General Biology Unit 2 NWMSU
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Ability of an organism
•Grow
•Replace old or damaged cells
•Reproduce sexually
Cell Division
Carries out cells abilities
Part of cell cycle
Life cycle of the cell
Cell Cycle
1. Interphase
2. Mitosis
3. Cytokinesis
Interphase
Longest stage: G1, S, and G2 stage
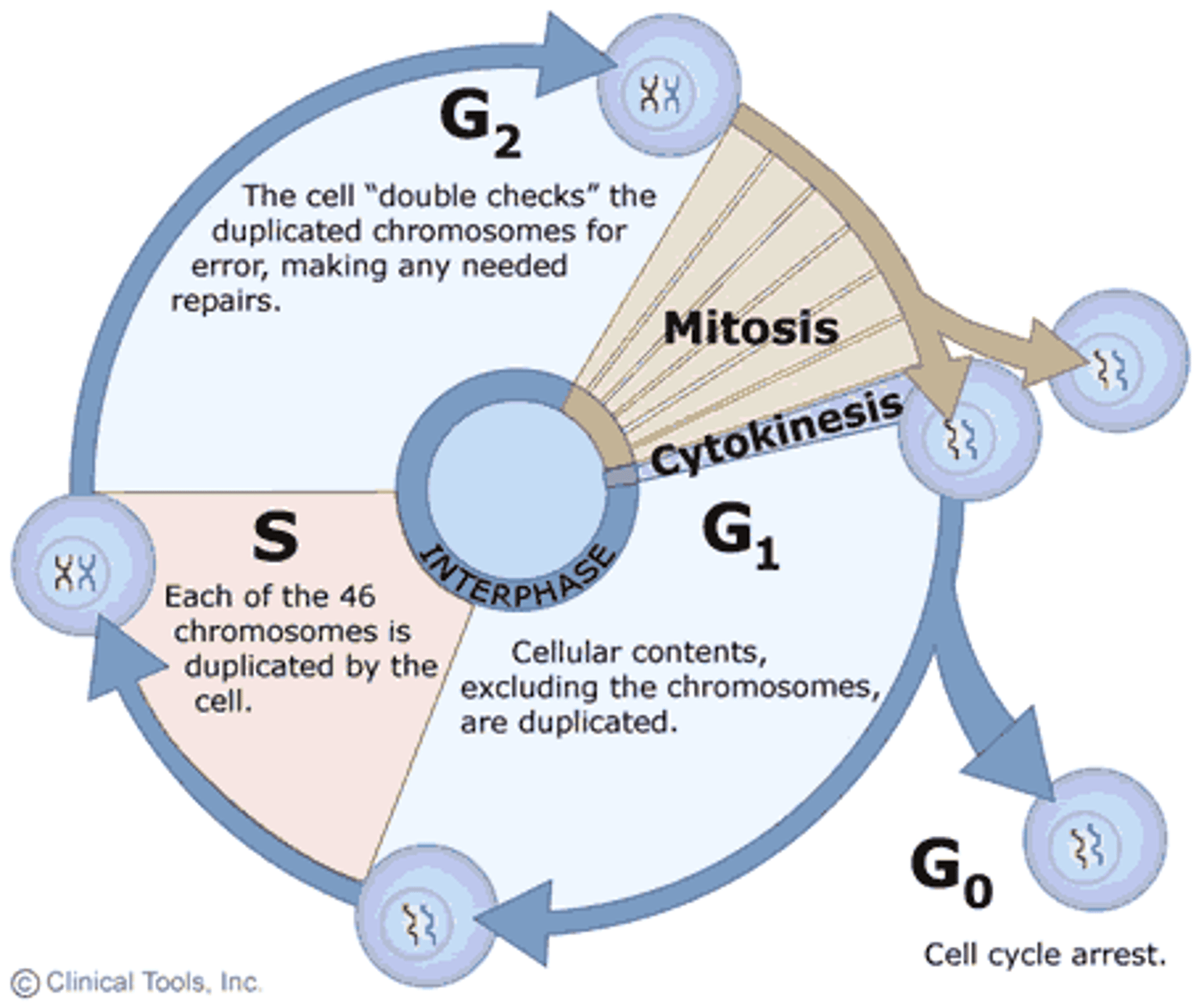
G1 stage
normal cell metabolism, controls rate of cell divis, varies significantly in duration from minutes to hundreds of years
