ANSC 311 - Midterm 1
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
William Beaumont
Physician
Alexis St-Martin shot in the stomach, did research on him
Left partially open to look inside
Tie bits of food on string and put in stomach
Saw secretion of things - HCl
See how fast things are digested
Started field of understanding digestion
Experiments and observations on the gastric juice, and the physiology of digestion
motility, secretion, digestion, absorption, communication, immune system, detoxification and modification via metabolism
Jobs of the gastrointestinal tract
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, forestomach (rumen, reticulum, omasum), stomach (abomasum), small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum), cecum, large intestine
Components of the GI tract
teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gall bladder, pancreas
Accessory organs of the GI tract
10-15 m
Length of small intestine in humans
Jejunum (6-7 m)
Longest section of the small intestine
Ileum (3-5 m)
Middle length section of the small intestine
Site of most absorption
Duodenum (12 inches)
Shortest section of small intestine
Tolerant to acid from stomach, buffered by base
Body size
Small intestinal transit rate is the same regardless of ________ of mature dog
Stratified squamous
Esophagus has a multi-layer _______ ________ epithelium
Thick bcs pokey things that haven’t been digested yet
Beyond esophagus everything is 1 cell layer
Gastric pits
Stomach has ____ ____ to protect against stomach acid
Small surface area to not absorb so much
Crypts of Lieberkuhn
The small intestine has vili to increase surface area for absorption with _____ __ _______ in between
Site of Paneth cells
Mucosa
Top Layer of the Intestinal Wall
Top of villi till first muscle layer
Epithelium
Lamina propria
Connective tissue and muscles
Capillaries, nerve fibers, smooth muscle (muscularis mucosa), lymphatic vessels (immune cells)
Lamina propria
Part of the mucosal layer of the intestinal wall
Made of Connective tissue and muscles
Capillaries, nerve fibers, smooth muscle (muscularis mucosa), lymphatic vessels (immune cells)
Submucosa
Second Layer of the Intestinal Wall
Nerves
Blood vessels
Contains glands (if they are present)
Muscularis externa
Third Layer of the Intestinal Wall
2 layers of muscle - for contraction to allow to move along tract)
Circular muscle (around)
Longitudinal muscle (along)
Inside goes around outside goes up and down
Nerves and muscle
Serosa
Fourth/Bottom Layer of the Intestinal Wall
Connective tissue
Peritoneum
Mucosa, Submucosa, Muscularis externa, Serosa
4 Layers of the Intestinal Wall
Columnar Absorptive Cells
Type of Epithelial Cell of GI Tract
Absorption
Most of cells
Mucous/Goblet Cells
Type of Epithelial Cell of GI Tract
Secrete mucous
Mucous = barrier to protect intestinal surface
