resistance increases, the light intensity decreases
Describe the relationship between the resistance and temp in a thermistor
As resistance increases, temp decreases
Formula with energy, charge and voltage
Energy = charge x voltage
Formula with power, energy, time
Power = energy/time