Unit 2 - Human Resource Mangemnent
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Human resources management
How an organization manages its human resources, including recruitment, training, compensation/benefits, motivations and specifying job responsibilities.
Demographic changes
Changes to the characteristics of a population.
E.g. birth rates, death rates, education levels, religion, ethnicity, age, etc.
Labour mobility
The ability of workers to move occupationally or geographically (within countries or internationally)
Immigration
The movement of people from one country to another country for residence.
Flexi-time
Flexible hours agreed and scheduled by the management and the employee.
Gig economy
The section of the economy that provides temporary work for freelancers. Workers can take work flexibly, but do not have the same protections and benefits as those on long-term employment contracts.
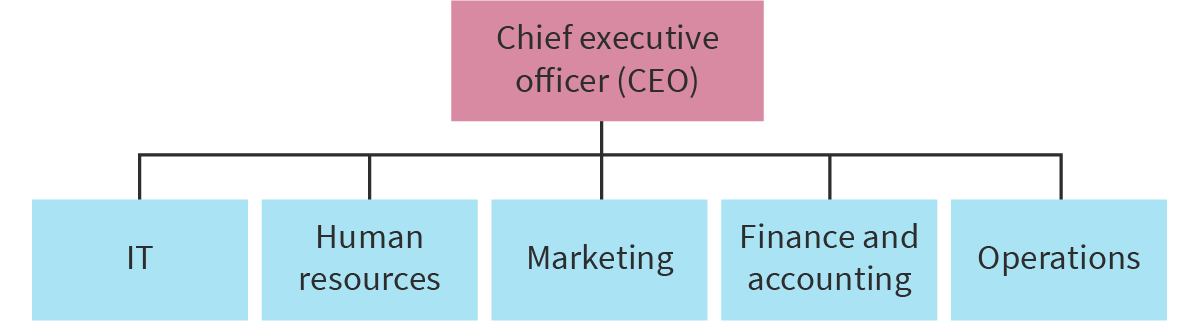
Organizational chart
Shows the reporting relationships within an organization.
