TV4101 SAM - ECG
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Clinical utility of ECG
For diagnosing and managing arrhythmias
Used to be used to assess chamber size but echocardiography is more commonly used
Can’t be used
ECG’s are a reflection of?
How is this activity made?
Electrical activity of the heart
Electrical activity is generated by movement of ions
What is needed for muscle contraction?
All ion movements are mediated by?
What are the active processes?
Movement of ions (generates voltage to “zap” muscle)
Voltage and energy mediated transport
Systole and diastole are active processes
Important terminology
Electrode?
Lead?
Electrode - physical electrical attachment to body
Lead - an electrical vector that calculates the velocity and speed of electricity between a positive and negative electrode
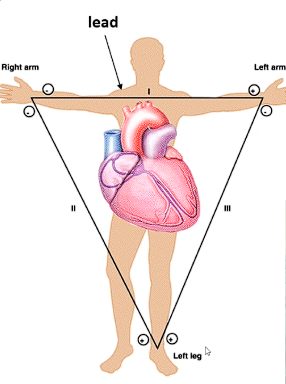
Why do we need leads?
ECG machine detects the current flowing towards positive electrode
Standard Lead Placement
How does it work?
Electrodes placed on body
Lead has a positive and negtive reference point
Allows tracing to reflect the direction of the current (should flow towards positive)
Standard Lead Placement
Why would we go above and below the baseline?
Towards +ve and away from negative is a deflection above the baseline (on paper)
Away from positive and toward negative is below the baseline
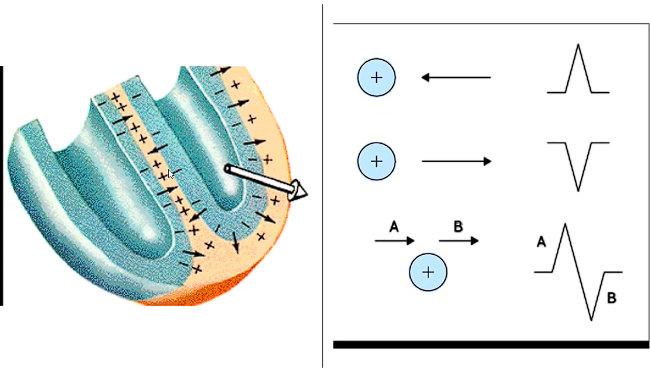
We plot current how?
If electricity is flowing directly at you, how does it appeafr on ECG?
If its flowing perpendicular to you, how does it appear?
By how its flowing towards you in direction and magnitude
Like a big spike
Like a smooth bump kinda thing
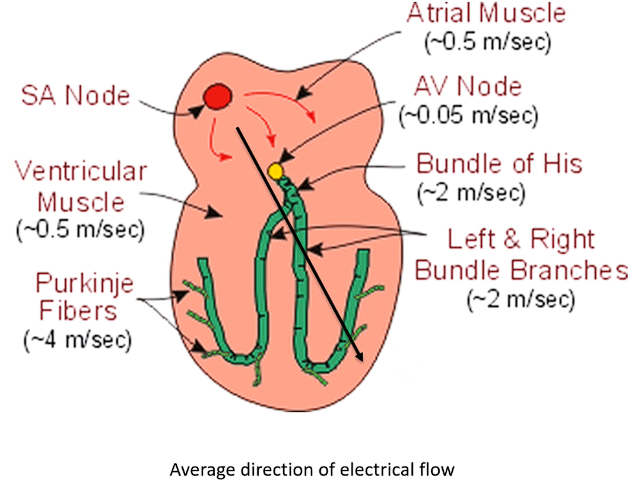
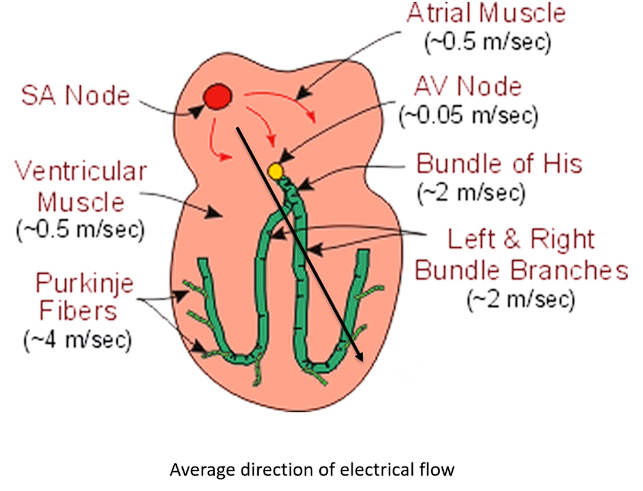
How does electricity travel?
