kamehamehahaeheahaehaeh
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/116
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
1
New cards
phytohormones
produced endogenously (within plant),
affects plant in very low concentrations,
provides communication,
site of action =/ site of synthesis
affects plant in very low concentrations,
provides communication,
site of action =/ site of synthesis
2
New cards
main groups of phytohormones (5)
auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, ethylene, abscisic acid
3
New cards
other phytohormone groups
salicylic acid, jasmonates, brassinosteroids
4
New cards
plant growth regulators PGR
natural OR synthetic but exogenously applied (added to plant by us/nuserymen)
PLANT GROWTH REGULATOR
PLANT GROWTH REGULATOR
5
New cards
all plant hormones are ---- but not all ---- are plant hormones
PGR’s
(Plant growth regulators, plant NEEDS to make these to survive/ complete growth cycles,endogenous)
(PGR’s can also be isolated/synthesized in a lab, therefore, not a ‘naturally’ produced hormones, exogenous)
(Plant growth regulators, plant NEEDS to make these to survive/ complete growth cycles,endogenous)
(PGR’s can also be isolated/synthesized in a lab, therefore, not a ‘naturally’ produced hormones, exogenous)
6
New cards
first discovered phytohormone/ and when?
IAA, 1930s
Indole Acetic Acid (auxin)
Indole Acetic Acid (auxin)
7
New cards
basipetally
from tip to base (moves to root crown/basal end)
8
New cards
auxins
define: know synthesis/transport
define: know synthesis/transport
* meristematic regions= highest concentration (leaf tip/new shoot)
* highest concentration: SAM (apical meristem= most young/juvenile area)
* lowest concentration: crown (crown= proximal, auxin=distal)
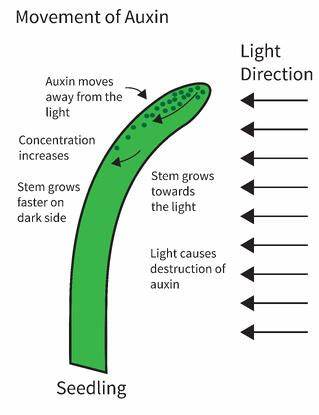
* cell elongation and division, root initiation, cambial growth (INITIATES ROOT GROWTH)
* areas of less light (light degrades auxin)
* TRANSPORTED BASIPETALLY (moved DOWN to roots\~ via xylem)
* highest concentration: SAM (apical meristem= most young/juvenile area)
* lowest concentration: crown (crown= proximal, auxin=distal)
* cell elongation and division, root initiation, cambial growth (INITIATES ROOT GROWTH)
* areas of less light (light degrades auxin)
* TRANSPORTED BASIPETALLY (moved DOWN to roots\~ via xylem)
9
New cards
common synthetic forms of auxins
__**IBA and NAA**__
\
Indole 3-butyric acid (IBA)
Naphthalene Acetic Acid (NAA) -more potent \[for difficult to roots/RECALCITRANT >:) \]
\
Indole 3-butyric acid (IBA)
Naphthalene Acetic Acid (NAA) -more potent \[for difficult to roots/RECALCITRANT >:) \]
10
New cards
totipotency
ability of a cell to divide and differentiate
\~has potential to become entire organism.
\~has potential to become entire organism.
11
New cards
dedifferentiation
originally somewhat “specialized” THEN → cell reverts back to active division
12
New cards
auxin is key to --- --- NOT to root elongation
root initiation
(STARTS THE ROOTS!!!)
(STARTS THE ROOTS!!!)
13
New cards
auxin shapes ----- expression and upregulation of ----
gene, (making more sensitive to auxin) genes
14
New cards
benefits of PGR’s (exogenous application)
* increases % success of rooted cutting
* increases root number and quality
* hastens rooting FASTER ROOTING
* increases rooting UNIFORMITY
* increases root number and quality
* hastens rooting FASTER ROOTING
* increases rooting UNIFORMITY
15
New cards
powder PGR application
* easy to use
* rooting less uniform
* may involve waste but easy to store
* rooting less uniform
* may involve waste but easy to store
16
New cards
liquid quick dip PGR application
* consistent results
* high concentrations
* 1/2 - 1 in for 5-15 seconds
* uniform rooting
* high concentrations
* 1/2 - 1 in for 5-15 seconds
* uniform rooting
17
New cards
dilute solution soak PGR application
* low auxin concentrations
* 3/4 in to 1 in of basal end of stem
* often left overnight
* 3/4 in to 1 in of basal end of stem
* often left overnight
18
New cards
preformed/latent root initials
develop naturally on the stem and are dormant i.e pothos
(pericycle) already formed!
(pericycle) already formed!
19
New cards
wound induced roots
develop only after wounding
20
New cards
steps of wound-induced rooting
1. outer/injured cells die
2. necrotic plate forms, sealing the wound
3. parenchyma/callus tissue form behind plate
4. cells near the vascular tissue begin to form adventitious roots
21
New cards
origins of adventitious root/bud/stem formation
preformed meristems (already present pre-formed tissue)
wound induced (initated only by wounding)
wound induced (initated only by wounding)
22
New cards
limiting factor in __**leaf cutting**__ propagation
formation of __**adventitious buds/shoots**__ NOT roots; want whole plant
23
New cards
Chimeras: how to propagate **thornless** blackberries
you must propagate chimeras by STEM CUTTINGS or you will get plants with thorns/etc
24
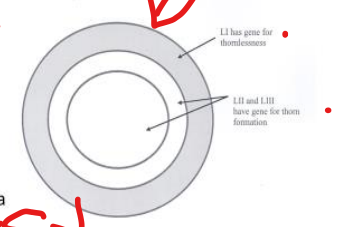
New cards
thornless blackberries: gene is found in the outermost layer:
only the __ meristematic layer has the no thorn gene
only the __ meristematic layer has the no thorn gene
LI
25
New cards
conditions/equipment for ideal process in producing __**stem cuttings**__
* sharp/sanitized shears (no disease/clean cuts)
\
* cuttings hydrated (turgid)
\
* uniform size (think for sales)
\
* treat with rooting compound if needed (how easy is it to propagate?)
\
* cuttings hydrated (turgid)
\
* uniform size (think for sales)
\
* treat with rooting compound if needed (how easy is it to propagate?)
26
New cards
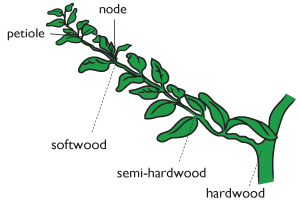
stem cutting plant types
* hardwood
* semi-hardwood
* softwood
* herbaceous
* semi-hardwood
* softwood
* herbaceous
27
New cards
Stem cutting: hardwood cuttings
* taken during dormant season
* basal cut just below a node and top cut just above a node (rot)
* 2-3 in
* tops can be waxed: polarity/rot
* at least 2 nodes
* basal cut just below a node and top cut just above a node (rot)
* 2-3 in
* tops can be waxed: polarity/rot
* at least 2 nodes
28
New cards
deciduous cutting planting
* direct fall planting (mild winters/full growing season)
* initiating roots with bottom heat (taken fall/late winter, planted w heat mats)
* direct spring planting (cutting material gathered during dormancy, wrap in moist stuff til spring)
* initiating roots with bottom heat (taken fall/late winter, planted w heat mats)
* direct spring planting (cutting material gathered during dormancy, wrap in moist stuff til spring)
29
New cards
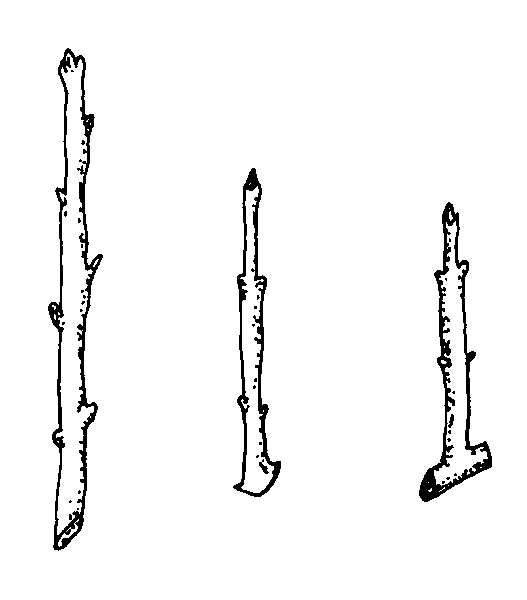
Stem cuttings:
deciduous cutting types (3)
deciduous cutting types (3)
1. straight/simple
2. heel (small portion of older wood attached)
3. mallet (small section of entire stem of older wood attached)
^ not from last flush
30
New cards
narrow leafed evergreen cuttings
* take dormant season
* slow to root/bottom heat
* 4-8in and only last seasons growth
* high light
* low growing species easiest vs upright
* take cuttings from side shoots, strip lower needles, fungicide
* container 4 in deep
* slow to root/bottom heat
* 4-8in and only last seasons growth
* high light
* low growing species easiest vs upright
* take cuttings from side shoots, strip lower needles, fungicide
* container 4 in deep
31
New cards
broad leafed evergreens
* late spring/midsummer
* 3-8in
* harvest early in day
* 70-80f
* 3-8in
* harvest early in day
* 70-80f
32
New cards
softwood cuttings
* cuttings taken in spring during growth
* tissue still soft
* intermittent mist key
* quicker/easier to get adventitious roots
* take early in morning
* 3-5 in
* medial > terminal
* tissue still soft
* intermittent mist key
* quicker/easier to get adventitious roots
* take early in morning
* 3-5 in
* medial > terminal
33
New cards
herbaceous cuttings
* 3-5in but depends on species
* auxin not usually required
* mist/high humidity
* auxin not usually required
* mist/high humidity
34
New cards
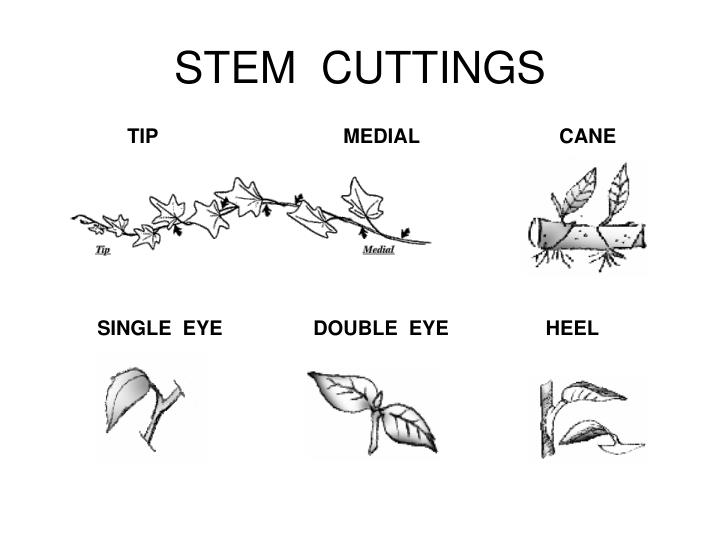
Stem Cuttings: types of herbaceous cuttings
* single eye - alt leaf plant
* double eye - opposite leaf plant
* split node - splitting of node of an opposite leaf plant
* cane - little branching, needs wounding, polarity
* double eye - opposite leaf plant
* split node - splitting of node of an opposite leaf plant
* cane - little branching, needs wounding, polarity
35
New cards
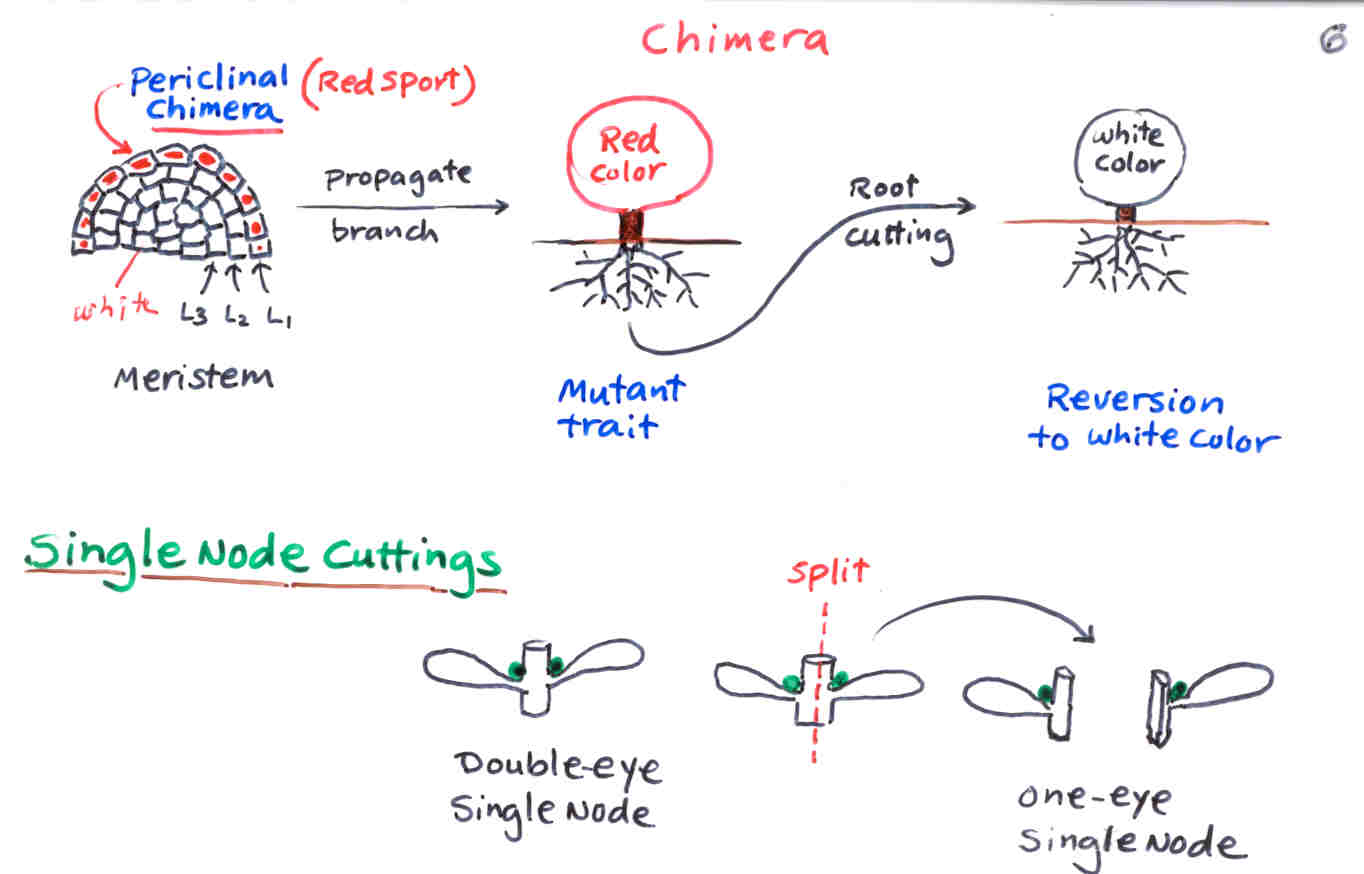
chimera
__**KNOW THIS DEFINITION:**__
__**plant with 2 or more genetically dissimilar tissues growing side by side**__
\
* higher plants have layered meristems originating from a few cells in the central zone of the SAM (LI, LII, LIII)
* outer layers maintain their integrity because they divide anticlinally
* arise from genetic changes in one or more layers in apical meristem
__**plant with 2 or more genetically dissimilar tissues growing side by side**__
\
* higher plants have layered meristems originating from a few cells in the central zone of the SAM (LI, LII, LIII)
* outer layers maintain their integrity because they divide anticlinally
* arise from genetic changes in one or more layers in apical meristem
36
New cards
anticlinally
* cell division perpendicular to surface of a plant organ
* anticlinal division forms a sheet of cells one layer thick while periclinal division results in plant **girth**!!!!!!!!
* anticlinal division forms a sheet of cells one layer thick while periclinal division results in plant **girth**!!!!!!!!
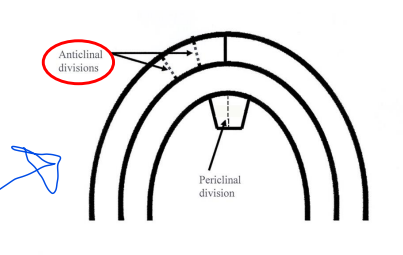
37
New cards
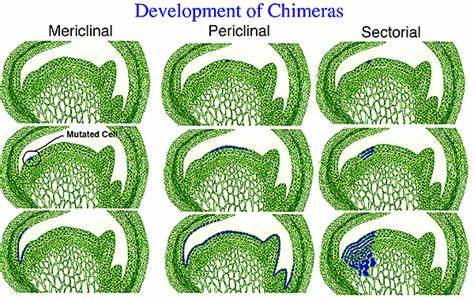
mericlinal chimera
genetically different tissue is found in PART OF A SINGLE LAYER of meristem, but not entire layer (LI, LII, LIII)
38
New cards
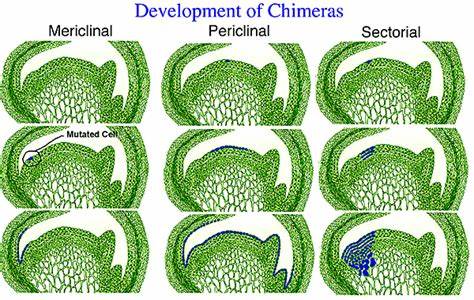
sectorial chimera
genetically different tissue found in part of ALL meristem layers LI,LII,LIII
39
New cards
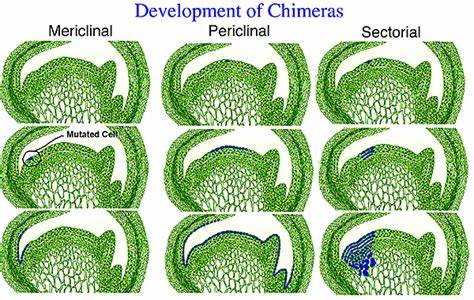
periclinal
genetically different tissue makes up ONE ENTIRE LAYER of meristem
40
New cards
which chimera can be reliably propagated, why?
periclinal
mutant tissue is found through an entire meristematic tissue layer
mutant tissue is found through an entire meristematic tissue layer
41
New cards
mericlinal and sectorial chimeras can be stabilized as -------------- by the selection of axillary buds
periclinal chimeras
42
New cards
how to propagate chimeras
STEM CUTTINGS
techniques that avoid adventitious bud formation; **leaf cutting does not work**
\
(Needs chimera plant’s bud tissue)
leaf bud cuttings
division, layering
budding and grafting
shoot cuttings
techniques that avoid adventitious bud formation; **leaf cutting does not work**
\
(Needs chimera plant’s bud tissue)
leaf bud cuttings
division, layering
budding and grafting
shoot cuttings
43
New cards
techniques that wont produce chimeras
leaf, root, tissue culture (unless contains axillary bud)
44
New cards
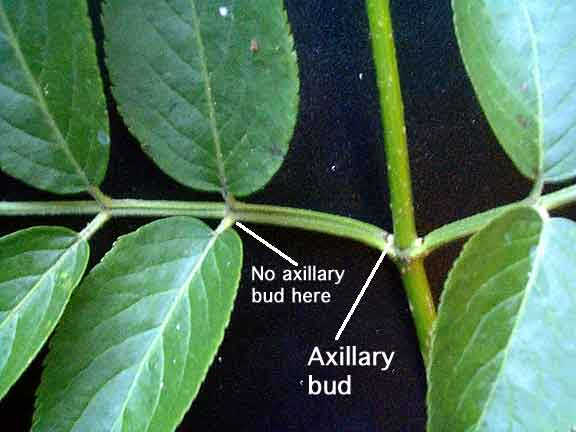