Enteroendocrine cells
Type of Epithelial Cell of GI Tract
Release hormones into blood circulation to communicate locally and systemically
Communicate with body and brain, but also locally to produce more cells, secrete more, etc.
Communication
Paneth cells
Type of Epithelial Cell of GI Tract
Remain at the crypt base
Secrete antimicrobial peptides/molecules to provide host defense against gut microbes
Found in the crypt (in the loop between vili)
Keeps an antimicrobial sterile environment
Protect intestinal stem cells
Intestinal Stem Cells
Type of Epithelial Cell of GI Tract
Give rise to above four cells
Divide and become all other cell types
Stem cells near bottom of villi either migrate up or down (paneth cells)
Peyer’s patches
Especially in ileum
Lymphoid structures (immune), where there is sampling through M-cells and dendritic cells to expose to immune cells
Not found in large intestine (no longer sampling)
Dendritic cells
Sample environment in gut and educates immune system
Work with M-cells in Peyer’s patches
3-5
Cells replaced every ______ days
Replication occurs from intestinal stem cells
mechanical, chemical, enzymatic, microbial
4 types of digestive processes
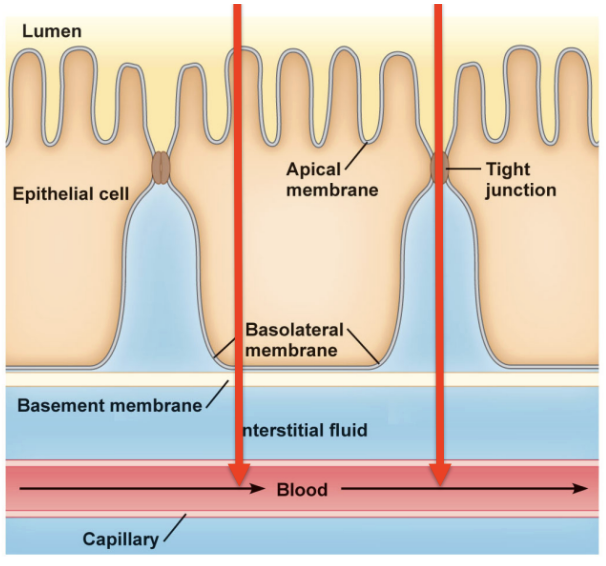
Transcellular
Type of Absorption
Going across the cells (through the apical and basolateral membranes)
Most of what will be discussed
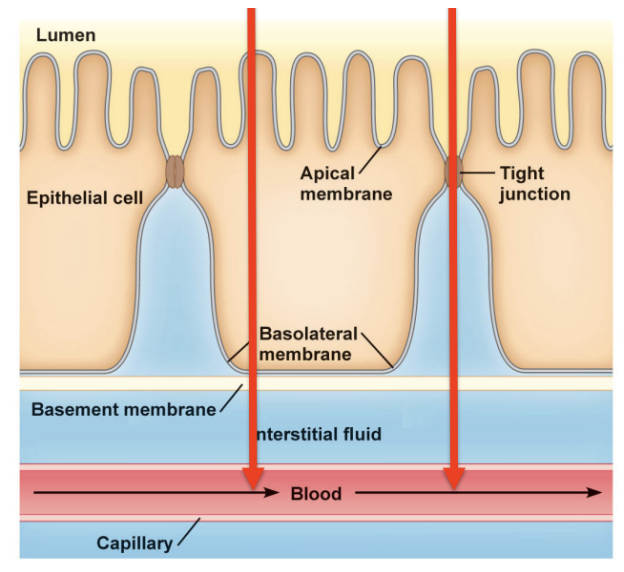
Paracellular
Type of Absorption
