Repro and Kidneys
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Renal Artery
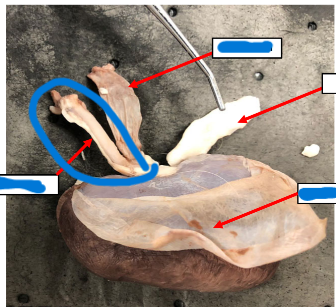
Renal Vein
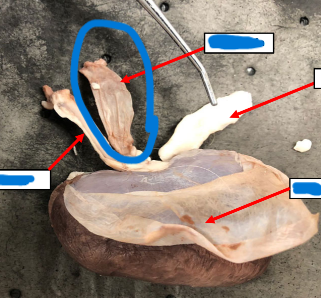
Ureter
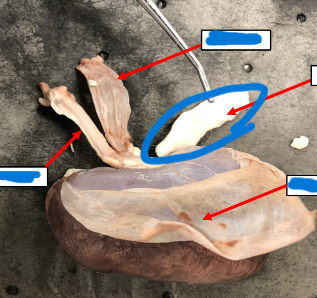
Fibrous Capsule
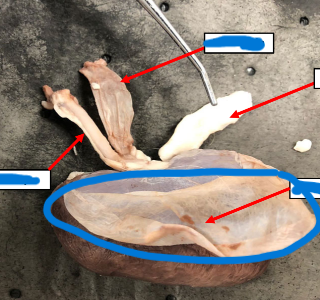
Adrenal Gland
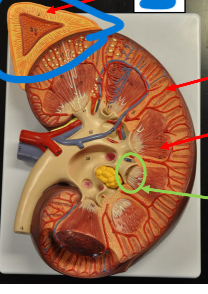
Cortex
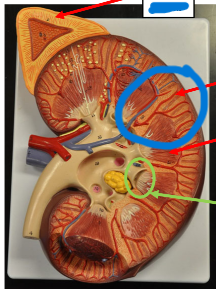
Medulla
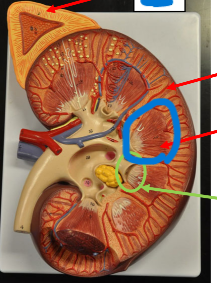
Calyx
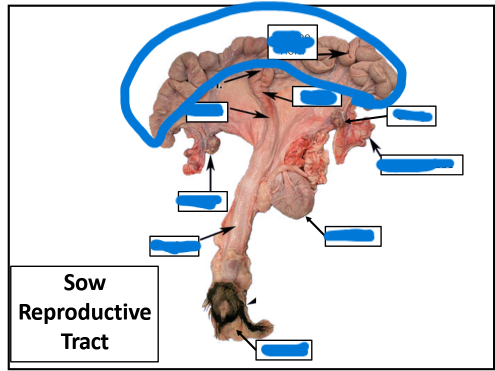
Vulva
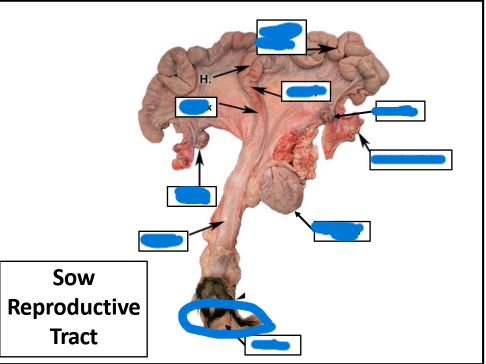
Vagina
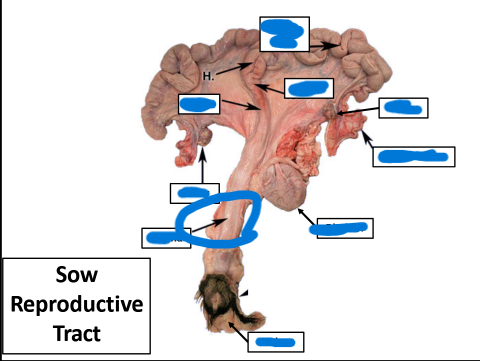
Badder
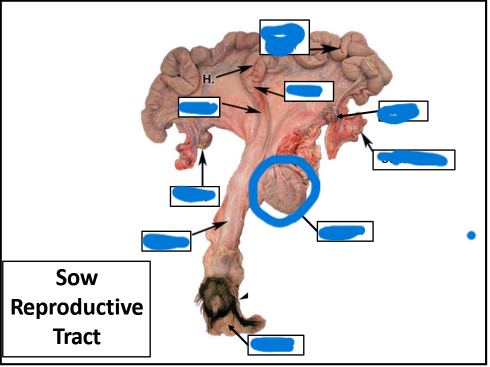
Ovary
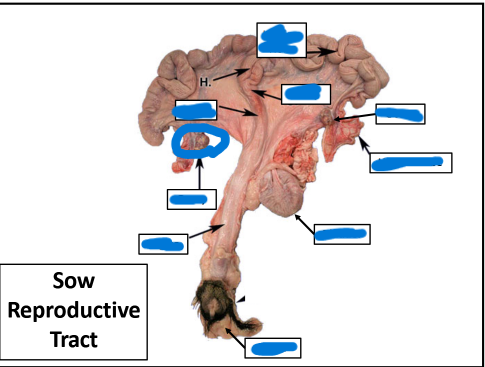
Uterine Tube
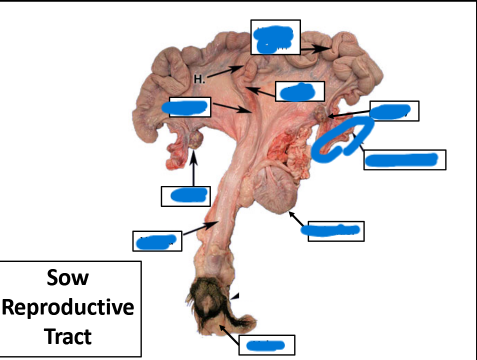
Cervix
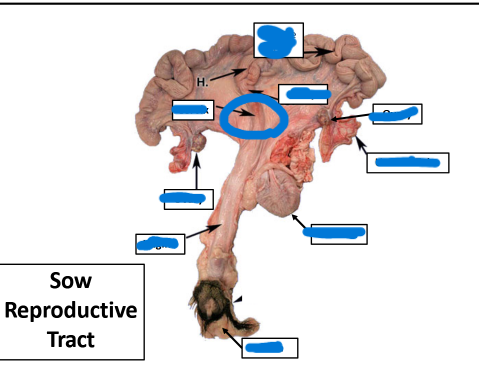
Body
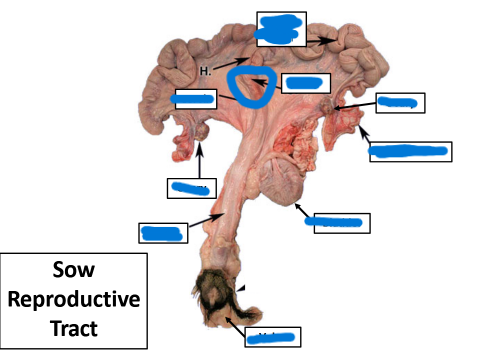
Uterine Horn
Seminiferous Tubules
Head of Epididymis
Body of Epididymis
Tail of Epididymis
Pampiniform Plexus
Spermatic Cord
Sheath
Glans Penis
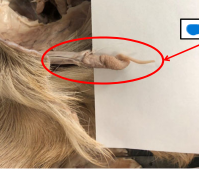
Body of Penis

Sigmund Flexure
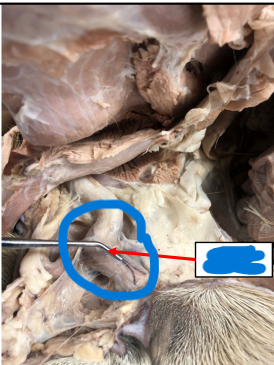
Tunica Albuginea
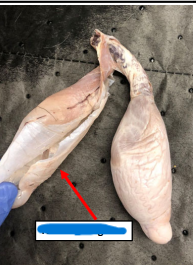
Scrotum
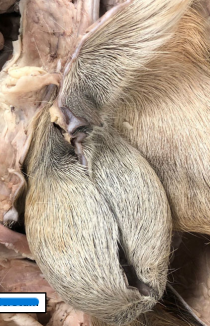
Right kidney
More cranial
– Contacts caudate lobe of the liver
Left kidney
More caudal (except in pig)