Hierarchy
A system organizing or ranking people according to power or importance.
Chain of command
The official hierarchy in an organization. It indicates who reports to who and who has authority over who.
Span of control
The number of people reporting to a specific manager.
Wide span of control → many people reporting to the manager
Narrow span of control → few people reporting to the manager
Delegation
Assigning authority or responsibility over specific tasks from one person, a manager, to someone lower in the organizational chart.
Bureacracy
Any organization with multiple layers of authority.
Centralization
A situation where the decision-making authority of an organization is held by one person, or a small group of people.
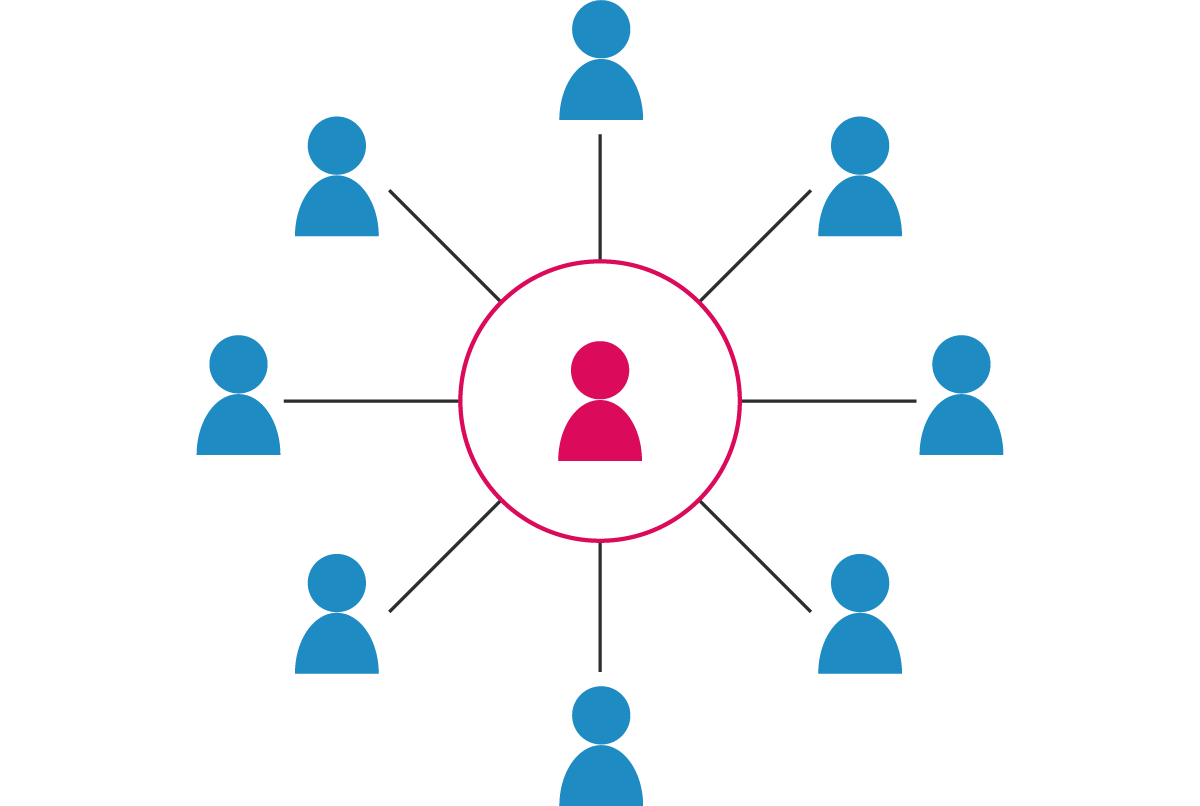
Decentralization
A situation where the decision-making powers are passed down to the lower levels in the organisation.
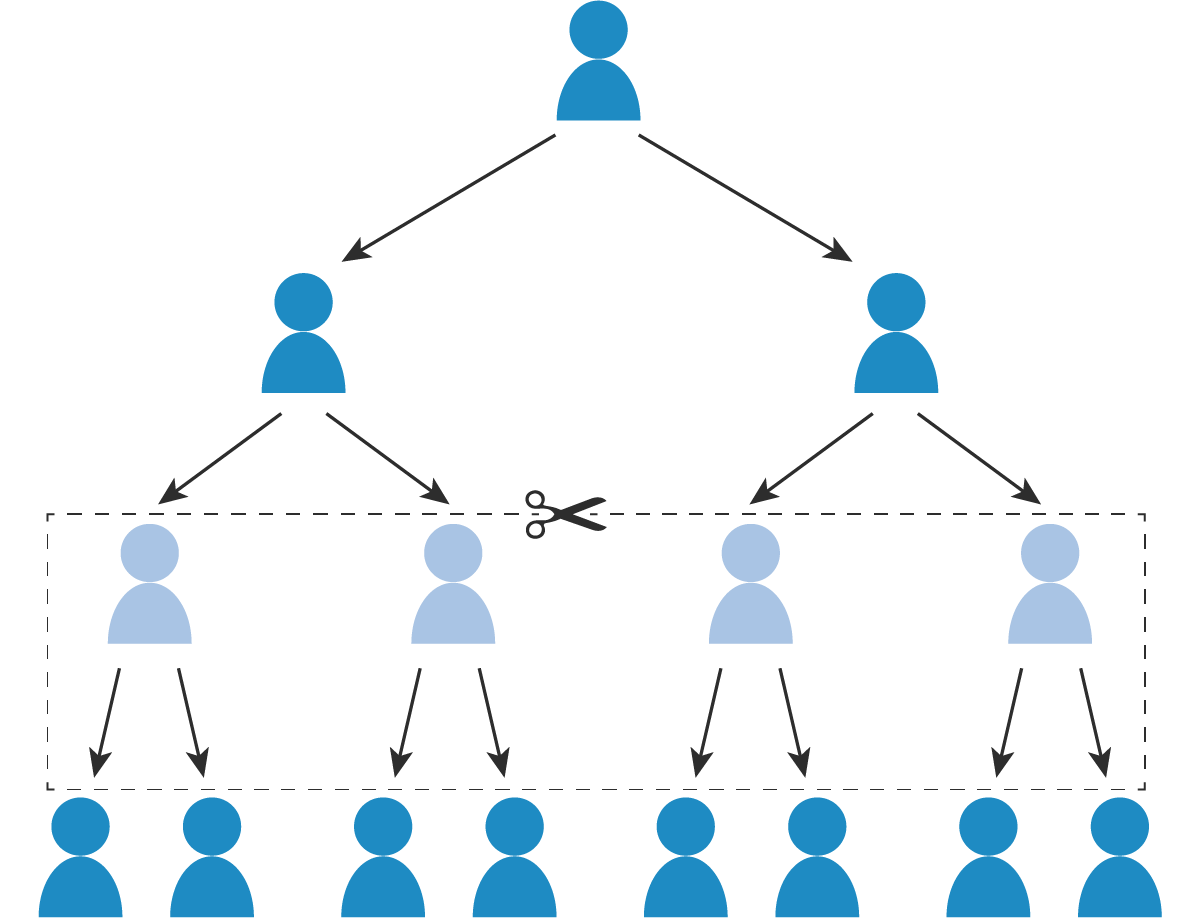
Delayering
The process of removing levels/layers of hierarchy in an organization to improve efficiency.