Going between the cells (through tight junctions)
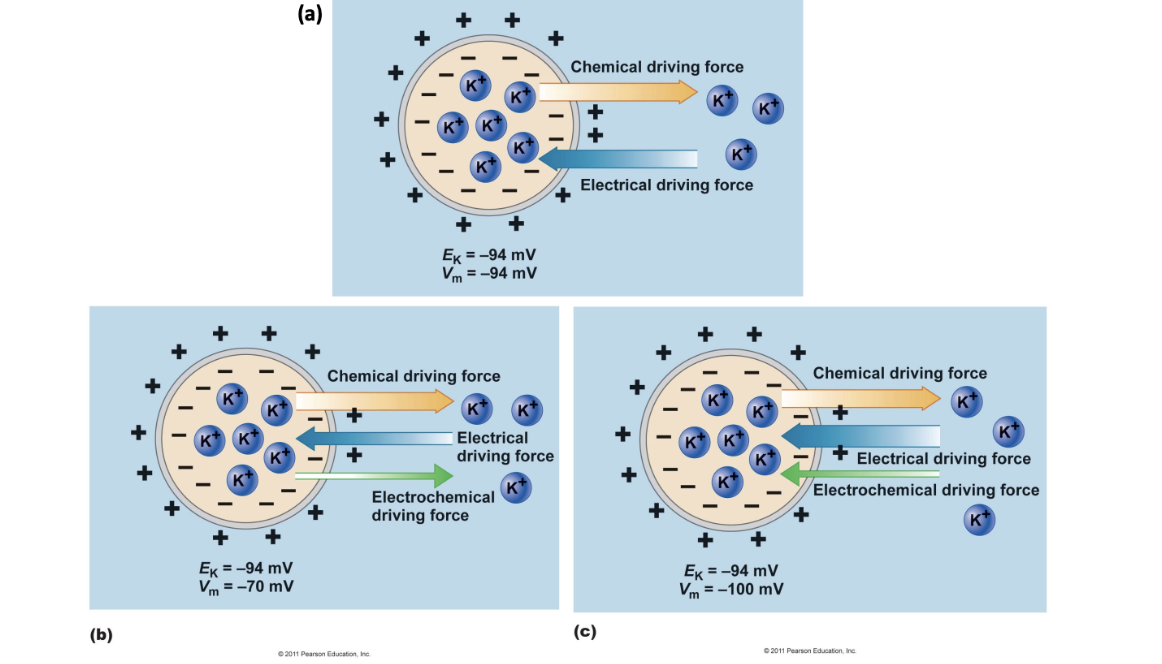
Chemical
Ek > Vm - _____ force is greater and combined electrochemical force is in the direction of the ______ force
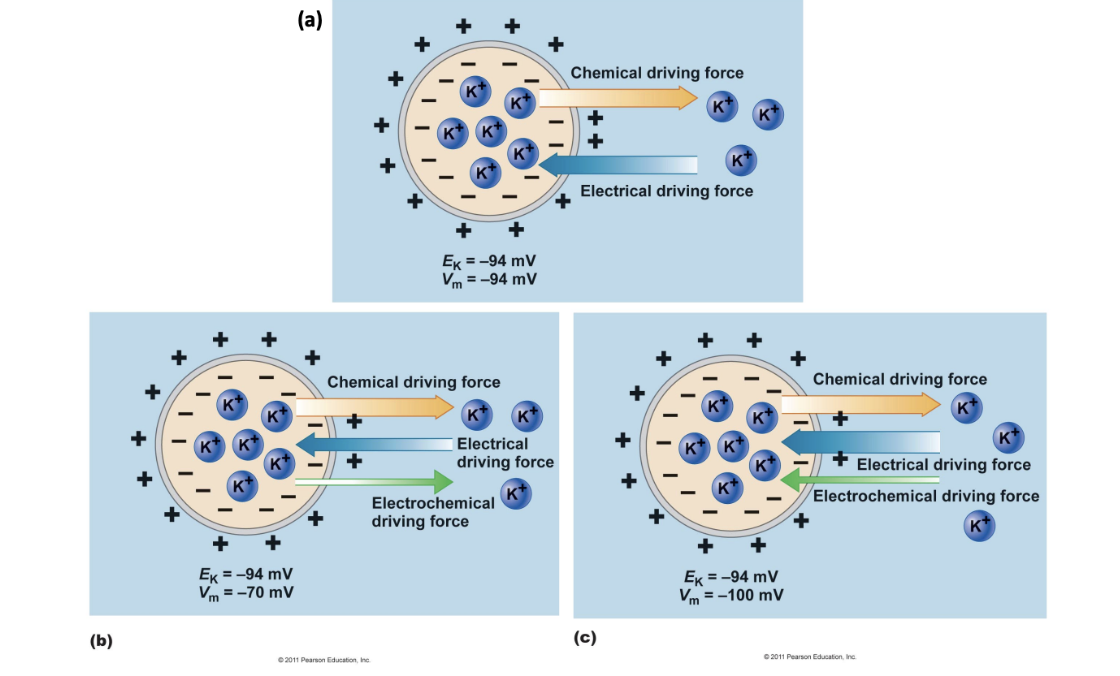
Electrical
Ek < Vm - ______ force is greater and combined electrochemical force is in the direction of the ______ force
Dextrins
mixtures of polymers of glucose units linked by α-1,4 or α-1,6 glycosidic bonds (hydrolysis of starch)
Salivary amylase → di and trisaccharides, dextrins
Pancreatic amylase → di and trisaccharides, dextrins
Brush border enzymes → monosaccharides
SGLT1 absorbs glucose by simple or facilitated diffusion and GLUT5 absorbs fructose by simple diffusion into cell
GLUT2 transports monosaccharides out of cell into bloodstream
Steps of Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrates
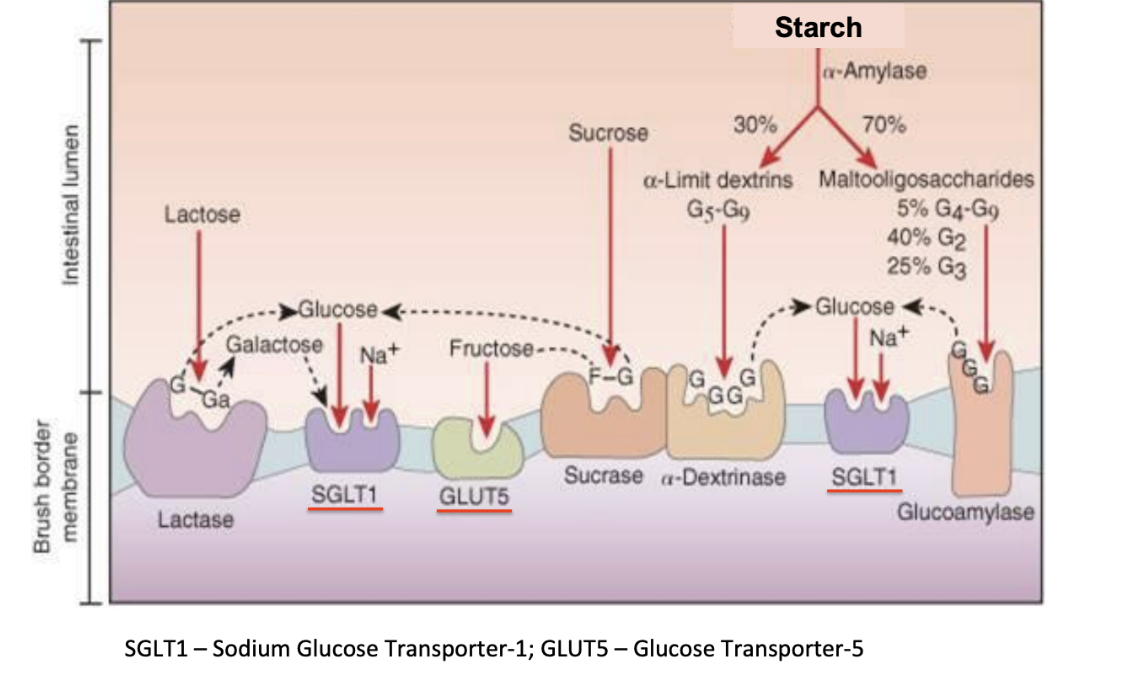
a-dextrinase, glucoamylase
Brush border enzymes
Break down starches into glucose which are sent to SGLT1 where glucose and sodium are absorbed into the cell
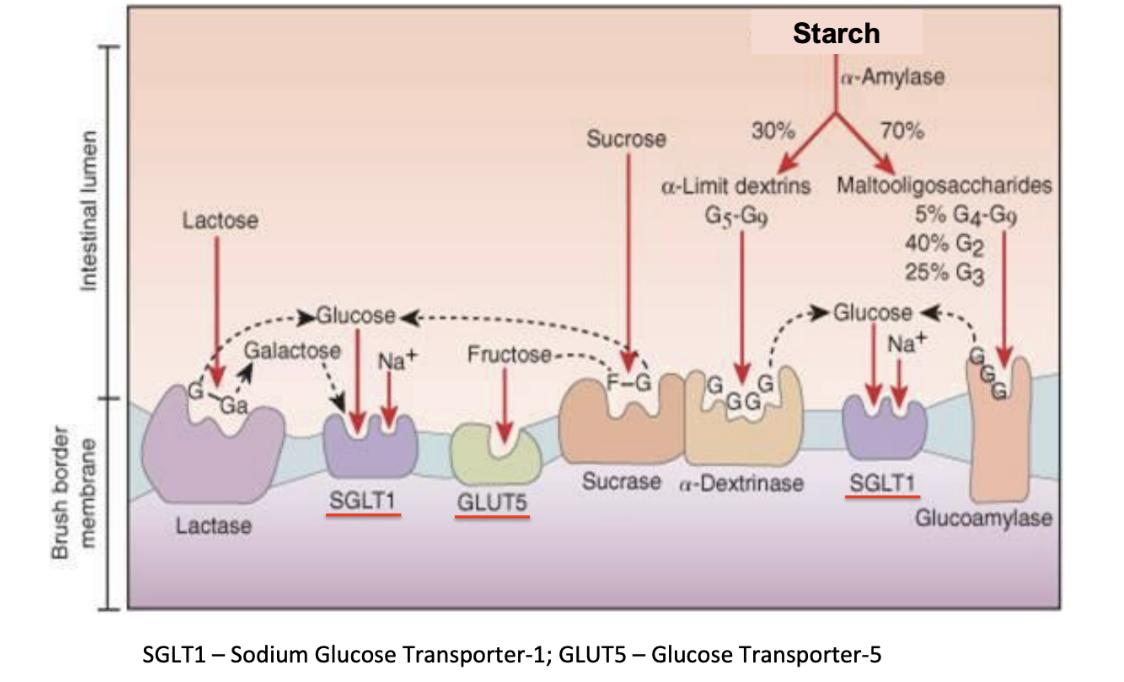
Sucrase
Brush border enzyme
breaks down sucrose into a glucose that goes to SGLT1 and fructose that goes to GLUT5 to be absorbed into the cell
Gains function as animal ages
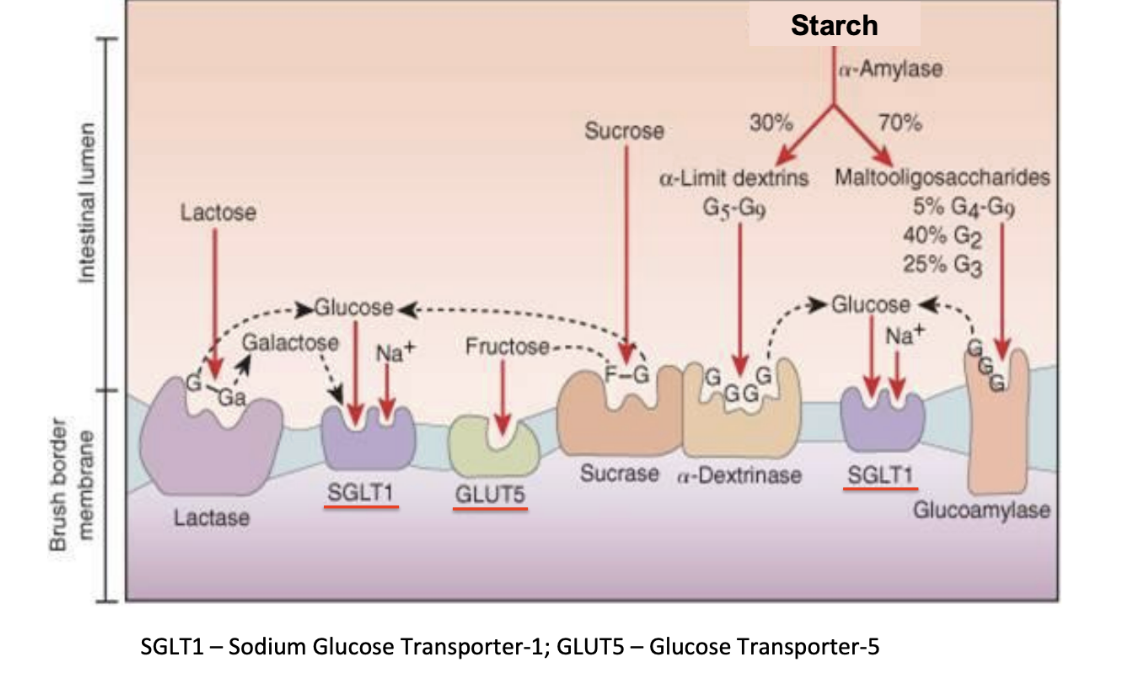
Lactase
Brush border enzyme
breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose which can both go through SGLT1