axillary buds are
preformed meristems
axillary buds are usually **dormant, inhibited by auxin produced by the apical meristem, which is known as apical dominance**.
(buds are compressed stems, these embryonic shoots develop exogenously from the outer-cortex layer of the plant at the axillary intersection and eventually grow into new stems.)
axillary buds are usually **dormant, inhibited by auxin produced by the apical meristem, which is known as apical dominance**.
(buds are compressed stems, these embryonic shoots develop exogenously from the outer-cortex layer of the plant at the axillary intersection and eventually grow into new stems.)
45
New cards
leaf bud cuttings, are they stem or leaf cuttings?
Stem cuttings, they contain stem tissue!

46
New cards

leaf cuttings advantages
* little expertise needed
* no need for elaborate facilities
* high humidity better than mist
* well drained substrate required
* no need for elaborate facilities
* high humidity better than mist
* well drained substrate required

47
New cards
leaf cutting disadvantages
* doesnt work with chimeras
* small propagules produced, takes a long time
* auxin may inhibit adventitious shoot formation
* small propagules produced, takes a long time
* auxin may inhibit adventitious shoot formation
48
New cards

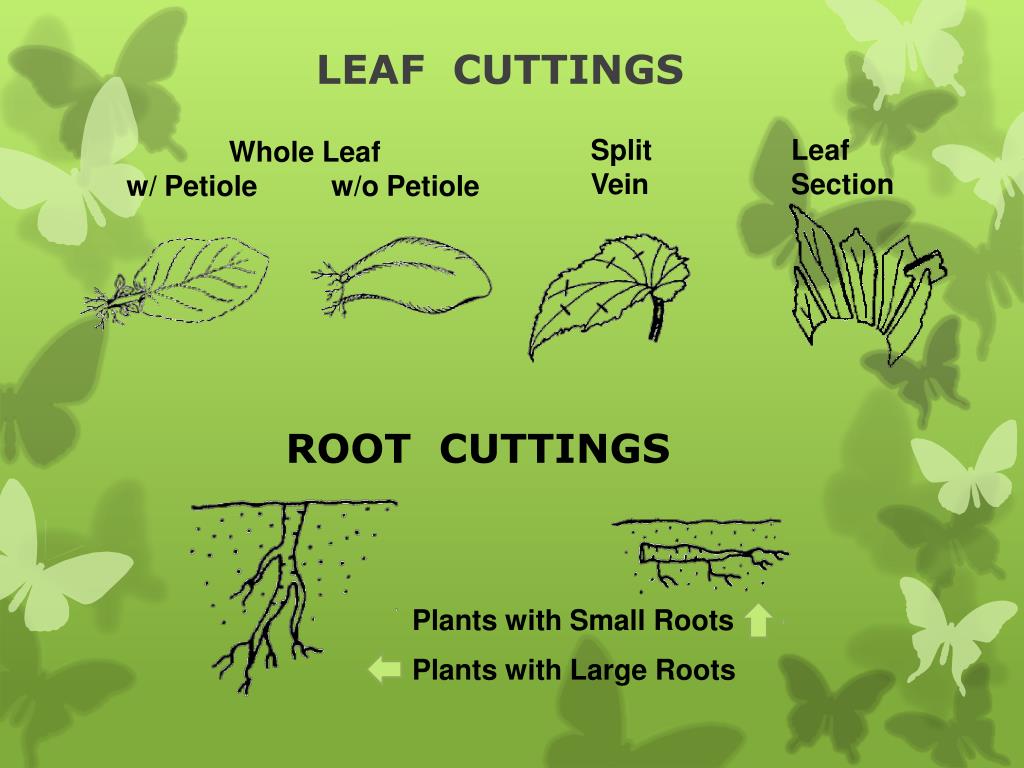
whole leaf with petiole
whole leaf cutting with petiole attached, ie: peperomia

49
New cards
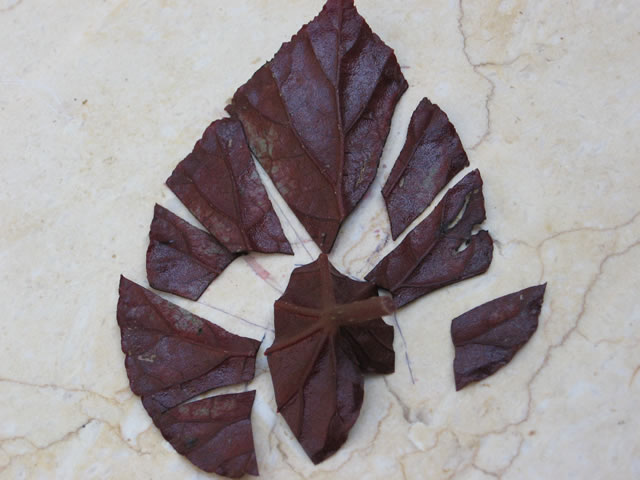

whole leaf: split vein
cutting the leaf tissues away along veins, planted with portion of vein. ie: rex begonia
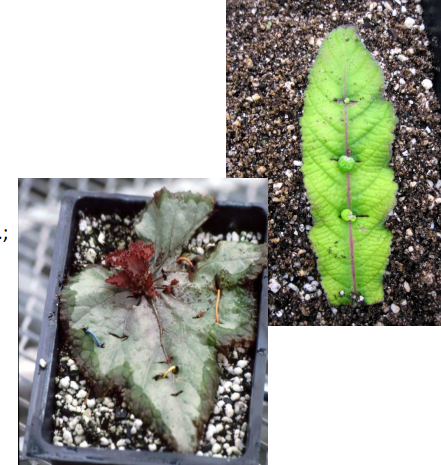

50
New cards

leaf section cutting
cutting a section from a whole leaf. ie: snake plant

51
New cards
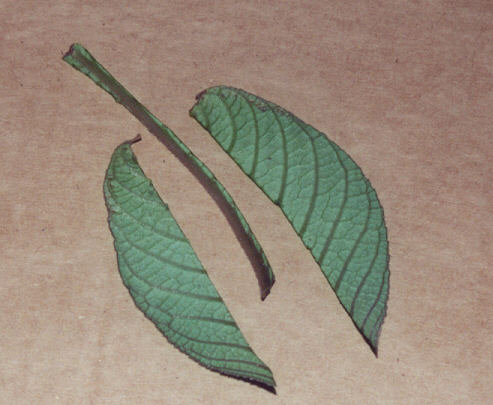

Vein removal/mid rib vein removal
can be used for any leaves that have a single central vein. cape primrose
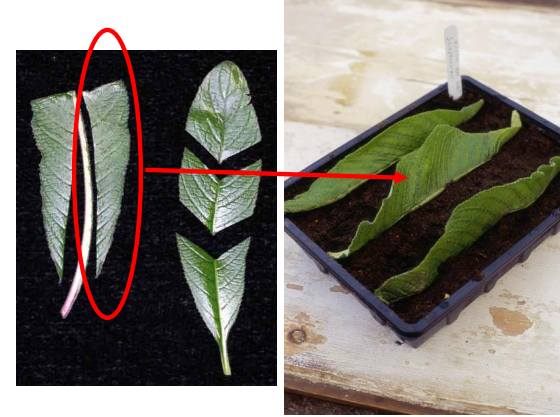

52
New cards
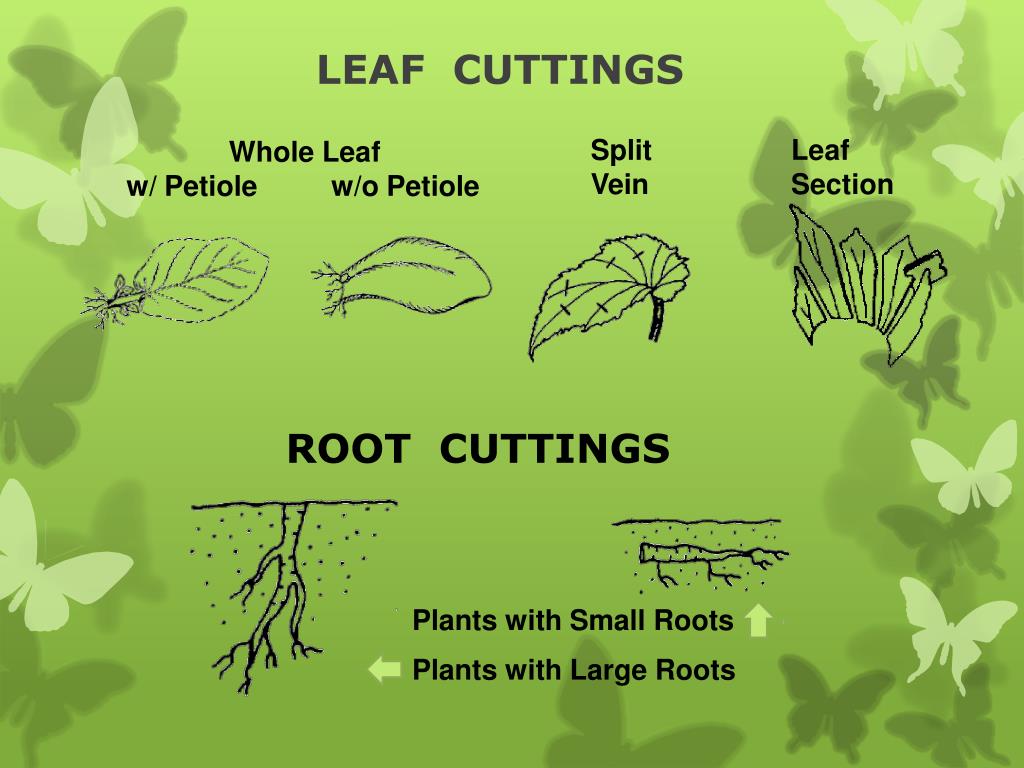
leaf cuttings summary
* herbaceous plants
* small pieces of stock plant/smaller prop area, large quantity produced
* polarity matters
* small pieces of stock plant/smaller prop area, large quantity produced
* polarity matters