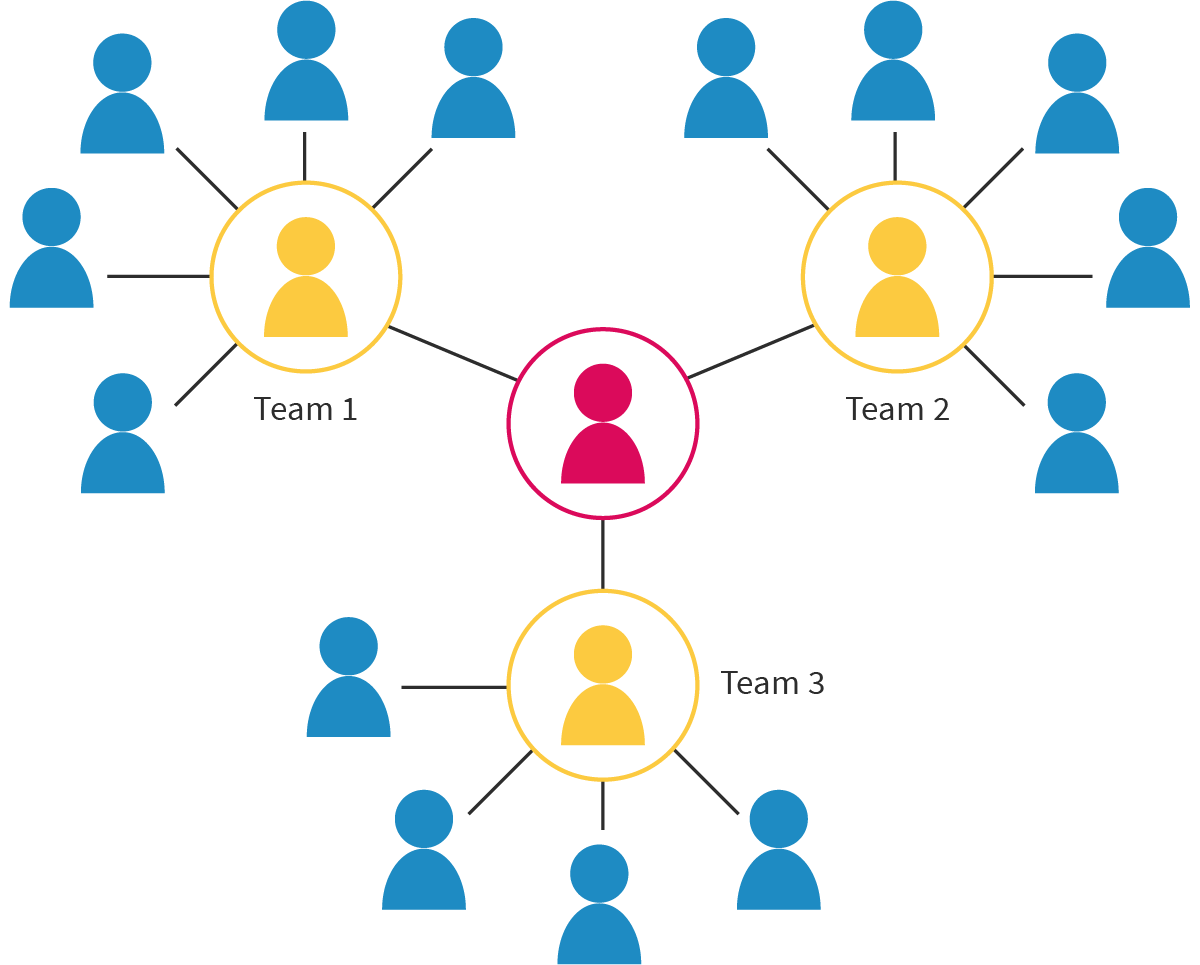
Matrix structure/Project-based organization
An organizational structure that has two or more reporting structures; employees working in teams on a project report to both a project manager and a department manager.
