MCAT Organic Chemistry - Bonding
1/22
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
principal quantum number, n
corresponds to the energy level of a given electron in an atom and is essentially a measure of size; the smaller the number, the closer the shell is to the nucleus, and the lower its energy; 1 to ∞
azimuthal quantum number, l
corresponds to subshells; ranges from 0 to n−1; 0, 1, 2, and 3 correspond to the s, p, d, and f subshells; energy increases as the azimuthal quantum number increases
magnetic quantum number, ml
corresponds to orbitals; ranges from −l to +l
orbital
describes the probability of finding an electron in a given region of space
s-orbital
spherical and symmetrical, centered around the nucleus
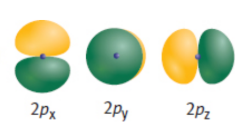
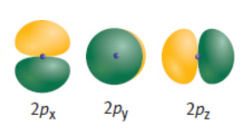
p-orbital
composed of two lobes located symmetrically about the nucleus and contains a node at the nucleus; ‘dumbbell’; three different orientations, along the x-, y-, or z-axis.
node
an area where the probability of finding an electron is zero
d-orbital
composed of four symmetrical lobes, the fifth looks like a donut wrapped around the center of a p-orbital, and contains two nodes; rare in org. chem.
spin quantum number, ms
correspond sto electrons; ±½
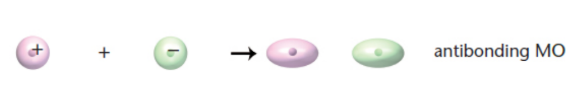
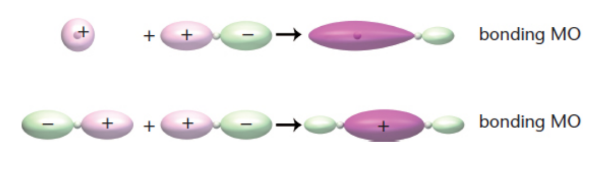
molecular orbitals
two atomic orbitals combine, obtained mathematically by adding or subtracting the wave functions of the atomic orbitals
bonding orbital
signs of wave functions are the same; lower energy, more stable; likely to find electrons between atoms

antibonding orbital
signs of wave functions are different; higher energy, less stable; unlikely to find electrons between atoms
sigma (σ) bond
bonding molecular orbital is formed by head-to-head or tail-to-tail overlap
single bonds
σ bonds, accommodating two electrons; free rotation; longest bond
pi (π) bond
two p-orbitals line up in a parallel (side-by-side) fashion and their electron clouds overlap in a bonding orbital ;cannot exist independently of a σ bond
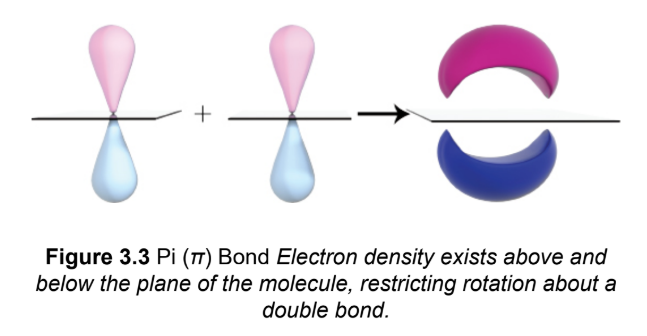
double bond
One π bond on top of an existing σ bond; hinders rotation; medium length bond
triple bond
A σ bond and two π bonds; hinders rotation; shortest bond
orbital hybridization
new orbital shapes formed by mixing different types of orbitals on one atom; a way of making all of the bonds to a central atom equivalent to each other
s-character
the percent of s-orbitals mixing into a hybrid orbital
ex. sp3 has 25%
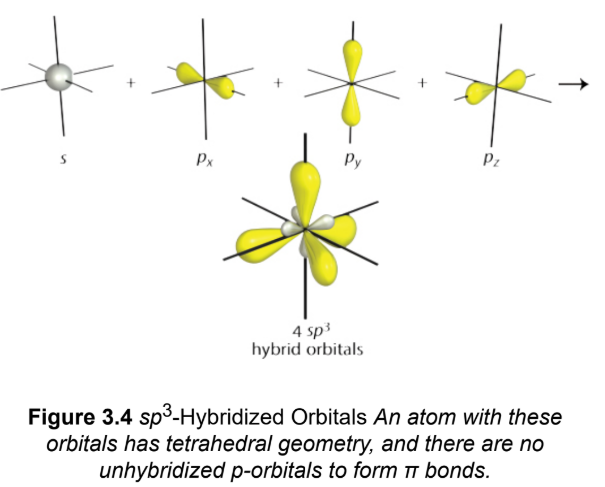
sp3
merge three p-orbitals and one s-orbital by promoting one of the 2s electrons into the 2pz-orbital,; four identical orbitals; tetrahedral geometry
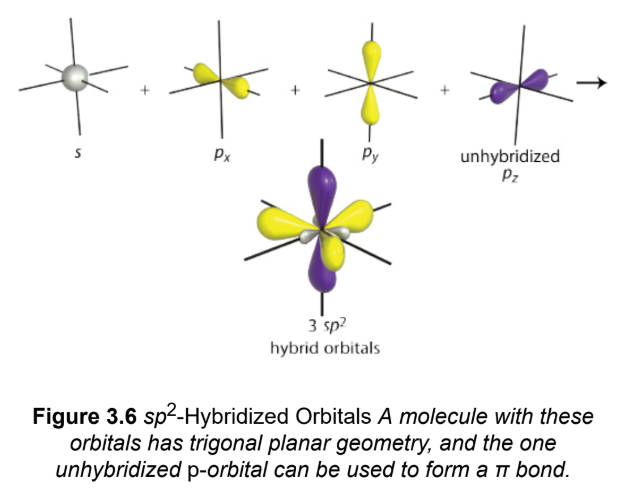
sp²
one s-orbital is mixed with two p-orbitals, three hybridized orbitals; third p-orbital of each carbon is left unhybridized and participate in a π-bond; trigonal planar geometry
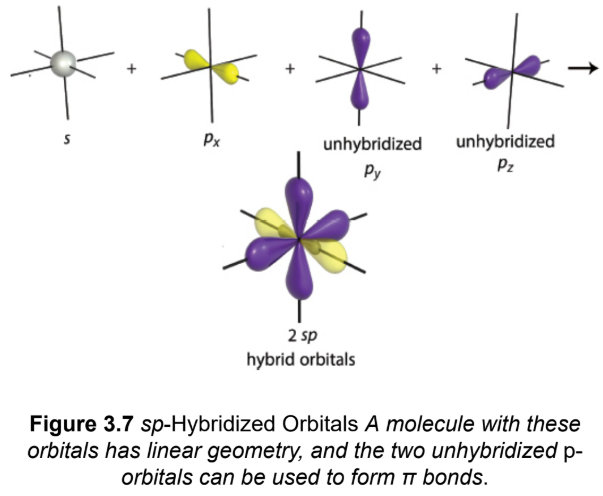
sp
one p-orbital will combine with the s-orbital to form two hybrid orbitals; two of the p-orbitals form π bonds; linear geometry
Conjugation
Resonance delocalization of electrons; requires alternating single and multiple bonds because this pattern aligns a number of unhybridized p-orbitals down the backbone of the molecule; electron density is distributed throughout, making the true form a hybrid of the resonance structures