Unit 4 APWH
1/36
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms

Caravel
Definition: A small, highly maneuverable sailing ship developed in the 15th century by the Portuguese.
Connections: Essential for transoceanic travel, maritime exploration, and establishing trading-post empires.
Characteristics: Lateen sails, shallow draft (allowing exploration of rivers and coastlines), sturdy construction.

Lateen Sails
Definition: Triangular sails that allowed ships to sail against the wind.
Connections: Key innovation enabling caravels and other ships to navigate effectively, crucial for maritime exploration and trade.
Characteristics: Maneuverability, ability to sail into the wind, adopted from Arab ships.

Compass
Definition: A navigational instrument that shows direction.
Connections: Enabled sailors to determine direction accurately, vital for transoceanic travel and maritime exploration.
Characteristics: Uses a magnetized needle, originated in China, adopted and improved by Europeans.

Astronomical charts
Definition: Detailed maps of the stars and celestial bodies.
Connections: Used for navigation, allowing sailors to determine latitude and position at sea.
Characteristics: Based on astronomical observations, improved over time, essential for long-distance voyages.
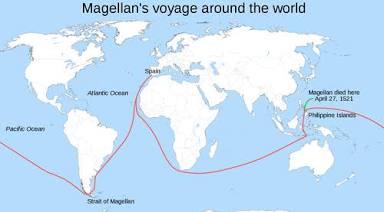
Transoceanic travel
Definition: Travel across oceans, particularly the Atlantic and Pacific.
Connections: Enabled by innovations in shipbuilding, navigation, and cartography; led to the Columbian Exchange, global trade, and colonization.
Characteristics: Long voyages, dangerous, transformative in its impact.
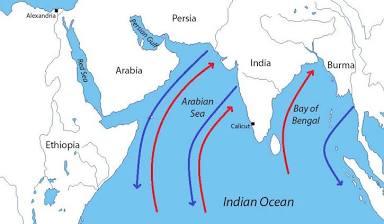
Monsoon winds
Definition: Seasonal winds in the Indian Ocean region.
Connections: Understanding and utilizing monsoon winds was crucial for maritime trade in the Indian Ocean, connecting Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
Characteristics: Predictable, reversed direction seasonally, influenced trade routes.

Maritime exploration
Definition: The exploration of the world’s oceans and coastlines.
Connections: Driven by “God, Glory, and Gold,” technological advancements, and the desire for new trade routes.
Characteristics: Led to the discovery of new lands, increased global interaction, and European dominance.
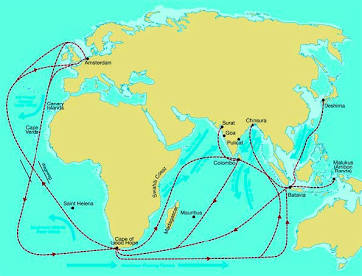
Trading post empire
Definition: A form of imperialism where European powers controlled trade routes and established fortified trading posts, rather than large-scale territorial conquest.
Connections: Established by the Portuguese and Dutch in the Indian Ocean and Asia.
Characteristics: Focused on controlling trade, not territory; relied on naval power; often involved alliances with local rulers.

Prince Henry the Navigator
Definition: A Portuguese prince who sponsored voyages of exploration along the coast of Africa in the 15th century.
Connections: Instrumental in the development of Portuguese maritime power and the Age of Exploration.
Characteristics: Established a navigation school, funded expeditions, sought new trade routes and Christian allies.

