TV4101 SAM - ECG
cARDIAC WORKUP AND HAVE AN arrthymia then you DX and manage that arrhythmia
Identify source of aarthymia
Used to be used to guess chamber size with ECG - not as accurate - use echo instead now
Not ideal to have on GA patient as have PQRST when heart isn’t beating so better to have stethoscope to hear heart physically beating

Heart contraction needed by movement of ions (gens volatage to zap muscle)
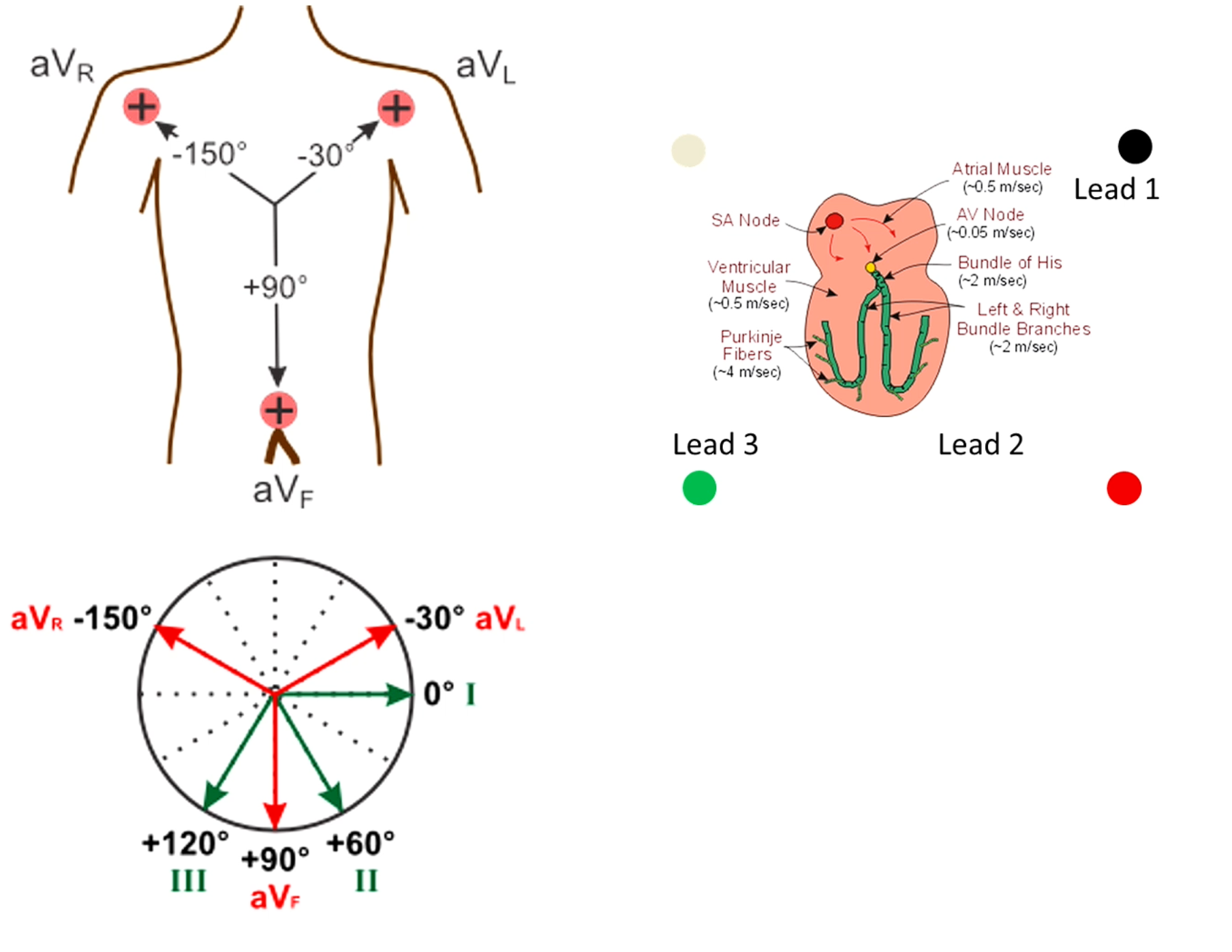
Electrode - the little clip or pad