Electricity generated in SA node
The travels into atria and arrives at electrically impermeable barrier between the left and right heart and atria and ventricle
Goes through atrial muscle → atria depolarises then heads to AV node
Then moves into ventricles → Bundle of Hiss and the Purkinje fibre system
At the AV node what is seen on an ECG? Why?
What is the AV node seen as on ECG?
Current at AV node is not seen on ECG - flatline between contractions
This slow current is slow so as to not cause the heart to contract at the same time
PQ interval
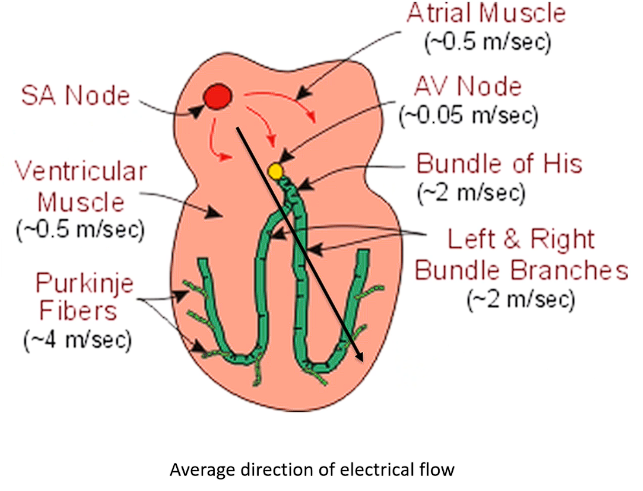
Describe the current flow speed in atria vs ventricles