Columbus
Definition: An Italian explorer who sailed for Spain and is credited with initiating sustained European contact with the Americas in 1492.
Connections: His voyages led to the Columbian Exchange, colonization, and the transformation of the Americas.
Characteristics: Sought a westward route to Asia, landed in the Caribbean, initiated European colonization.
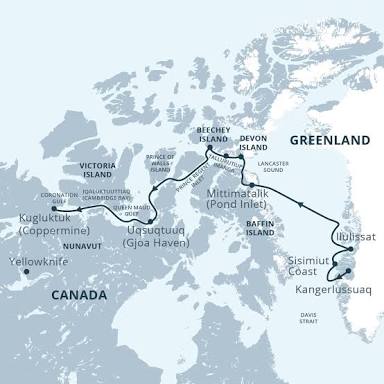
Northwest passage
Definition: A sea route through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America, connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
Connections: European powers sought this route to facilitate trade with Asia, but it proved difficult to navigate.
Characteristics: Difficult to navigate due to ice, not successfully traversed until the 20th century.
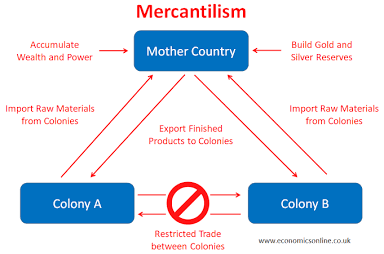
Mercantilist
Definition: An economic theory that promoted government regulation of a nation’s economy to increase its power and wealth.
Connections: Drove European colonialism and the establishment of trade monopolies.
Characteristics: Emphasis on accumulating gold and silver, favorable balance of trade, protectionist policies.
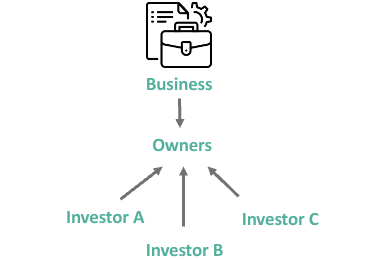
Join stock companies
Definition: Businesses formed by groups of investors who pooled their money together to finance large-scale ventures.
Connections: Used to finance colonization, trade, and exploration; reduced individual risk.
Characteristics: Limited liability for investors, allowed for the accumulation of large amounts of capital.
Monopolies
Definition: Exclusive control of a particular market or industry.
Connections: Granted by European governments to trading companies, allowing them to control trade in specific regions or commodities.
Characteristics: Eliminated competition, allowed for price fixing, generated large profits.
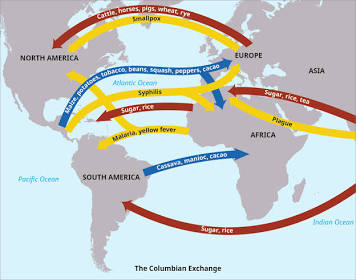
Colombian exchange
Definition: The widespread transfer of plants, animals, culture, human populations, technology, diseases, and ideas between the Americas, West Africa, and the Old World in the 15th and 16th centuries.
Connections: Resulted from Columbus’s voyages and subsequent European colonization.
Characteristics: Transformed agriculture, diets, and populations worldwide; led to both positive and negative consequences.
Smallpox
Definition: A highly contagious and deadly disease.
Connections: Introduced to the Americas by Europeans, devastating indigenous populations.
Characteristics: High mortality rate, caused widespread epidemics, weakened indigenous societies.

The Great Dying
Definition: The demographic collapse of indigenous populations in the Americas due to disease, warfare, and exploitation.
Connections: A direct result of the Columbian Exchange and European colonization.
Characteristics: Massive population decline, led to labor shortages, facilitated European control.

