LECOM MMS Immunology 4A Humoral Immune System I and II Part 2
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
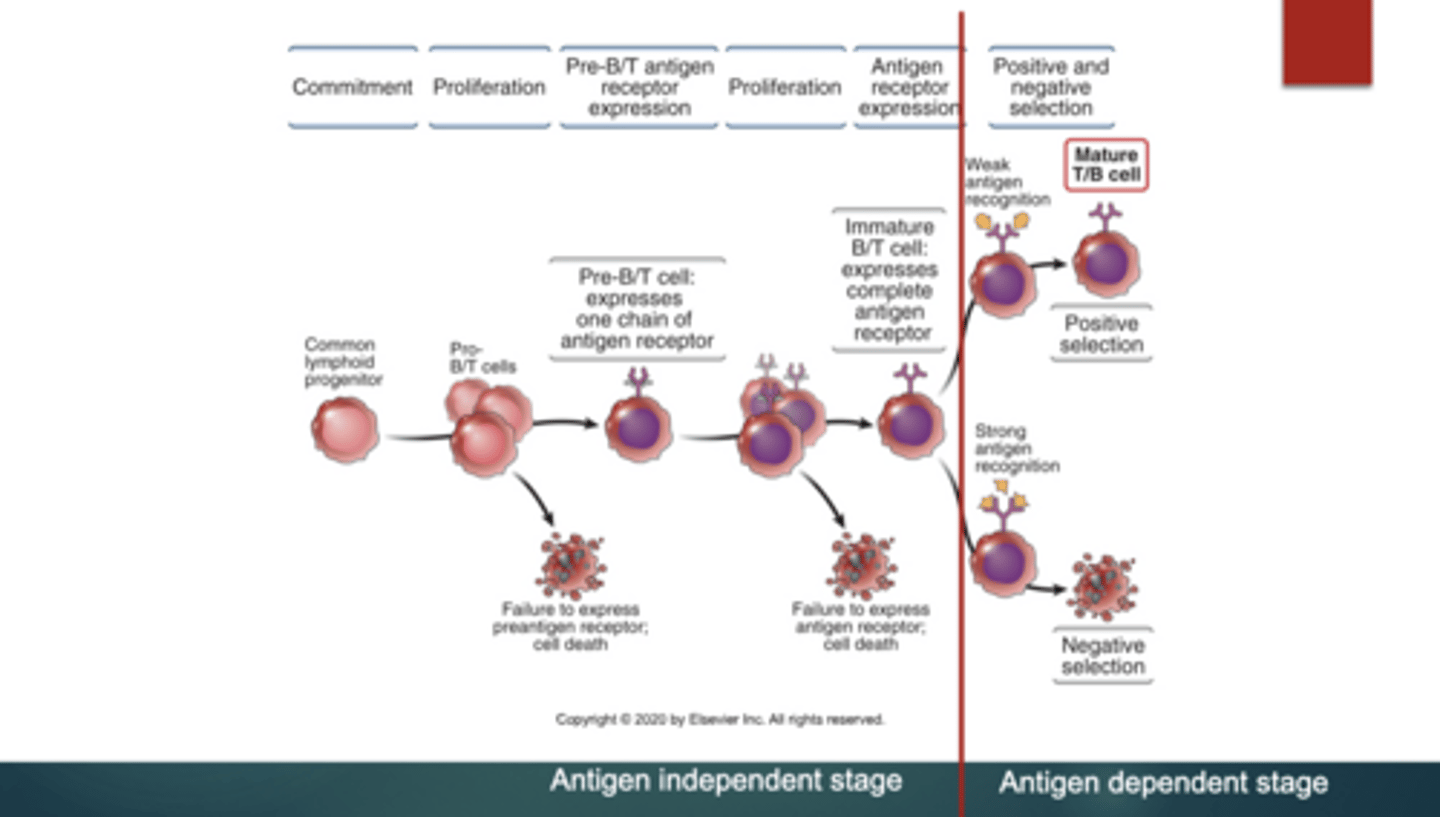
Where does the Antibody independent stage of B-cell development occur?
In the bone marrow
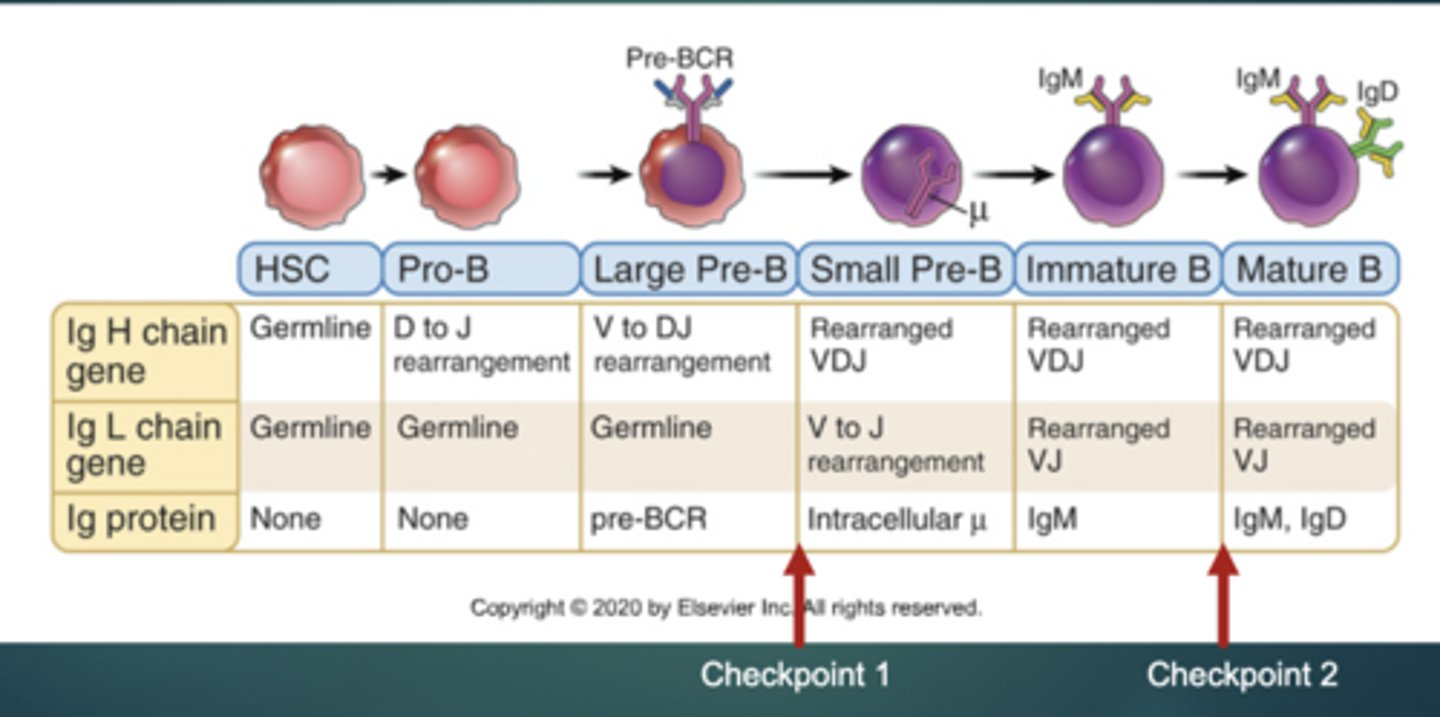
What are the checkpoints associated with B cell development?