How is this portrayed on ECG?
Atrial depolarisation (and contraction) - much slower movement from slower current → P wave is seen as a smooth small bump due to dec magnitude
Ventricular contraction (and depolarisation) is much faster and more direct current flowing → Large short peak
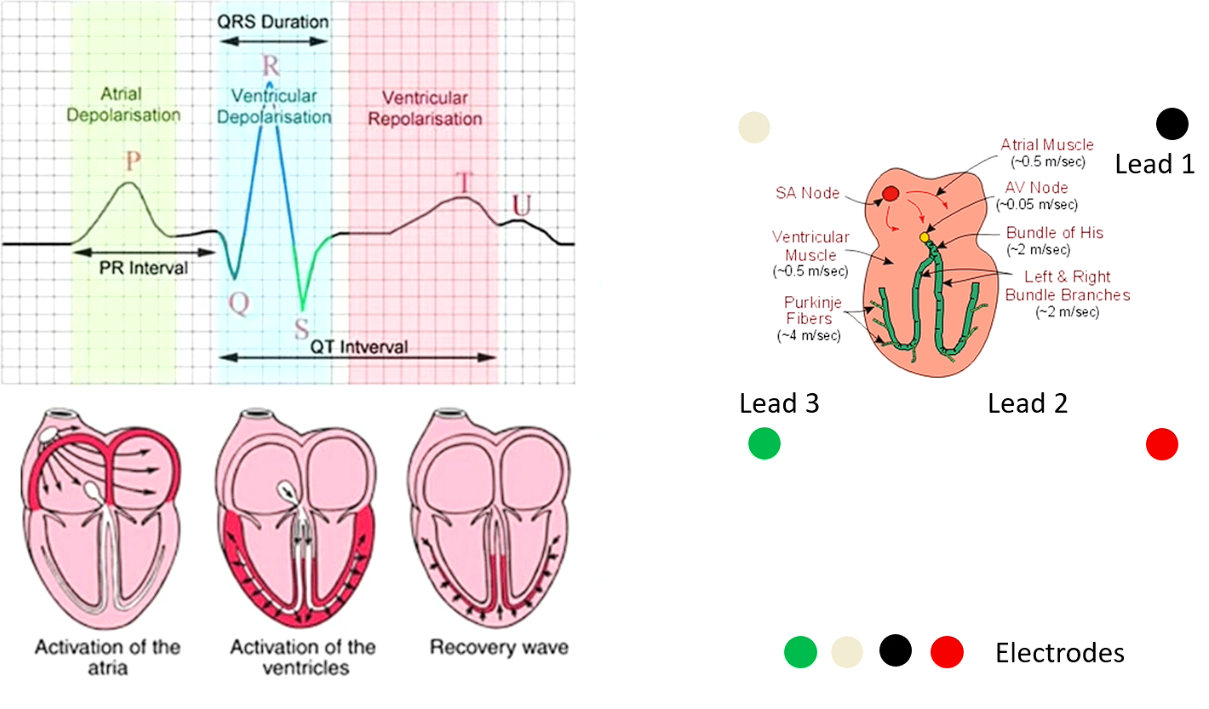
On an ECG - where does atrial depole (and contraction occur)
Atrial repole?
Ventricular depole?
Ventricular repole?
P wave
QRS - complex (electrical activity hidden by ventricular depole’s intensity)
QRS complex
T wave
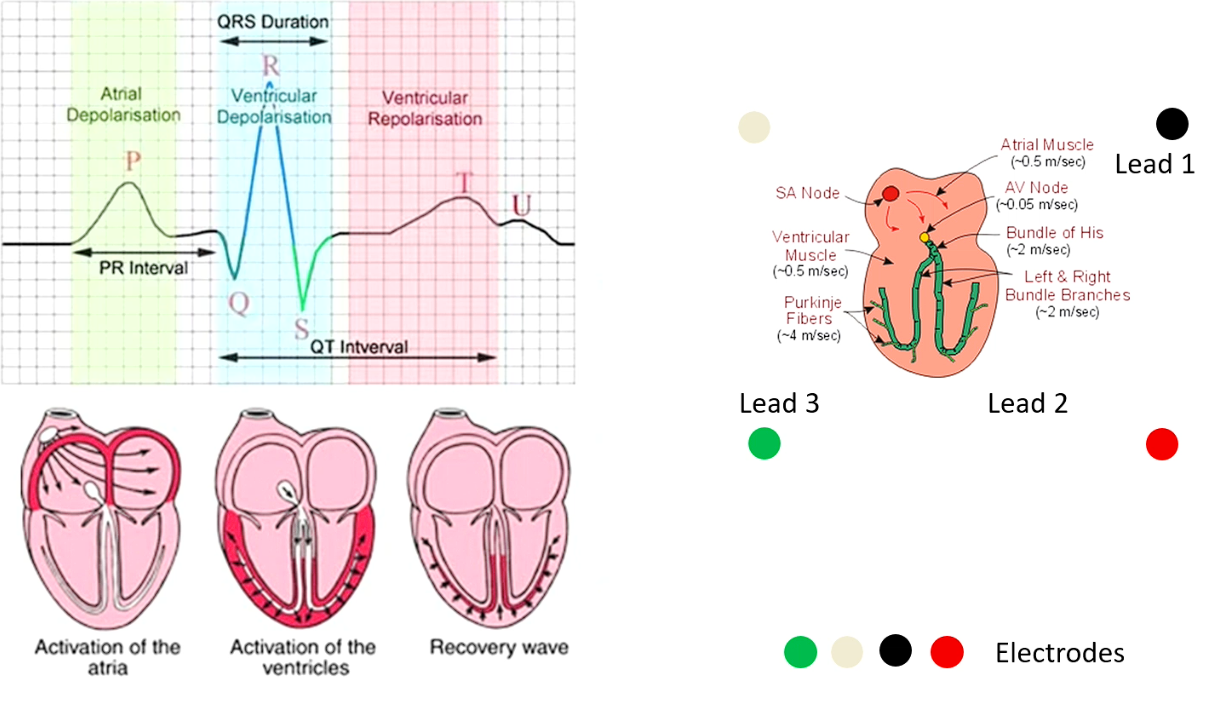
Ventricular Repole - looks similar to P wave but it differs, why?