Loses function as animal ages
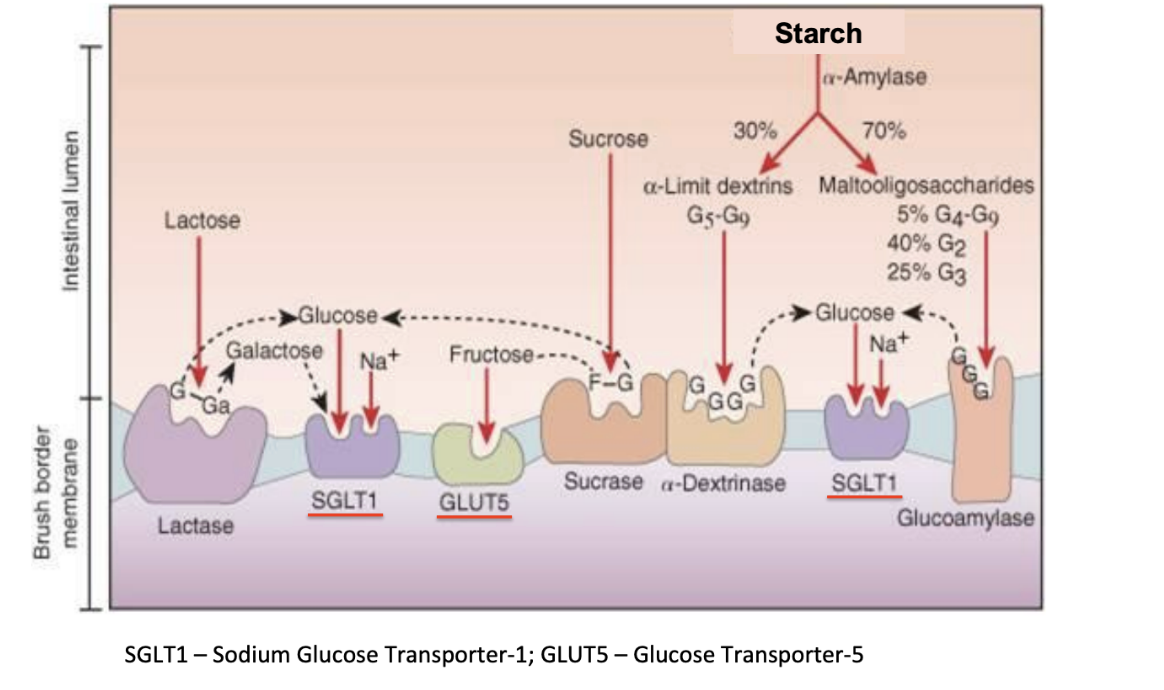
SGLT1
Brush border carrier
Allows glucose and galactose along with Na to pass from luminal space across the brush border membrane into the epithelial cell
Can go against concentration gradient (secondary active transport)
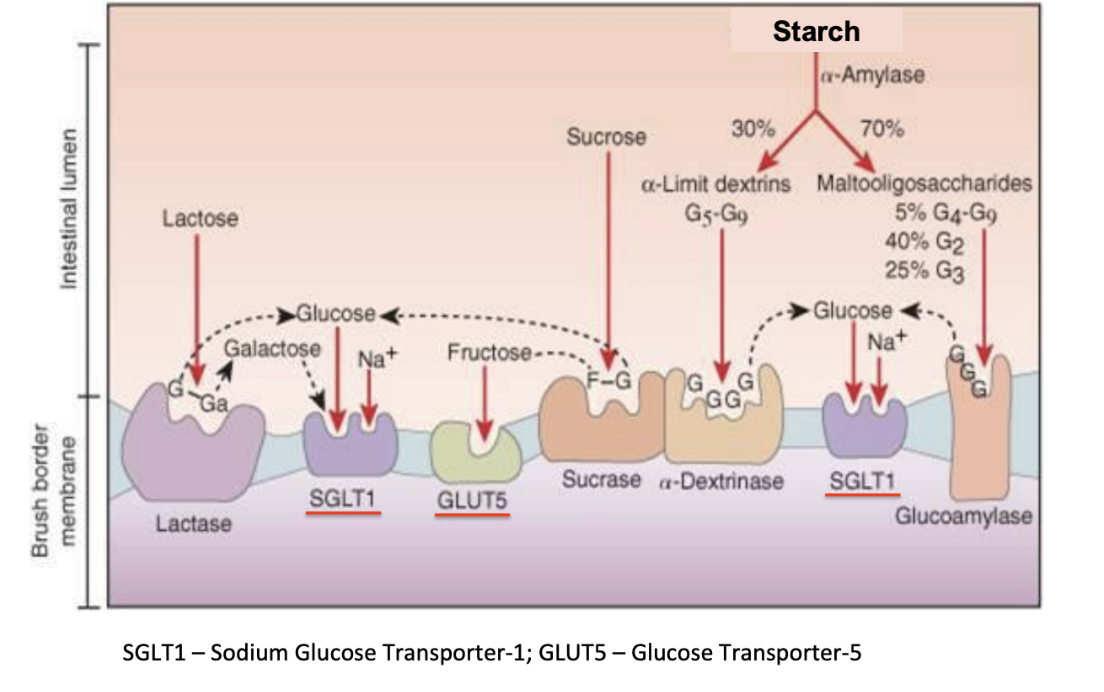
GLUT5
Brush border carrier
Allows fructose to pass from luminal space across the brush border membrane into the epithelial cell
Facilitated diffusion
Luminal phase
Step 1 of carbohydrate digestion
Have salivary and pancreatic amylase that breakdown large glucose complexes into smaller chunks (2-4 glucose units)
Brush border phase
Step 2 of carbohydrate digestion
Occurs in duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Brush border enzymes (isomaltase, maltase, lactase, sucrase) convert to single glucose units and allow for absorption
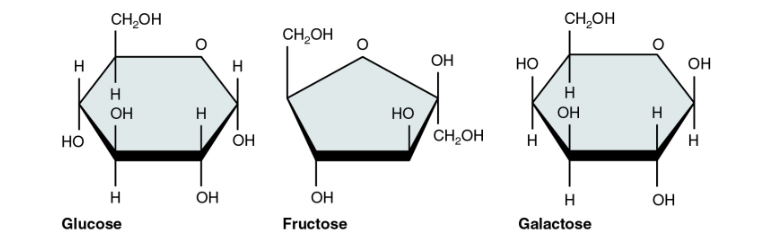
Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
3 types of monosaccharides
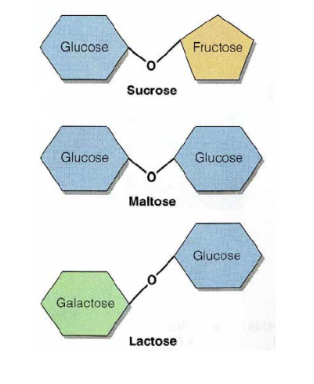
sucrose (gl+fr), maltose(gl+gl), lactose(gl+ga)
3 types of disaccharides
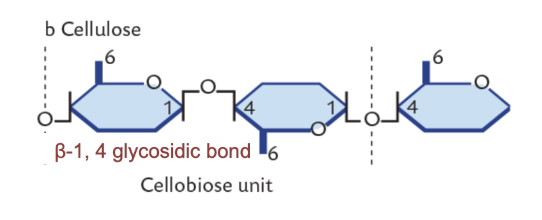
Cellulose
Polysaccharide
B-1,4 glycosidic bonds
Unlike starch, humans cannot digest
Microbes contain enzymes to digest
Amylose
Polysaccharide
Starch
has a-1,4 glycosidic bonds, but just a straight chain
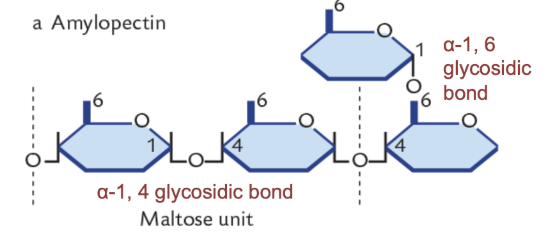
Amylopectin