Checkpoint 1: make a functional heavy chain to make a pre-BCR
Checkpoint 2: make a functional light chain and bind it to the heavy chain to make a BCR
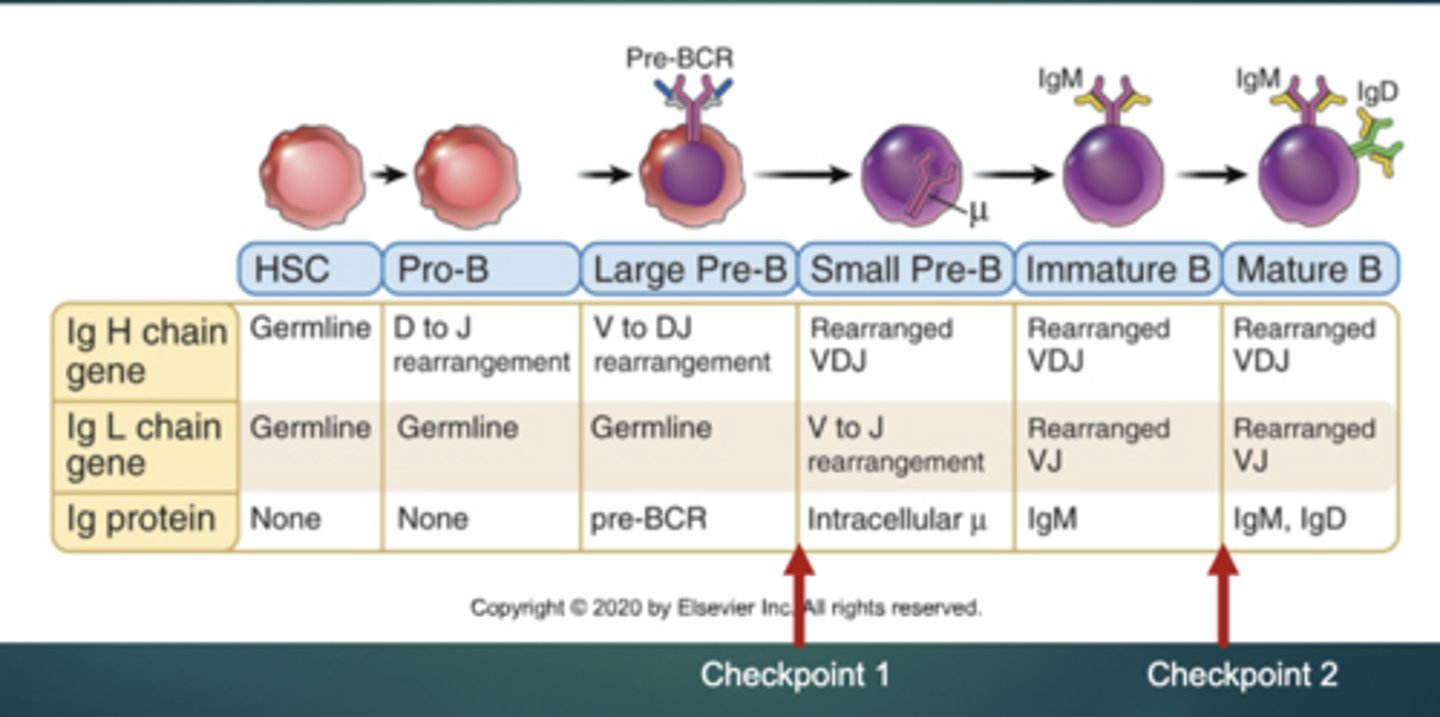
What is needed at Checkpoint 1 in B cell development?
Rag 1 and 2 to make the Variable domain of the heavy chain
What are Iga and IgB involved in?
