Unit 9: Ecology Vocab Squares
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Ecology
study of interactions between organisms and their environment
related to: Biotic and abiotic factors, ecosystems
roots: Eco-environment
ecosystem
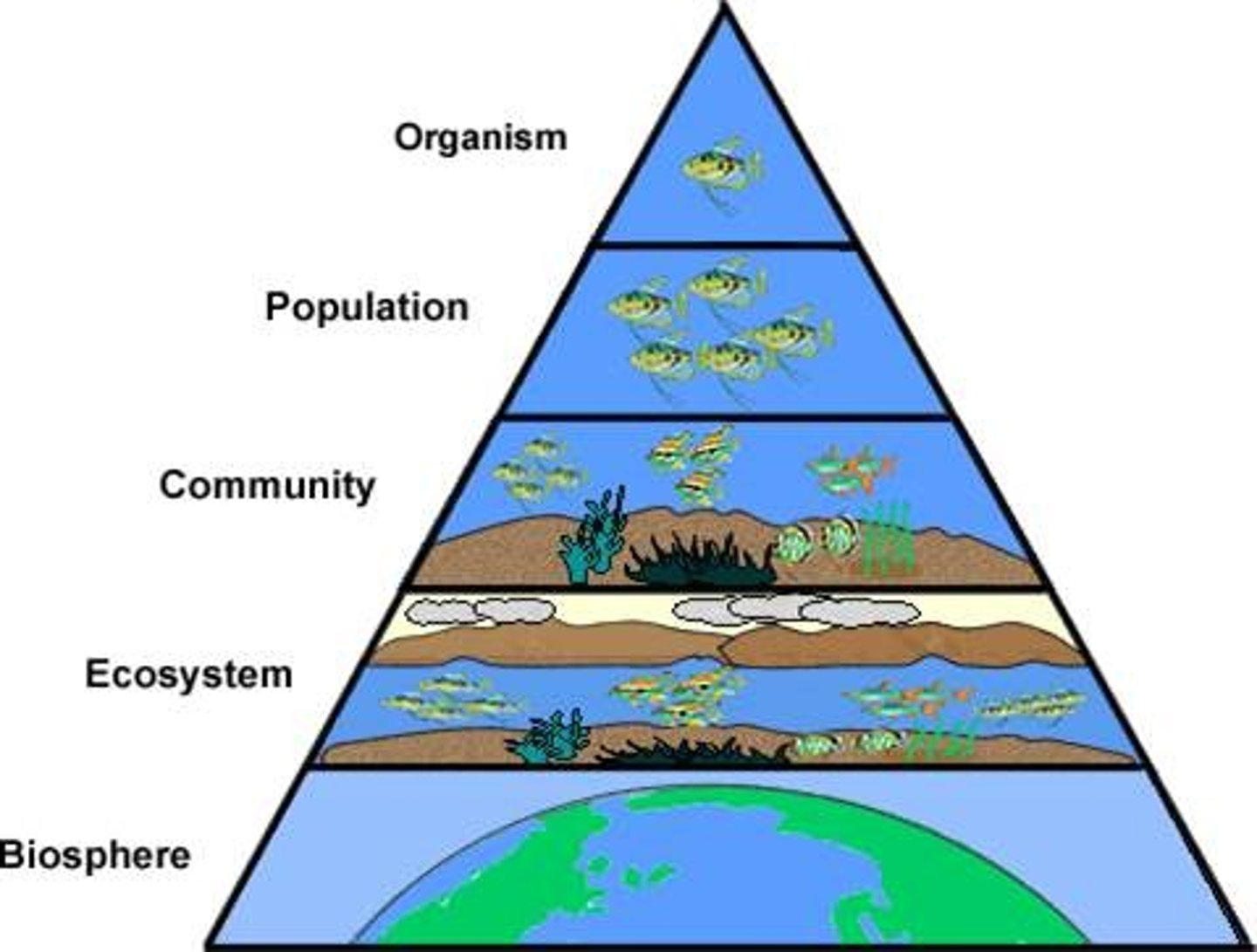
all the living and non-living things in an environment
related to: the Scale: Biosphere, ecosystem, community, population, and organism!