Lead - the machine determining the elcetrical flow btw electrodes
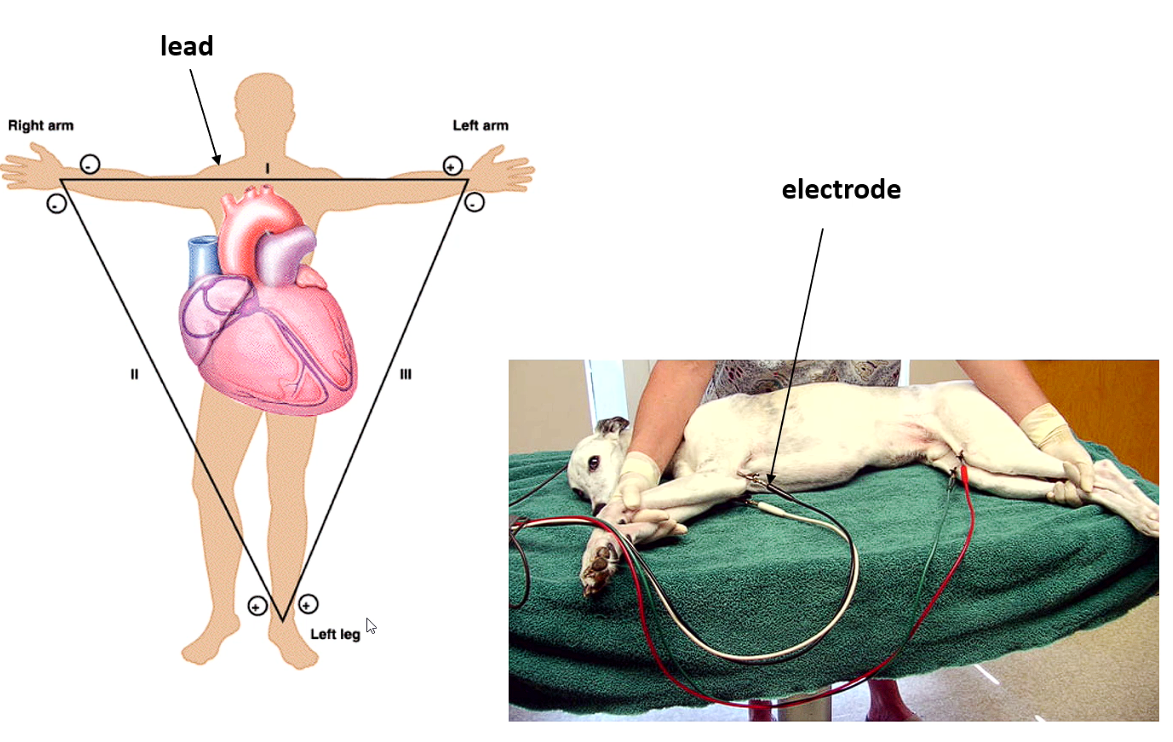
Leads are bipolar either positive or negative
Lead 1 - from left to right (
Why do we need leads - machine detects the current flowing towards positive electrode


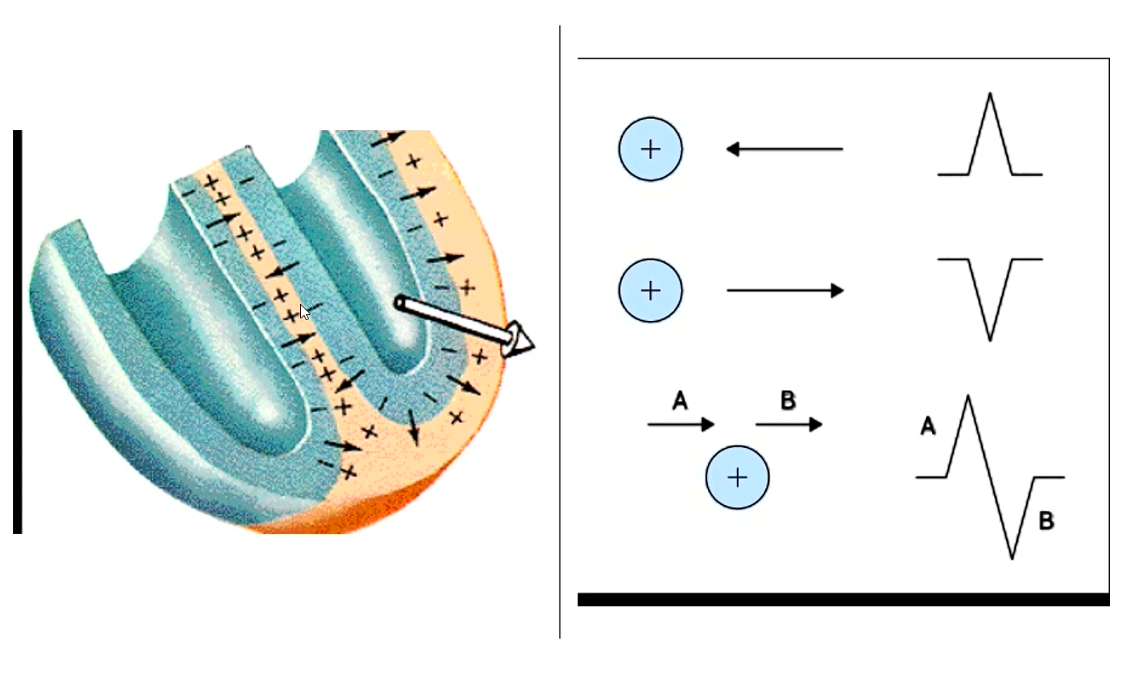
We plot current flowing towards you in direction and magnitude OH YEAH
So if dead at you makes a big spike, if perpendiculr to you then its a lil bump kinda thing