It doesn’t repolarise with purkinje fibres but instead the muscles, which is a slower movement
Describe the appearance of P waves
Rounded (slow conduction)
Shouldn’t be bilobed or spiked
Atrial rate = ventricular rate
Should be positive on all leads except aVr
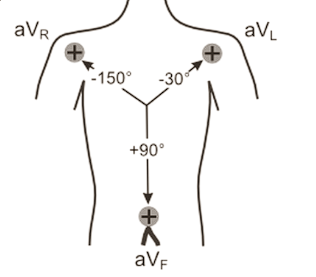
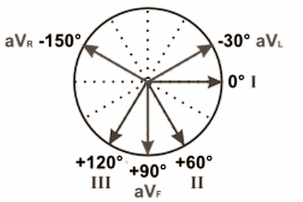
If we were to perform a three lead ECG, list the degrees relative to the heart, where they would be (for orientation, 0 degrees is at the 3 ‘o’ clock position)
Lead 1 - 0 degrees
Lead II - +60 degrees
Lead III - + 120 degrees
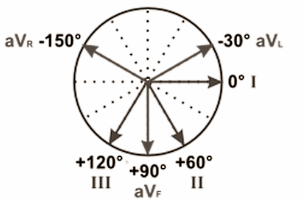
Performing a 6 lead ECG - where do the other leads go? (Use 0 degrees at the 3 o clock position as orientation)
aVl - -30degrees
aVf - +90 degrees
aVr - -150 degrees
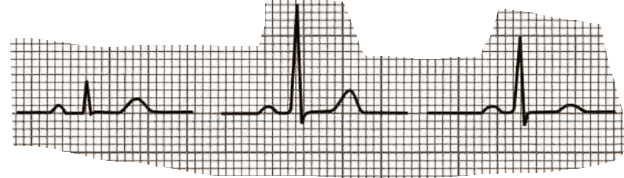
Which is which? Describe any notable features if aplicable
Left - Lead I - Picks up a weak trace, lower amplitude and speed
Middle - Lead II - Much stronger trace (in the right degrees to get good current flowing towards it)
Right - Lead III - similar to Lead II for similar reason
Where does electricity usually flow degree wise?
60-120 degrees
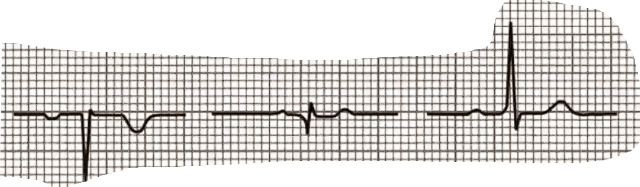
Which is which? Describe any notable features if aplicable
Left - Lead aVr - directly opposite lead II - everything is the opposite
Middle - Lead aVl - Pretty similar to Lead I as close to Lead I
Right - Lead aVf - In btw Lead II and III so similar appearance
If aVr is positive, why would that happen?
Abnormal, either placement error of electrodes or heart on that side is enlarged (all the current is going in that direction)
Ekectrical Events in Atria
Electrical events at the AV junction
Disease results in?
Other features
Blocks, delays or supraventricular tachycardias
AV node is a pacemaker
Conduction speed - 0.05m/S (very slow)
Why does the heart need an electrical circuit?
Causes the contractions to be coordinated
What does QRS complex rep? Why does it look like that?
Ventricular depolarisation - very fast and rpaid movement hence the spike
PR interval reps what?
Current delay in the AV node