S stage
synthesis of DNA, chromosomes replicate and centrioles replicate and begin to move toward opposite poles
G2 stage
Prepares for mitosis
G2 and S stage
do not vary much in duration
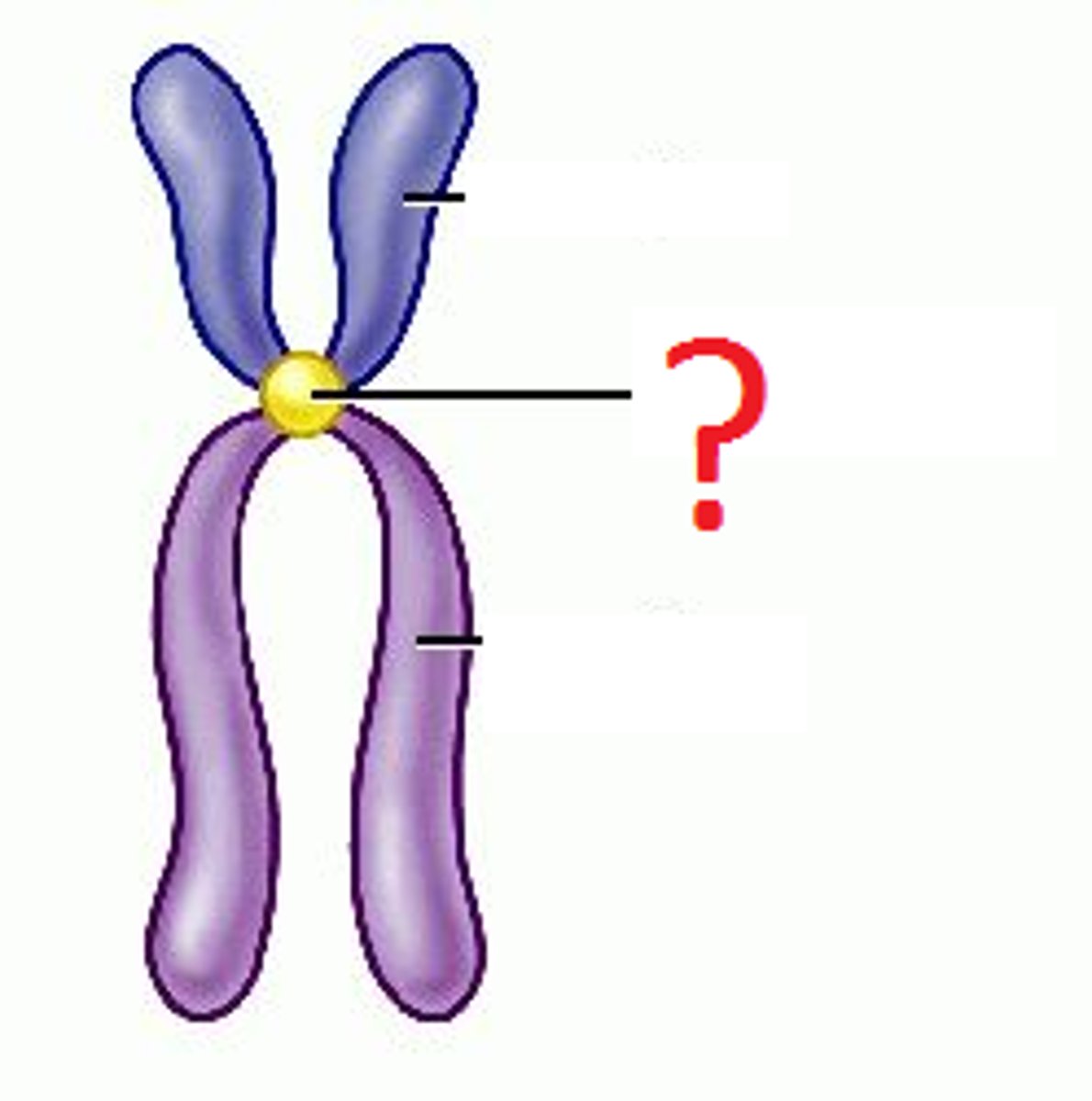
Chromosome structure
DNA + complex histones
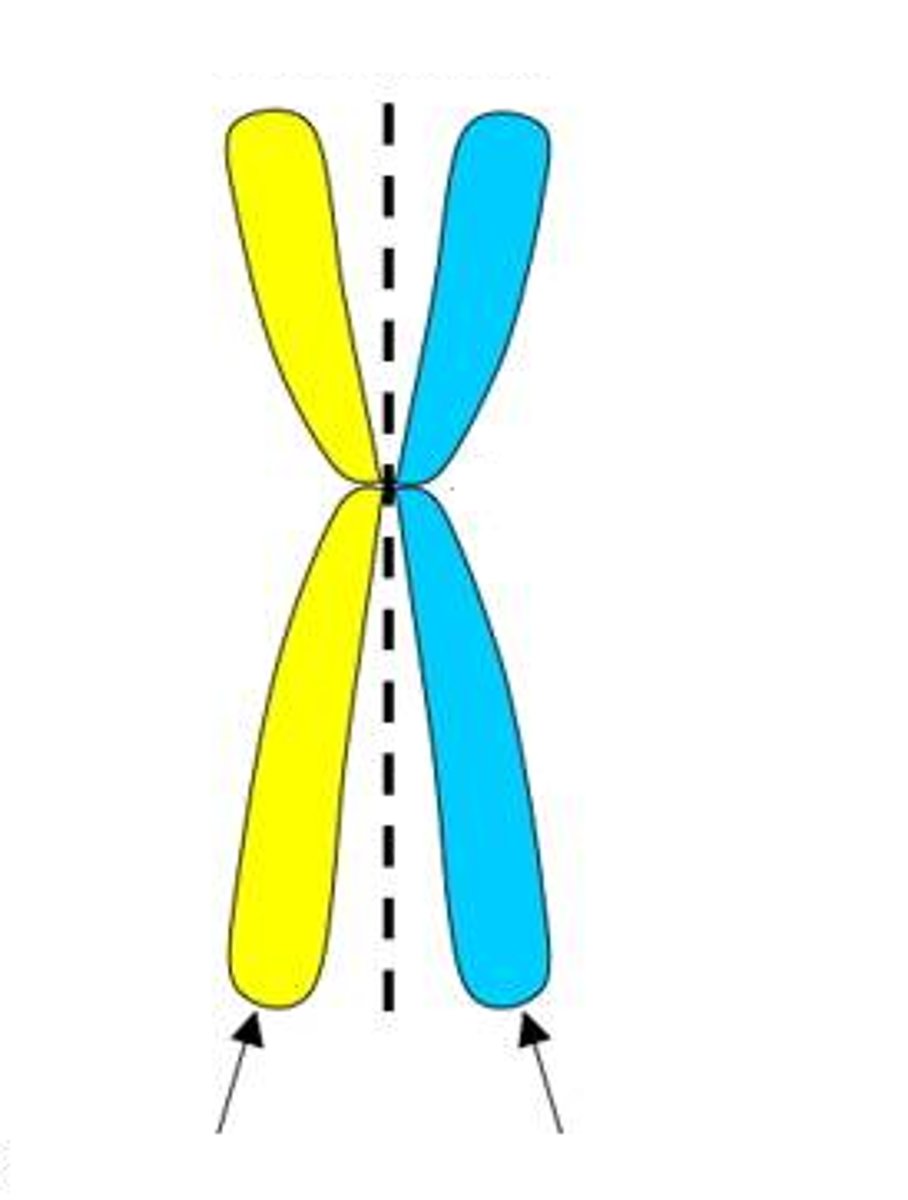
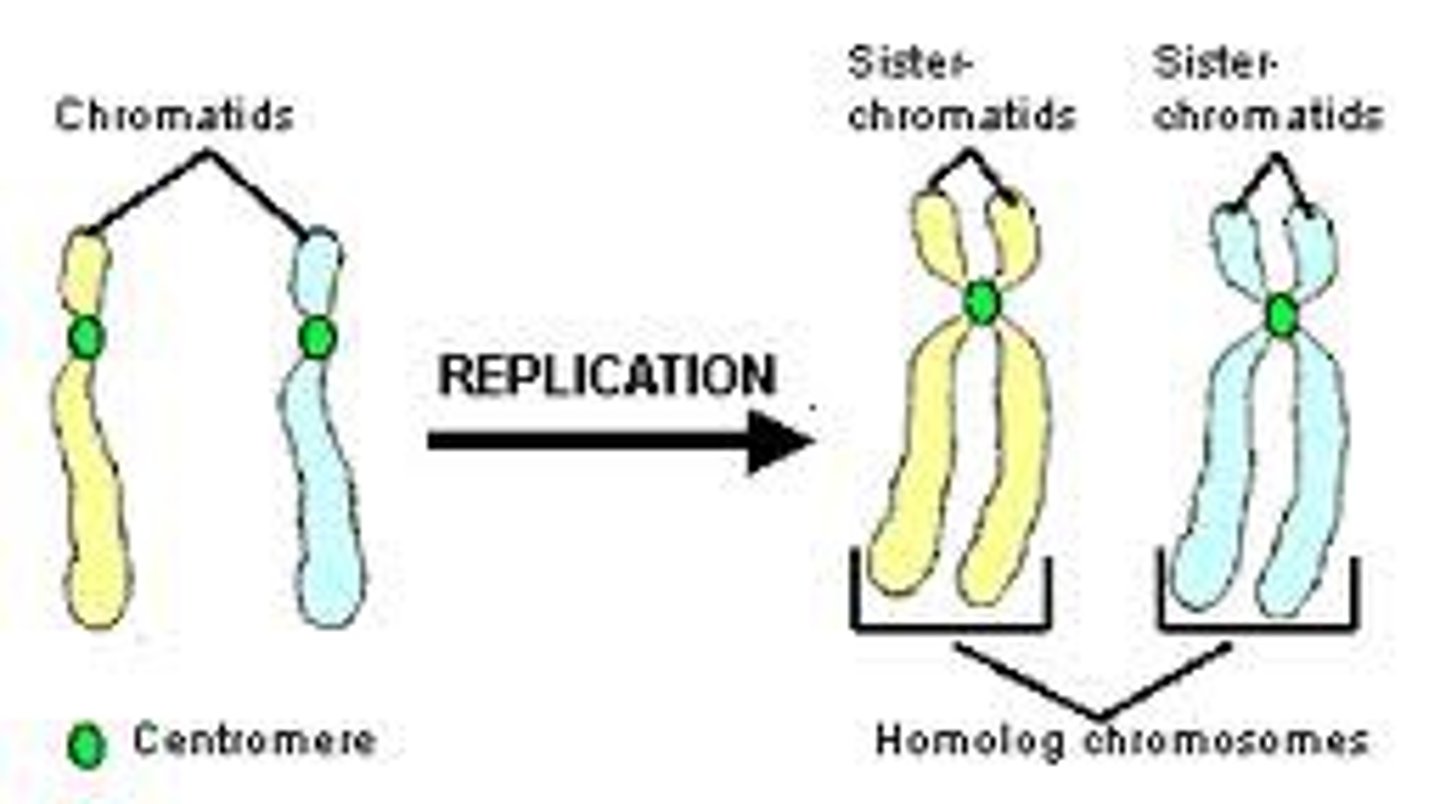
Chromatid
one of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome
Kinetochore
Protein complex around centromere
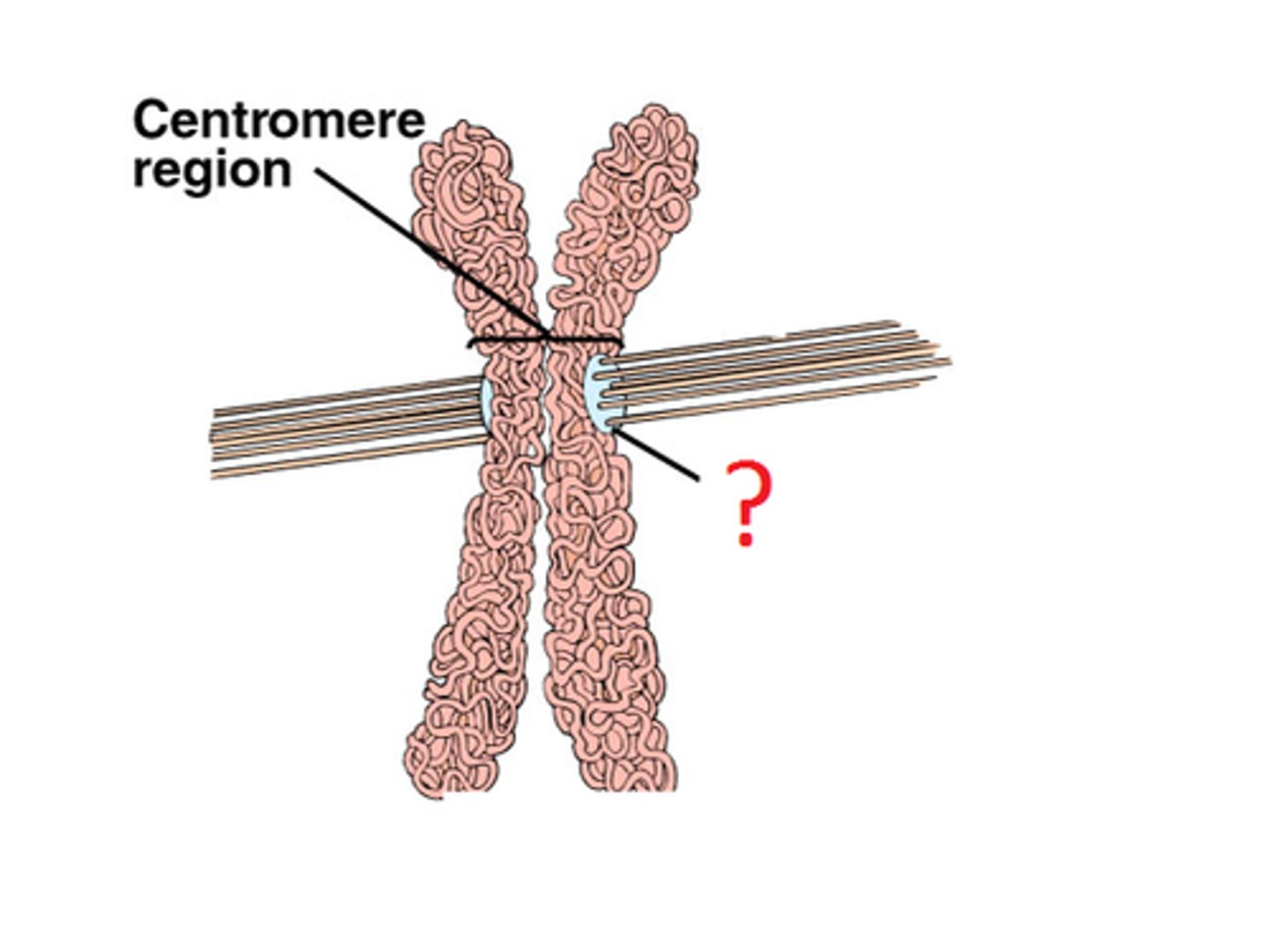
Centromere
Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach
Sister chromatids
one of two identical halves of a replicated chromosome
genetically related to one another
Kinetochore microtubules
spindle microtubules that attach to the kinetochores and push and pull them around
Mitosis
•Refers specifically to event is the nucleus
•Does not refer to cell division