Signal transduction
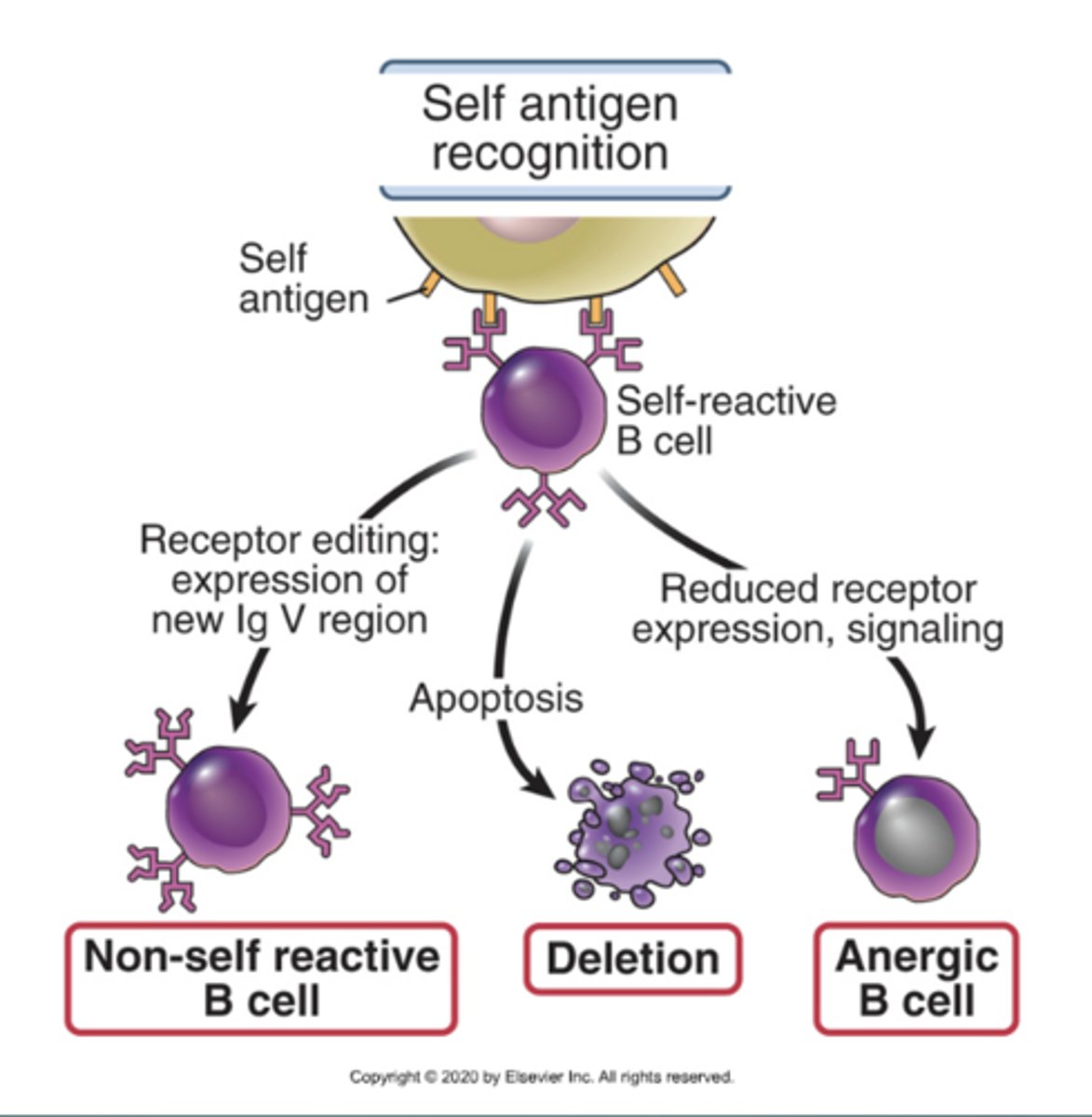
What are the different possibilities for when a B cells recognizes a Self-antigen?
1. Non-self reactive B cell
2. Deletion (apoptosis)
3. Anergic B cell (reduced expression)
When are Rag 1 and 2 expressed?
Only during development and maturation of B cells and T cells
- Pro, pre, immature B cell
What is Tdt expression involved in?
Increasing Junctional Diversity
- Pro and pre-B cell
What is the role of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (btk)?
It is a downstream signaling kinase that has an important role in B cell development. If btk is lacking, then Checkpoint 1 cannot be passed. It is required for pre-BCR signaling
What happens if a person lacks Bruton's tyrosine kinase (btk)?
No B cells will be formed; however, there will be sufficient T cells
What are MHC II, CD19, CD20, CD21, and CD40 involved in?
Pro B cell --> memory B cell
In the Antigen Dependent Stage, what are the fates of an Activated B cell?