Polysaccharide
Starch
has a-1,4 and a-1,6 glycosidic bonds, branched
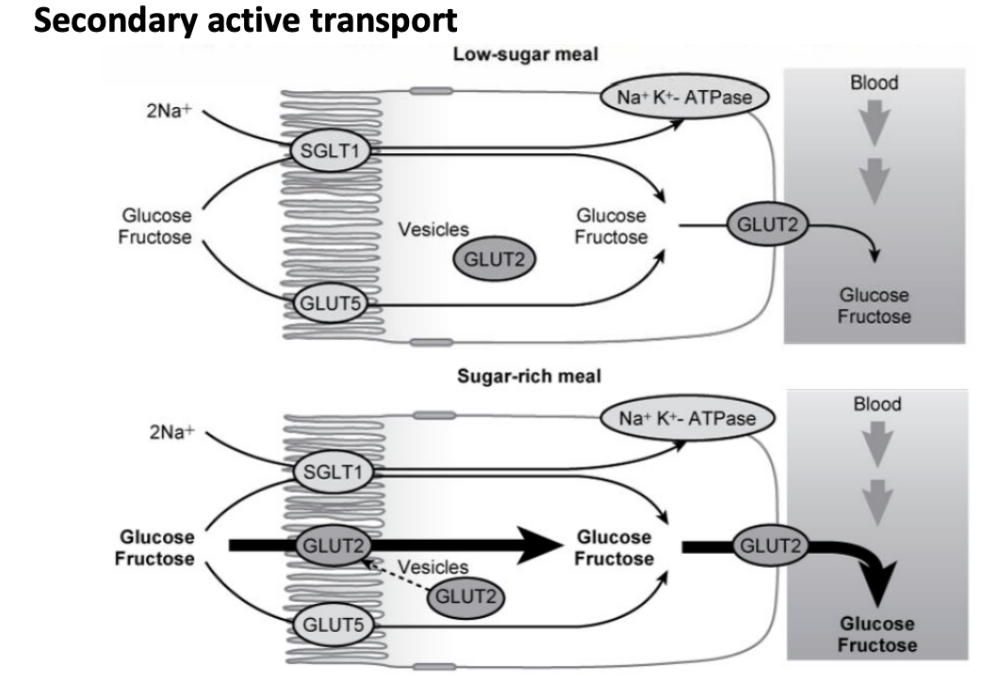
GLUT2
Carrier
Transports monosaccharides out of cell into bloodstream
Through secondary active transport or during sugar-rich meals, facilitated diffusion
Gastric HCl denatures proteins down to primary structure
Pepsinogen is converted to Pepsin when exposed to HCl and Pepsin begins to break down the primary structure of proteins
Pancreatic proteases are activated by enterokinase on the brush border → large peptides, di and tripeptides, amino acids
Brush border peptidases further break down large peptides
Carriers allow amino acids, di, and tripeptides to cross the brush border membrane into the cell
Cytoplasmic peptidases break down di and tripeptides into aa (a small amount escape)
AA and di and tri peptides enter bloodstream through carriers via secondary active transport
Steps of Digestion and Absorption of Proteins
HCl
Begins protein and nucleic acid digestion in the stomach
Denatures proteins and linearizes it down to the primary structure
Converts pepsinogen to active form pepsin
Pepsinogen
a pro-enzyme that is converted to Pepsin when exposed to HCl
Pepsin starts to break down the primary structure of the proteins in the stomach
Pepsin
Active form of pepsinogen
Starts to break down the primary structure of the proteins in the stomach
Enterokinase
On the brush border