Roots: eco' environment
Food Chain
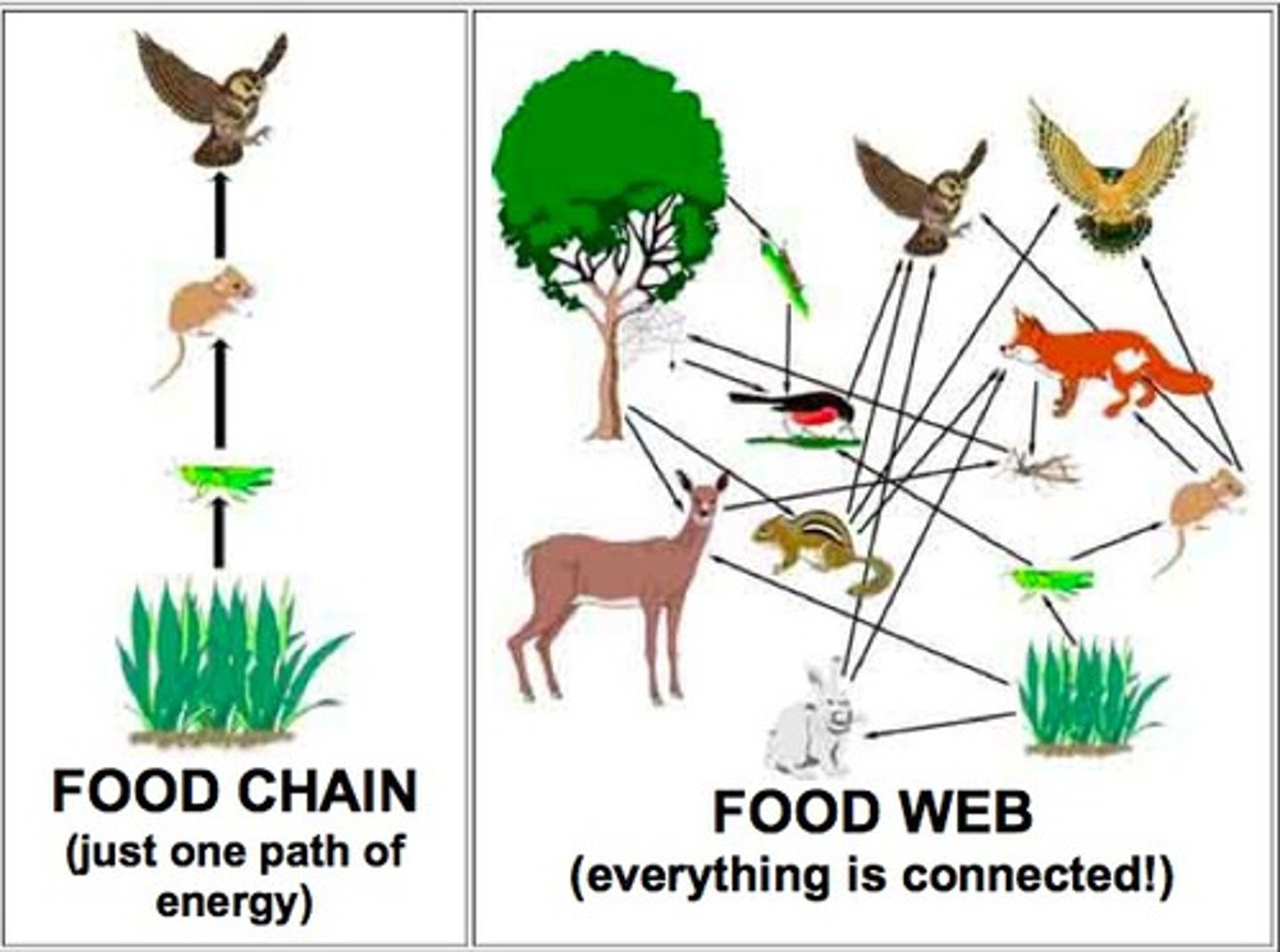
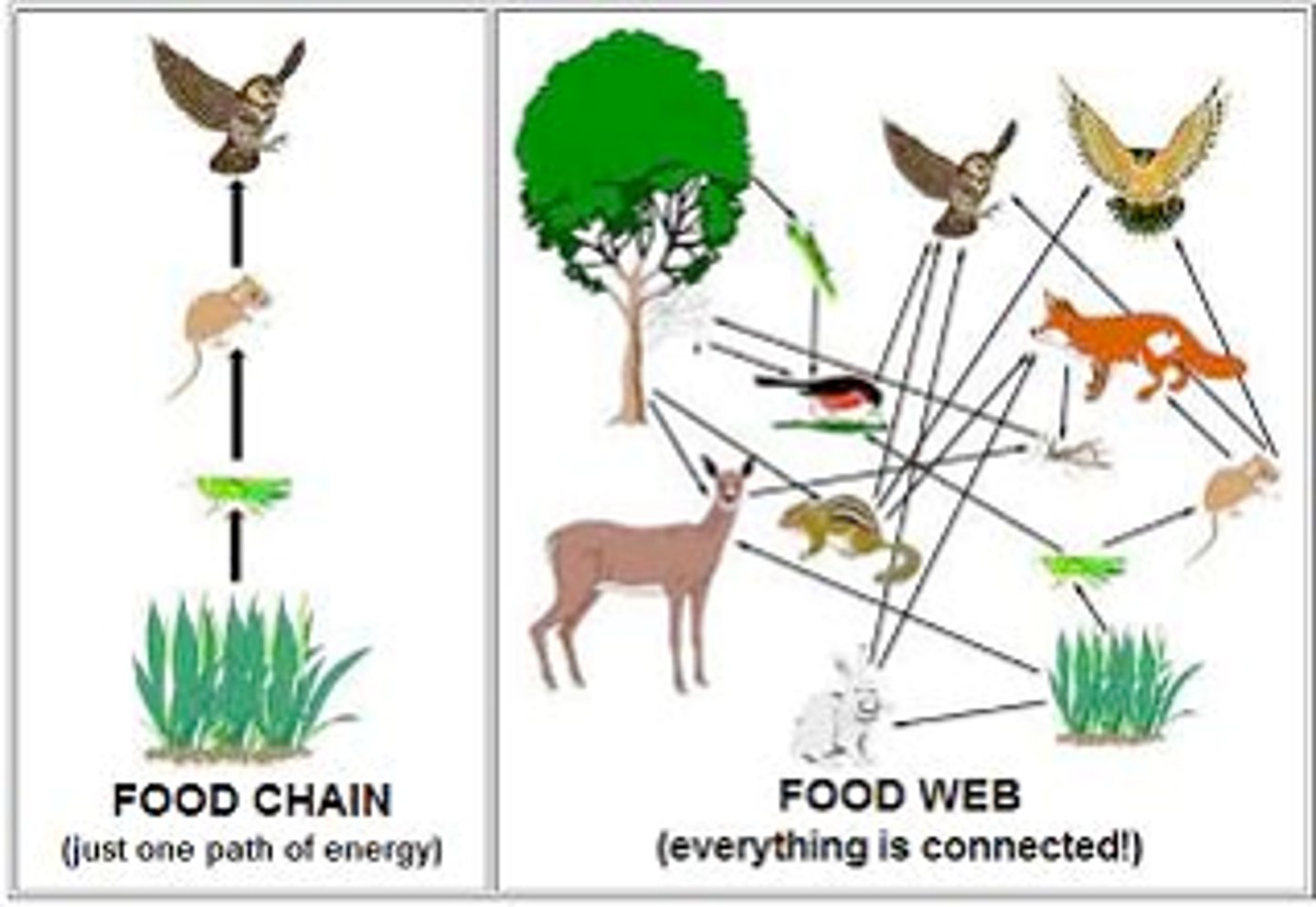
Food Chain- Simple model of energy flow.
Related to: Trophic levels. producers, consumers (herbivore, carnivore, onmivore)
Roots: ENERGY FLOW
food web
