Lecture 8 - Adrenergic Neurotransmission
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
catecholamines
chemical messengers (neurotransmitters and hormones) like dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), produced mainly by the adrenal glands
where does NE function
neuroeffector junction and CNS
catecholamine SAR
• Catechol: 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl; phenols and catechols are weak acids (pKa ~ 10)
• Amine: 1o or 2o amines, strongly basic (pKa ~ 9). Predominantly ionized at pH 7.4. Ionized form (+ charge) is required for binding to adrenergic receptors.
• Phenylethyl: spacer + aromatic ring
• Optical isomerism: Norepinephrine (NE) and Epinephrine (Epi) (β-OH group). The R-enantiomers are more potent than the S-enantiomers
catecholamine instability (what rxns can it go through)
oxidation to turn -OH on catechol to O=C, COMT O-methylation to turn a -OH on catechol into H3CO
biosynthesis of catecholamine location
presynaptic neurons
overall mechanism of catecholamine biosynthesis
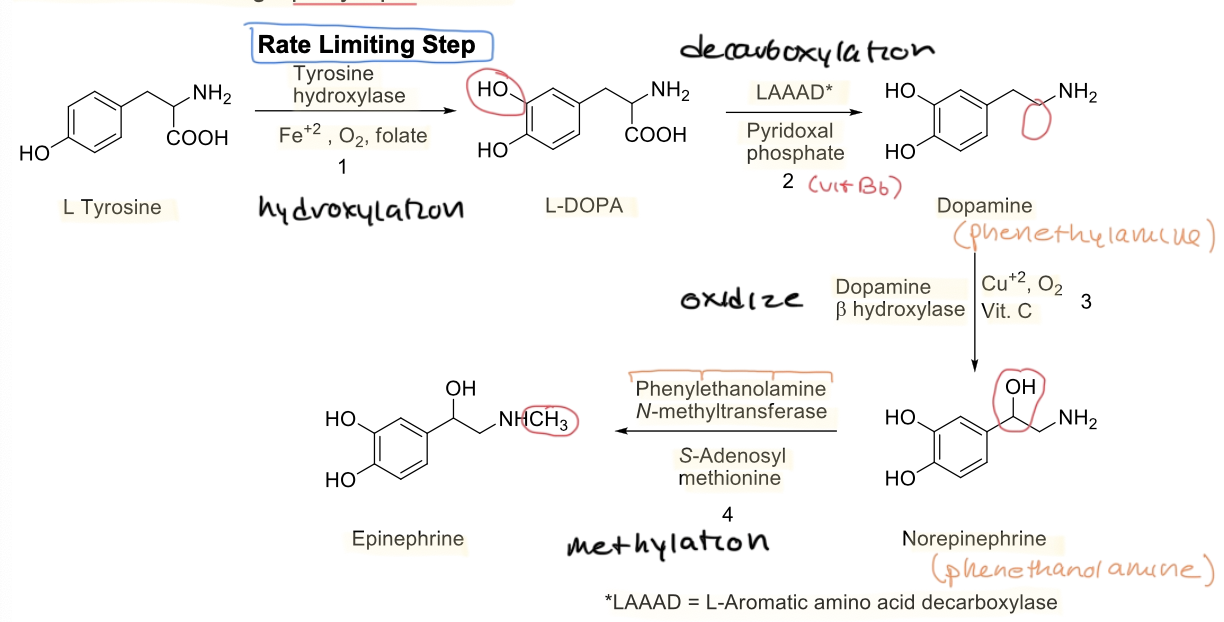
rate limiting step of of catecholamine biosynthesis
L tyrosine —> L-DOPA via tyrosine hydroxylase and Fe2+,O2,folate
order of catecholamine formation
dopamine —> norepinephrine —> epinephrine
where is norepinephrine stored
adrenergic presynaptic nerve terminals in storage vesicles as granules
when is NE released
Released in response to an action potential, which depolarizes the neuronal cell membrane.
what lets NE get into synaptic cleft
Ca2+ entering nerve ending due to action potential
what happens when NE binds the presynaptic alpha 2 receptor (in synapse)
1. Amount of NE released is DECREASED.
2. Reuptake of NE from the synapse into presynaptic neuron is INCREASED.
3. Biosynthesis of NE is DECREASED
goal when NE binds to presynaptic neuron in synapse
lessen adrenergic neurotransmission (vacuum up what’s in synapse)
where are adrenergic receptors located
both pre- and -post synaptically
what does alpha1 – Gq do
activation of PLC (effector) which catalyzes the hydrolysis of PIP2 to produce DAG and IP3 (second messengers)
what does alpha 2 – Gi do
inhibits adenylate cyclase (effector) and decrease formation of cAMP (second messenger)
what does beta - Gs do
beta 1-cardiac, beta 2-bronchial, uterine, vascular smooth muscles, beta 3-adipose stimulate adenylate cyclase (effector) and increase cAMP (second messenger) production
how does NE interact with receptors
3 point contact interaction
where are most adrenergic receptors found
post-synaptically
stereochemistry and NE binding interactions (in terms of -OH group)
R enantiomer lets beta -OH group form H-bond with hydroxyl site, while S-enantiomer and desoxy derivative have beta -OH facing away from hydroxyl site and don’t bond as effectively
2nd messenger when alpha 1 stimulated
PIP2 —> IP3 + DAG and Ca2+ channel
2nd messenger when alpha 2 stimulated
inhibits AC presynaptically, involved in post synaptic Ca2+ channel
2nd messenger when beta 1 stimulated
stimulate AC
2nd messenger when beta 2 stimulated
stimulate AC
what does AC stand for
adenyl cyclase
major route of NE termination
reuptake by presynaptic neuron via active uptake transporter
role of MAO (monoamine oxidase)
breaks down (oxidizes) monoamine neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine
degradation of NE via MAO
through oxidative deamination and oxidation, gets back to COMT
degradation of NE via COMT
through O-methylation, NE becomes inactive