•Occurs in somatic cell (body cells)
•Involve one nuclear division
•One diploid (2n) mother cell gives rise to 2 diploid daughter cells
Diploid
Double set of chromosomes
Most organisms, like humans, are this 23*2=46
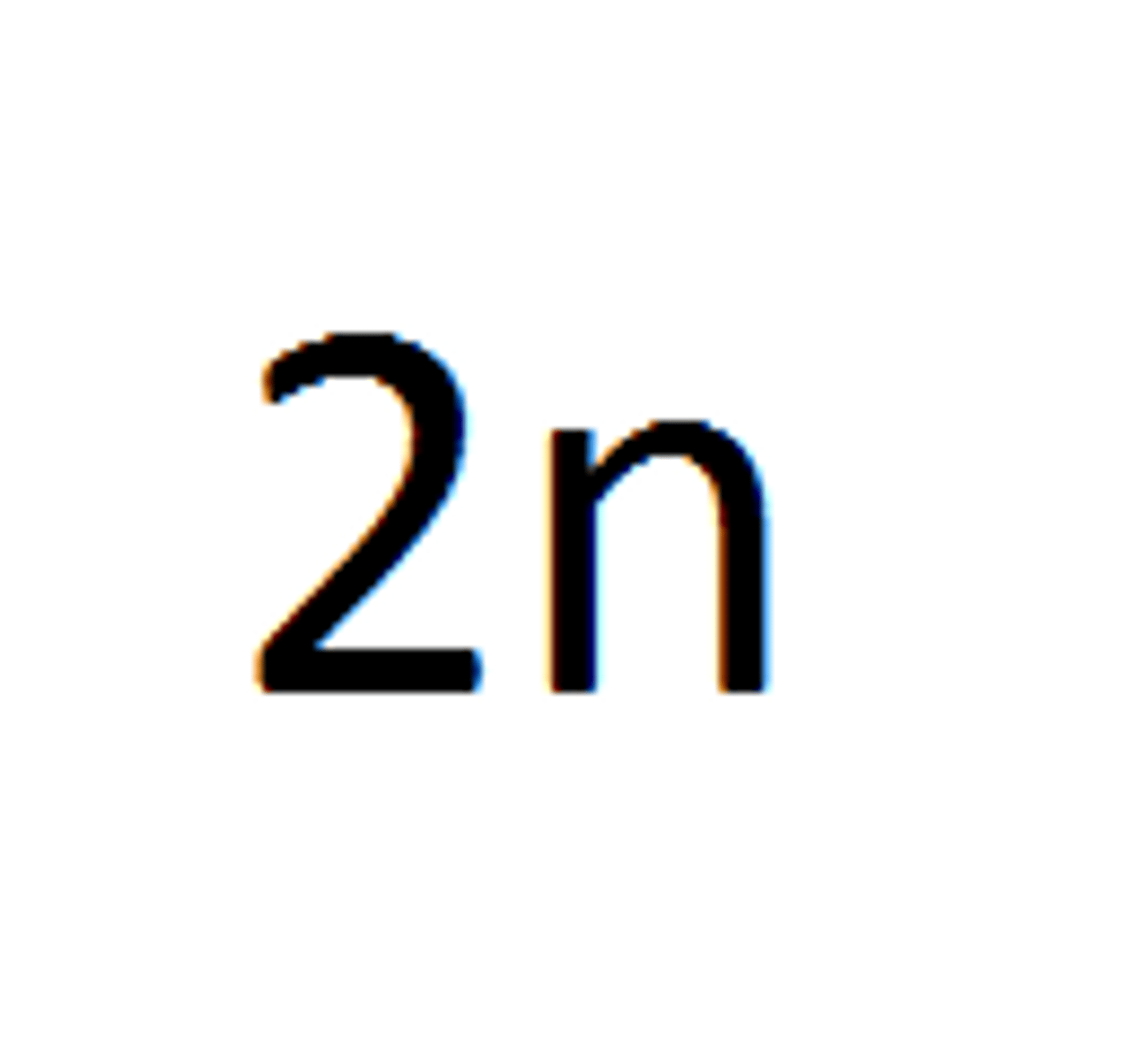
46
Chromosome number for humans
Mitosis process
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase
Prophase
•Chromo begin to condense
•Spindle fibers or spindle apparatus (MT) begin to form

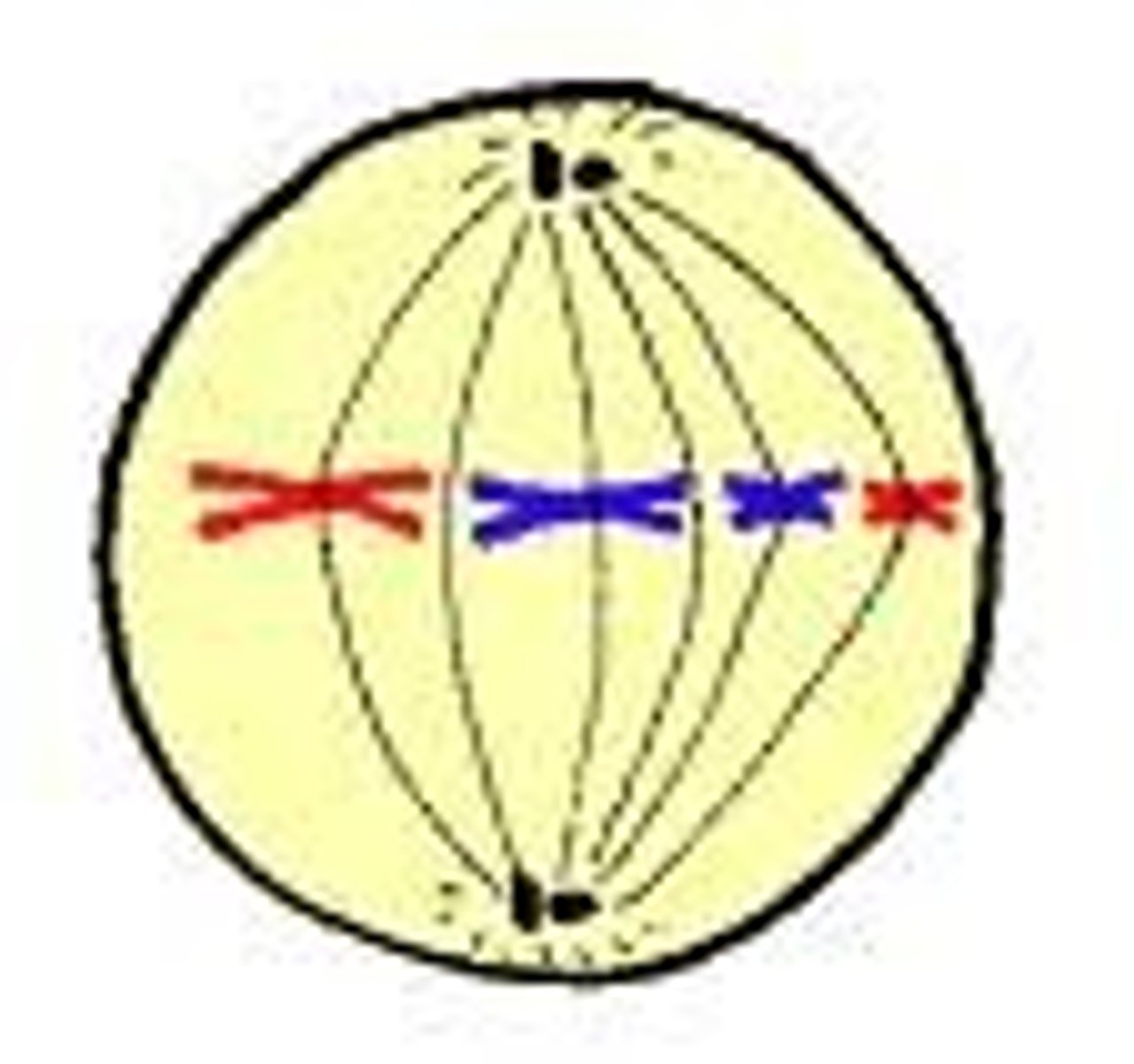
