victims and witnesses
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
The Victims Code
Domestic Violence, Crime and Victims Act 2004 (revised in 2021)
Outlines what each criminal justice agency must do for victims and the timeframe in which they must do it
12 over-arching rights
The Witness Charter
Sets out the basic standards of service that you can expect from the criminal justice system in England and Wales as a witness of crime.
No legal requirement to meet the standards
Special Measures
Youth Justice and Criminal Evidence Act 1999 (YJCEA)
A range of provisions designed to help vulnerable and intimidated witnesses give the best evidence they can to the court and mitigate some of the associated stress.
Screens
Evidence by live link
Evidence given in private
Removal of wigs and gowns
Video recorded evidence in chief
Video recorded cross-examination or re-examination
Examination of witness through intermediary
Communication Aids
YJCEA 1999 Vulnerable Witness
•All child witnesses (under 18); and
Any witness whose quality of evidence is likely to be diminished because they:
are suffering from a mental disorder (as defined by the Mental Health Act
1983),have a significant impairment of intelligence and social functioning;
or have a physical disability or are suffering from a physical disorder.
YJCEA 1999 Intimidated Witness
Those suffering from fear or distress in relation to testifying in the case.
Complainants in cases of sexual assault
Specified gun and knife offences
The court should take into account:
Nature and circumstances of the alleged offence
Age of the witness
Behaviour towards the witness
Vulnerable Witness eligibility
Category of witness | Legislative provision | Eligibility |
Child | YJCEA 1999, s 16(1)(a). | Eligible in all cases so long as under the age of 18 at time of hearing. |
Adult mental or physical A 199. 5 | YICEA 1999, s 16(2). | Eligible in all cases where their evidence is likely to be diminished as a result of their condition. |
Adult: fear or distress | YICEA 1999, s 17(2). | Eligible in all cases where their evidence is likely to be diminished by reason of fear or distress. |
Adult: sexual offences complainant | YJCEA 1999, s 17(4). | Eligible in all cases unless the witness expresses a wish not be treated as one. |
Adult: violent offences | YJCEA 1999, s | Eligible in violent cases where a firearm or knife was used. No need to prove |
Evidence on live link - Doherty-Sneddon & McAuley (2000)
Face to face or across a live link. No differences in total correct/relevant info during free narrative, or style of questioning used by interviewer.
Older children provided more free narrative info in face to face.
BUT more incorrect info in response to specific-closed questions when face-to-face, younger children more resistant to leading questions across the live link.
Communicating effectively via a television link is an acquired skill for both lawyers and witnesses.
Evidence on live link - Applegate (2006)
Live link encourages children to give evidence, improves the quality of information and softens the adversarial process.
The use of live link removed most of the negative issues relating to giving evidence in person from the court room
Evidence given in private - Victims Commissioner (2021)
All of the magistrates and district judges who felt able to comment said it was rarely or never used, and nearly all Crown Court judges (98%) said the same.
Comments from rape survivors emphasised how intimidating survivors often found the public gallery:
The experience was traumatising. I could see the public gallery and the friends of the perpetrator glared at me whilst I provided my evidence.
I felt the screen was appropriate for me but would have preferred the public gallery to have been empty when my video interview was shown and I was cross examined as the details of my abuse was for all to see by those in the public gallery
Video recorded evidence - Hamlyn et al (2004)
95% of child complainants of sexual abuse gave their evidence-in-chief in the form of a videotaped interview.
43% of those giving their evidence-in-chief on video valued not having to appear in the courtroom.
98% of those who gave pre-recorded interviews maintained they had been given the opportunity to say everything they wished, compared to 53% of those who were taken through their evidence by the prosecutor at court.