Shamrock organizaton
A structure that has three types of employees:
Core employees
Contract employees
Temporary workers
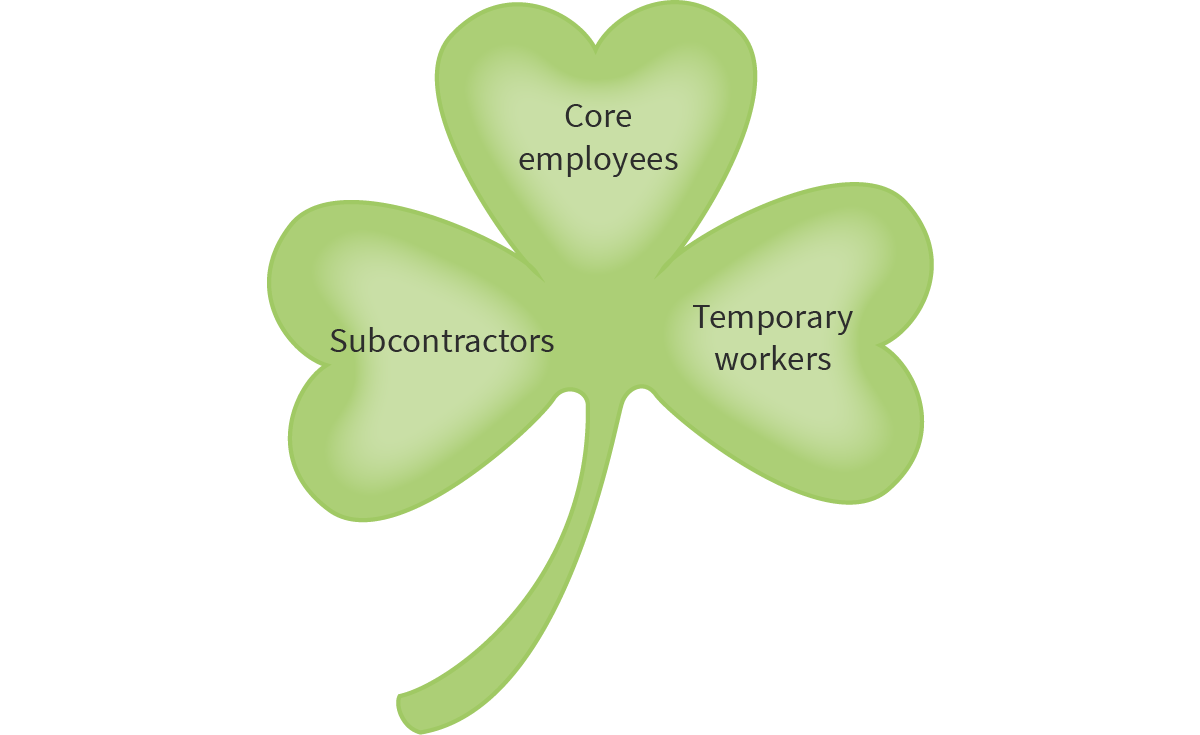
Core employees
Permanent employees who fulfil the core mission of the business.
Contract employees
Workers subcontracted to complete specialized tasks.
Temporary employees
Workers hired only as needed as the business expands or contracts.
Management
The work of planning, decision-making, organizing, leading, motivating and controlling the financial, human, physical and information resources of a business.
Leadership
The process of motivating a group of people to work towards the goals of a business.
Autocratic leaderhsip
A domineering and possibly tyrannical leadership approach. It is strong and rule-oriented.
Paternalistic leadership
With this leadership style, the organization’s interests and its employees are looked after as if they were family.
Demographic leadership
This leadership style values inclusiveness and employees’ input. It is the opposite of autocratic.
Laissez-faire leadership
This leadership style gives employees considerable freedom to make decisions on their own.
Situational leadership
When leaders adapt their leadership style to the nature of the situation/task and the ability/expectation of employees.
Motivation
The reasons why a human being does something.
Intrinsic motivation
When a person engages in an activity because there is a reward or pleasure in the activity itself.
Extrinsic motivation
Where a person engages in an activity because of a reward outside the activity itself, such as being paid.