– Located medially in ruminants
Fibrous Capsule
Thin, fibrous tissue that covers external surface
Renal Hilus
Medial, indented border of kidney
• Opens into the renal sinus
• Entrance for renal vessels & ureter
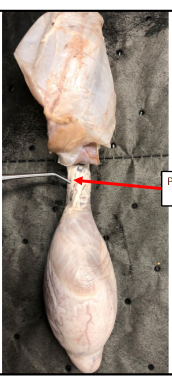
Ureter
Muscular tube that propels urine from kidneys to urinary
bladder
Renal Artery
Brings oxygenated blood to the kidney
Renal Vein
Carries deoxygenated blood from kidney
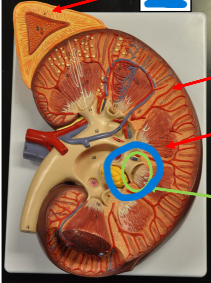
Adrenal Gland
Endocrine glands located cranially and medially to each
kidney
• Secrete many hormones
Cortex
Outer layer of the kidney’s parenchyma
– Contains the convoluted tubules & renal corpuscle
Medulla
Internal portion of kidney’s parenchyma
– Contains the Loop of Henle and collecting duct
Urinary Bladder
Hollow & Distensible
– Passes urine from ureter to urethra
Urethra
Tubular
– Transports urine from bladder
– Female: opens into floor of repro tract
– Male: divided into 2 parts (pelvic & penile)
Ovaries
primary female reproductive organs
Cortex of the Ovary
External portion
Medulla of the Ovary
Internal portion
Infundibulum
Move oocyte towards the uterine tube
Uterine Tube
Fallopian Tube or Oviduct
• Transport ova & sperm
Cervix
most caudal, tough & fibrous
Body
between cervix & uterine horns