Food Web: A complex model with MANY food chains interconnected.
Related to: Trophic levels. producers, consumers (herbivore, carnivore, onmivore)
Roots: ENERGY FLOW
Trophic Level
Feeding Levels....Each step in a food chain or food web
Related to: Consumers, food chains and webs
Roots: Troph- Feeding
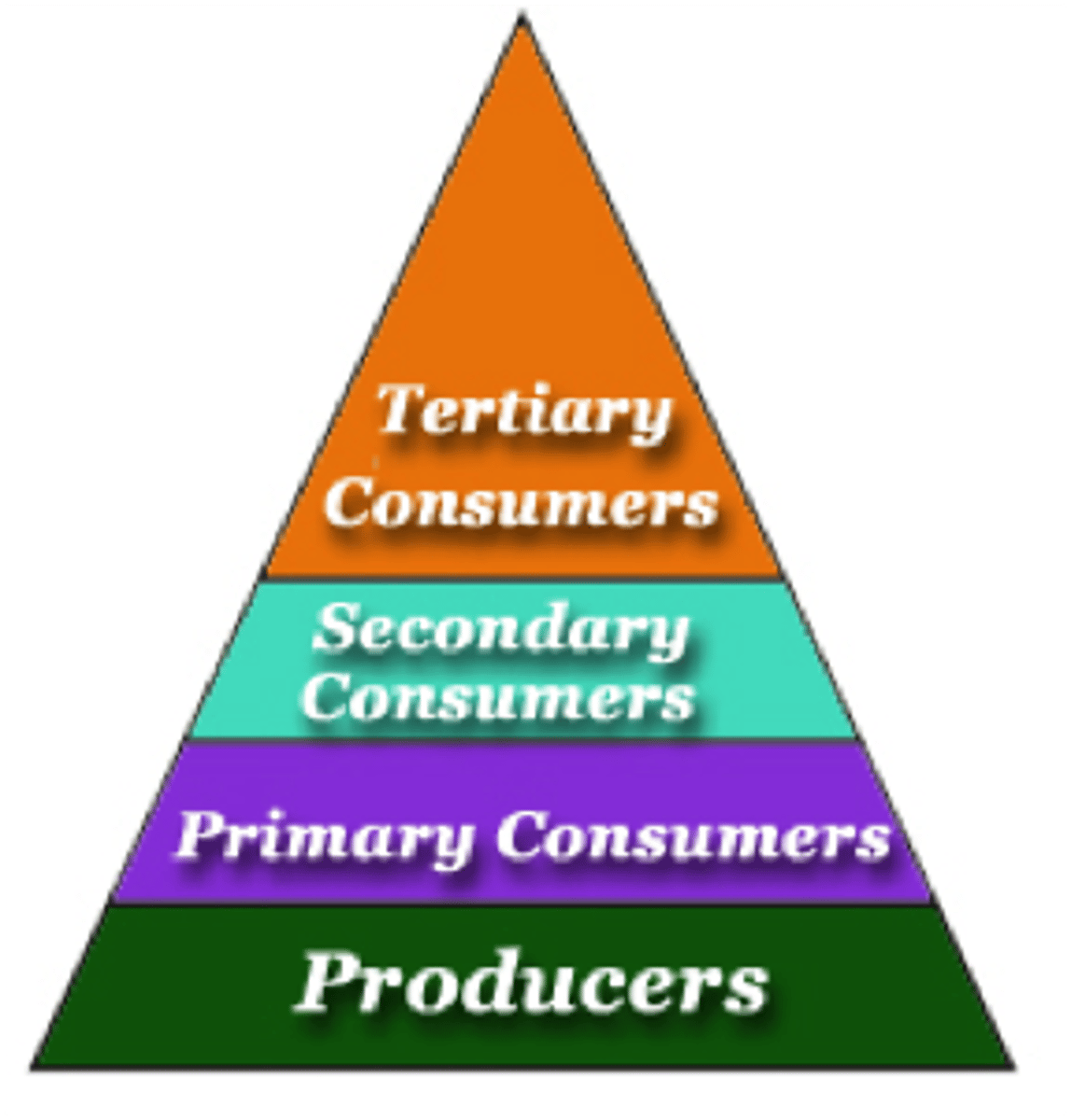
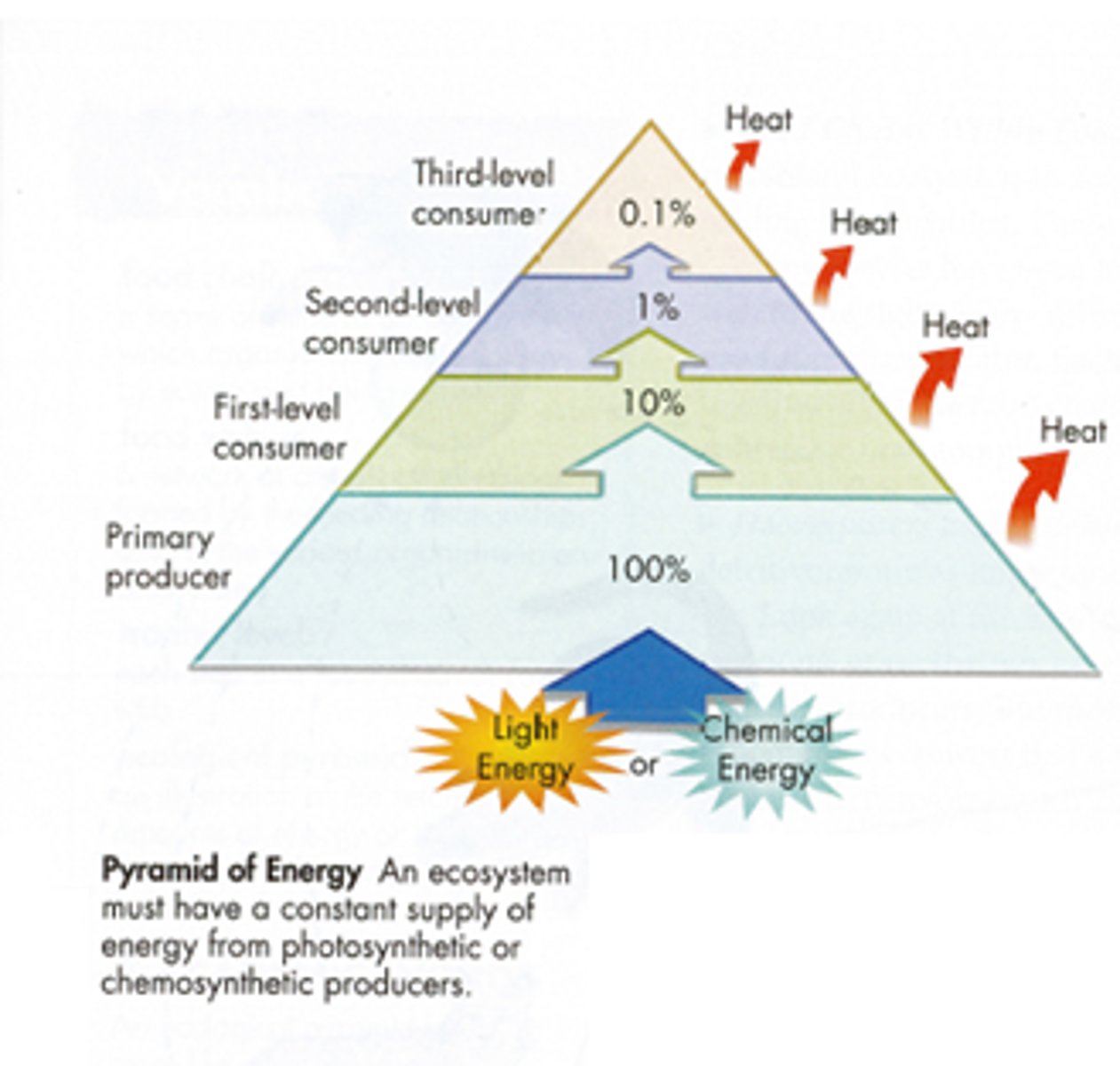
10% Rule
Only 10% of available energy will transfer to next trophic level
Related to: Food Webs/Chains, Energy, trophic levels
Rotos: None.