53
New cards
Phytohormones are active in a plant in ____ concentrations
LOW
54
New cards
What makes a plant “difficult to root” aka: recalcitrant
1. absent CO-FACTORS
2. mature tissues
55
New cards
How to make a difficult to root plant root?
wounding
exogenous application of auxins
etiolation
exogenous application of auxins
etiolation
56
New cards
Mature- define (different than old)
Ability to sexually reproduce (think fruiting & flowering)
57
New cards
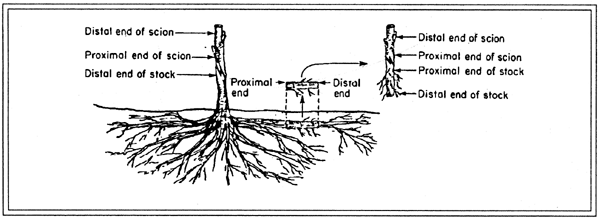
Polarity: Distal & Proximal - DEFINE for root/stem cuttings
__**root cutting-**__
__proximal__= closest to root crown/cone of juvenility
__Distal__= Furthest from root crown/cone of juvenility (end of root NEAREST to new root tips)
\
__**stem cutting-**__
__Proximal__= Closest to closest to root crown/cone of juvenility (roots come from here! polarity!)
__Distal__=Furthest from root crown/cone of juvenility (shoots come from here! polarity!)
__proximal__= closest to root crown/cone of juvenility
__Distal__= Furthest from root crown/cone of juvenility (end of root NEAREST to new root tips)
\
__**stem cutting-**__
__Proximal__= Closest to closest to root crown/cone of juvenility (roots come from here! polarity!)
__Distal__=Furthest from root crown/cone of juvenility (shoots come from here! polarity!)
58
New cards
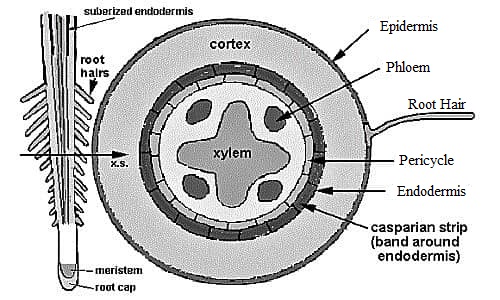
Root Cutting- new adventitious shoot formation: 2 locations/types
\
\
1. __**Pericycle**__: Endogenous or inside the endodermis; contains “additional bud” in YOUNG ROOTS
2. __**Phellogen**__: Exogenously; “reparative bud” or cork cambium in OLD ROOTS; replaces the epidermis. wounding required.
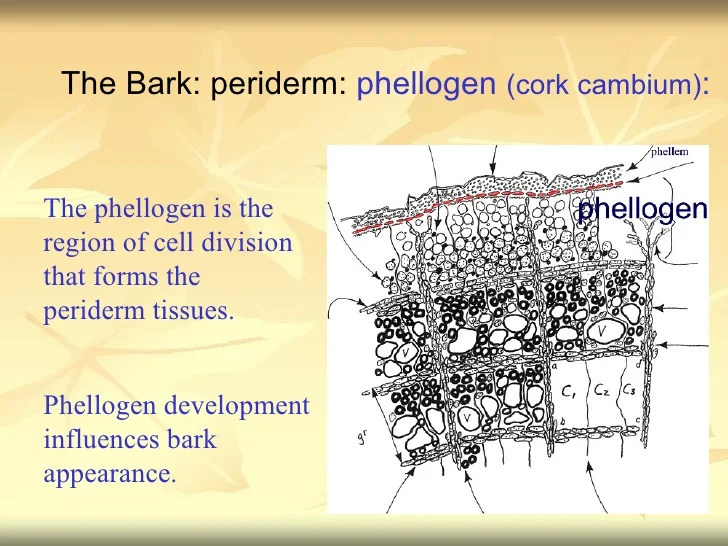
59
New cards
Crown- define
Where the roots/stem tissue meet
60
New cards
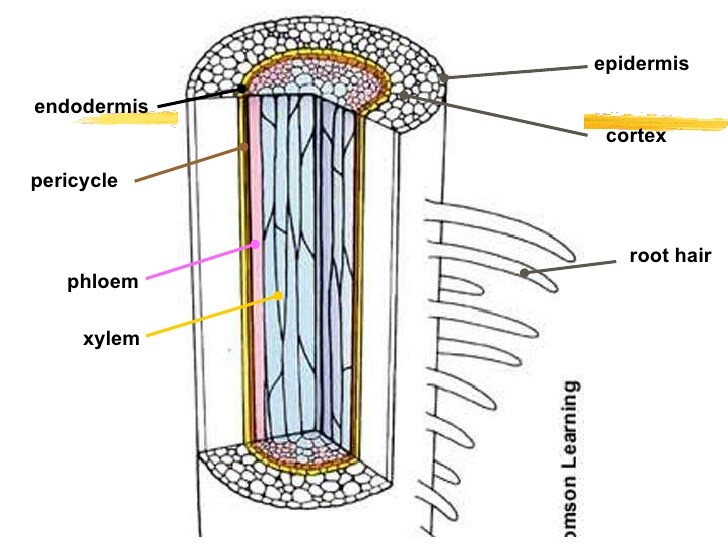
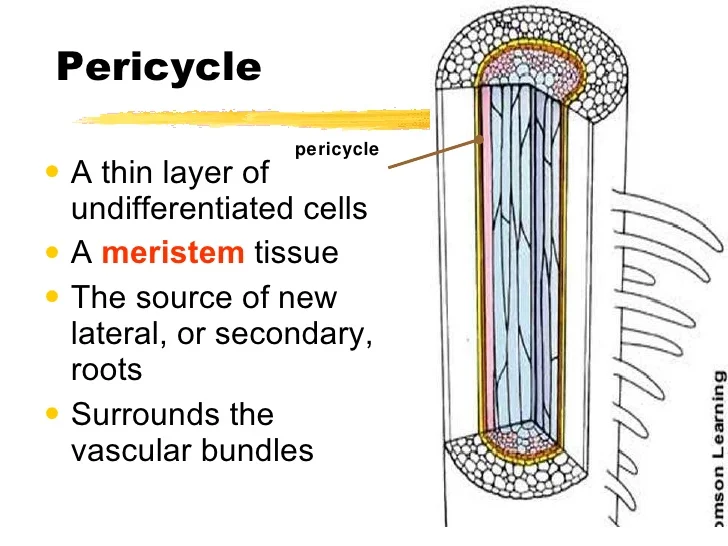
Know: Where and why the PERICYCLE in a root. (why= why we focus on it?)
pericycle, where: layer under the endodermis, surrounds vascular bundles
pericycle, why: undifferentiated cells, site of **new root formation**
pericycle, why: undifferentiated cells, site of **new root formation**
61
New cards
62
New cards
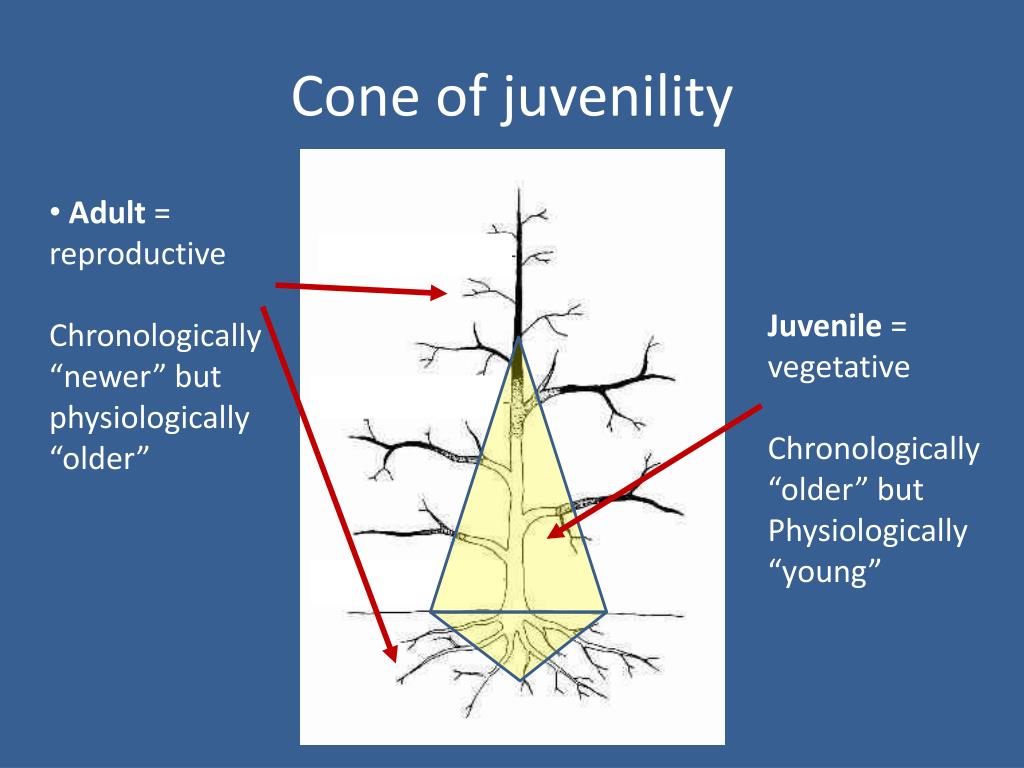
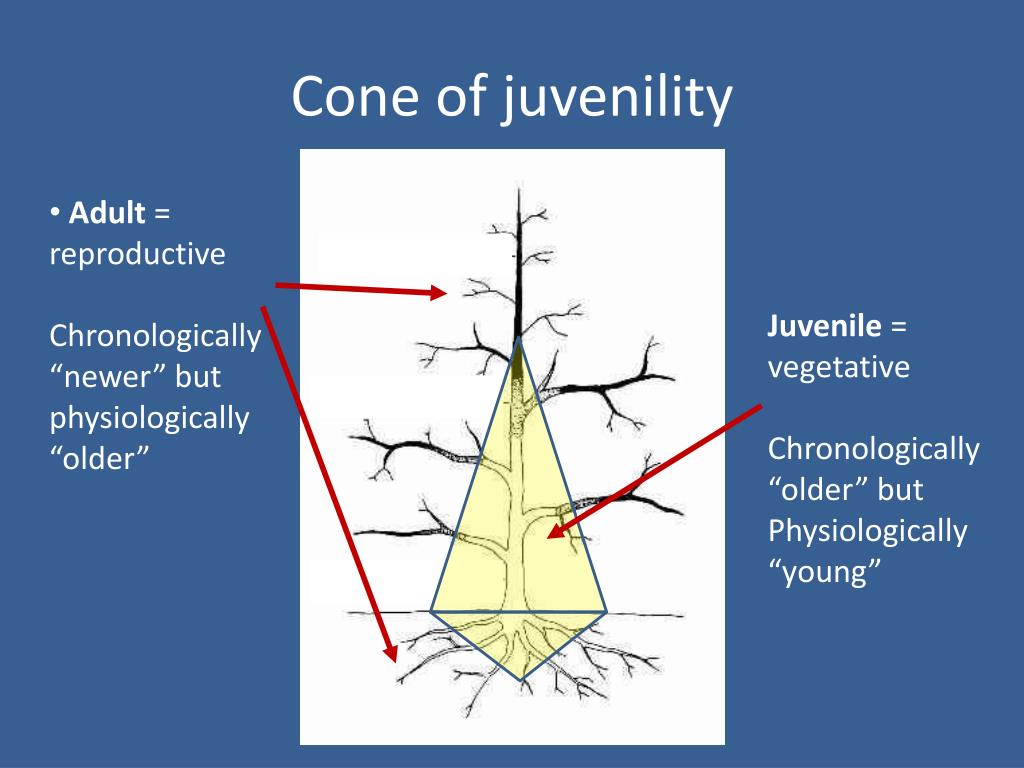
Cone of juvenility- what is it/ why is it important?
high amounts of meristematic tissue, active cell division, juvenility= ideal propagation material
63
New cards
Leaf Cuttings advantages
1. Little expertise needed
2. No need for elaborate facilities
3. High humidity better than mist
4. Well drained substrate required (1 part peat: 1 part sand, perlite or vermiculite)

