WJEC AS Physics Unit 1.7 - Particles and Nuclear Structure
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Lepton
Low mass fundamental particles such as electrons, electron neutrinos and analogous pairs of the so-called second and third generations which exist in isolation
Hadron
High mass particles consisting of quarks and antiquarks bound together. Only hadrons (and quarks or antiquarks themselves) can ‘feel’ the strong force
E.g. mesons
Baryon
A hadron consisting of 3 quarks or 3 antiquarks
E.g. the nucleons; protons and neutrons
Meson
A hadron consisting of a quark and antiquark pair
E.g. pion
Quark
Elementary particles not found in isolation which combine to form hadrons and mesons
E.g. up quark/down quark
Antibaryon
A hadron consisting of 3 antiquarks with the same mass and opposite charge
E.g. antiproton
What quarks combine to form
Hadrons and baryons
Composition of a hadron
Quarks and/or antiquarks
Composition of a Baryon
3 quarks
Composition of an Antibaryon
3 antiquarks
Composition of a Meson
A quark and antiquark pair
Example of a Baryon
A proton or a neutron
Example of an Antibaryon
Antiproton
Example of a Lepton
Electron or electron neutrino
Matter
composed of quarks and leptons, of which there are 3 generations (only do calculations with the first)
Fundamental Particle
A particle that cannot be broken down into smaller constituents
Laws which reactions involving subatomic particles must obey
Conservation of energy
Conservation of momentum
Conservation of charge
Conservation of lepton number
Conservation of baryon number
The 4 fundamental forces
Gravitational
Weak
Electromagnetic (e-m)
Strong
Properties to identify the force involved in a reaction
Strong interactions;
Only hadrons involved
Not felt by leptons
Total quark number conserved
Occur in times of the order 10^-23 s
No change in quark flavour
Typically involved in collisions between particles
Electromagnetic interactions;
absorption of emission of photons
Typically take 10^-16 s
The total quark number is conserved
Particles must be charged or have charged components (neutron is uncharged but made up of charged quarks)
No change in quark flavour
One or more photons may be emitted
Weak interactions;
typically take 10^-8 s
Neutral leptons (neutrinos) are involved
May be a change in quark flavour
Characteristics of gravitational forces/interactions
Very weak; negligible except between large objects such as planets
What gravitational forces/interactions are experienced by
All matter
Range of gravitational interactions
Infinite
Characteristics of weak forces/interactions
Only significant when the e-m and strong interactions do not operate
Within the nucleus
Relative strength of gravitational force
10^-40
What weak forces/interactions are experienced by
All particles; All leptons, all quarks and so all hadrons
Range of weak forces/interactions
Very short
Relative strength of weak forces/interactions
10^-6
Characteristics of electromagnetic forces/interactions
Also experienced by neutral hadrons as these are composed of quarks
What electromagnetic forces/interactions are experienced by
All charged particles
Range of electromagnetic forces/interactions
Infinite
Characteristics of strong forces/interactions
Also affects interactions between hadrons, e.g. binding energy
What strong forces/interactions are experienced by
All quarks, so all hadrons
Range of strong forces/interactions
Short
Relative strength of strong forces/interactions
1
Quark structure of a proton
Two up quarks, one down quark (uud)
Quark structure of a neutron
Two down, one up (ddu)
Pions
First generation antiquarks combine to form the pions
Antimatter
Have the same mass, equal and opposite charge of their matter particles