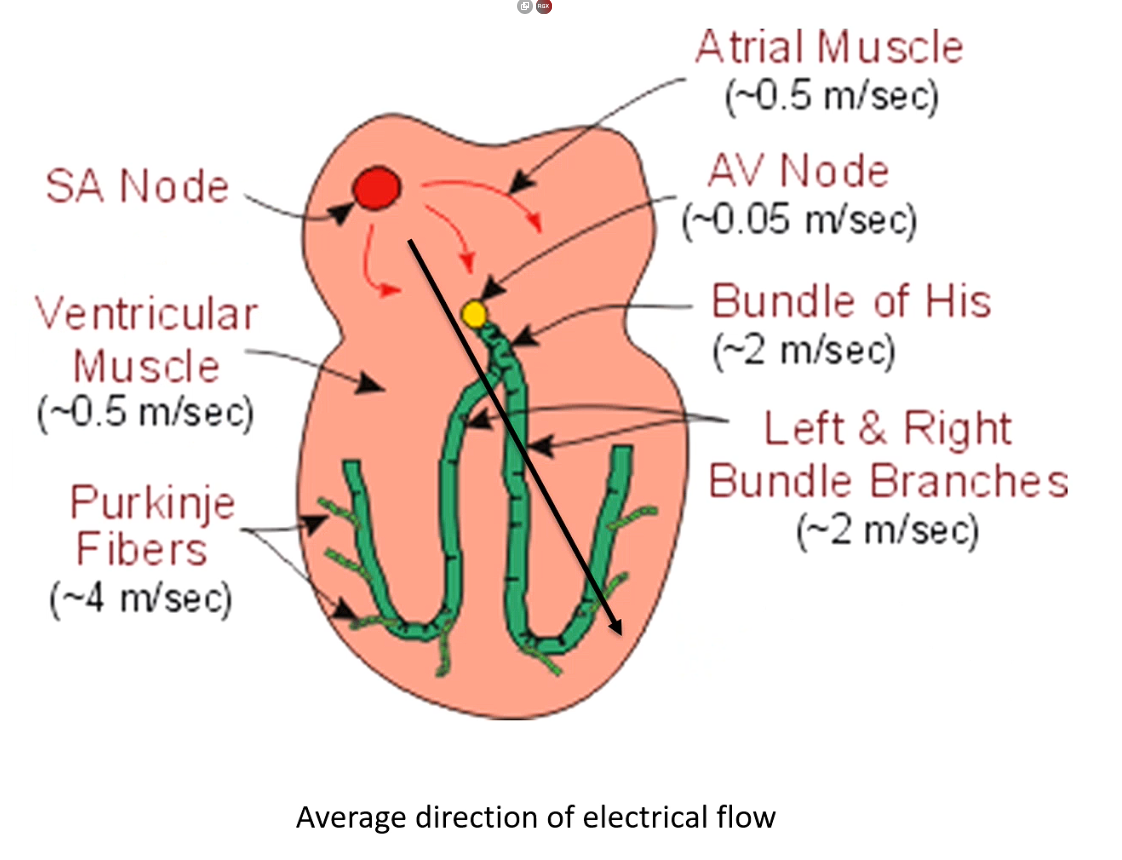
Electricity generated in SA node then travels into atria
then arrives at electrically impermeable barrier - btw l and r heart and atria and ventricle
Goes through atrial muscle → atria depolairses then heads to av node
av node is not seen on ecg tracing → while current is in av node this is the PQ interval (ecg is flatline btw the contractions)
Why is it so slow? So the different parts of heart don’t contract together
Then moves into ventricule