64
New cards
Leaf Cutting Disadvantages
1. Doesn’t work with chimeras
2. Small propagules produced
3. takes a long time
4. Auxin may inhibit adventitious shoot formation (auxin inhibits cytokinin)
65
New cards
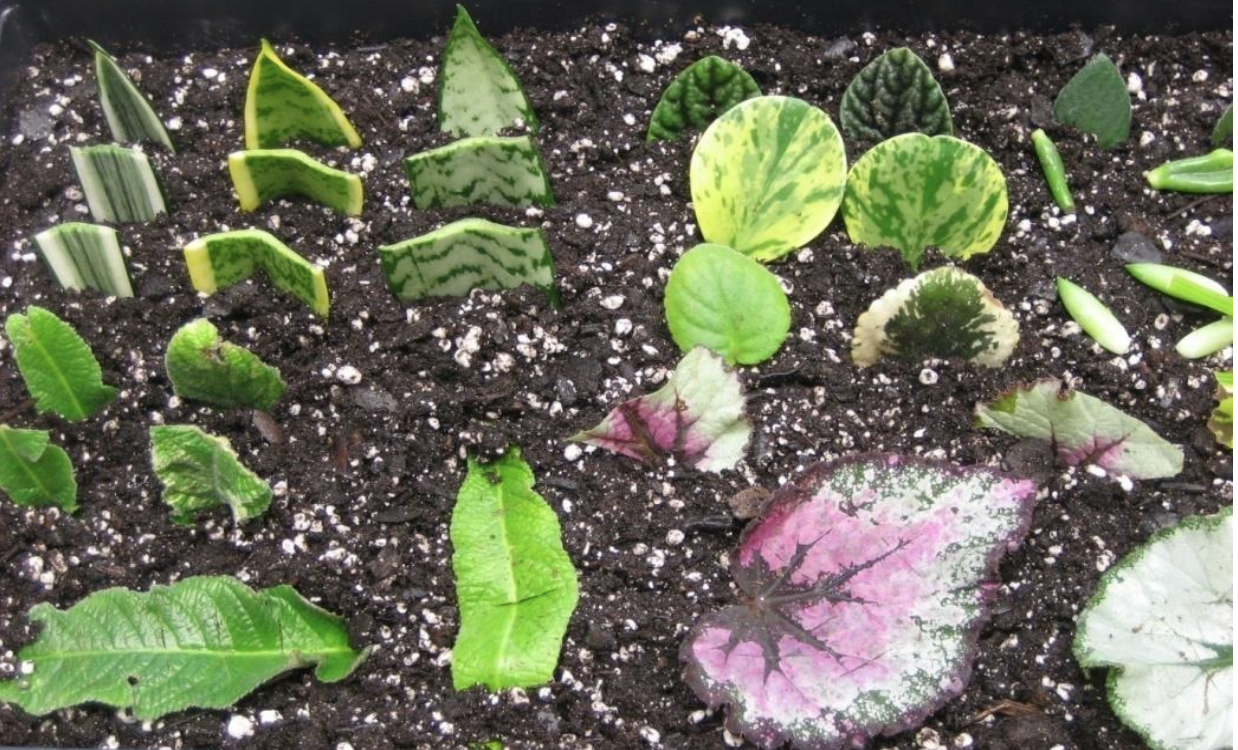