- Antibody secretion
- Isotype switching
- Affinity maturation
- Memory B cell
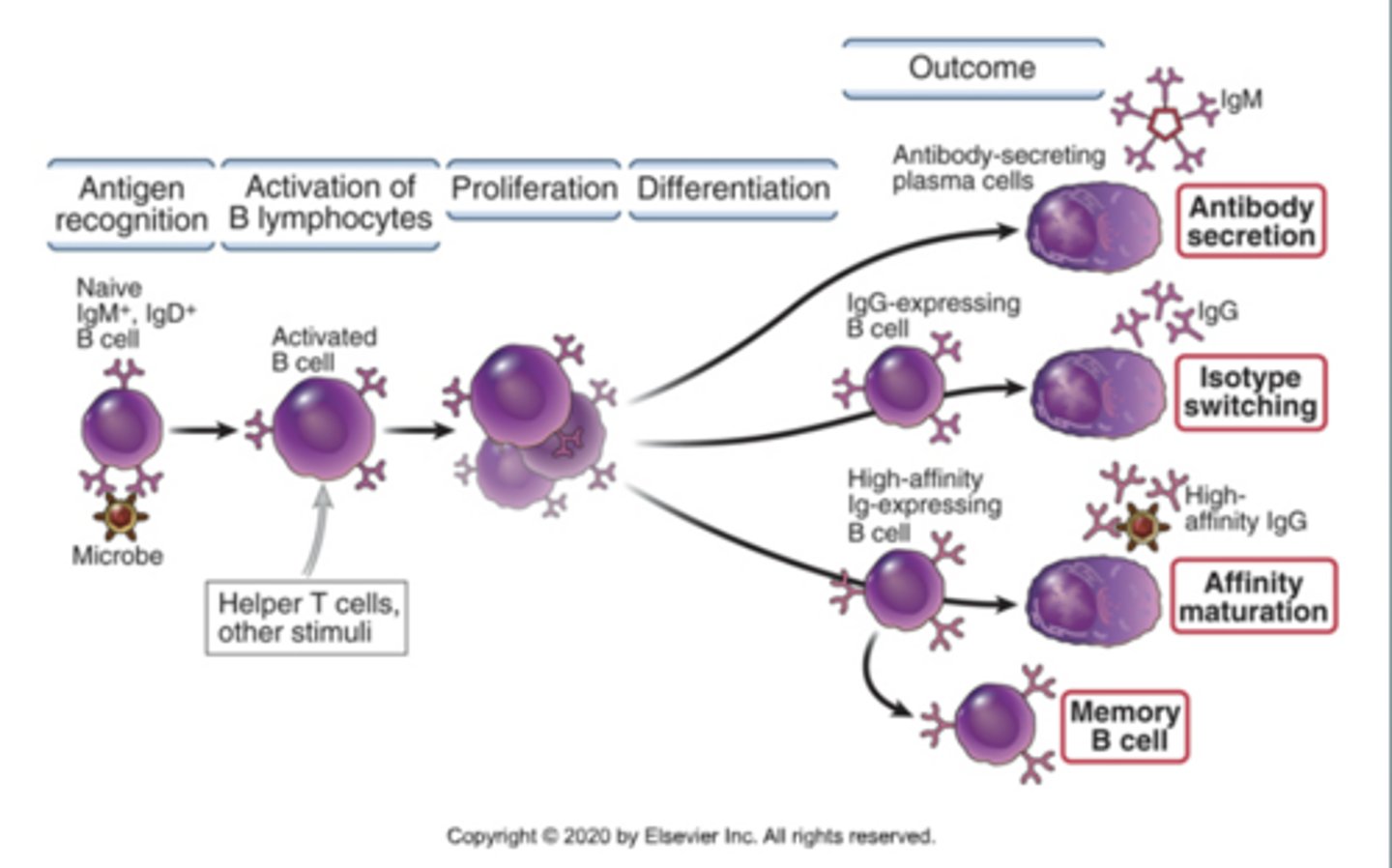
Where does the Antigen Dependent Stage occur?
In the periphery
What happens in T-Independent B cell Activation?
B cells are activated without T cell help, but they require cross linking
In T-Independent B cell Activation, is there a strong antibody response or a weak antibody response?
Weak antibody response (IgM - no class switching)
In T-Independent B cell Activation, is there a short-lived response or a long response?
Short-lived response
In T-Independent B cell Activation, what do they recognize?
Polysaccharides, nucleic acid, lipids, etc.
In T-Independent B cell Activation, is there formation of memory B cells?
No
What does T-Independent B cell activation lead to?
- Mainly IgM
- Low-affinity antibodies
- Short-lived plasma cells
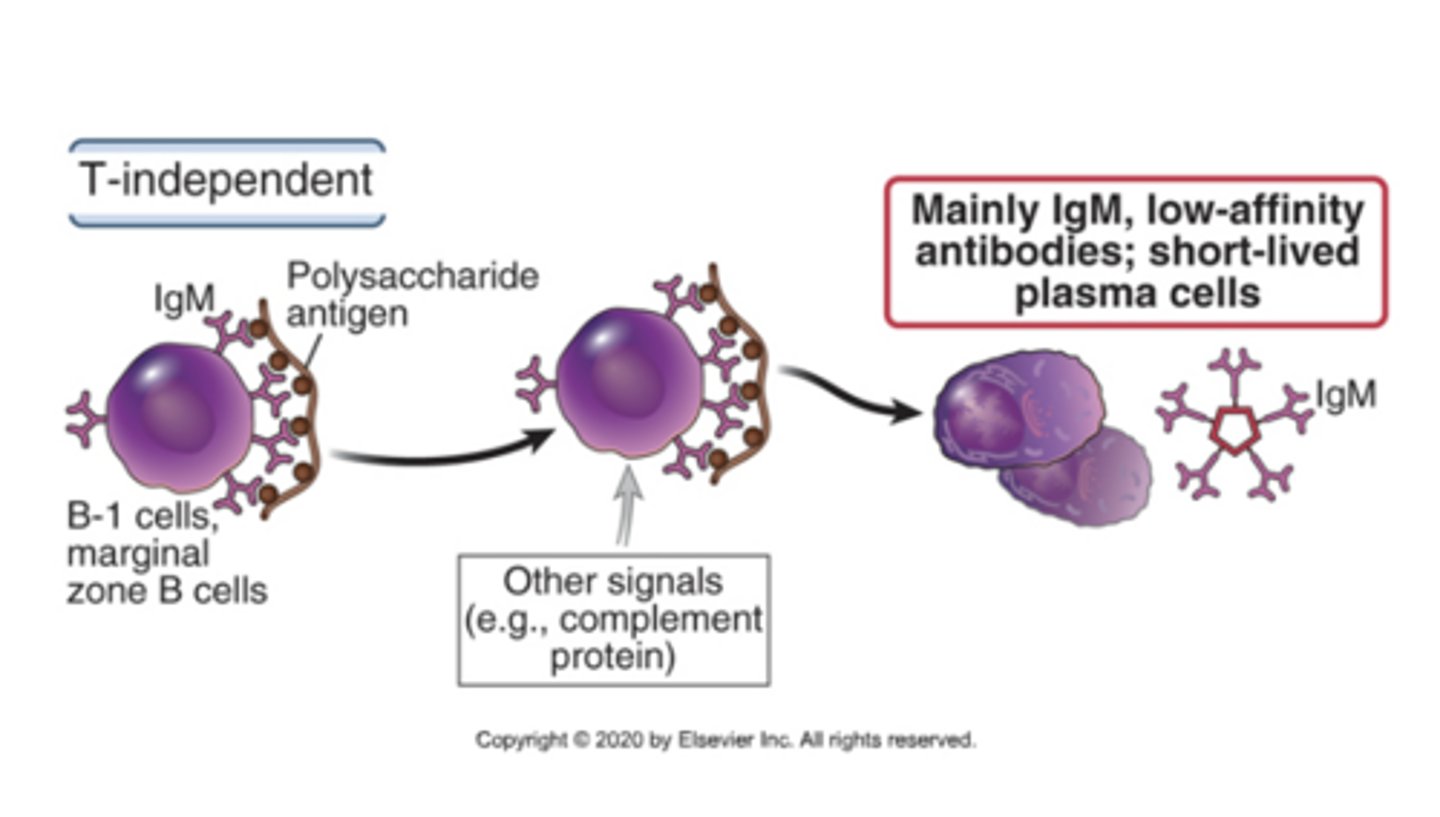
What are B cells dependent on in T-dependent B cell activation?
