chem ch 4
0.0(0)Studied by 2 people
Card Sorting
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:37 AM on 9/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
1
New cards
________- the particles that determine the identity of an element.
Protons
2
New cards
Negative charge, -1 g (amu), outside the nucleus.
Electrons
3
New cards
________= discovered the nucleus; did the gold leaf expierement
Rutherford
4
New cards
Individual building blocks of matter; pieces of elements from the table.
Atoms
5
New cards
- the particles found in the nucleus.
Protons and neutrons
6
New cards
Anything made up of at least 2 non- metal atoms; can either be the same element.
Molecules
7
New cards
Proposed atoms are made of earth
Greeks
8
New cards
Worked with cathode ray and discovered that the rays are deflected by electric and magnetic fields
Jj thomson
9
New cards
Discovered the neutron
Chadwick
10
New cards
Identified the electron
Jj thomson
11
New cards
positive charge, 1+ g (amu), inside the nucleus
Protons
12
New cards
neutral charge, 0g (amu), inside the nucleus
Neutrons
13
New cards
Protons + neutrons
mass number
14
New cards
Protons + electrons
Net force/charge
15
New cards
Which particles affect the charge of an atom or ion
Electrons
16
New cards
Element symbol
What is normally in place of A
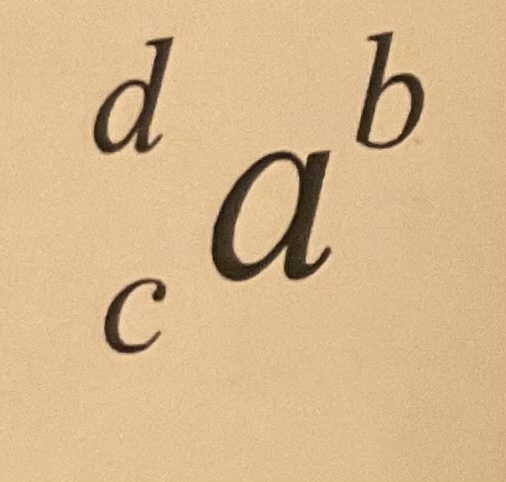
17
New cards
Net force/charge
What is normally in place of b
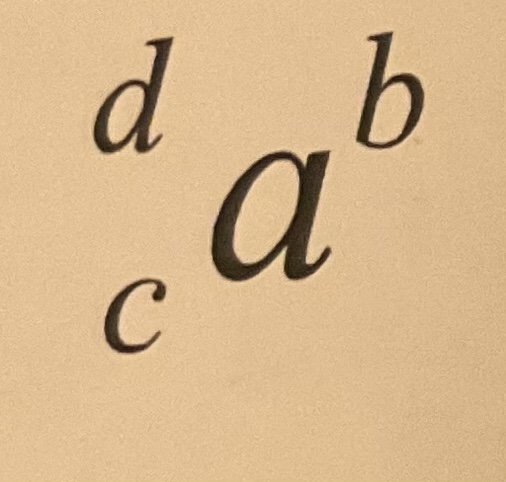
18
New cards
atomic number
what is normally in place of c
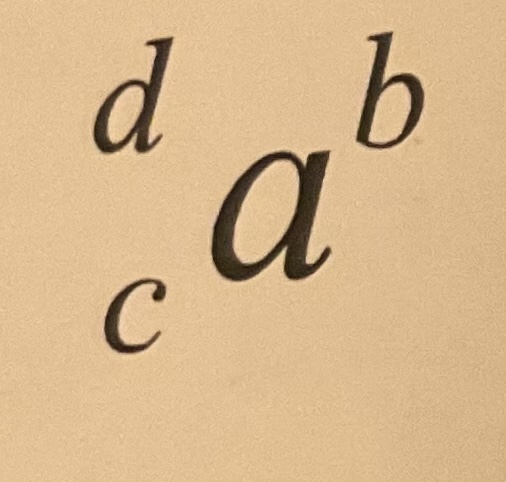
19
New cards
Atomic mass
What is normally in place of d
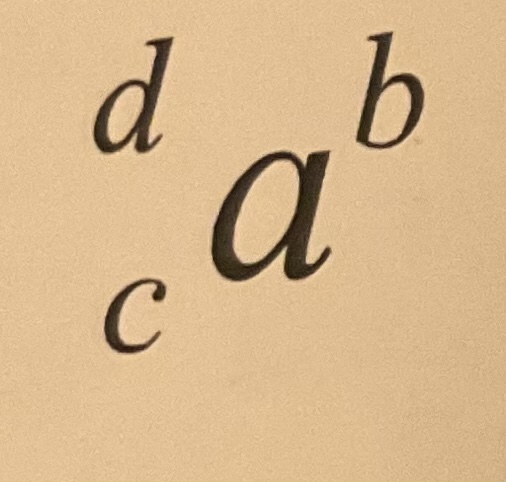
20
New cards
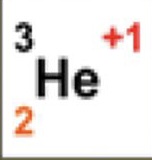
3
What is the atomic mass
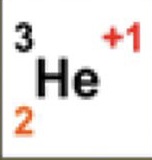
21
New cards
2
What is the atomic number
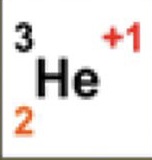
22
New cards
+1
What is the charge
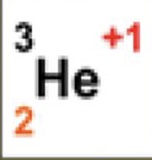
23
New cards
1
How many neutrons are there
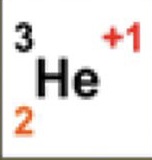
24
New cards
2
How many protons are there
25
New cards
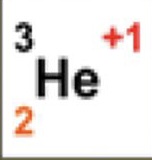
1
How many electrons are there
26
New cards
What two things must be true for an element to be an isotope
Diff number of neutrons/mass and the same number of protons/same element
27
New cards
An atom or molecule that gained or lost electrons
Ion
28
New cards
a positively charged ion; an ion that has lost electrons
cation
29
New cards
a negatively charged ion; an ion that has gained electrons
anion
30
New cards
What are the two forces that work in the nucleus
Strong nuclear force and electromagnetic repulsion
31
New cards
How do u calculate molar mass
Add together the molar mass from each individual atom in the compound (found on periodic table)
32
New cards
What are the units for molar mass
G/mol
33
New cards
What is the formula for calculating AAM
AAM= A(%A)+ B(%B) +…
34
New cards
In what order do u convert mass to atoms (mmpa)
Mass, mols, particles, atoms
35
New cards
What are the units for average atomic mass
amu
36
New cards
How do all atoms of the same element react
Chemically the same
37
New cards