NAME ALL OF THESE LEAF CUTTING TYPES
whole leaf
whole leaf with petiole
leaf section
Split vein/vein removal leaf cutting
whole leaf with petiole
leaf section
Split vein/vein removal leaf cutting
66
New cards
Chimera: generally speaking, what tissue is REQUIRED to maintain chimera expression in propagation & methods (6) to achieve this
BUD TISSUE
methods:
1\.Leaf-bud cuttings (bud is present)
\
2\. Division (cut crown)
\
3\. Layering (grown from parent plant)
\
4\. Budding and grafting (splicing?)
\
5\. Tissue culture (involving callus tissue, oogenesis, or somatic embryogenesis/ AXILLARY BUD TISSUE)
__Tissue culture is ONLY possible with specific tissues__
\
6\. Shoot cuttings (MOST COMMON)
methods:
1\.Leaf-bud cuttings (bud is present)
\
2\. Division (cut crown)
\
3\. Layering (grown from parent plant)
\
4\. Budding and grafting (splicing?)
\
5\. Tissue culture (involving callus tissue, oogenesis, or somatic embryogenesis/ AXILLARY BUD TISSUE)
__Tissue culture is ONLY possible with specific tissues__
\
6\. Shoot cuttings (MOST COMMON)
67
New cards
DEFINE: chimera (regarding plants)
Plant with two or more genetically dissimilar tissues growing side by side
68
New cards
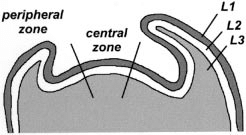
CHIMERAS: Know the 3 layers of meristematic tissue of the apical meristem shoot center (SAM= shoot apical meristem)
LI:
LII:
LIII:
LI:
LII:
LIII:
LI- epidermis \[Tunicate Layer\]
LII- endodermis (subepidermal layer) \[tunicate layer
LIII- most interior layer that can contain chimera genes \[Corpus\]
LII- endodermis (subepidermal layer) \[tunicate layer
LIII- most interior layer that can contain chimera genes \[Corpus\]
![LI- epidermis \[Tunicate Layer\]
LII- endodermis (subepidermal layer) \[tunicate layer
LIII- most interior layer that can contain chimera genes \[Corpus\]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e9da0ed09d3441c6b785b01c12a51aff.jpeg)
69
New cards
3 kinds of Chimera development- describe the differences (description for where would you find their genetic material)
1. __**Mericlinal**__ – genetically different tissue is found __**in**__ __**part of**__ **a** __**single meristem layer**__
\
2. __**Sectorial**__ – genetically different tissue found __**in**__ __**part of**__ __**all**__ **meristem layers**
\
3. __**Periclinal**__ – genetically different tissue makes up __**one entire meristem layer**__ (LI meristem here)
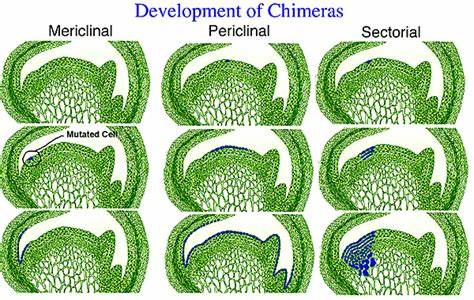
70
New cards
Of the 3 Chimera types, which one is reliably propagated?
__**Periclinal**__- Periclinal chimeras will reliably reproduce themselves because the **mutant tissue is continuous through a meristematic layer (axillary buds!!)**
Mericlinal and Sectorial chimeras are unstable in propagation (imagine trying to pinpoint where the chimera genes would be found?? this tiny section or this one part of one layer??!)
Mericlinal and Sectorial chimeras are unstable in propagation (imagine trying to pinpoint where the chimera genes would be found?? this tiny section or this one part of one layer??!)
71
New cards
Chimeras: Remember the two general categories of stem meristems in __**asexual propagation**__:
(classify the 2 types of possible formations of meristem)
(classify the 2 types of possible formations of meristem)
1. __**Pericycle**__: Techniques forming shoots from preformed meristems (Cells are dormant OR already present)
Preformed 1° meristems - cells still meristematic; __**already there = PRE-FORMED**__
\
2. __**Phellogen:**__ Techniques forming shoots adventitiously (Wound induced requires dedifferentiated cells)
Wound-induced 2° meristems - **dedifferentiated** **cells** that become meristematic, __**needs wounding = REGENERATIVE**__