Matter + antimatter
Annihilate each other
Mass of the particles is converted into energy
Annihilation
Matter + antimatter → annihilate each other
Mass → energy (total energy of the photons = mass energy + KE of the photons)
Gamma photons emitted and spread out in opposite directions for momentum to be conserved
Momentum is conserved
Energy of The photons depends of the mass of individual particles and the KE they were travelling with
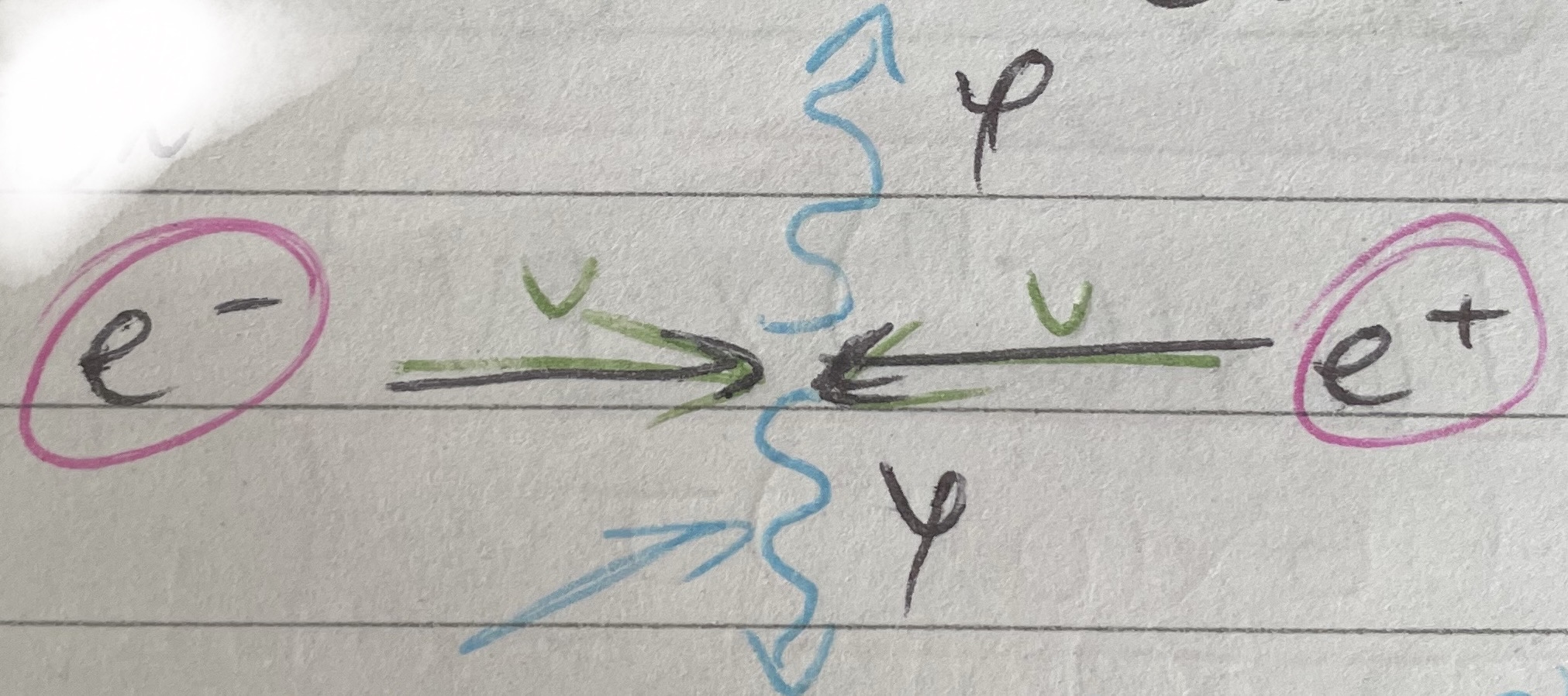
Pair Production
Opposite of annihilation
High E photon can produce an electron-positron pair
Pair travel in opposite directions away from one another
Mass is conserved
Some E → mass
Some E → KE of particles
Momentum is also conserved
Gamma photon would need to interact with something, e.g. atomic nucleus
eV and J
eV → J; x 1.6×10^19
J → eV; / 1.6×10^-19
Mass-Energy
E=mc²
m=E/c²
Mass-energy (MeV per c²)
Mass= MeVperc² x (1.6×10^-13) / 9×10^16
Atomic mass unit
1u=1.66×10^-27 kg
kg → MeV/c²=xc² and divide by 1.6×10^-3
Charge of an electron
-1
Charge of an electron neutrino
0
Baryon number
depends on quark makeup
Quark; +1/3
Antiquark; -1/3
Lepton number
lepton = 1
Not a lepton = 0
Antilepton = -1
Building a proton
p→ u + u + d
Q= 2/3+2/3+(-1/3)=1
B=1/3+1/3+1/3=1
Q=+1 (+e)
B=1 (conserved quantity)
Determining the particle in a reaction
Conservation of momentum
Conservation of mass-energy
Conservation of charge
Conversation of Baryon number (in any interaction between particles in a system, the total baryon number in the system must not change)
Conservation of lepton number (in any interaction between particles in a system, the total lepton number in the system must not change)
Determine these values in order to determine the particle
charge of a proton
+1
Baryon number of a proton
1
charge of a neutron
0
Baryon number of a neutron
1
Delta baryons
delta++; uuu, Q=2
Delta+; uud, Q=1
Delta0; udd, Q=0
Delta-; ddd, Q=-1
+ and 0 have same Q as proton or neutron. Delta are heavier. Not protons or neutrons despite the same composition
Decay → other particle combinations with mass or photon with energy
Are in an excited state so more mass so less h-l than proton or neutron
Charge of an anti-up quark
-2/3e
Charge of an anti-down quark
+1/3e
Composition of an antineutron
anti up, anti down, anti down.
Q=-2/3+1/3+1/3=0
B=-1/3-1/3-1/3=-1
Composition of an antiproton
Anti up, anti up, anti down
Q=-2/3+-2/3+1/3=-1
B=-1/3+-1/3+-1/3=-1
Charge of an antineutron
0
Baryon number of an antineutron
-1
Charge of an antiproton
-1
Baryon number of an antiproton
-1
Lepton number of an antineutron
0
Lepton number of an antiproton
0
Pion+
Up and anti down
Q=1
B=0
Pion-
down and anti up
Q=-1
B=0
Pion 0
up and anti up OR down and anti down
Q=0
B=0
Meson reactions
charge conserved
Baryon number conserved
Quark flavour conserved so can determine force responsible as well as particles
Charge of an electron
-1 or -e
Lepton number of an electron
1
Charge of an electron neutrino
0
Lepton number of an electron neutrino
1
Charge of a positron
+1
Lepton number of a positron
-1
Charge of an anti electron neutrino
-1
Lepton number of an anti electron neutrino
-1
Baryon number of an electron
0
Baryon number of an electron neutrino
0
Baryon number of a positron
0
Baryon number of an anti electron neutrino
0
Stability of atoms due to forces
atoms are stable due to the 3 non-gravitational forces
e-s bound to protons (e-m)
Strong nuclear force holds protons and neutrons together (opposes e-m repulsion)
Weak nuclear force responsible for B- decay (B- or B+)
The force responsible for a particular interaction
The force responsible for a particular interaction is the strongest one felt by all particles on both sides