Labour turnover
The percentage of workers leaving the business in a period of time.
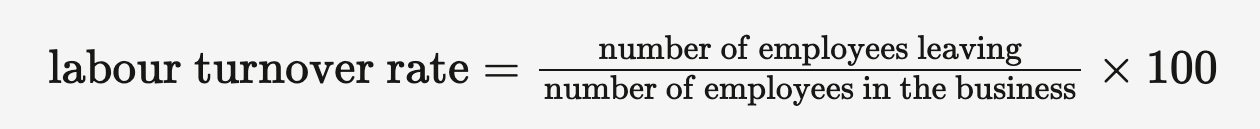
Internal recruitment
When a position becomes available at an organization and the organization recruits someone who is already working there to take on the new position.
External recruitment
When an organization recruits employees who are not presently employed by the organization.
Induction
The introduction of new employees to an organization.
On-the-job training
Traning employees at their place of employment during their normal working hours.
Off-the-job training
Training employees offsite.
Appraisal
An assessment of an employee's performance.
Formative appraisal
Occurs during the training or work of the employee. It is ongoing and is intended to improve employees’ performance.
Summative appraisal
Occurs at the end of the training or at a fixed time during the year. They are the formal, documented evaluation of employees, and measure employees’ performances.
360-degree feedback
A process in which an employee receives feedback from all of the people with whom they come into contact via surveys.
E.g. peers, customers, supervisors, etc.
Self-appraisal
When an employee evaluates their own performance. It can be part of a formative or summative.
Financial rewards
Rewards for employees that involve monetary compensation for work.
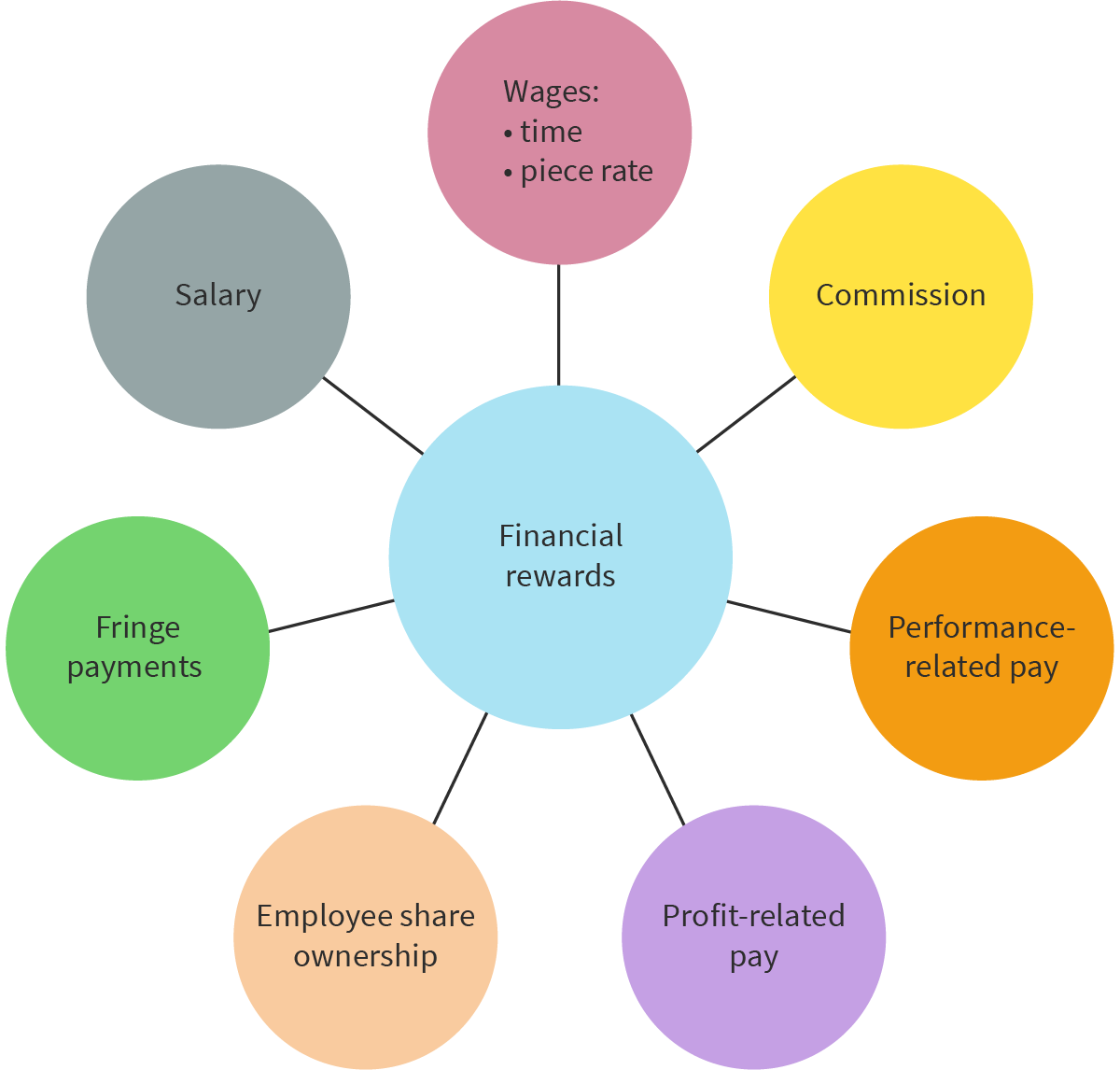
Salary
A fixed, regular payment to employees, typically on a bi-weekly or monthly basis.