Metaphase
•Chromo completely condensed
•Spindle MT have aligned chrom in center of cell
Anaphase
•Centromere of each chromo separates so that now, technically, there are two chromo; sister chromatids
•MT begin to depolymerize pulling chromo toward opposite poles
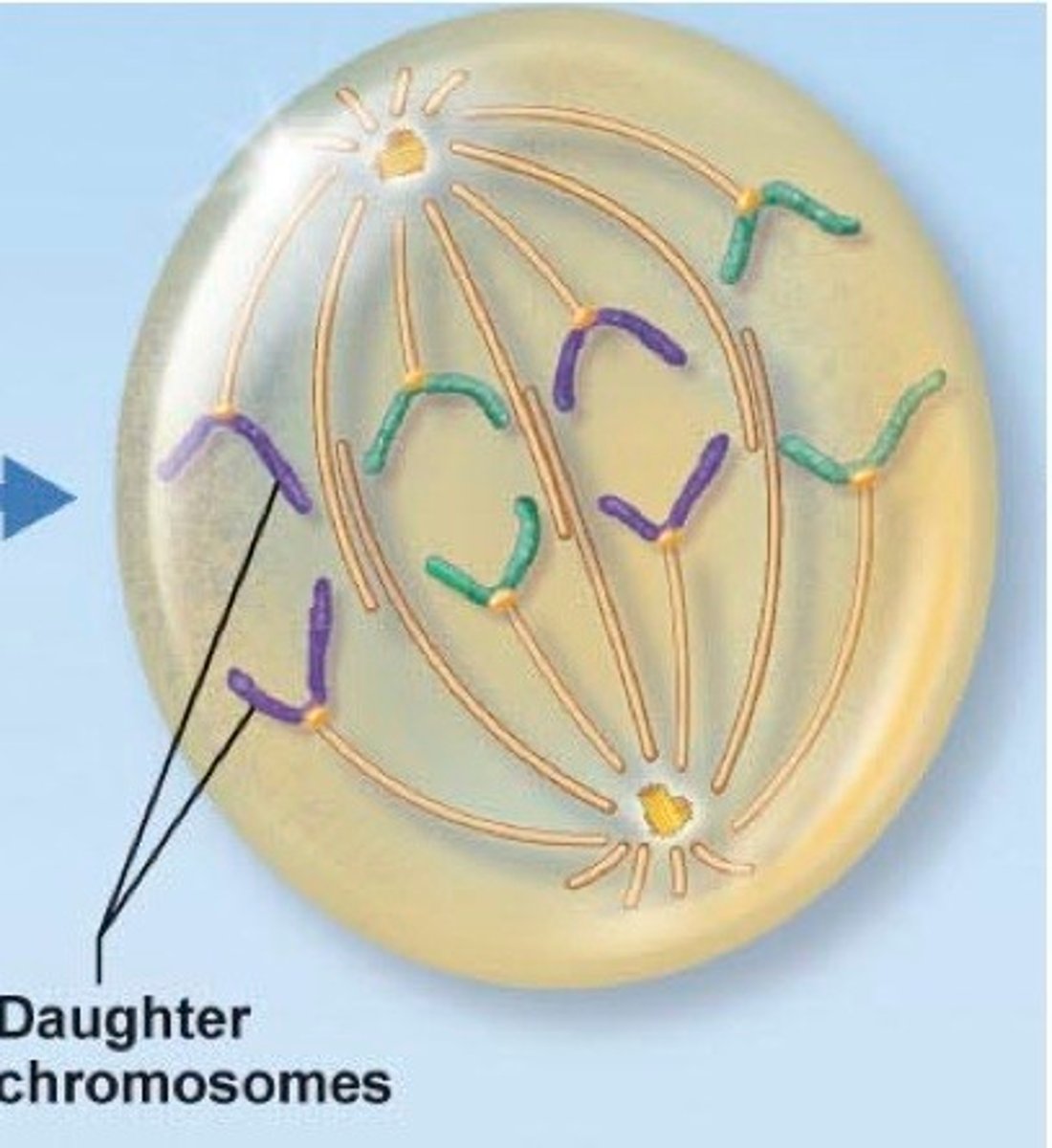
Telophase
•Spindle MT begin to disappear
•Chromo begin to unravel
•Nuclear membrane begins to reform
•Once nuclear membrane formed, telophase over