Staple crops
Definition: Basic food crops that are a major part of a region’s diet.
Connections: The Columbian Exchange introduced new staple crops to both the Americas and the Old World, transforming agriculture and diets. Examples: Potatoes, corn, cassava.
Characteristics: High in calories and nutrients, easily grown, widely consumed.
Cash crops
Definition: Crops grown for sale rather than for subsistence.
Connections: Grown on plantations in the Americas, fueled the transatlantic slave trade. Examples: Sugar, tobacco, cotton.
Characteristics: High demand in Europe, labor-intensive, generated large profits.
Plantations
Definition: Large-scale agricultural estates that specialized in the production of cash crops.
Connections: Relied on slave labor or indentured servitude, contributed to the growth of the transatlantic slave trade.
Characteristics: Large-scale, monoculture, labor-intensive, focused on export.
Encomienda
Definition: A Spanish labor system that granted colonists the right to demand labor and tribute from indigenous people.
Connections: Exploited indigenous labor, led to abuse and population decline.
Characteristics: Forced labor, tribute payments, theoretically required colonists to provide protection and Christian instruction.
Mit’a System
Definition: A traditional Andean labor system that required community members to provide labor for public works projects.
Connections: Adapted by the Spanish for mining and other labor-intensive activities, leading to exploitation and abuse.
Characteristics: Forced labor, often in dangerous conditions, disrupted traditional social structures.
Chattel slavery
Definition: A system of slavery in which enslaved people are treated as property and can be bought, sold, and inherited.
Connections: Used extensively on plantations in the Americas, fueled the transatlantic slave trade.
Characteristics: Enslaved people had no rights, were subjected to brutal treatment, and were considered property.
Indentured Servitude
Definition: A system in which people agreed to work for a certain period of time in exchange for passage to the Americas, food, and shelter.
Connections: Used to provide labor in the Americas, particularly in the early years of colonization.
Characteristics: Contractual agreement, limited freedom, often harsh working conditions.
African Disopora
Definition: The dispersal of people of African descent throughout the world, primarily due to the transatlantic slave trade.
Connections: Resulted from the forced migration of millions of Africans to the Americas and other parts of the world.
Characteristics: Loss of culture and identity, creation of new African-influenced cultures, ongoing struggle for equality and justice.
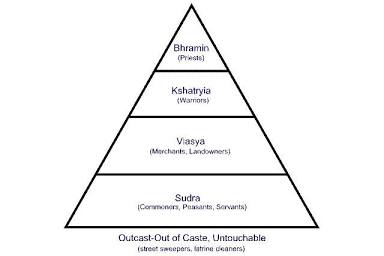
Casts System
Definition: A hierarchical social system in Spanish America based on race and ancestry.
Connections: Determined social status, rights, and opportunities.
Characteristics: Spanish elites at the top, indigenous people and Africans at the bottom, mixed-race categories in between.

Pueblo revolts
Definition: Uprisings by Pueblo Indians in the late 17th century against Spanish colonizers in present-day New Mexico.
Connections: Resistance to Spanish religious and cultural oppression.
Characteristics: Drove the Spanish out of New Mexico for a time, demonstrated indigenous resistance to colonization.
Fronde
Definition: A series of civil wars in France between 1648 and 1653, during the reign of Louis XIV.
Connections: Resulted from resentment of royal power and high taxes.
Characteristics: Involved nobles, commoners, and the French army, weakened the monarchy but ultimately failed.

Maroon societies
Definition: Communities formed by escaped slaves in the Americas.
Connections: Resistance to slavery, preservation of African culture.
Characteristics: Often located in remote areas, self-governing, engaged in raids on plantations.
God, Glory, Gold
Definition: A phrase summarizing the primary motivations for European exploration and colonization.
Connections: Drove European expansion, shaped the interactions between Europeans and other cultures.
Characteristics: Religious zeal, desire for fame and power, pursuit of wealth.
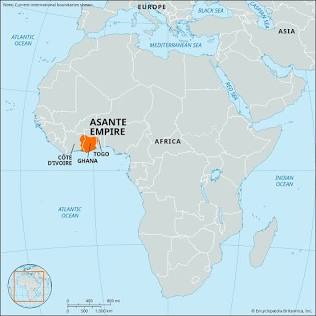
Asante
Definition: A powerful West African kingdom that emerged in the 17th century.
Connections: Traded with Europeans, participated in the transatlantic slave trade.
Characteristics: Strong military, centralized government, controlled gold production.
Kingdom of Kongo
Definition: A kingdom located in present-day Angola and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Connections: Traded with the Portuguese, converted to Christianity, eventually weakened by the slave trade.
Characteristics: Centralized government, sophisticated culture, early adopter of Christianity.

Muslim European Rivalry
Definition: A long-standing conflict between European and Muslim powers, particularly in the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean.
Connections: Drove European exploration, shaped trade routes, led to religious and political tensions.
Characteristics: Competition for trade, religious differences, military conflicts.

Biodiversity
Definition: The variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Connections: The Columbian Exchange and globalization impacted biodiversity through the introduction of new species, habitat destruction, and the spread of diseases.
Characteristics: High biodiversity is generally associated with healthy ecosystems, while loss of biodiversity can have negative consequences.
Isolationist trade policies
Definition: Policies that limit or prohibit trade with other countries.
Connections: Some countries, like Japan, adopted isolationist policies in response to European expansion.
Characteristics: Aimed to protect domestic industries and culture, limited foreign influence.