72
New cards
Axillary buds are ___ ___ ____ _(what kind of meristem)
Axillary buds are **fully formed meristems (preformed)**
73
New cards
Best time/conditions to harvest Broad-leafed Evergreen (hardwood cuttings)
1. between 70 to 80 degrees F substrate temperature
2. Harvest cuttings early in the day; maintain turgor
3. Cuttings taken late spring to mid-summer (buds have elongated and stems are firm)
74
New cards
Softwood Cuttings: best time/conditions to harvest
root and shoot temperatures 70 to 80 degrees F
Take cuttings early in the morning; Turgid
Tissue is still soft (little lignification); flexible but breaks when bent
Cuttings taken in spring during flush of growth or during subsequent flushes on multi-flush plants
Take cuttings early in the morning; Turgid
Tissue is still soft (little lignification); flexible but breaks when bent
Cuttings taken in spring during flush of growth or during subsequent flushes on multi-flush plants
75
New cards
Herbaceous Cuttings- define herbaceous plant trait:
Typically produce no woody tissue
76
New cards
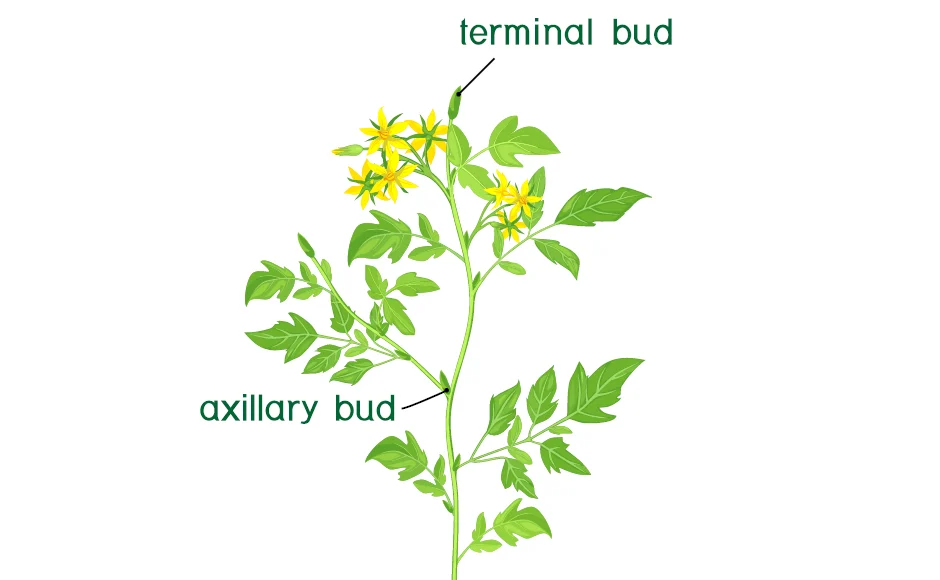
Types of Herbaceous cuttings: terminal (1) medial (4)
Terminal – contains a terminal bud
Medial – no terminal bud
1. Single-eye – alternate leafed plant
2. Double-eye – opposite leafed plant
3. Split-node – splitting of the node of an opposite leafed plan
Cane - little branching needs wounding
Medial – no terminal bud
1. Single-eye – alternate leafed plant
2. Double-eye – opposite leafed plant
3. Split-node – splitting of the node of an opposite leafed plan
Cane - little branching needs wounding
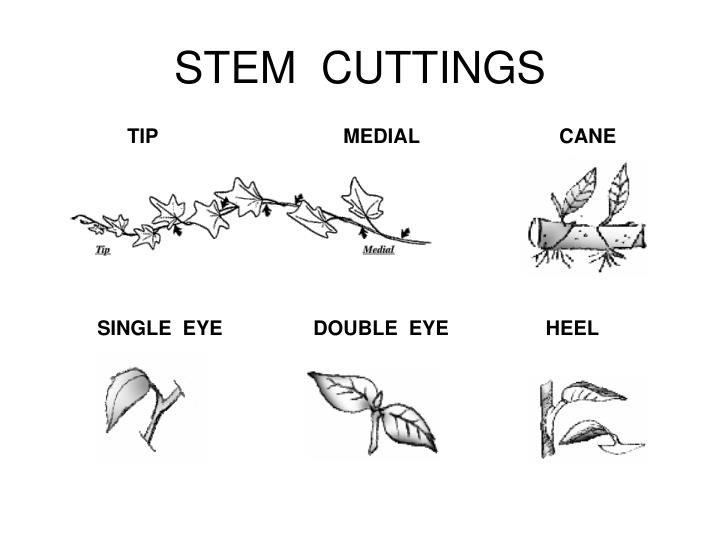
77
New cards
Hardwood Cuttings: DEFINE basal cut
Basal cut- cut closest to basal stem (crown) just below a node.
top cut just above a node (to prevent rot!)
top cut just above a node (to prevent rot!)
78
New cards
Hardwood cuttings: why would you wax the tops? why wouldn’t you wax the bottoms?
Tops can be waxed preventing desiccation and rot (hollow pithed species);
also polarity (shows which end is up)
Bottom waxing will prevent root initials from penetrating into soil
also polarity (shows which end is up)
Bottom waxing will prevent root initials from penetrating into soil
79
New cards
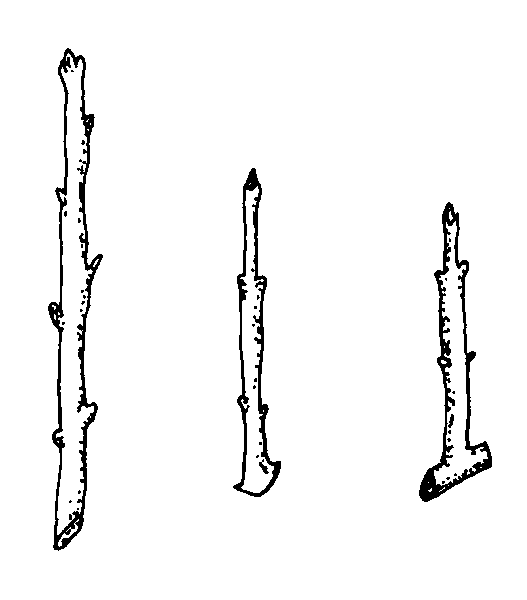
hardwood cuttings: three types
1. Mallet – small section of entire stem of older wood attached; not from last flush .
2. Heel – small portion of older wood attached; not from last flush of growth
3. Straight or simple
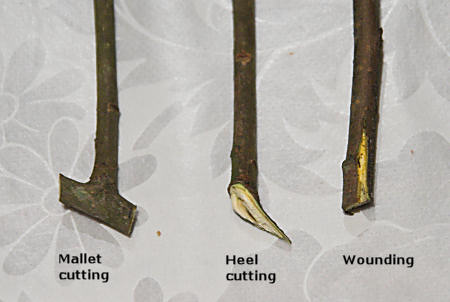
80
New cards
General Process of Producing Stem Cuttings
Sharp, sanitized shears/knife
Keep cuttings hydrated
Trim cuttings to a standard size - critical for uniform success
Treat with rooting compound (PGR), if needed
Keep cuttings hydrated
Trim cuttings to a standard size - critical for uniform success
Treat with rooting compound (PGR), if needed
81
New cards
Auxin Application Methods
Liquid Quick Dip, Talc or Powder Dip, and Dilute Soak, Gel (Eakes hates this tho\~ so wasteful)
82
New cards
Stem Cutting Types (4)
(__**plant type**__ characteristics that help decide what stem cutting you may use) is it a tree? is it a rose?
(__**plant type**__ characteristics that help decide what stem cutting you may use) is it a tree? is it a rose?
• Hardwood cuttings (Deciduous species & Narrow-leafed evergreen species)
winter harvest- evergreen pines/tougher leaf drop winter dormant
\
• Semi-hardwood cuttings (Broad-leafed evergreens & Leafed deciduous species )
spring-midsummer harvest- less tough than pines, maybe oak trees etc.
\
• Softwood cuttings
spring harvest- SOFTER issue, still green! think a rosemary bush!
\