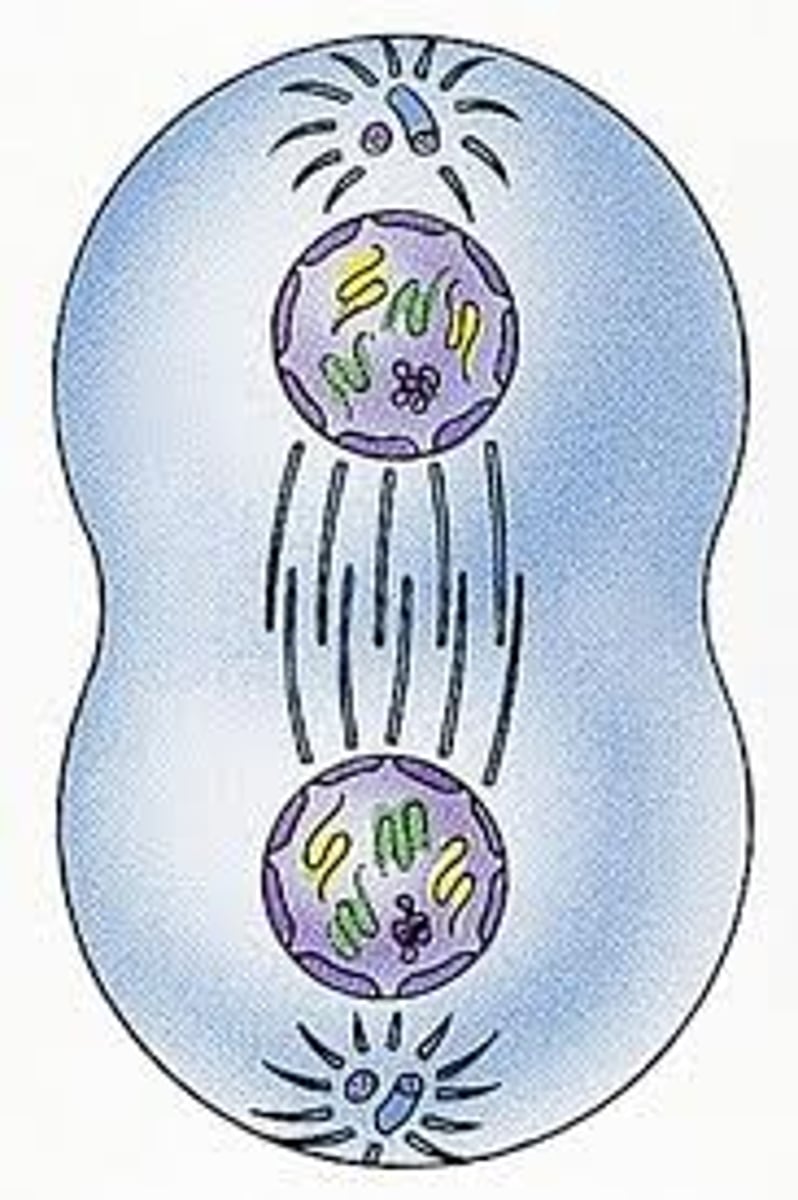
Cytokinesis
Typically, but not always, occurs at same time as telophase forming two new nuclei so that you have two new cells each 2n
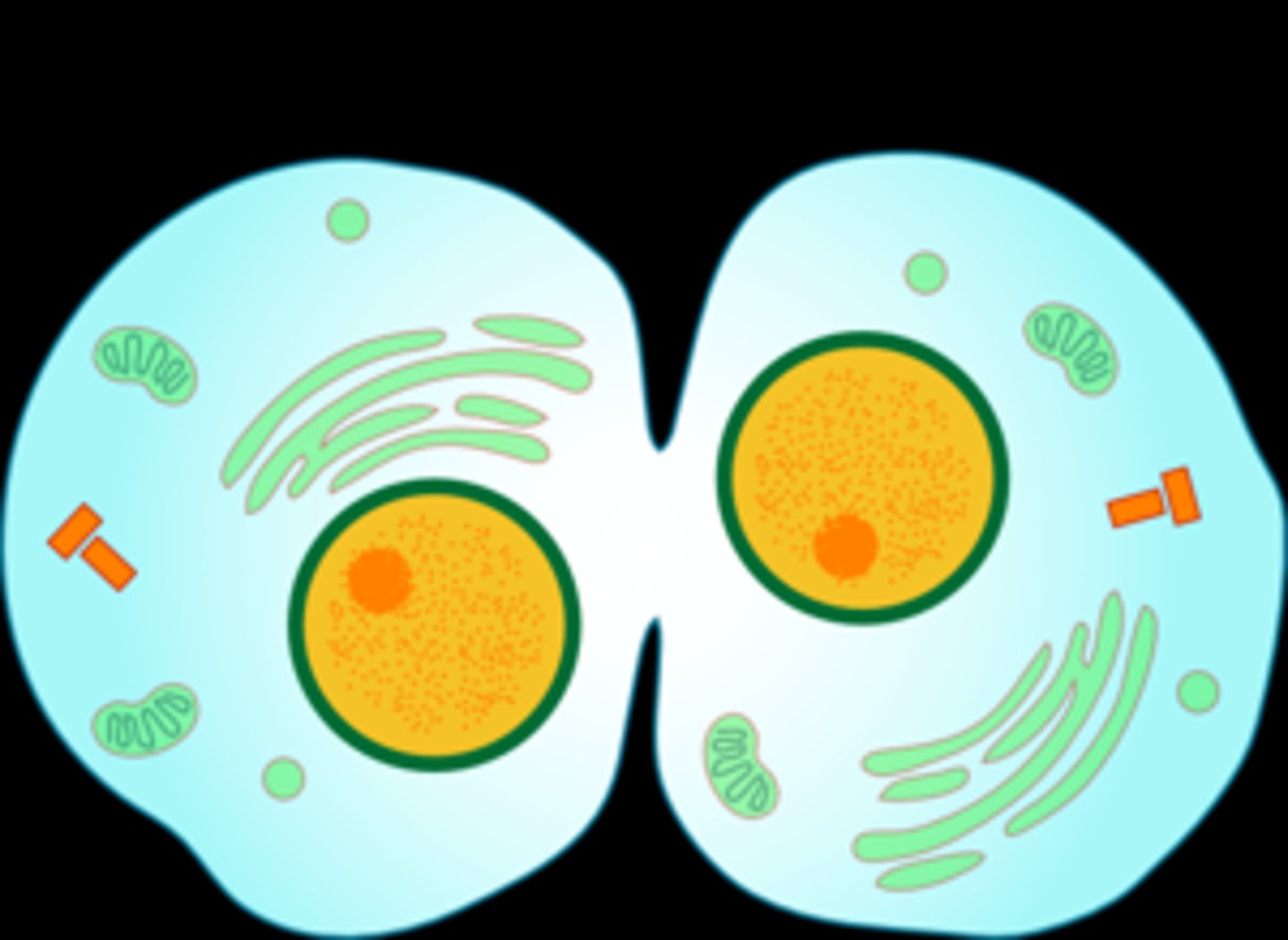
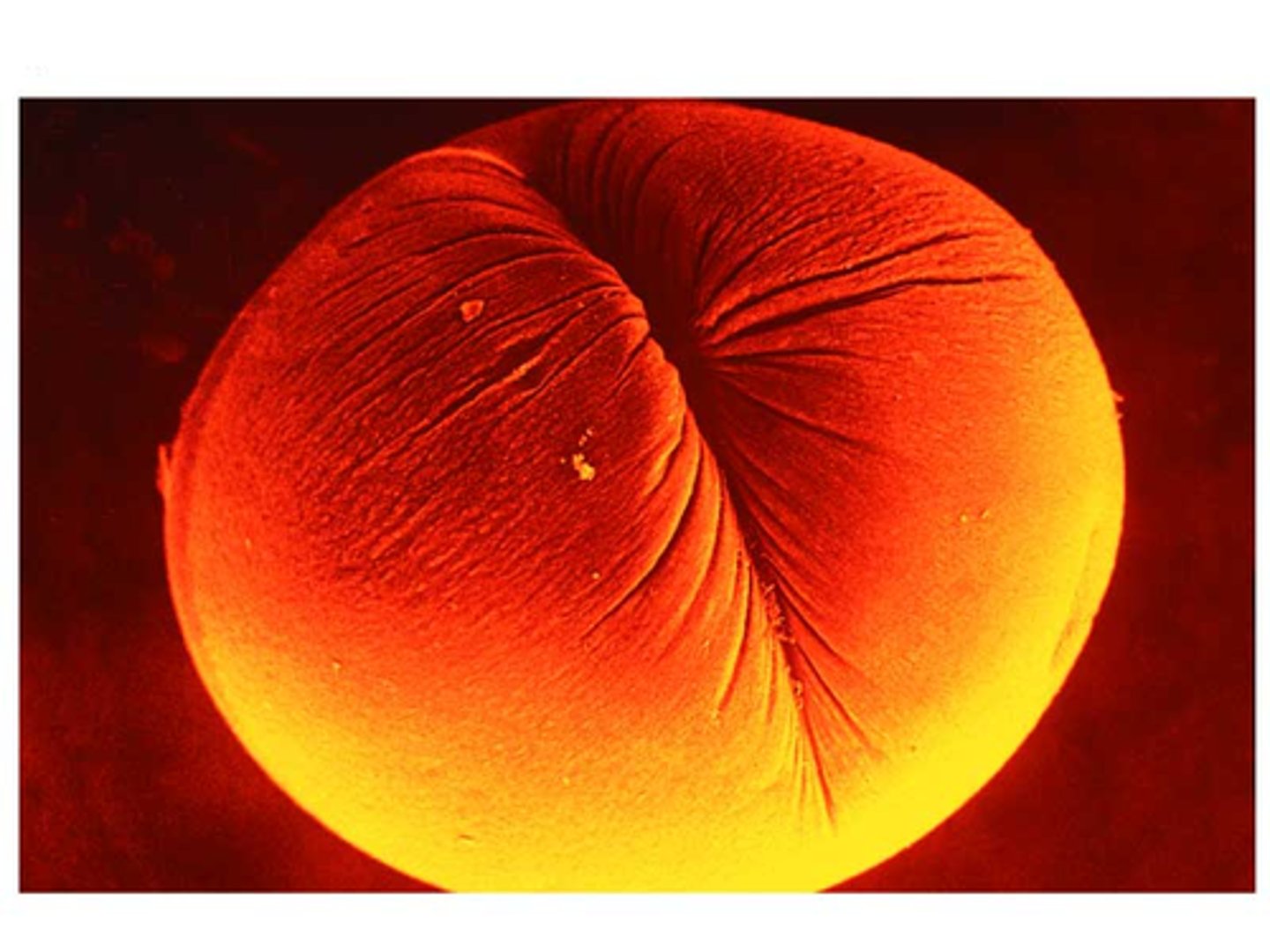
Cleavage furrow
The area of the cell membrane that pinches in and eventually separates the dividing cell in animal cells
Cell plate
In a plant cell, midline of dividing cells. Becomes the cell wall eventually.