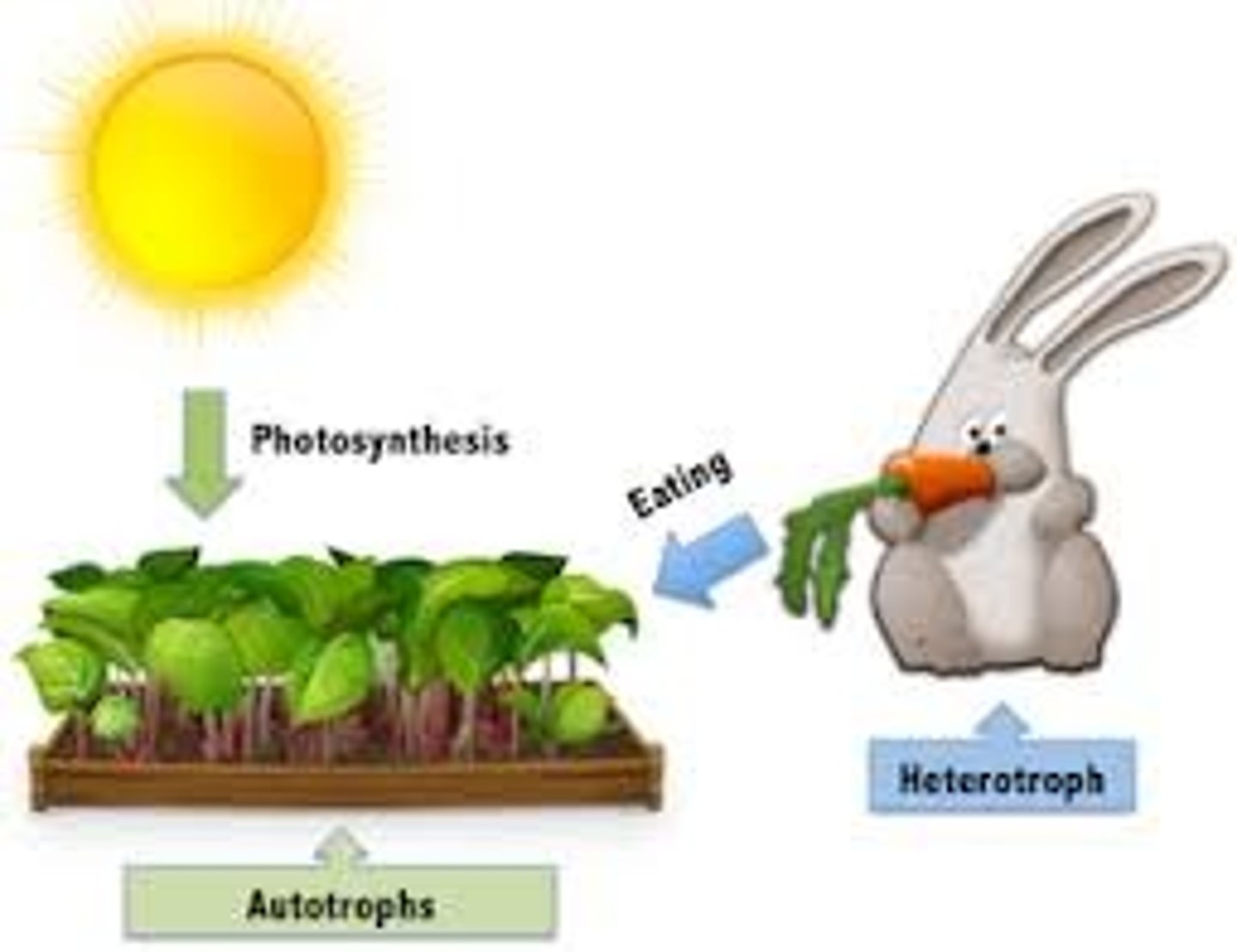
Heterotroph
Heterotroph- Feed on different organisms, CONSUMERS
Related to: Herbivore, Carnivore, Omnivore, Food Chains/Webs
Roots: Hetero-Different, Troph- Feeding level
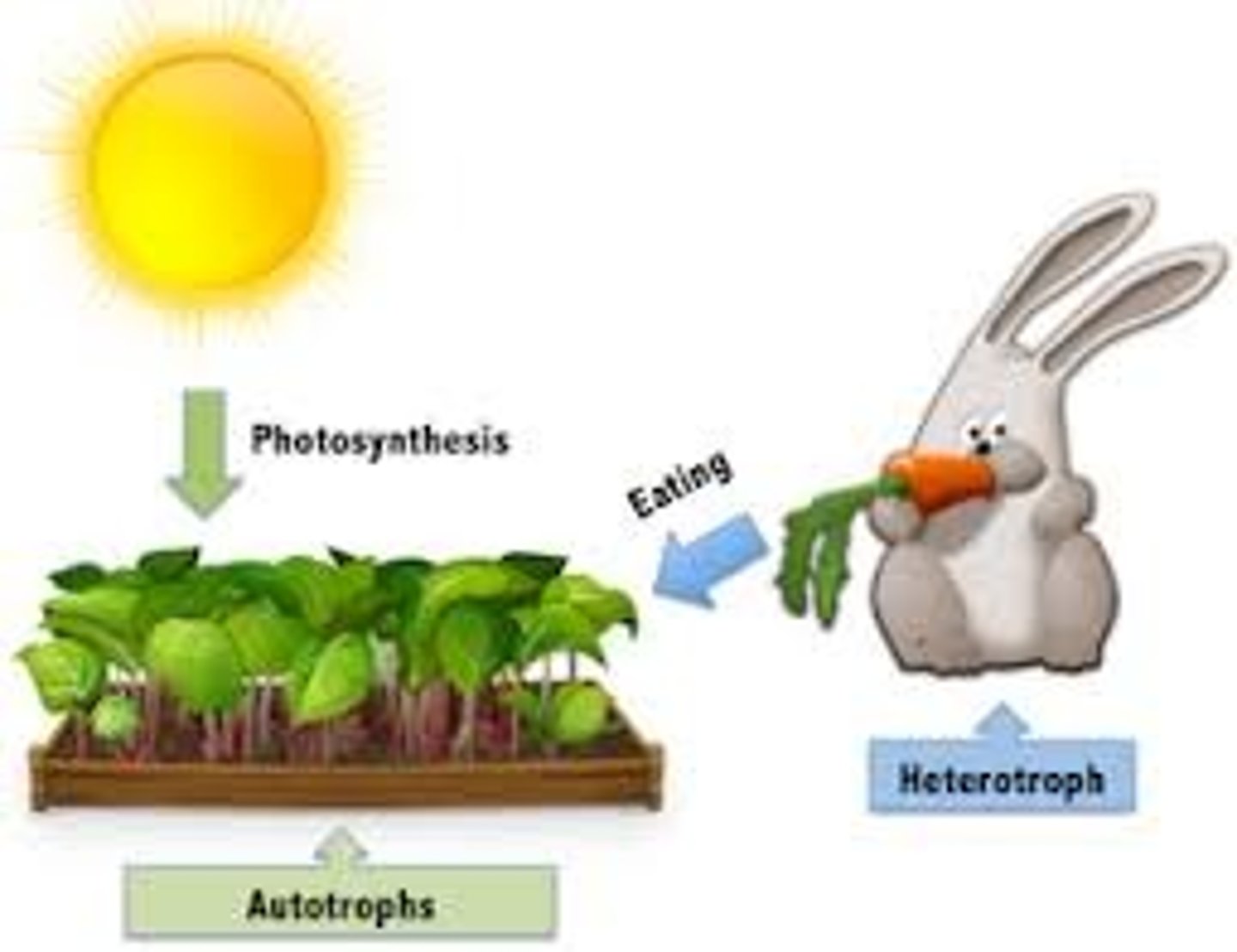