Wages (time and piece rates)
Employees are either paid a periodic sum based on the number of hours they work (e.g. $15 per hour) or based on the number of units or ‘pieces’ they make or complete (e.g. $5 for every item completed).
Commision
A type of payment to an employee or agent based on the number of sales or a percentage of the value of sales.
Performance-related pay
A financial reward where employees receive a bonus in addition to their usual pay.
Employee share-ownership schemes
A financial reward where employees receive shares in the business or are allowed to buy shares at below-market price.
Fringe payments
These rewards are given to the employee in addition to their pay, and may include benefit such as a company car, housing or school allowance, free meals, gym membership and other rewards.
Non-financial rewards
Methods of recognizing employee efforts and improving motivation through improved job titles or recognition like “employee of the month”.
Job enrichment
A non-financial reward whereby an employee is given additional challenging tasks that make the work more interesting and lead to professional growth.
Job rotation
A non-financial reward where employees are regularly rotated into different positions, allowing them to gain experience and acquire new skills.
Job enlargement
A non-financial reward where more tasks, usually of the same skill and difficulty level, are officially added to an employee’s job description.
Culture
The achievements, arts, attitudes, customs, norms, social institutions and values of a particular nation.
Organizational culture
The achievements, arts, attitudes, customs, norms, social institutions and values of a particular organization.
Power culture
An organizational culture where an individual or a selected group of people makes decisions for the organization and communication is highly centralized.
Role culture
An organizational culture that is defined by clear rules and hierarchies for the smooth operation of an organization; people have power through their position, rather than their own qualities.
Task culture
An organizational culture focused on specific problems. In this context, power shifts from person to person as different people are suited to different tasks or issues.
Person culture
An organizational culture where individuals believe themselves to be superior to the organization; free spirits.
Culture clash
When two different cultures come into conflict. This could happen in the event of a merger or acquisition between two different organizations.
Formal communication
The official and formally recognized methods of communication in an organization.
E.g. meetings, emails, reports, etc.
Informal communication
The various ways information can casually be shared.
E.g. conversations, gossip, etc.
Barriers to communication
Anything that interferes with the transfer of information in an organization.
E.g. linguistic, psychological, structural, etc.
Conflict in the workplace
Conflict between management and organized groups of workers → often over pay, benefits and control over the work.
Collective bargaining
When employees of an organization work together when bargaining with management about wages and work conditions. Often occurs with unionized employees.
Work-to-rule
When employees precisely follow the rules of their existing contract, so they do the minimum required.
Strike action
When workers stop working because they are dissatisfied with work conditions or compensation.
Threats of redundancies
When management threatens to eliminate employment positions if workers don’t accept terms in an industrial dispute.
Changes of contract
When agreement is reached over new contract terms in collective bargaining and negotiation.
Lockout
When management locks up the company or factories to prevent workers from entering them as a part of the negotiating process.
Closure
The permanent or temporary shutdown of a work site.
E.g. factory, plant, office, etc.
Conciliation
When a third party mediator mediates between management and labour and offers ideas that may help the two sides come to an agreement.
Arbitration
When a third party arbitrator mediates between management and labour and has the authority to decide how the conflict between management and labour will be resolved.