Bio 2 Lab Practical
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
1
New cards
What is the main focus of the Ghost Shrimp lab?
To observe the effects of plant-derived chemicals on the shrimp’s circulatory system.
2
New cards
What type of circulatory system do ghost shrimp have?
Open circulatory system.
3
New cards
What are the three drugs tested in the lab?
Caffeine, Nicotine, Ethanol.
4
New cards
What effect do stimulants have on heart rate?
They increase the heart rate.
5
New cards
What effect do depressants have on heart rate?
They decrease the heart rate.
6
New cards
How is the shrimp’s heart rate measured?
By counting the pulsations in the dorsal blood vessel under a microscope.
7
New cards
What is the importance of calculating standard deviation in experiments?
It shows the variability and precision of the data.
8
New cards
What color is ghost shrimp blood, and why?
Blue, due to copper-based hemolymph.
9
New cards
Why are ghost shrimp a good model for circulatory experiments?
Their transparent bodies allow for easy observation of blood flow.
10
New cards
What is the purpose of the recovery time measurement?
To see how long it takes for shrimp to return to normal heart rate after drug exposure.
11
New cards
What is natural selection?
A process where organisms with favorable traits survive and reproduce more successfully.
12
New cards
What is genetic drift?
A random change in allele frequencies due to chance events, especially in small populations.
13
New cards
What is gene flow?
The transfer of alleles from one population to another due to migration.
14
New cards
What is the Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE)?
A theoretical state where allele frequencies remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of evolutionary forces.
15
New cards
What are the five conditions for HWE?
1) Large population size, 2) No mutations, 3) Random mating, 4) No gene flow, 5) No natural selection.
16
New cards
What is the Hardy-Weinberg equation for allele frequencies?
p + q = 1, where p is the dominant allele frequency and q is the recessive allele frequency.
17
New cards
What is the Hardy-Weinberg equation for genotype frequencies?
p² + 2pq + q² = 1, where: p² = homozygous dominant (BB), 2pq = heterozygous (Bb), q² = homozygous recessive (bb).
18
New cards
How do you calculate allele frequency?
Dominant allele: p = [(2 × BB) + Bb] / (2 × total individuals), Recessive allele: q = [(2 × bb) + Bb] / (2 × total individuals).
19
New cards
How does selection pressure affect allele frequencies?
Negative selection decreases the frequency of less fit alleles, while positive selection increases favorable allele frequencies.
20
New cards
How does genetic drift impact allele frequencies?
It causes random fluctuations in allele frequencies, which are more significant in smaller populations.
21
New cards
What was the purpose of using colored beads in the evolution lab?
To simulate allele inheritance and track changes in allele frequencies over generations.
22
New cards
What happens to a population under 100% negative selection pressure?
The selected genotype is eliminated over generations, leading to a decrease in its allele frequency.
23
New cards
How does gene flow affect two separate populations?
It makes allele frequencies more similar between populations over time.
24
New cards
What is the bottleneck effect?
A drastic reduction in population size due to an event, leading to reduced genetic diversity.
25
New cards
What is the founder effect?
When a small group starts a new population, leading to reduced genetic variation.
26
New cards
How do you interpret a genotype frequency graph?
A stable line suggests equilibrium, while a changing trend indicates evolutionary forces at work.
27
New cards
How does standard deviation help in evolutionary studies?
It measures variation in allele frequencies and determines if changes are significant.
28
New cards
What does a genetic drift simulation show?
That allele frequencies fluctuate randomly, potentially leading to fixation or loss of alleles.
29
New cards
What role does sample size play in genetic drift?
Smaller populations experience more extreme allele frequency changes due to chance.
30
New cards
What does it mean if allele frequencies deviate from HWE predictions?
Evolution is occurring due to factors like selection, mutation, or migration.
31
New cards
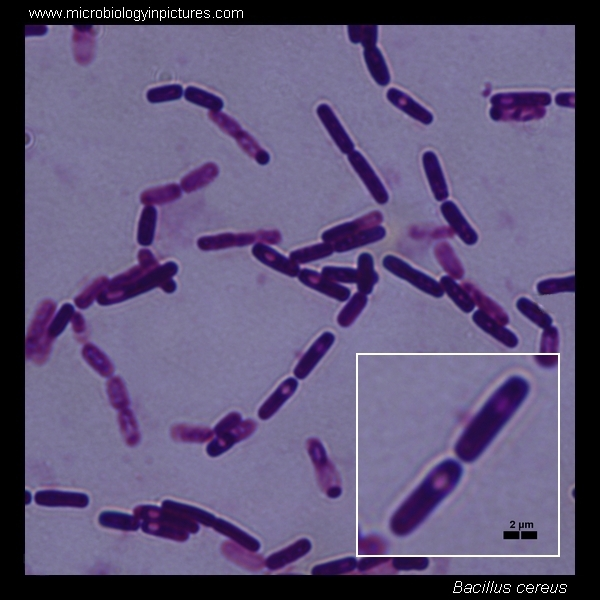
Bacillus cereus
32
New cards
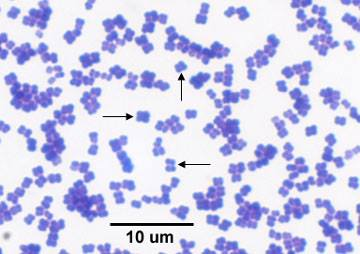
Micrococcus luteus
33
New cards
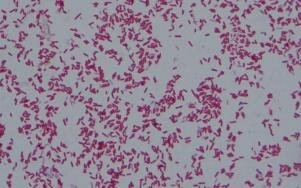
Escherichia coli
34
New cards
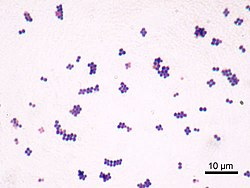
staphylococcus aureus
35
New cards
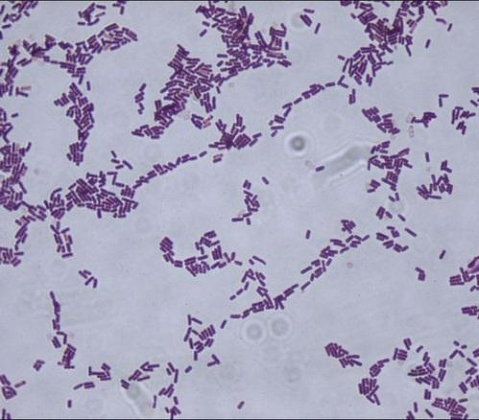
Bacillus subtilis
36
New cards
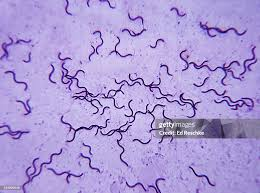
Spirillum volutans