Uterine Horns
extension of body
Vagina
between cervix & external orifice
Vulva
external portion of female tract
Vestibule
shared space for urinary & repro tracts
Testis
• Produce male gametes & release hormones
• Develop in abdomen & migrate to scrotum
Tunica Albuginea
fibrous covering of the testicle
Endocrine Activity of the Testicle
• Leydig cells → produce testosterone
• Sertoli cells → stimulate spermatogenesis
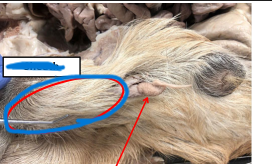
Scrotum
Retains the testis, epididymis, and distal spermatic cord
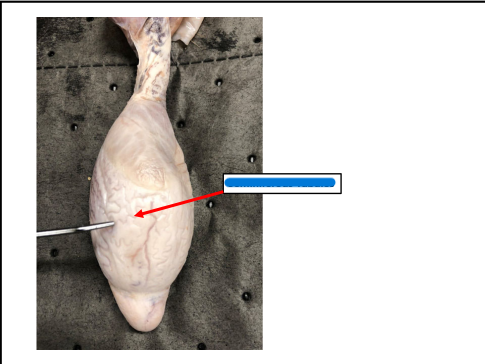
Epididymis
Site of sperm maturation and storage
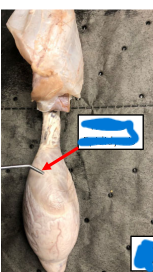
Head of Epididymis
concentrate sperm
• Receives efferent ducts
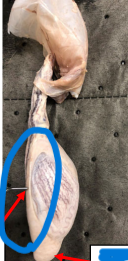
Body of Epididymis
acquire mobility
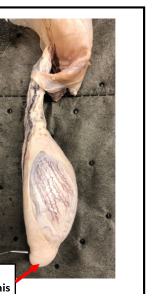
Tail of Epididymis
houses mature sperm
Ductus Deferens
Transitions into spermatic cord
• Leaves scrotum
• Crosses beneath ureter & penetrates prostate
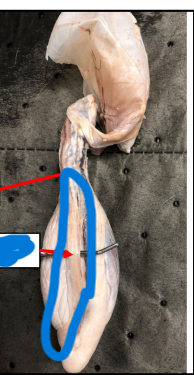
Spermatic Cord
• Receives deferent duct
• Cremaster muscle located within the cord
Pampiniform Plexus
• Complex arrangement of veins around artery
• Cools blood before reaching testicle
Sigmoid Flexure:
S‐shaped curve in the ruminant
and boar