T cells (recognizes proteins ony)
In T-dependent B cell activation, do B cells require help?
Yes, T cell help (MHC II + TCR)
Do B cells require Co-stimulation in T-dependent B cell activation?
Yes, with CD40/40L and Cytokines
What does T-dependent B cell activation lead to?
- Isotype-switched, high-affinity antibodies
- Memory B cells
- Long-lived plasma cells
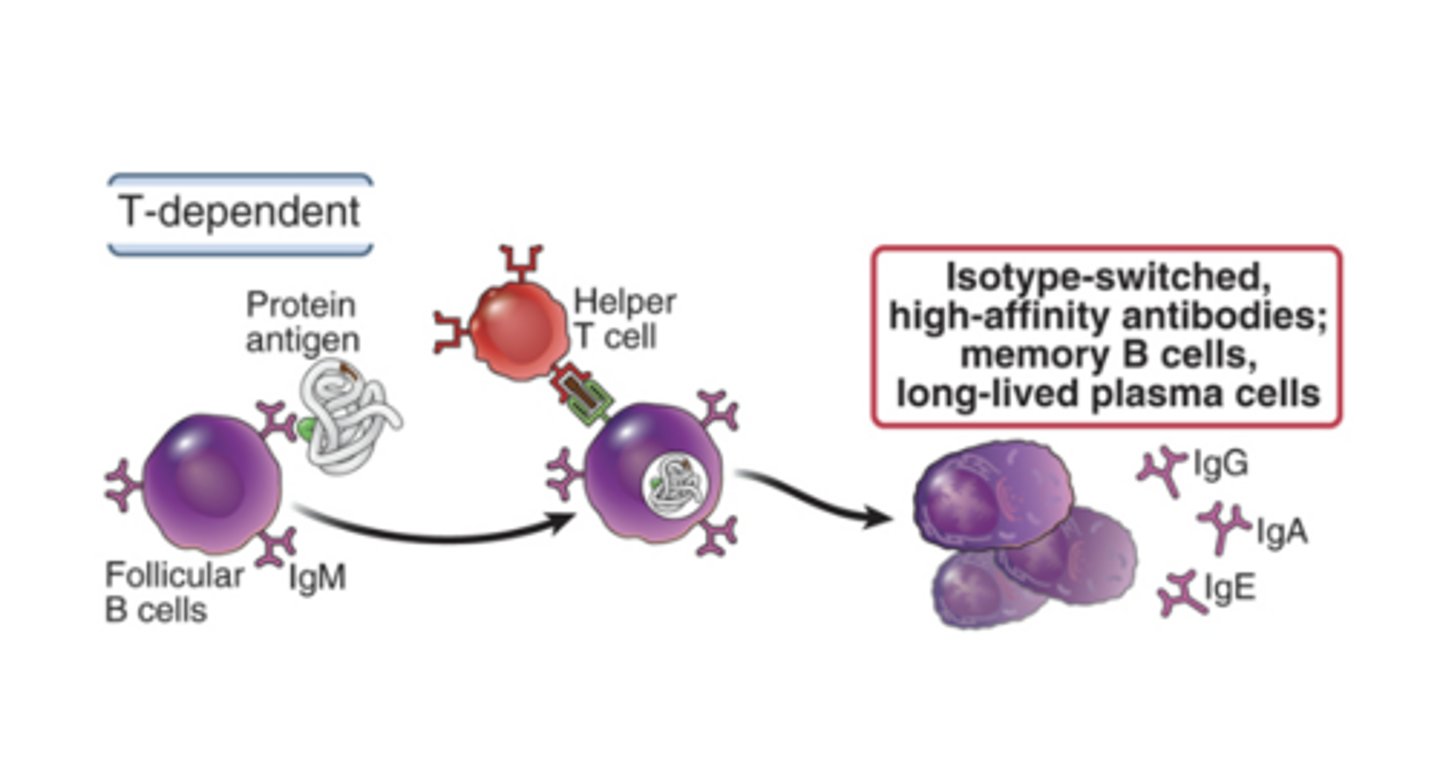
What 3 steps are need for a B cell to go through Affinity Maturation and Class Switching?