Converts pancreatic pro-enzymes to their active forms for further protein digestion
trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase, carboxypeptidase A, carboxypeptidase B
5 pancreatic proteases (active forms)
trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, proelastase, procarboxypeptidase A, procarboxypeptidase B
5 pancreatic proteases (inactive forms → proenzymes)
Cytoplasmic peptidases
Once proteins are in the cell ______ further break down di and tripeptides into amino acids
A small amount of di and trisaccharides can escape that and be brought out into circulation - important bcs a lot of bioactive peptides and need to be intact to have effect
Bile acids
Emulsify lipids for digestion and absorption
Produced by liver and stored in gallbladder
One part is negatively charged (hydrophilic) and the other part is hydrophobic (act as a detergent)
Eventually reabsorbed by secondary active transport in the end of the small intestine in the ileum
Lipids are emulsified by bile acids
Pancreatic lipase, supported by colipase, break down large droplets into smaller micelles
Monoglycerides and free fatty acids pass through brush border membrane into cell via simple diffusion
Reform into triglycerides in the cell
Smooth ER packages triglycerides into chylomicrons
Golgi apparatus puts chylomicrons into vesicles and ships them out of the cell via exocytosis
Enter lacteal
Travels up to thoracic duct and enters bloodstream
Steps of Digestion and Absorption of Lipids
Pancreatic lipase, colipase
_______ supported by _____, break down large droplets into smaller micelles
Begins lipid digestion
Chylomicrons
Combination of triglycerides, cholesterol, lipoproteins, and phospholipids
Formed in the smooth ER of intestinal epithelial cells
Bring triglycerides from intestinal epithelial cells into lacteal
Denatured by gastric acid
Broken down into nucleotides by pancreatic nucleases (ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease)
Phosphatase on brush border cleaves phosphate ion
Nucleosidase breaks bond btw nitrogenous base and pentose sugar
Pentose sugar absorbed through facilitated diffusion, nitrogenous bases absorbed through active transport
Steps of Digestion and Absorption of Nucleic Acids
histones, nucleosomes
Strands of DNA wrap around a protein (_____) forming _______
chromatin, chromosomes
Nucleosomes coil together forming _______, which supercoils to form ________
Pancreatic nucleases (ribonuclease, deoxyribonuclease)
Break down denatured nucleic acids into individual nucleotides
Phosphatase
Once broken down into nucleotides by pancreatic nucleases
______ on brush border cleaves off phosphate ion
Nucleosidase
Once broken down into nucleotides by pancreatic nucleases
Phosphatase on brush border cleaves off phosphate ion
Then, ____ catalyze breaking of covalent bond between nitrogenous base and pentose sugar