Cell Structure Part A
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Isoprene?
5-carbon compound generated in the mevalonate pathway
Isoprene purpose
Is used by Archaea (and some bacteria) in the synthesis process of membrane lipid ethers; used by Eukarya to make cholesterol
Cell wall purpose
gives the cell shape and allows it to withstand turgor pressure
Turgor pressure?
osmotic pressure caused by differences in concentrations across the membrane
Peptidoglycan/murein composition?
glycan chains that are linked across by peptide cross-bridges
Glycan composition?
Glycan is made up of long polymer chains of two amino sugars (N-acetylglucosamine & N-acetylmuramic, NAG & NAM) connected glycosidic/sugar bonds
What amino acids make up the peptide cross-bridges?
L-Alanine, D-Glutamic acid, m-Diaminopimelic acid, D-Alanine
Between which two amino acids does the cross-link form?
m-DAP and D-alanine.
Which sugar of the glycan is the peptide cross-bridge attached to?
N-acetylmuramic (NAM)
How does penicillin/cephalosporin affect cell wall/peptidoglycan formation?
They blocks the release of D-Alanine. Specifically, the enzyme transpeptidase (during Transpeptidation) so no cross-links form
How does vancomycin affect cell wall/peptidoglycan formation?
Vancomycin blocks croos-bridge formation (blocks Transglycosylation) by binding D-Ala—D-Ala instead of D-Ala—DAP in gm- & D-Ala—Lys in gm+
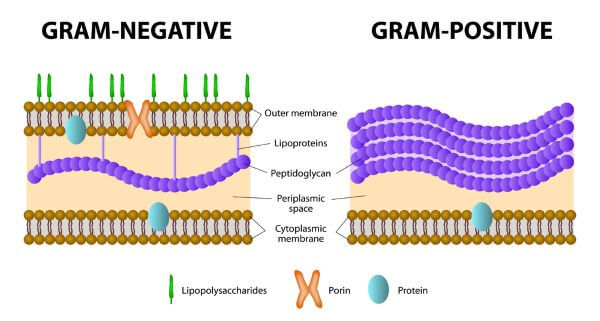
Peptidoglycan differences in Gm(+) vs. Gm(-)
Gm- : direction connection of DAP—D-Ala; Thin peptidoglycan layer; moderate strength
Gm+: connection via interbridge (5 Gly) connecting D-Ala—L-Lys; thick multi-layered peptidoglycan + extra coss-links = very strong
Where does synthesis of peptidoglycan occur?
Occurs in the cytoplasm and the extracytoplasmic (periplasmic) space
Describe the process of synthesizing PG (8 steps)
1.) Amino acids are added to UDP-NAM
2.) D-Alnine peptide attaches
3.) NAM pentapeptide picked up by bactoprenol, UMP leaves, molecule is moved (this is known as Lipid I)
4.) UDP-NAG linked up to the NAM and UDP leaves (this is now Lipid II)
5.) Flippase flips NAM-NAG outside the membrane
6.) Transglycosylation: NAM-NAG disaccharide added to existing PG chain (sugar-sugar backbone)
7.) Transpeptidation: A pentaglycine forms the cross-link sidechains (L-Lys—D-Ala + pentaglycine bridge for Gm(+) and D-Ala—m-DAP for Gm(-))
8.) One phosphate removed, and lipid returns to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. Process starts again
What are Transglycosylase and Transpeptidase?
PBPs, Penicillin-binding proteins
What does bacitracin do in PG formation?
Inhibit incorporation of disaccharide units during transpeptidation
Phylum?
a group of organisms that share a common ancestor that diverged early from other bacteria, based on rRNA sequence
Gram-positive bacteria example?
Bacillus anthracis— anthrax, thick cell wall
Gram-negative bacteria example?
Escherichia coli, thin cell wall + outer membrane
Teichoic acids? What’s special about them? Where are they present?
Long polymers made out of glycerol or ribitol units that are linked by phosphates.
Have - charge due to them
In Gm(+) cell wall
Purpose of teichoic acids? (4 things)
Bind divalent metal ions (ex: Mg2+ & Ca2+), aid in ion transport, help wall stability, act like antigens
Lipoteichoic acids? Where are they present?