1. Activated helper T cell expresses CD40L, secretes cytokines
2. B cells are activated by CD40 engagement, T cell releases cytokines to tell the B cells what to do.
3. B cell proliferation and differentiation
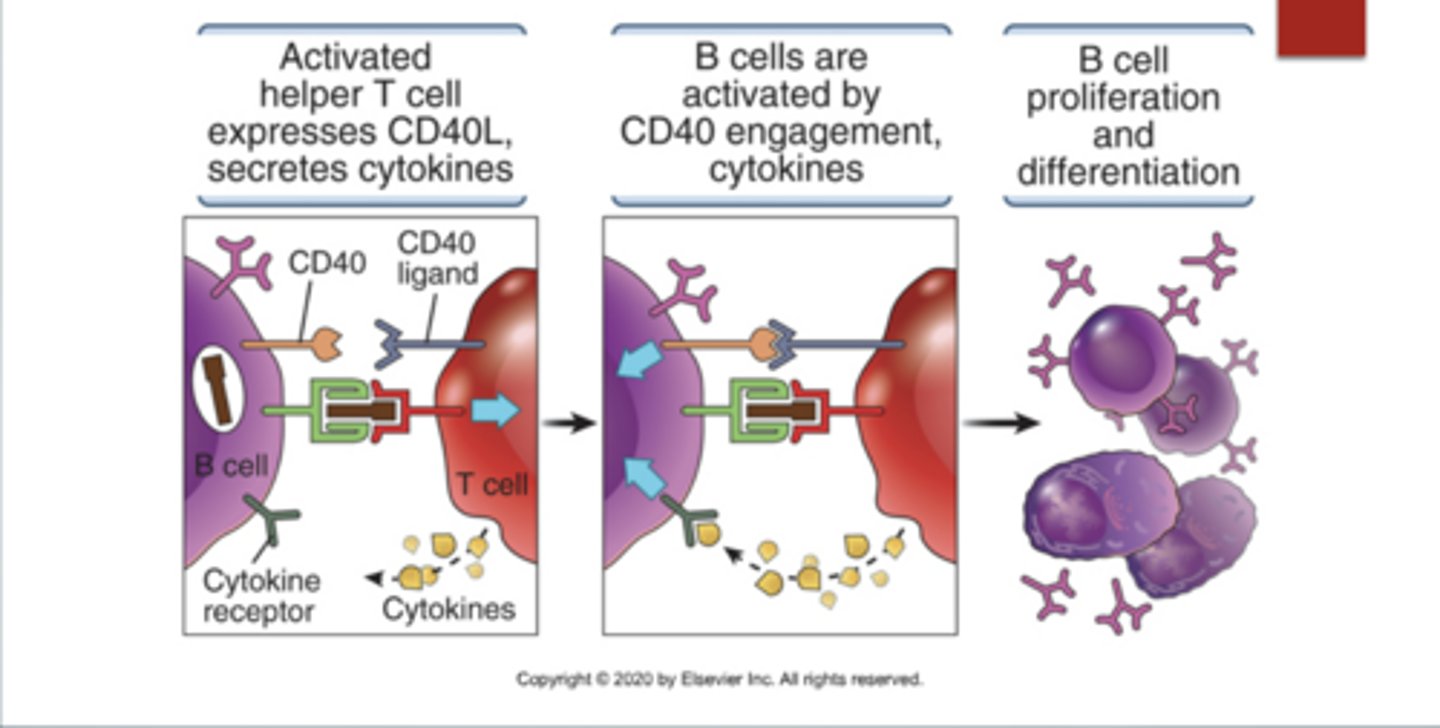
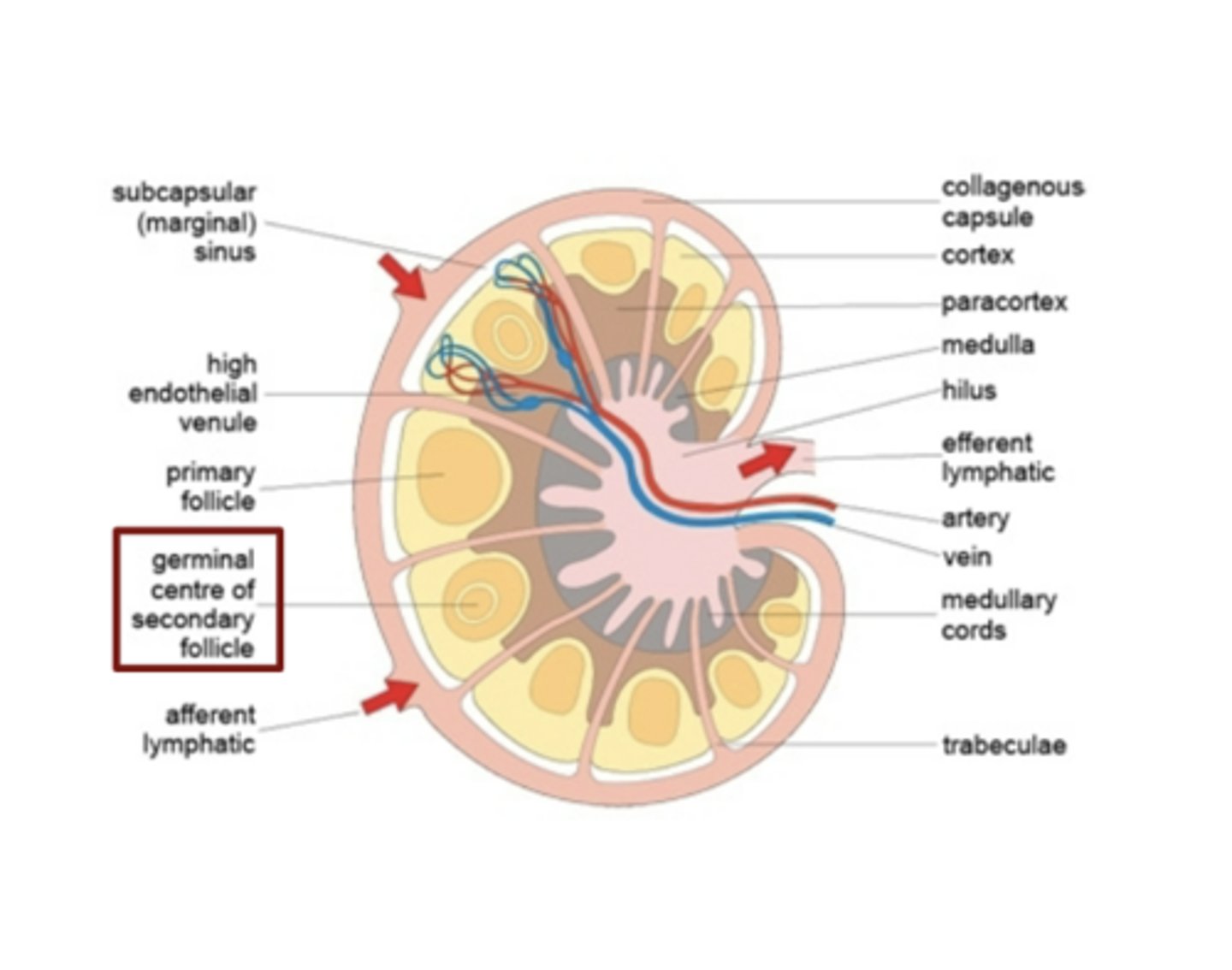
Where does Isotype/Class switching, Affinity maturation, Plasma cell formation, and Memory cell formation occur?