Moves quick in bundle of his and bundle branches
Summary, slow movement through atria → delayed at AV node →→ very fast in the Bundle of His and Purkinje system
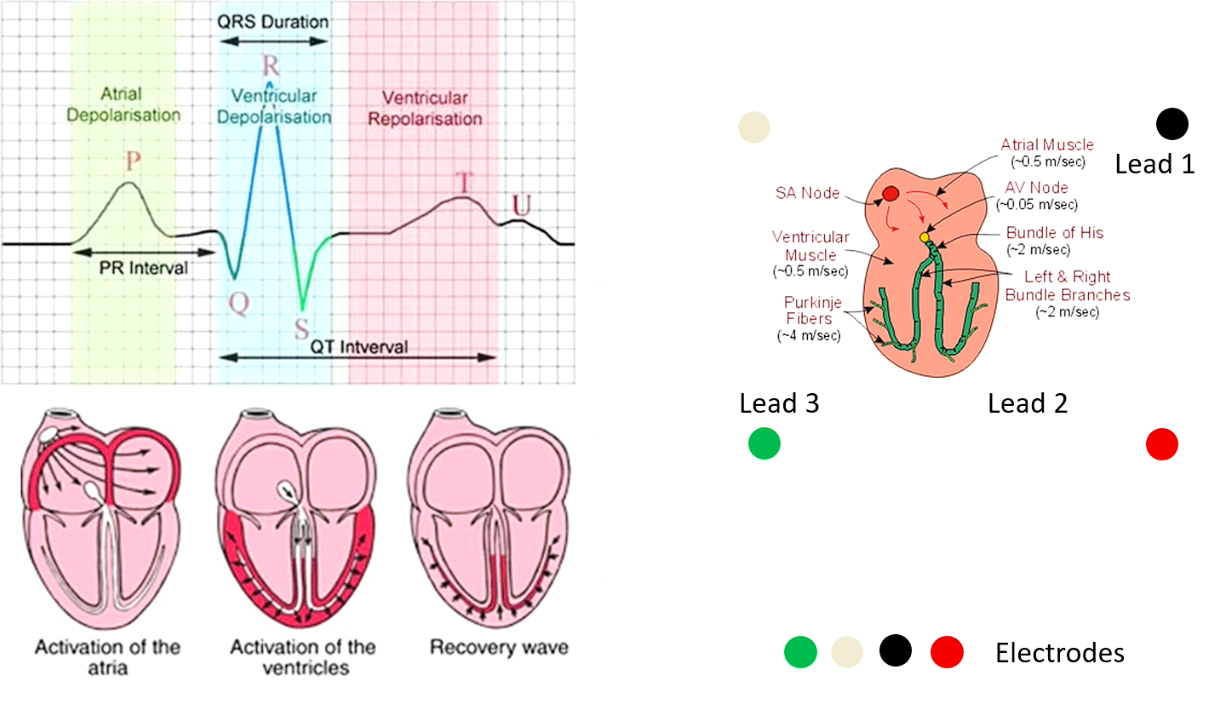
Atrial contraction is a slower movement from slower current → P is a smooth bump magnitude is much lower
current at av node - flat section between the p and q indicates this
Recovery wave - ventricles repolarise
Ventricles repolarisation - looks like p wave - doesn’t repolarise with purk but repolarises with muscles (a slower movement)