proposed that atoms weren’t indivisible, but made up of smaller partciles called subatomic particles (proton, neutron, electron)
thomson
38
New cards
what did dalton’s atomic theory state and how does it relate to modern science
1. states all matter is made of tiny indivisible particles called atoms (proven wrong)
◦ modern science: atoms are not indivisble
2. atoms of the same element are exactly alike + have same mass; atoms of different elements have different masses
◦ modern science: concept of isotopes —> not quite right
3. in chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged
4. atoms of diff elements combine in whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds
◦ modern science: atoms are not indivisble
2. atoms of the same element are exactly alike + have same mass; atoms of different elements have different masses
◦ modern science: concept of isotopes —> not quite right
3. in chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged
4. atoms of diff elements combine in whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds
39
New cards
who developed the law of multiple proportions which states that when elements form compounds, the proportions of the elements in those chemical compounds can be expresses in small whole number rations (elements on the periodic table)
dalton
40
New cards
conducted experiments to determine the charge-to-mass ratio and the mass of the electron
milikan
41
New cards
found out that the electron is 9.109x10^-31kg
milikan
42
New cards
◦ found out that all atoms are able to produce electrons and atoms are not indivisble
milikan
43
New cards
determined the magnitude of electron charge
milikan
44
New cards
found that most alpha particles passed through, some angled slightly, and a tiny fraction bounced back
rutherford
45
New cards
found out that atom is mostly empty space, (+) particles are concentrated at the center of the nucleus (little nut), and that (-) particles orbit the nucleus
rutherford
46
New cards
who found out the purpose of the neutrons
chadwick
47
New cards
what is the purpose of neutrons
to stabalize the nucleus
48
New cards
◦ danish physicist proposed a model of the atom in which the electrons orbit the nucleus without losing energy
◦ calls each possible orbit a quantom
◦ based his theory on the work of planck
◦ proposed that light is made up of units of energy of a definite amount, each of which is called a energy level
◦ calls each possible orbit a quantom
◦ based his theory on the work of planck
◦ proposed that light is made up of units of energy of a definite amount, each of which is called a energy level
bohr
49
New cards
a group of elements that have the same amount of protons but different masses/# of neutrons
isotopes
50
New cards
what is the difference between atoms and molecules
atoms are singular neutral particles
molecules are bonded neutral atoms (2 or more atoms)
molecules are bonded neutral atoms (2 or more atoms)
Explore top notes
Explore top flashcards
ANAPHY: U13.3 Digestive System (Nutrition, Metabolism, Body Temperature Regulation)
86Updated 160d ago0.0(0)
ANAPHY: U13.3 Digestive System (Nutrition, Metabolism, Body Temperature Regulation)
86Updated 160d ago0.0(0)