Germinal center of the secondary follicle; this happens during T-dependent B cell Activation
What does Class (Isotype) Switching require?
T cell help (Requires CD40-CD40L interaction)
What is the function of Activation-induced deaminase (AID)?
It adds uracil in the place of cytosines; it also makes different antibody isotypes and changes the constant heavy region
Once the constant region is changed, can it be reversed? Is the variable region changed?
No to both
What can Somatic Hypermutation do to Affinity Maturation?
It can increase affinity by 100-10,000-fold
During Affinity Maturation, what type of antibodies are selected?
Higher affinity antibodies
During Affinity Maturation, what happens to the lower affinity antibodies?
They go through apoptosis
During Affinity Maturation, what do higher affinity B cells do?
They bind better and receive signal to survive
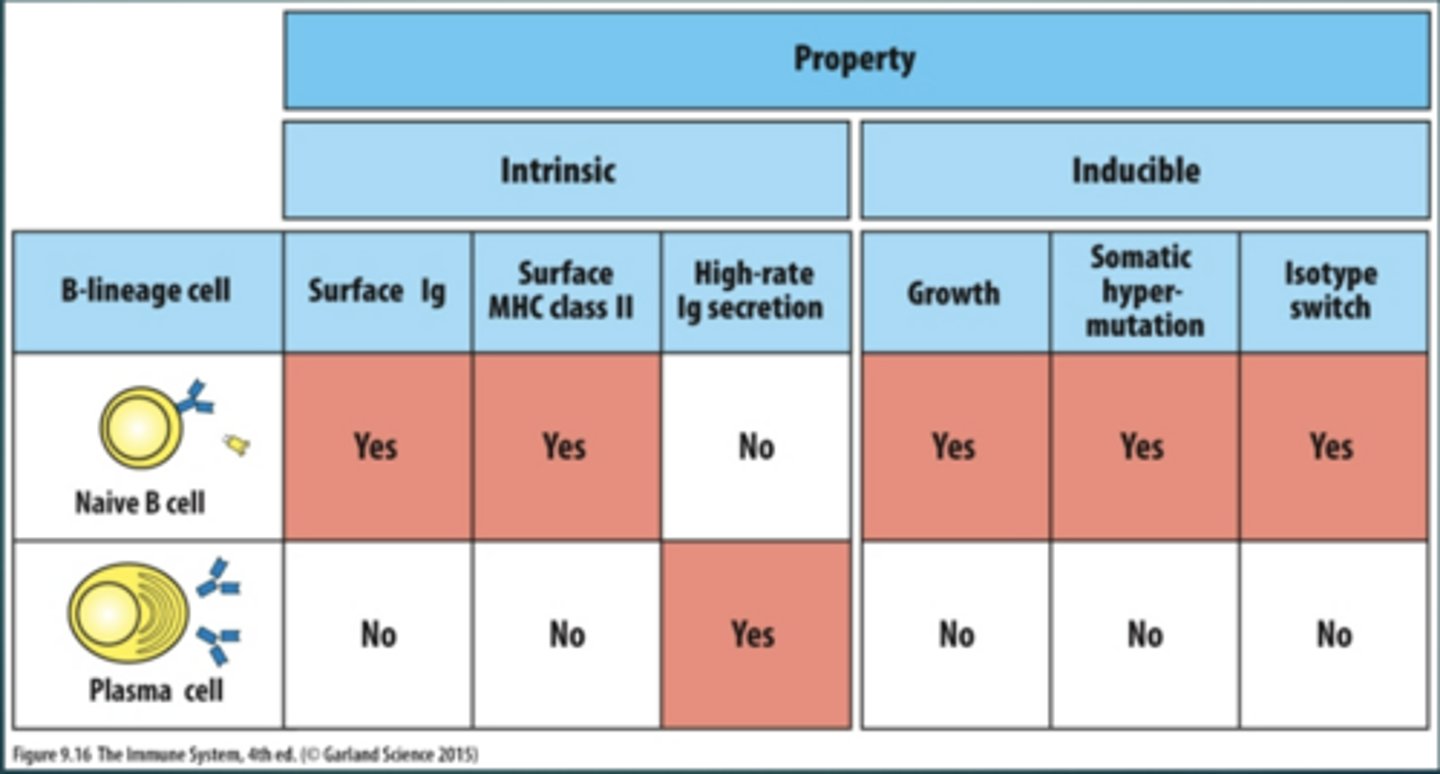
Do Plasma Cells have an MHC II?