Autotroph
Autotroph- Self Feeder, PRODUCER, plants
Related to: Photosynthesis, Food Chains/Webs
Roots: Auto- Self, Troph- Feeding level
Energy Pyramid
Shows how much energy at each trophic level in a food chain or food web
Related to: Energy/10% Rule, Trophic levels
Roots: None
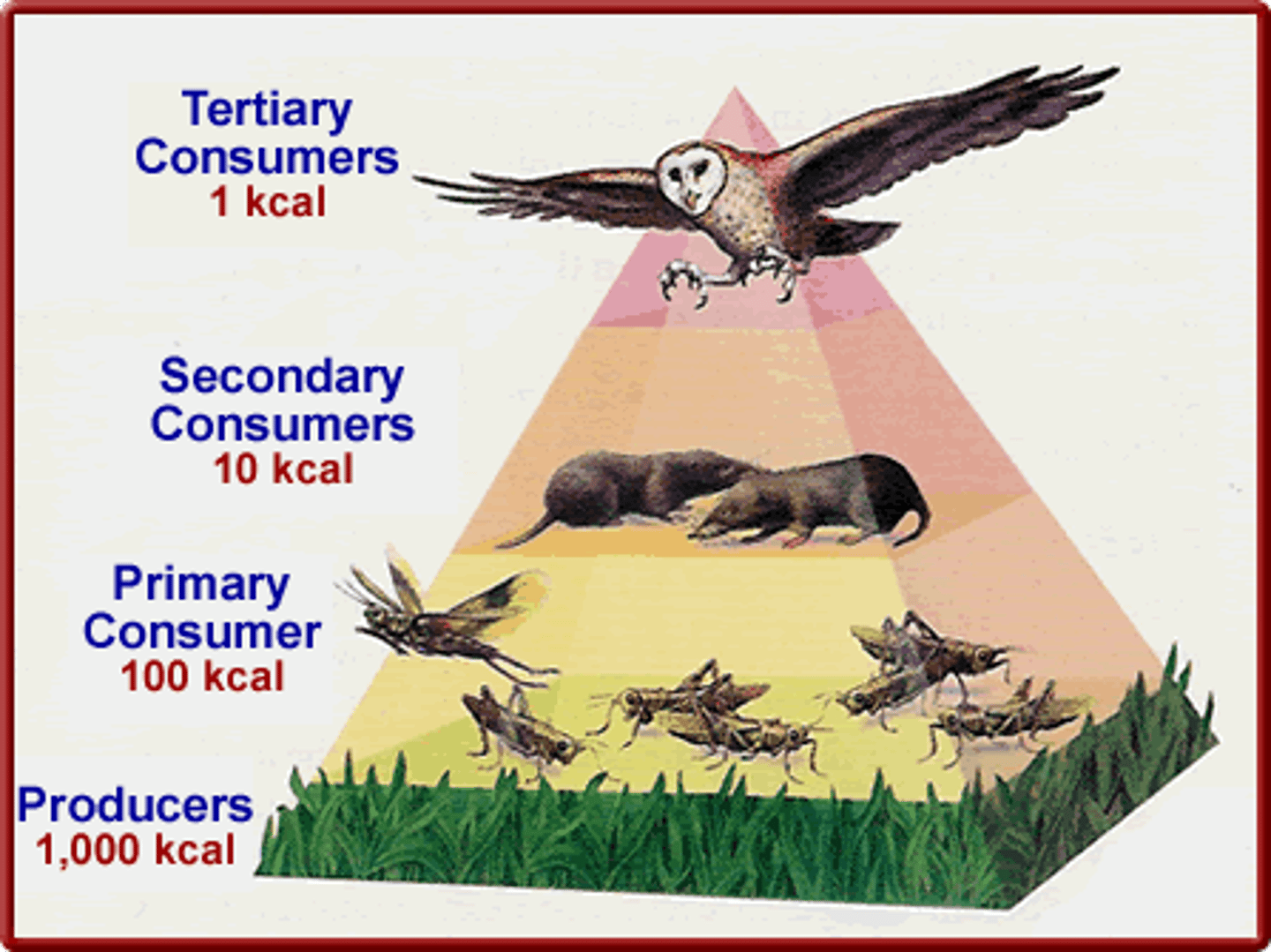
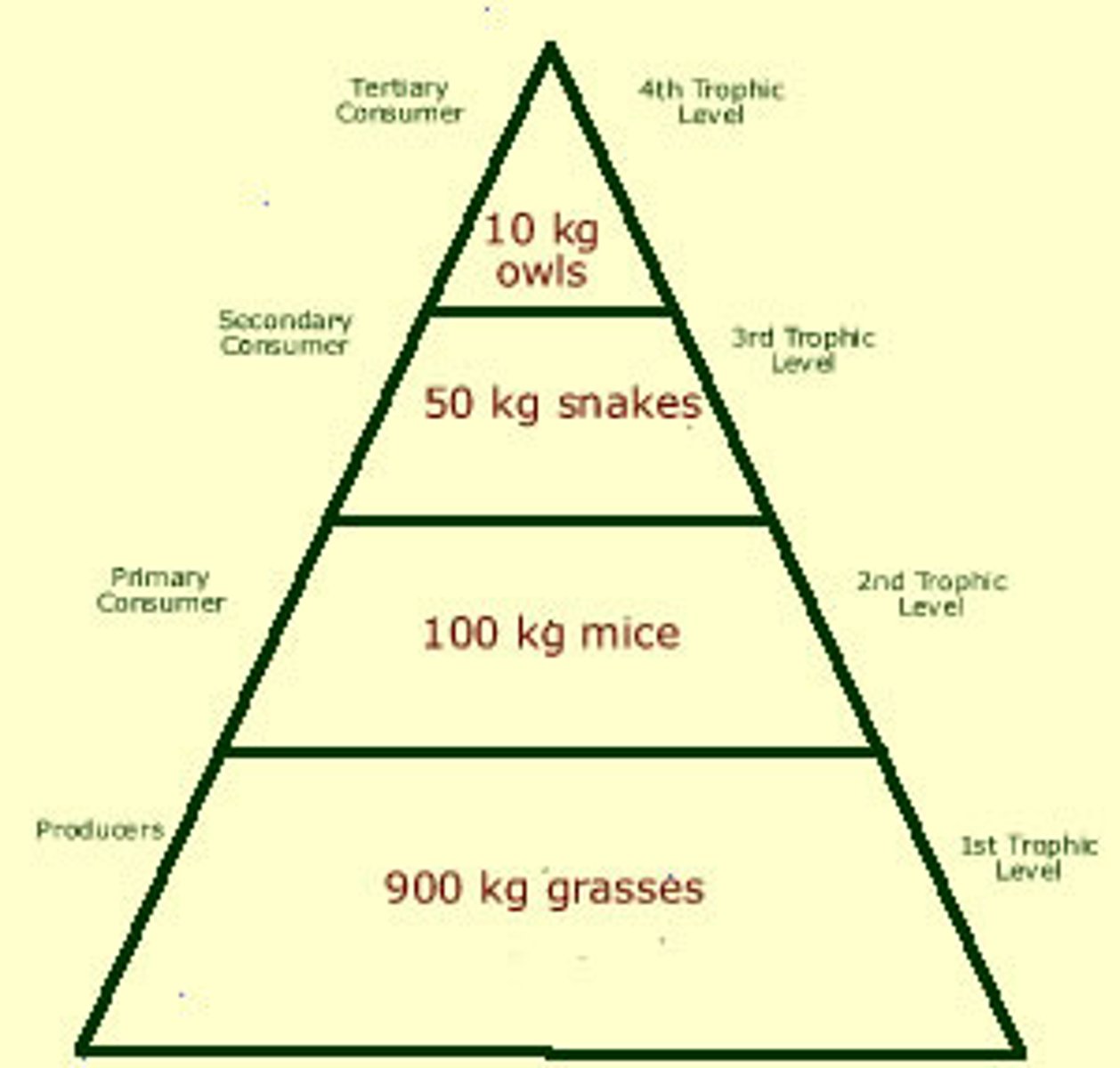
Biomass Pyramid
Diagram representing the biomass in each trophic level of an ecosystem
Significance: Greater amount of producers then top consumers