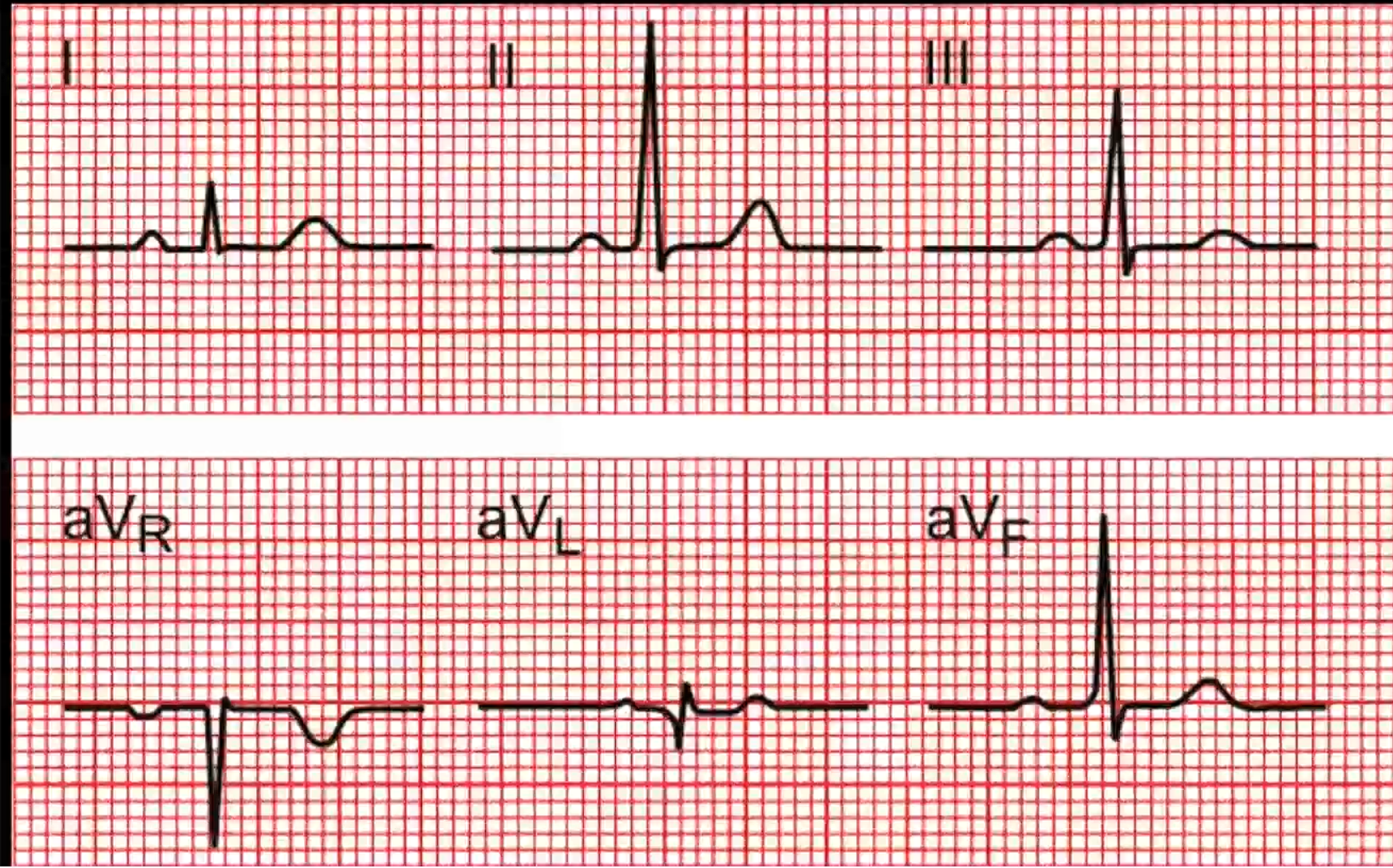
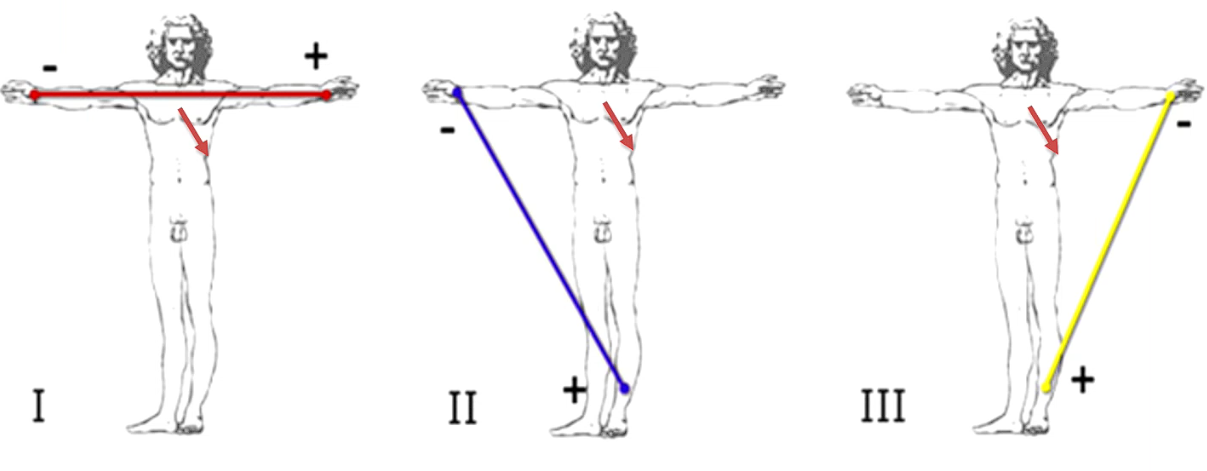
Elec usually flows 60-120 degrees
Lead I - Picks up a little trace, lower amplitude and speed
Lead II - Much stronger trace
Lead III -
Lead aVr - directly opposite lead II - everything is the opposite
Lead aVl - Pretty similar to Lead I as close to Lead I
If aVr is positive - abnormal, either placement error of electrodes or heart on that side is enlarged (all the current is going in that direction) - don’t use the enlarged aspect much anymore prefer echo




electrical circuit causes contractions to be cooridinated
P wave = atrial depolairsation → current magnitude is quite low and slow
PR interval - av node
QRS complex reps - ventricular depolarisation - very fast and rpaid movement hence the spike
Atrial repolarisation is not visible on ecg why? Buried in ventricular depolarisation i.e. happening at same time but isn’t visible