• Herbaceous/tropical cuttings (what we have been doing in Lab)
SUPER DELICATE- think seedum
winter harvest- evergreen pines/tougher leaf drop winter dormant
\
• Semi-hardwood cuttings (Broad-leafed evergreens & Leafed deciduous species )
spring-midsummer harvest- less tough than pines, maybe oak trees etc.
\
• Softwood cuttings
spring harvest- SOFTER issue, still green! think a rosemary bush!
\
• Herbaceous/tropical cuttings (what we have been doing in Lab)
SUPER DELICATE- think seedum
83
New cards
Basal Cut Position on Stem Cuttings: Basal cut should be _____
Basal should be __**at an angle**__
84
New cards
Why should basal should be at an angle?
Position of cut can impact adventitious root formation (more surface area), remember polarity!
85
New cards
“Nodal cut” or “nodal cutting” has the basal cut about ____ below bottom node. why?
basal cut about 1/8” below bottom node \[bud(s)\]
Helps prevent fungal rot
Insures a **bud is below substrate surface**
Helps prevent fungal rot
Insures a **bud is below substrate surface**
![basal cut about 1/8” below bottom node \[bud(s)\]
Helps prevent fungal rot
Insures a **bud is below substrate surface**](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d9fb46ad8e674fb3b5f92f886f240710.jpeg)
86
New cards
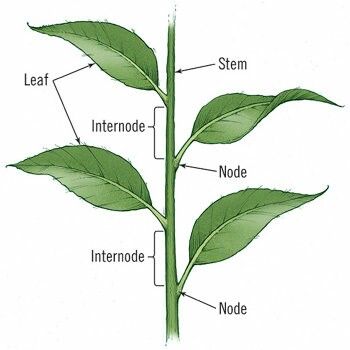
“**Internodal cut**” or “**internodal cutting**” has the basal cut about ____ below bottom node. why?
**Does not insure bud below substrate surface**
Does not reduce fungal growth in wide-pithed or hollow-pithed species
Does not reduce fungal growth in wide-pithed or hollow-pithed species
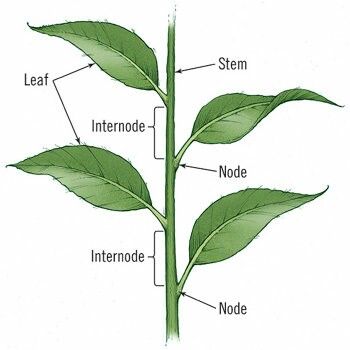
87
New cards
Location of Adventitious Root Formation:
•Herbaceous plants -originate outside and between vascular bundles
•Woody perennials - originate from cambium or young phloem
•Woody perennials - originate from cambium or young phloem
88
New cards
Summary of **Wound-Induced Rooting** (4 stages)
1. Outer/Injured cells die
2. Necrotic plate forms, sealing the wound (suberized=waterproof)
3. Parenchyma cells (callus tissue) begins to form behind the plate
4. Cells near the vascular tissue (i.e. phloem parenchyma) begin to form adventitious roots (c)
89
New cards
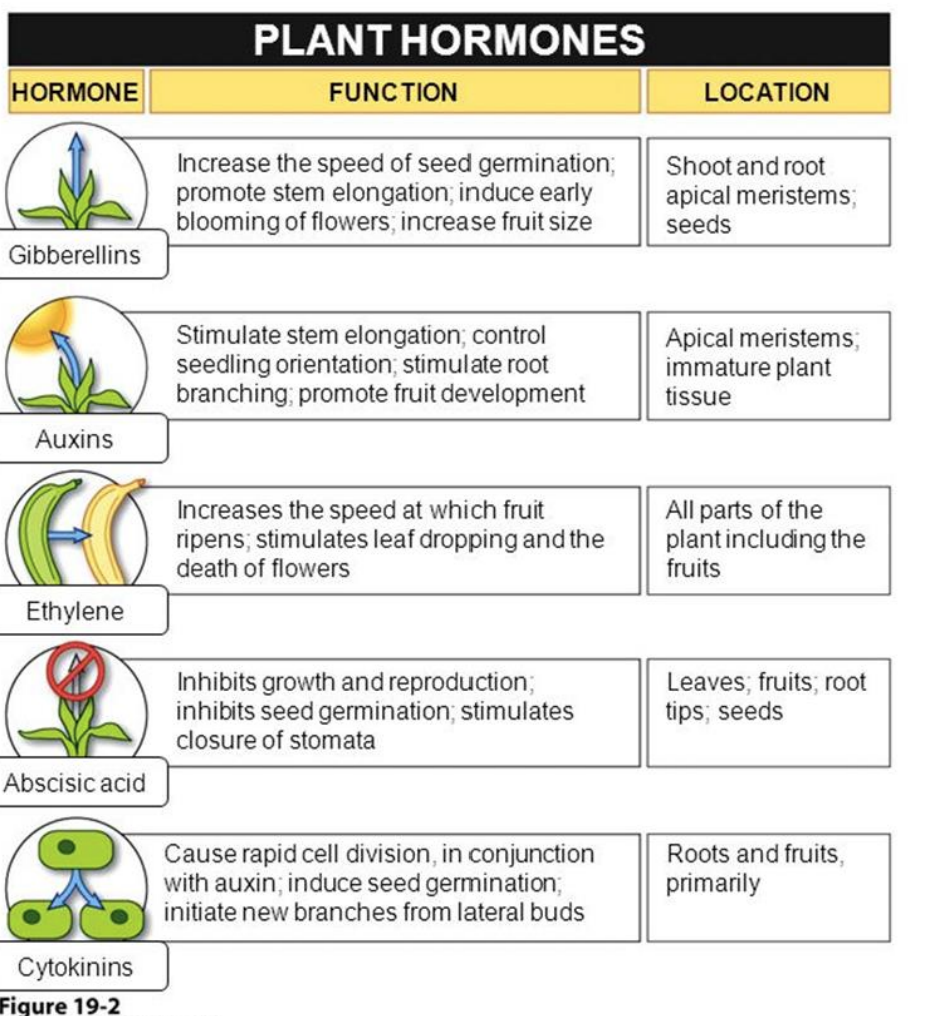
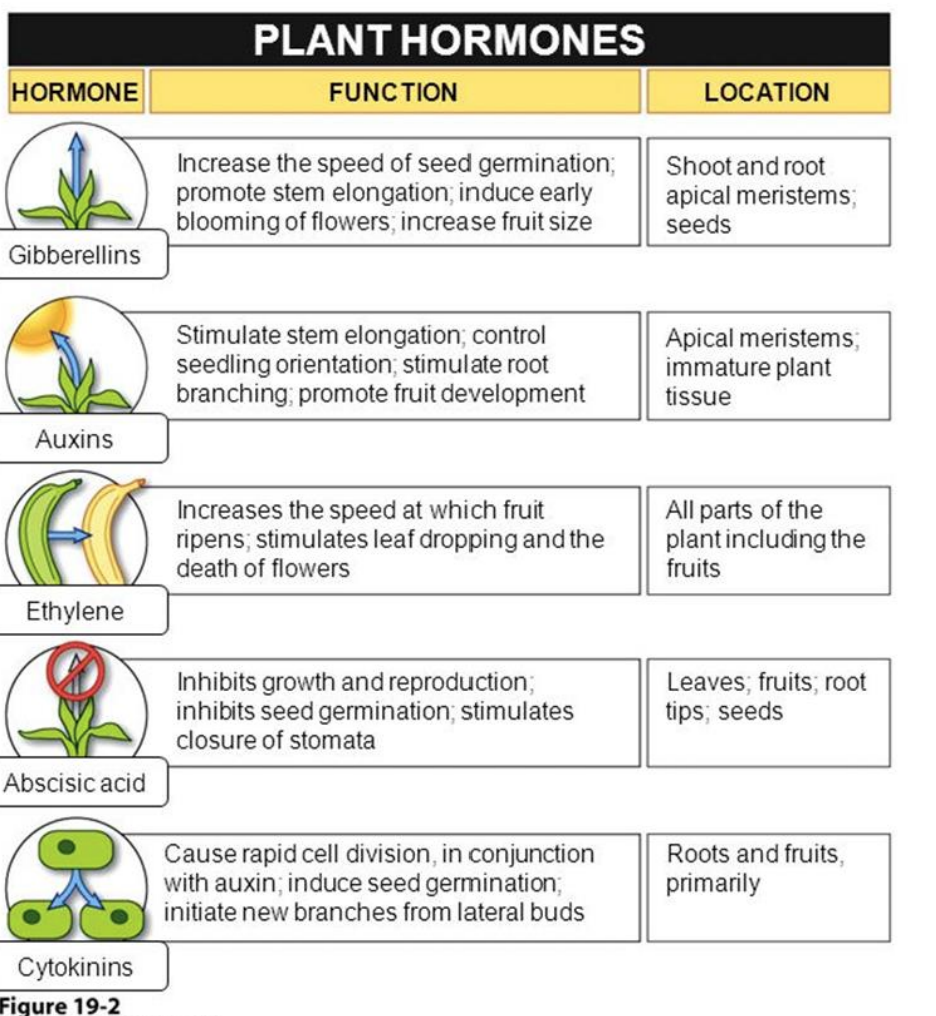
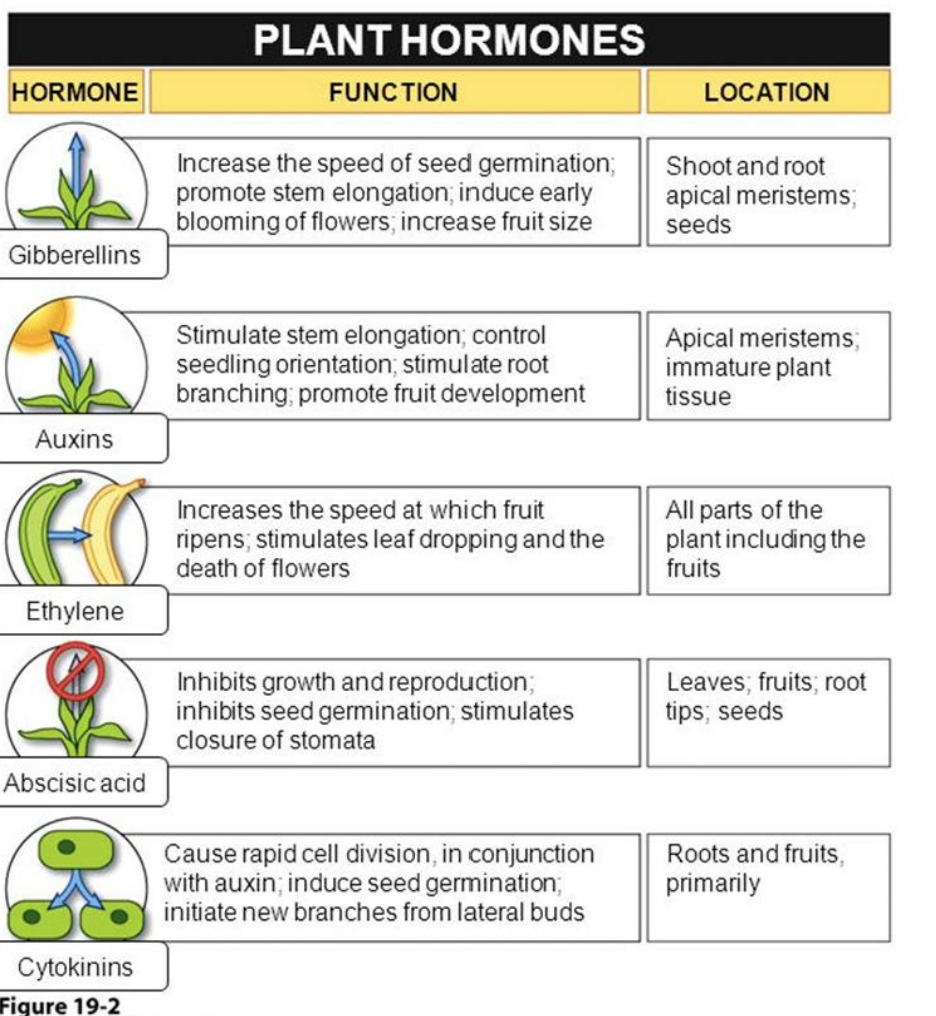
Auxin (PGR phytohormone) what does it do?
INITIATE ROOT GROWTH (inhibits cytokinin)
Stimulates cell elongation
Involved in cell division of root initials
\
Synthesized in meristematic regions, apical meristems, and actively growing organs
(embryos of developing seed)
Stimulates cell elongation
Involved in cell division of root initials
\
Synthesized in meristematic regions, apical meristems, and actively growing organs
(embryos of developing seed)
90
New cards
Gibberellins (PGR/phytohormone) what does it do?
Stem/internode elongation,
Flower initiation and sex expression (male flowers promoted, i.e. Cucumis)
speed of seed germination
Causes parthenocarpic fruit production (seedless fruit)
Flower initiation and sex expression (male flowers promoted, i.e. Cucumis)
speed of seed germination
Causes parthenocarpic fruit production (seedless fruit)
91
New cards
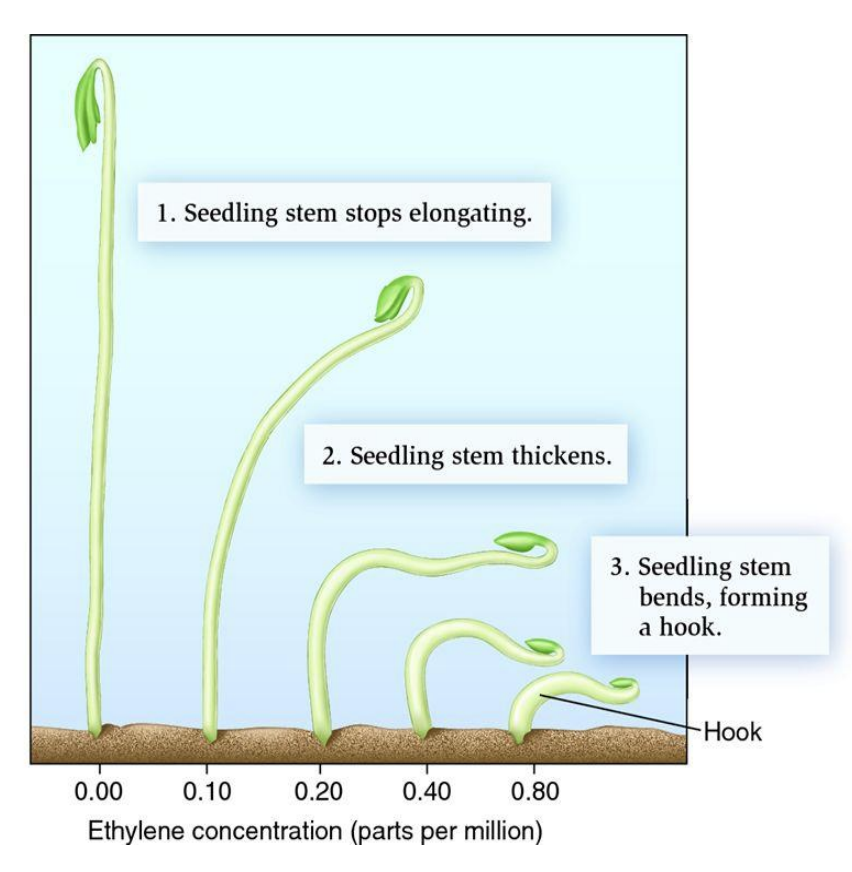
Ethylene (PGR phytohormone) what does it do?
Plant decrease in longitudinal growth, thickening of the shoot → switch to horizontal growth
Stimulates fruit ripening ,
Flower initiation
Changing sex expression of flowers (female flowers in cucumber and pumpkins; increased yield)
Stimulates fruit ripening ,
Flower initiation
Changing sex expression of flowers (female flowers in cucumber and pumpkins; increased yield)
92
New cards