Binary fission
a pinching in equal halves of a cell in prokaryotic cells
As the cell replicates its single chromosome, the copies move apart and the growing membrane then divides the cells
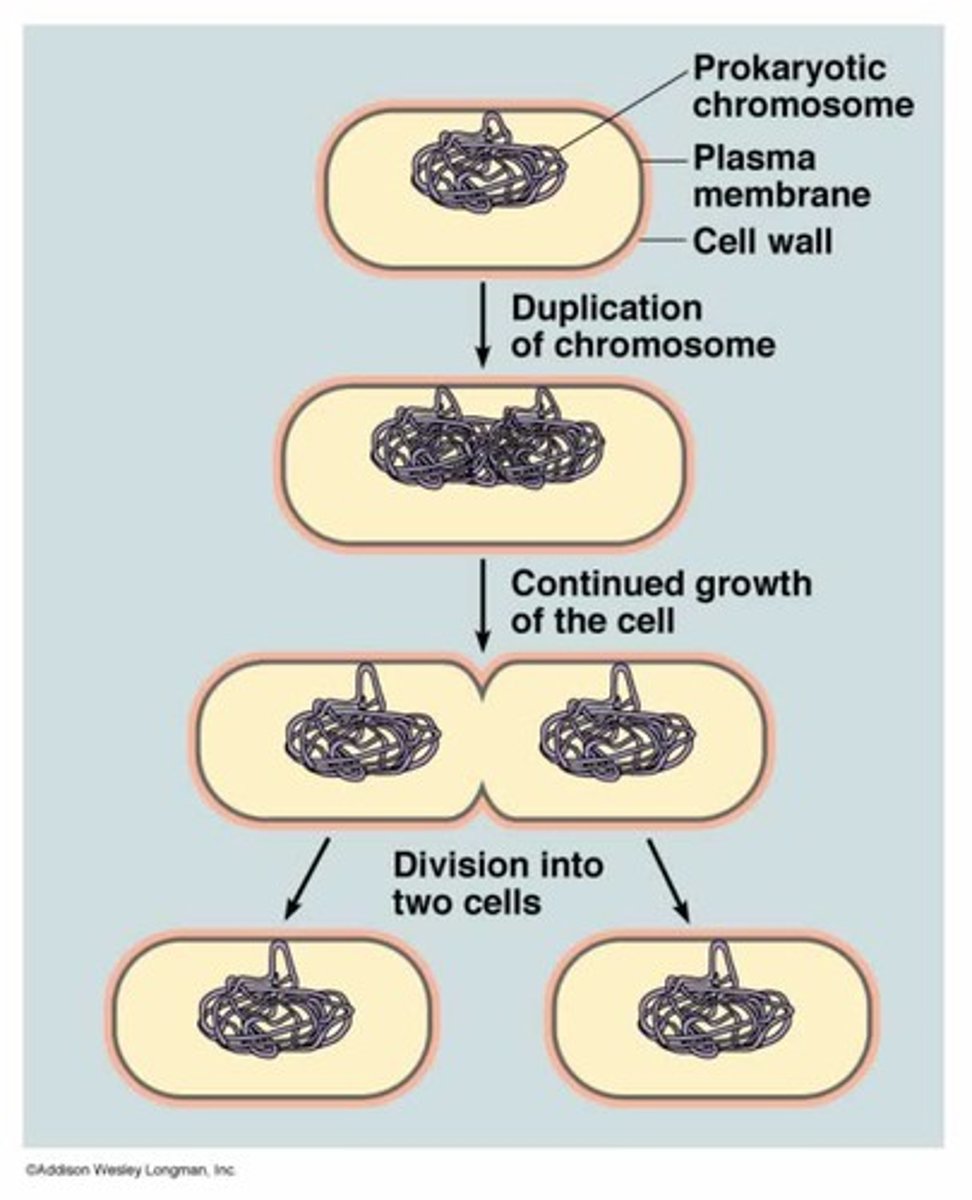
How Prokaryotic cells reproduce
asexually by cell division
Check points
control mechanisms in eukaryotic cells which ensure proper division of the cell.
Chemotherapy
targets cell cycle
Interferes with DNA replication, chromosome separation
Cancer drugs
Look to plants as a source of drugs
Taxol
Highly effective chemotherapy agent; extracted from the Pacific yew tree, Taxus brevifolia
Meiosis
• Refers specifically to event in the nucleus
• Does not refer to cell division
• Occurs in germ cells, ovaries and testes, formation of gametes
• Involved 2 nuclear divisions
• One diploid mother cell gives rise to haploid daughter cells
• DON'T EQUATE WITH CELL DIVISION
homologous
23 pairs of chromo
they are genetically related
Meiosis I
Starts out similar to mitosis
reduction division
Prophase I
Stage in Meiosis I
•Similar to prophase of mitosis
• Synapse (pair) of homologous chromosomes (generates the haploid condition)
• Here each homologous binds, gene-for-gene
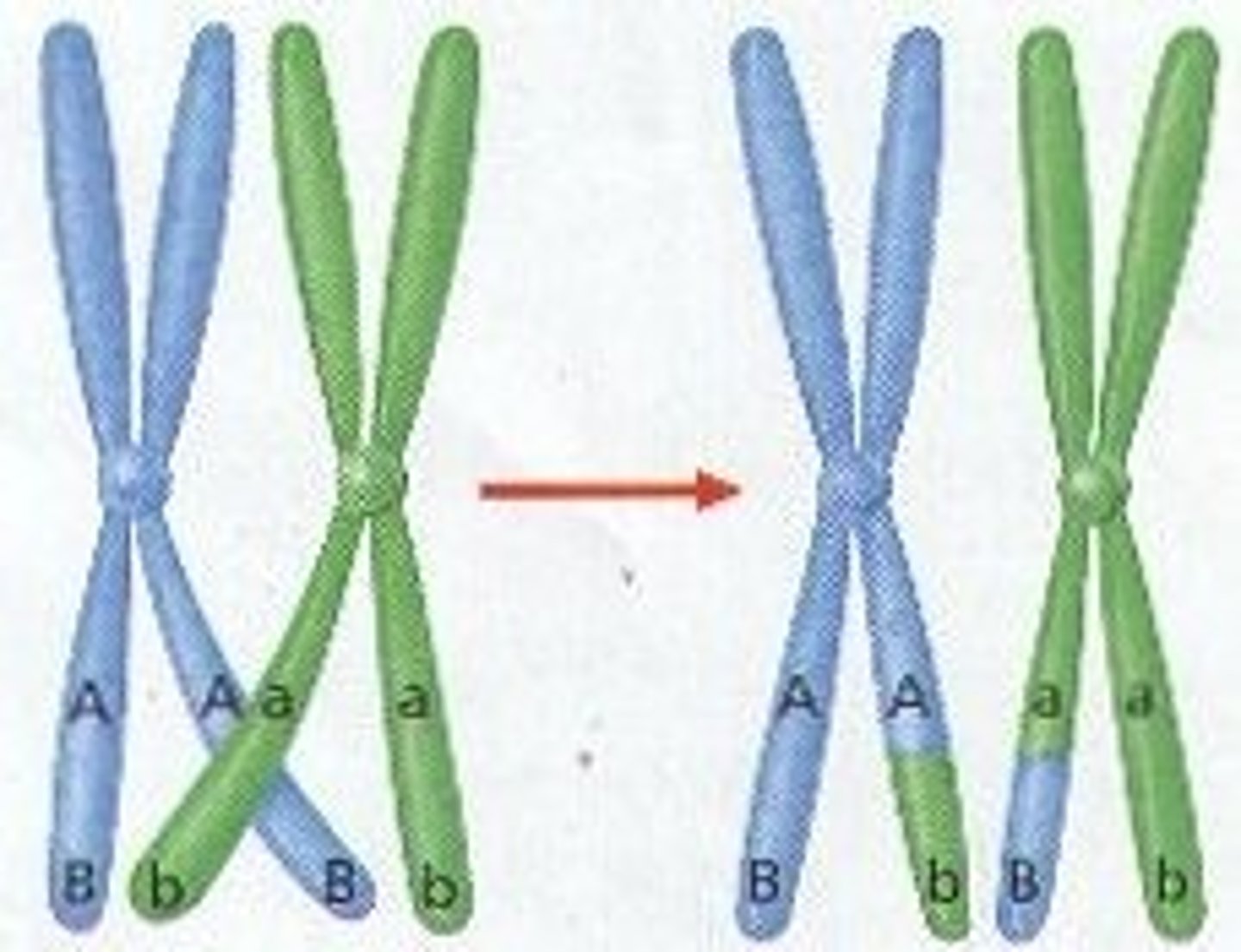
• Crossing-over occurs producing recombinant chromatids (chromosomes), mixes parental genes, creates genetic variation
Synapse
Pair
homologous chromosomes
generates the haploid condition
a pair of chromosomes having the same gene sequences
Crossing-over
the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis
recombinant chromatids
Mixed parent genetics
Metaphase I
• Similar to mitosis, except that not all 46 chromo align, but rather the 23 homologous pairs
• Each homol pair align in the equator of the cell independent of all others= independent assortment
Create genetic variation in gametes
independent assortment
Each homol pair align in the equator of the cell independent of all others
Anaphase I
Stage in meiosis I
homologous chromosomes separate
Telophase I
Stage of meiosis I
chromosomes arrive at the spindle poles.
Cytokinesis I
Stage in Meiosis I
2 haploid cells, replicated
Prophase II thur Telophase II
• Similar to mitosis, except only half number of chromo
• No different than mitosis I but it's only half
Cytokinesis II
4 haploid cells are formed, not identical but similar
Evolutionary importance of the meiosis
lies in genetic variation produced by recombination
Sources of recombination
a. Crossing-over and production of recombinant chromatids
b. Independent assortment and rearrangement of chromosomes in gametes
c. Fertilization (recombining of gene sets) and production of viable, fertile individual
Chromosomes and Human Genetics
Most organisms sex is determined genetically
autosomes
Humans have 22 pairs of...
sex chromosomes
Humans have 1 pair of...
X and Y chromosomes
Each chromosome has its own characteristics of
size, length, centromere location
karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
amniocentesis
routinely done for pregnant women over age 35 in procedure
chorionic villi sampling (CVS)
sampling of fetal tissue from the placenta
Has higher risk of abortion
XX
Female
XY
Male
Aneuploid of autosome
humans- 45 or 47
Monosomy
45 chromosomes usually lethal
Trisomy
• 47 most autosomal trisomy are lethal
• Could be trisomy 21 or down syndrome, can have mental, muscle, heart problems, nondisjunction of chromo #21
X0
Turner's Syndrome
Turner's Syndrome
a. Nondisjunction in sperm
b. People are females, w/o sex hormones
c. Short, infertile, reduced development of sexual characteristics