Video recorded in evidence - burton et al (2006)
Widespread perception among lawyers and judges that videotaped statements do not have the same emotional impact as statements made in person in the courtroom
Video recorded in evidence - Landstrom (2008)
Observers perceive those giving videotaped testimony in a less positive light than those who give their evidence in person
Video recorded cross examination- Baverstock (2016)
A number of key findings from the results of a pilot of the procedure:
Better recall of evidence
Cross-examinations were perceived as more witness-friendly
The length of time in the child being called to take part in the cross-examination procedure was comparatively short
The length of time the child was cross-examined reduced
Video recorded cross examination -Dame Vera Baird QC, Victims' Commissioner for England and Wales
Over 500 pre-recorded cross-examinations have taken place since February 2020
'This has the potential to transform the criminal justice experience for so many vulnerable victims'
Questions regarding previous sexual behaviour
Section 41(5): where evidence or questions in cross-examination are necessary to rebut prosecution evidence;
Section 41(3): where the evidence or questions in cross-examination relate to an issue set out in the subsection, as follows:
S41(3)(a): where the issue is not consent
S41(3)(b): where the issue is consent and the complainant's sexual behaviour is alleged to have happened about or at the same time as the sexual activity in question at trial
41(3)(c): where the issue is consent, and the evidence relating to the complainant's sexual behaviour is so similar to that alleged to be part of the event which is the subject of the proceedings, or to any other sexual behaviour which took place at or about the same time as the event, and which cannot reasonably be explained as a coincidence
Are special measures working? - Hamyln et al (2004)
Witnesses using special measures rated them very highly; for example nine in ten witnesses using the live TV link found this helpful
33% of witnesses using any special measure said that they would not have been willing and able to give evidence without them.
Witnesses using special measures were less likely than those not using them to experience anxiety and had a more favourable opinion of the CJS
Are special measures working? - burton et al (2006)
Overall, special measures were having a positive impact, the mechanisms used to identify vulnerable witnesses and assess their individual needs had to be improved.
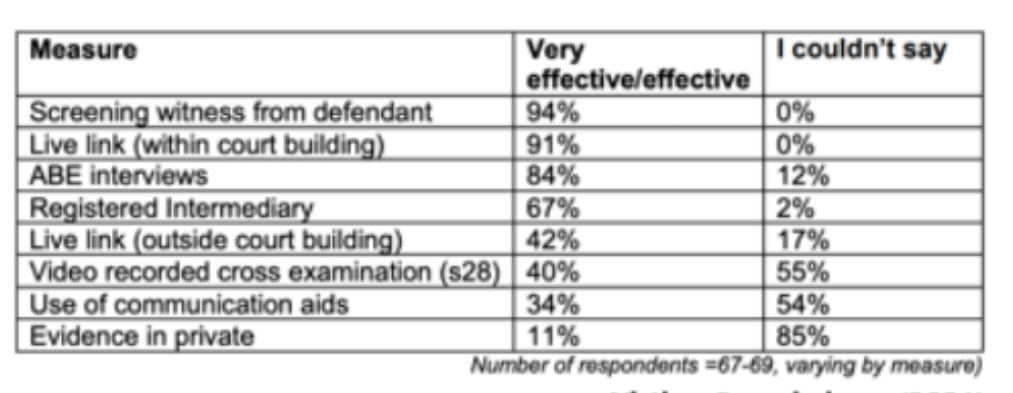
Are special measures working? - victims commissioner (2021)
Picture
Intermediaries
Meets with person and assesses their communication
Writes a full report for the court with recommendations for how to communicate with the person
The RI having taken the intermediary oath, assists during the giving of evidence.
They can explain verdicts and sentencing to the person.
Intermediaries - Plotnikoff and Woolfsons (2007)
Ris assisted with witnesses communication
RI's helped witnesses cope with the stress of providing testimony.
Ris increased access to justice, estimating that at least half of the cases would not have reached trial without the involvement of the intermediary
Intermediaries - Collins et al (2016)
Perceptions of child's behaviour and the quality of the cross examination better with intermediary
Rated as more truthful, credible, believable, responsive, co-operative, comfortable, confident, consistent, accurate, less vulnerable, less suggestible and less stressed;
• More child-centered, child appropriate, better quality interaction