Teichoic acids bound to membrane lipids (they long)
In Gm(+) cell walls
Sortase enzymes? Where are they mainly found?
convalently link proteins to the amino acids of the PG cross-links via peptide bonds.
Gm(+) cells
Glycosyl chains in Gm(+) cell walls?
Chains of NAM-NAG sugars
Not always present, but sometimes
Help maintain shape and resist osmotic lysis
What does Gm(-) bacteria envelope look like?
plasma/inner membrane + periplasmic space + outer membrane
What is the outer membrane? Where is present?
The outer membrane is a bilayer with inner and outer facing surfaces
Present in Gm(-) bacteria
What do Bruan’s/Murein lipoproteins do?
Are attached to the inner surface of the outer membrane via 3 fatty acids; are also attached to the peptidoglycan layer, thus connecting the two via covalent bonds
Porin complex purpose?
Allow small molecules and ions to enter, but not large ones
Periplasmic space?
Space between the outer membrane and the cytoplasmic membrane/inner membrane in Gm(-)
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)?
Lipid molecule on the outside of the outer membrane that responds to infection in the host
What happens is a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is free floating?
It is an endotoxin and will stimulates defenses in the host, can lead to endotoxic shock
Core polysaccharide?
Part of LPS that links together Lipid A and the O antigen.
O-antigens purpose?
Prevent phagocytosis (where cell eats bacteria, debris, dead cells, etc.) by the host cells
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) structure?
O side chain (O antigen), core polysaccharide, lipid A
Lipid A has sugars with branched lipids and short fatty acids
What proteins does Gm(-) outer membrane have?
Has porin and transporter proteins (make it more permeable than inner membrane)
What makes Mycobacterium tuberculosis & M. Leprae cell envelopes special?
Mycolic acids & Arabinogalactans (Note: structure goes cell membrane—> PG—> Galactan—> Arabinan—> Mycolic acid—> capsule)
Mycolic acids? Purpose?
Very long chains of fatty acid
They form a thick waxy/hydrophobic outer layer that traps the dye carbol fuchsin during acid–fast staining
Purpose of outer membrane?
Permeability barrier to large molecules and harmful chemicals.
Arabinogalactans? Purpose?
an unusual polysaccharide that acts like a linker between the PG layer and the mycolic acid layer
Results of Mycobacterial special features?
Typically harder to stain, harder for antibiotics to enter, and harder for the host immune system to kill (why tuberculosis is so difficult to treat)
S-layer?
A crystalline layer of thick protein or glycoprotein subunits, which unit contains large pores
S-layer function?
Contributes to cell shape, protects from osmotic stress, helps in biofilm formation, and in pathogenicity (causing disease)
S-layer differences in Gm(+) vs. Gm(-)?
Gm(-): adheres to inside of outer membrane
Gm(+): adheres to the PG surface
Who has s-layer?
Found in archaea and in bacteria
Structure of archaeal envelopes and cell walls?
They do not have PG, and no OM
Typically have s-layer and cytoplasmic membrane
SOMETIMES have cytoplasmic membrane + pseudopeptidoglycan/pseudomurein + s-layer
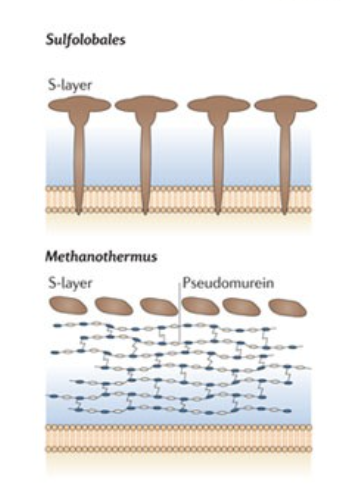
What is pseudopeptidoglycan/pseudomurein? Where is it found?
A polysaccharide composed of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylalosaminuronic acid
In archaeal cells between cytoplasmic membrane & S-layer
Mycoplasma? Features?
No cell wall
Design and synthesis of minimal bacterial genome (lowkey just a membrane). Takes nutrients from host cell
Thermoplasma? Features?
Archaea, growth at low pH and high temperature
No S-layer, but some have glycocalyx (polysaccharide)