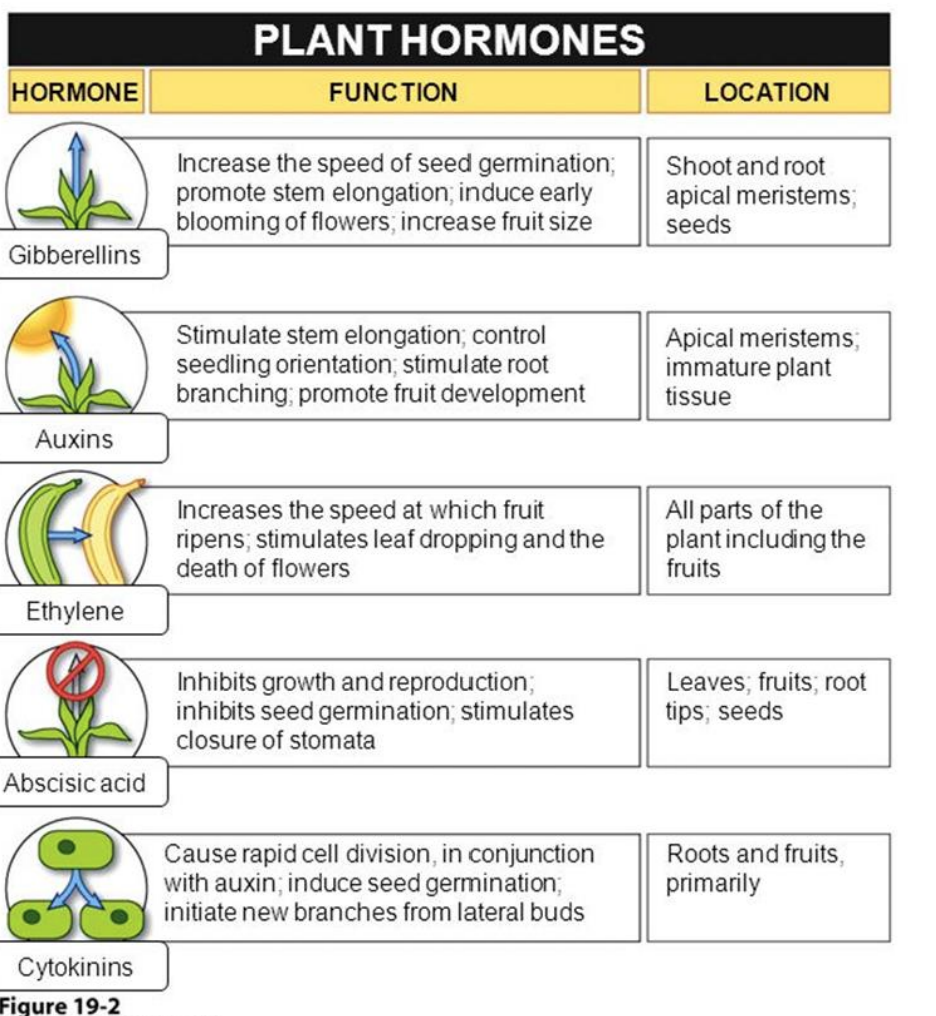
Abscisic Acid (PGR phytohormone) what does it do?
ABA (natural, no synthetic forms available)mostly in mature leaves, but also roots\~ Transported in both xylem and phloem
\
__MOST IMPORTANT:__
Important signal for plant water relations, stomatal activity (STIMULATES STOMATA COLSURE) responds to CO2 concentration and light/darkness
\
Regulation of seed development, accumulation of seed proteins; preventing “precocious seed germination” (premature seed germination, like within a tomato)
\
\
__MOST IMPORTANT:__
Important signal for plant water relations, stomatal activity (STIMULATES STOMATA COLSURE) responds to CO2 concentration and light/darkness
\
Regulation of seed development, accumulation of seed proteins; preventing “precocious seed germination” (premature seed germination, like within a tomato)
\
93
New cards
Stem Formation for __**Root Cuttings:**__ ideal cutting candidates?
Plants that sucker are the best candidates for root cuttings
94
New cards
physiologically, how does the __growth process__ differ in Stem/Leaf Cuttings VS Root Cuttings? (describe first stages for both)
Stem/Leaf Cuttings: Develop/encourage **root growth first**, then shoot growth
\
Root Cuttings: Develop/encourage **shoot growth first**, then more root growth
\
Root Cuttings: Develop/encourage **shoot growth first**, then more root growth
95
New cards
Why is Etiolation used for propagation
prevent tissue from lignifying.
young/juvenile tissue is more responsive to PGR’s
Light exclusion from tissue where adventitious roots desired (“blanching” or “etiolation”)
young/juvenile tissue is more responsive to PGR’s
Light exclusion from tissue where adventitious roots desired (“blanching” or “etiolation”)
96
New cards
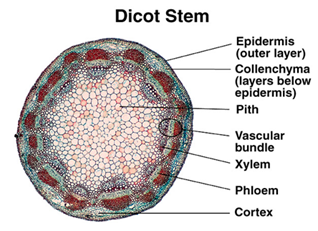
in a __**DICOT**__ stem, where are the xylem and phloem oriented in the vascular bundles? How are the vascular bundles organized?
xylem=inner layer (closer to pith)
phloem=outer layers (further from pith)
vascular bundles= organized in a ring outside of pith
phloem=outer layers (further from pith)
vascular bundles= organized in a ring outside of pith
97
New cards
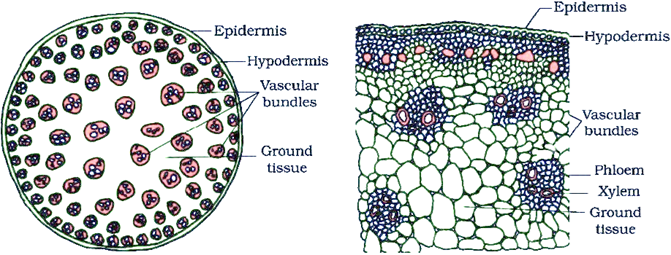
in a __**MONOCOT**__ stem, where are the xylem and phloem oriented in the vascular bundles? How are the vascular bundles organized?
xylem= inner portion of vascular bundles, surrounded by phloem
phloem= bulk of the vascular bundle, contains xylem
vascular bundles= random organization
phloem= bulk of the vascular bundle, contains xylem
vascular bundles= random organization
98
New cards
DEFINE: Totipotency
**innate ability of a plant cell to create an entirely new plant**
99
New cards
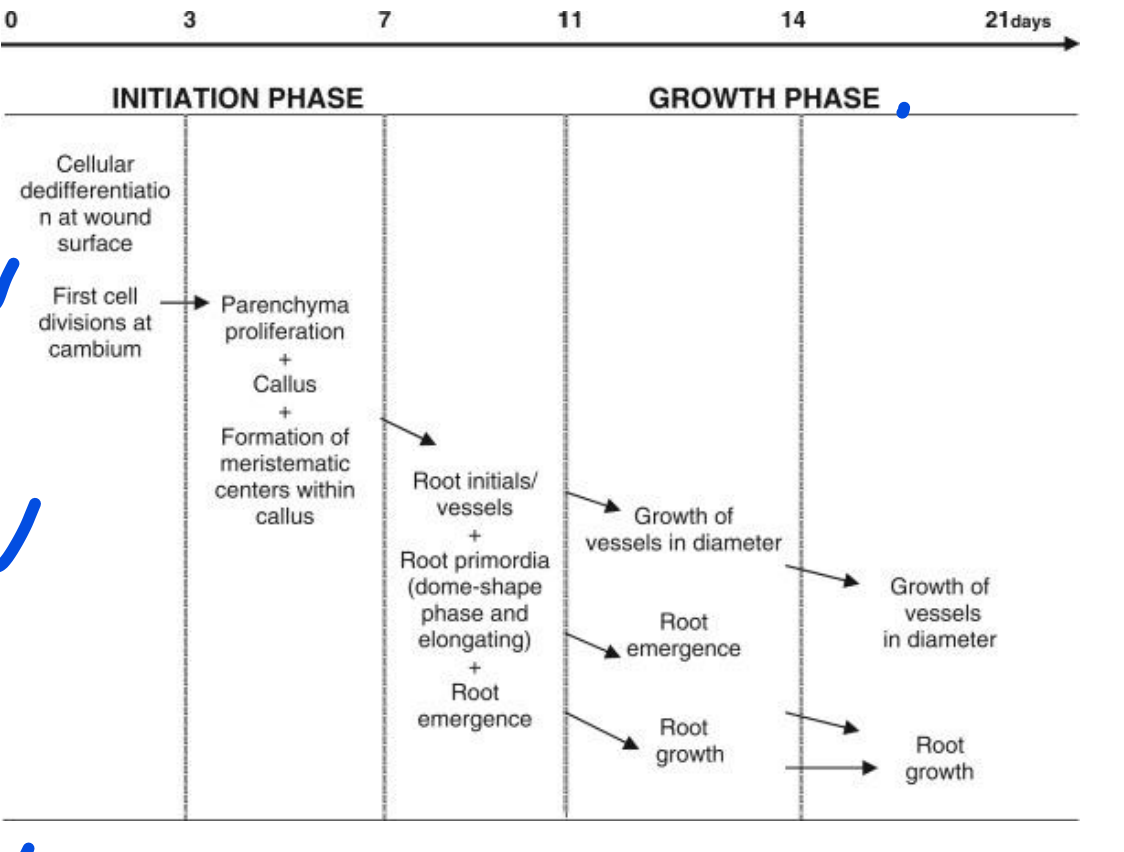
AUXIN: Root Formation and Growth- initiation phase, know how to **describe initiation phase**.
Wound response - Dedifferentiation of cells at wound (cambium/cortex near phloem)
\
Proliferation of parenchyma cells - callus, formation of meristematic tissue (root initials)
\
Formation of root primordia (very beginning)/xylem vessels
\
Proliferation of parenchyma cells - callus, formation of meristematic tissue (root initials)
\
Formation of root primordia (very beginning)/xylem vessels
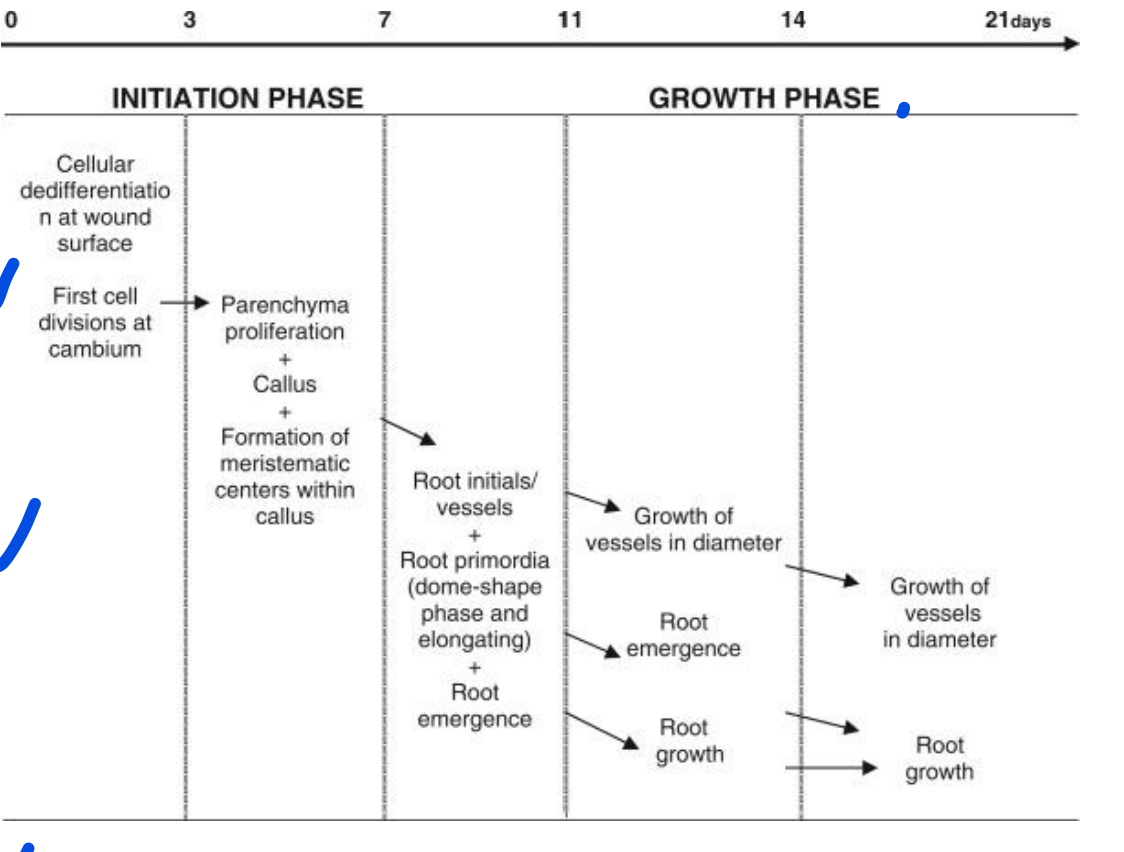
100
New cards
AUXIN: Root Formation and Growth- elongation phase, know how to **describe elongation**.
REMEMBER\~ Auxin relates to roots!
\
Root initiation - along the cambium/cortex tissue near phloem; emergence of vessel growth
Root and vessel enlargement - connection to stem vessels
\
Root initiation - along the cambium/cortex tissue near phloem; emergence of vessel growth
Root and vessel enlargement - connection to stem vessels