No
Do Plasma Cells have a surface Ig?
No
Do Plasma Cells have a high-rate Ig secretion?
Yes
What do Plasma Cells secrete?
Up to 2000 antibodies per second
Difference Between B Cells and Plasma Cells
Where are Long-Lived Plasma Cells found?
In the bone marrow and gut
How long do Long-Lived Plasma Cells survive?
For decades
What is the function of Long-Lived Plasma Cells?
Continue to make antibodies
* Maintains a steady-state level of antibodies
What are Long-Lived Plasma Cells responsible for?
Serological memory
* "History" of an individual's response to infection or vaccination
What do Long-Lived Plasma Cells require survival signals from?
Stromal cells
What are Memory B cells responsible for?
Secondary adaptive immune response
What are Memory B cells induced by?
T cells
Are Memory B cells easily activated compared to naïve B cells?
Yes
What have Memory B cells undergone?
Isotype switching and Affinity Maturation
What do Memory B cells provide?
Protection for decades or life
Which CD marker is located only on Memory B cells?
CD27
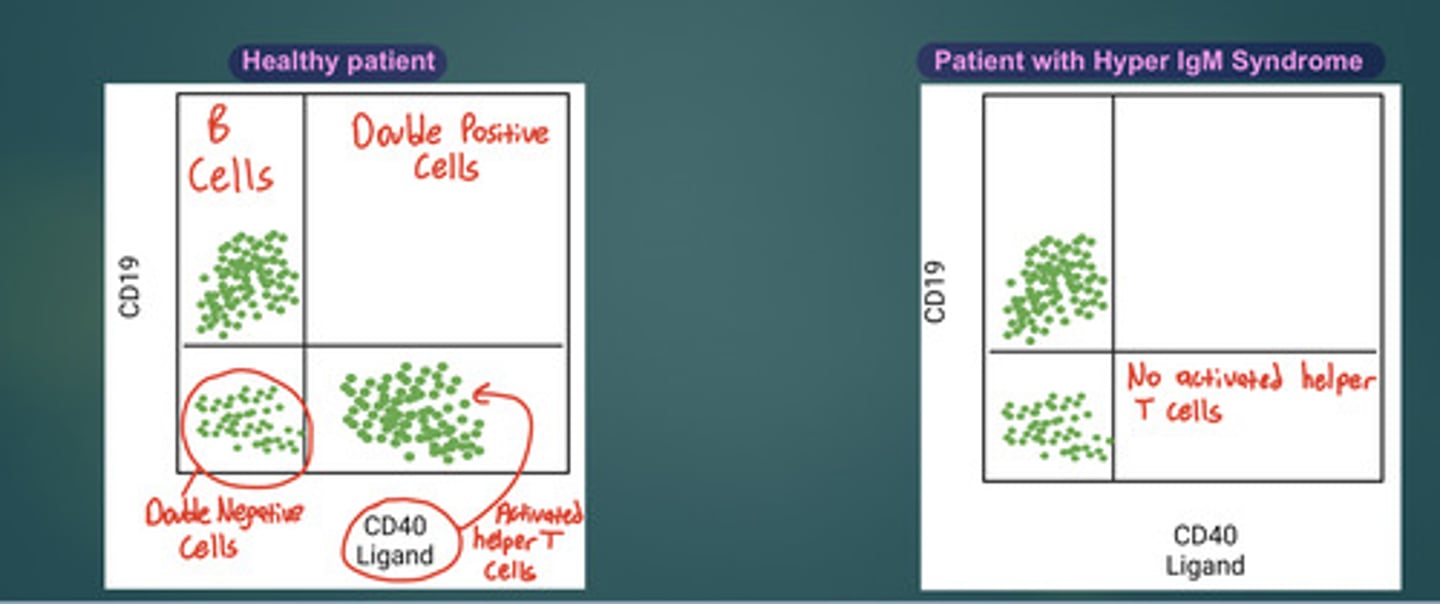
What is Hyper-IgM Syndrome?
Very high levels of IgM
* Deficiency of IgG, IgA, and IgE
Why does Hyper-IgM Syndrome happen?
Due to a lack of activation by T helper cells
* No CD40L on TH cells
What does Hyper-IgM Syndrome lack?
Germinal centers
What is Hyper-IgM Syndrome associated with?
Increased susceptibility to Bacterial and Fungal infections
Be able to identify a Diagnosis with Flow Cytometry
Which of the following is associated with plasma cells but not naïve B cells? (Select all that apply)
A. Can be induced to class switch
B. Can be induced to proliferate
C. Lack of cell surface Ig
D. Lack of MHC II
E. Secrete antibodies
F. Presence of CD27
C. Lack of cell surface Ig
D. Lack of MHC II
E. Secrete antibodies
Which of the following statements is correct? (Also prepare to explain why the others are incorrect)
A. A person with a mutation in the AID enzyme can still create antibodies involved in ADCC
B. A person with a mutation in the AID enzyme can still create antibodies that activate the classical complement pathway
C. A person with a mutation in the AID enzyme will lack CD19 cells
D. The AID enzyme is required during B cell development
E. The AID enzyme is required for endogenous antigen processing
A 7-month-old male was hospitalized with pneumonia due to a fungal infection. The lab determines the causative fungus is Pneumocystis jirovecii. The lab also determines the patient has normal numbers of B cells, T cells, increased levels of IgM, but very low levels of IgG, IgA, and IgE. Which of the following genes is most likely mutated?
A. CD4
B. CD19
C. CD27
D. CD40 ligand
E. Rag
D. CD40 ligand