d. Monosomy--45
XXY
Klinefelter syndrome
Klinefelter Syndrome
a. Nondisjunction in egg 67% of the time
b. Males that tall and usually sterile due to reduced develop of testes
c. Little facial hair and some breast development
d. Trisomy 47
XYY
normal male
XXX
normal female
Variation
among individual or is a long noticed
pattern
resemblance between parents and offspring
blending inheritance (incorrect idea)
Offspring traits were a blend of mix of the parents
Gregor Mendel
• An Austrian monk
• Considered "Father of modern genetics"
segregation of alternative traits
He described process...
published in 1865
F1 generation
Mix of 2 traits
F2 Generation
selfening of F1). This allowed for alternative traits to segregate
reciprocal crosses
A process by which plants were crossed (mated with each other) in both directions.
monohybrid cross
A cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits
dominant trait
a trait that masks the expression of another trait
recessive trait
a genetic factor that is blocked by the presence of a dominant factor
Mendel's Law of Segregation
1. theory of blending inheritance is wrong
2. Traits are passed from one generation to another as discrete information Exactly how not known then
chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
alleles
Different forms of a gene
Every individual possess 2 doses for a particular trait or gene. If individual are diploid
anaphase I
When gametes form, alleles segregate from each other
Phenotypes
are expressions of genotypes or exact allelic combinations for particular trains
PP
homozygous dominant
pp
homozygous recessive
Pp
heterozygous individuals
Punnett Square
possible outcomes of a cross can be identified
dihybrid cross
following two traits at same time
A cross between individuals that have different alleles for the same gene
phenotypic ratio
3:1
Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment
the law that states that genes separate independently of one another in meiosis
metaphase I
Pairs of homologous chromosomes move to the equator of the cell.
sex-linked
Genes fond on the sex chromosomes are...
X-linked
A recessive trait determined by a gene most commonly found on the X chromosome
X-linked recessive inheritance
• Hemophilia A- blood clotting
• Duchene muscular dystrophy- muscle cells atrophy
• Red/green color blindness
Carrier
Has trait, but it's not expressed
X-Linked dominant inheritance
Faulty enamel trait, failure of enamel coating on teeth to develop
Here a heterozygous female will express the trait
Autosomal Recessive Disorder
• Cystic Fibrosis
• Common more among Caucasians in US
• Faculty channel protein (CFTR protein) normally when CI- passes thru, water does too
• Mutant protein fails to pass CI- ion
• Mucus in bronchial tubes and pancreatic ducts is thick
• Interferes with breathing and release of digestive enzymes, respectively
Autosomal Dominant Disorders
Huntington Disorder
Huntington Disorder
• Progressive degeneration of nervous system leading to poor muscle coordination and mental decline- usually not expressed until 40's
• Mutation of gene (huntingtin gene) coding for protein called huntingtin
• Usually not expressed until middle age
• Death 10-15 years after expressed
Incomplete dominance
the phenotype of the heterozygous phenotype is distant from and often intermediate to the phenotypes of the homozygous phenotypes
Ex hair texture
Codominance and Multiple Alleles
Phenotype are A, B, AB, O controlled by three alleles and produced by 6 different genotypes