Roots: Bio- Life Mass- Grams
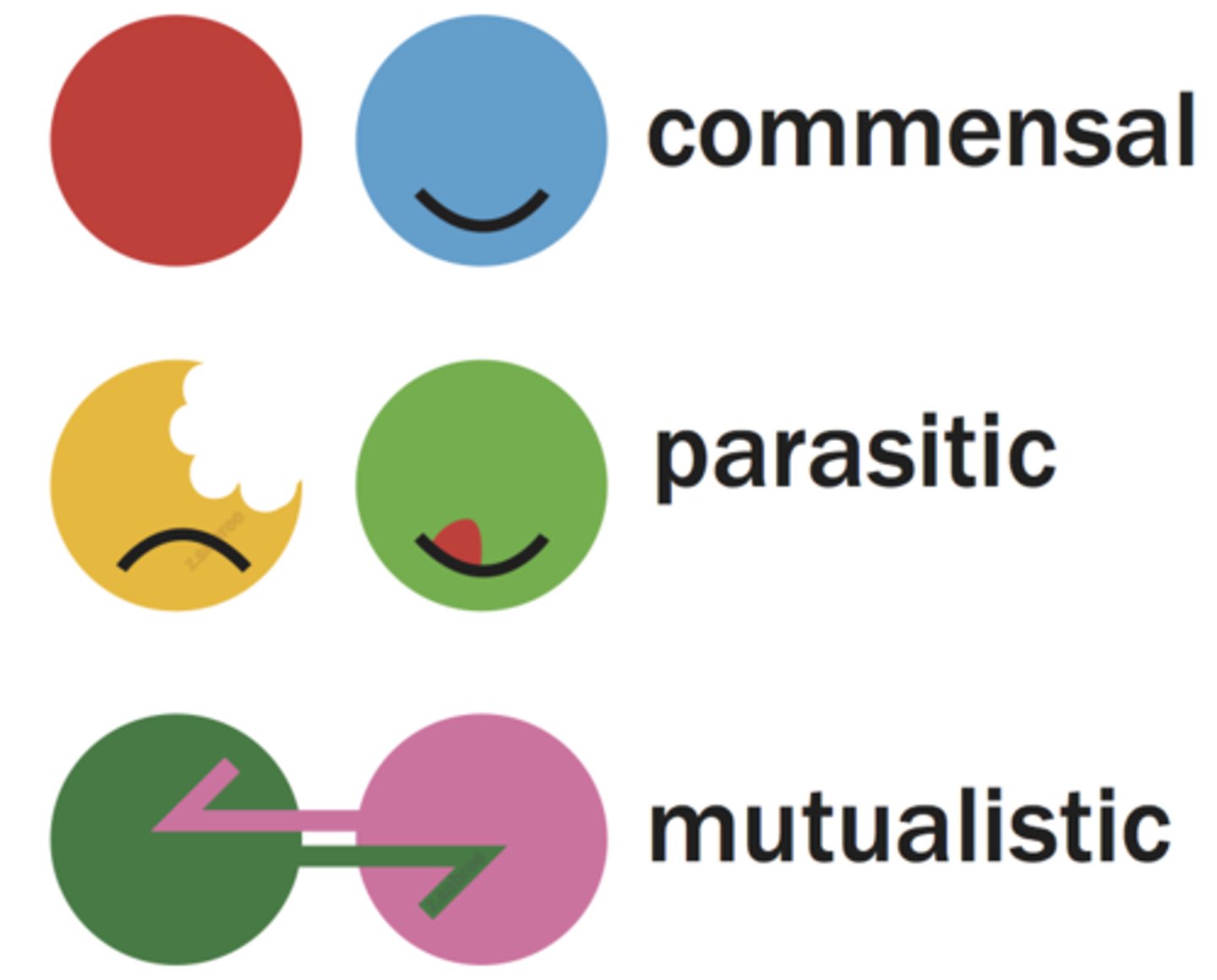
Mutualism, Parasitism, Commensalism
Symbiotic relationships between 2 species
Mutualism (+, +)
Parasitism (+, -)
Commensalism (+, 0)
Related to: Symbiosis
Roots: Bi- two, two species
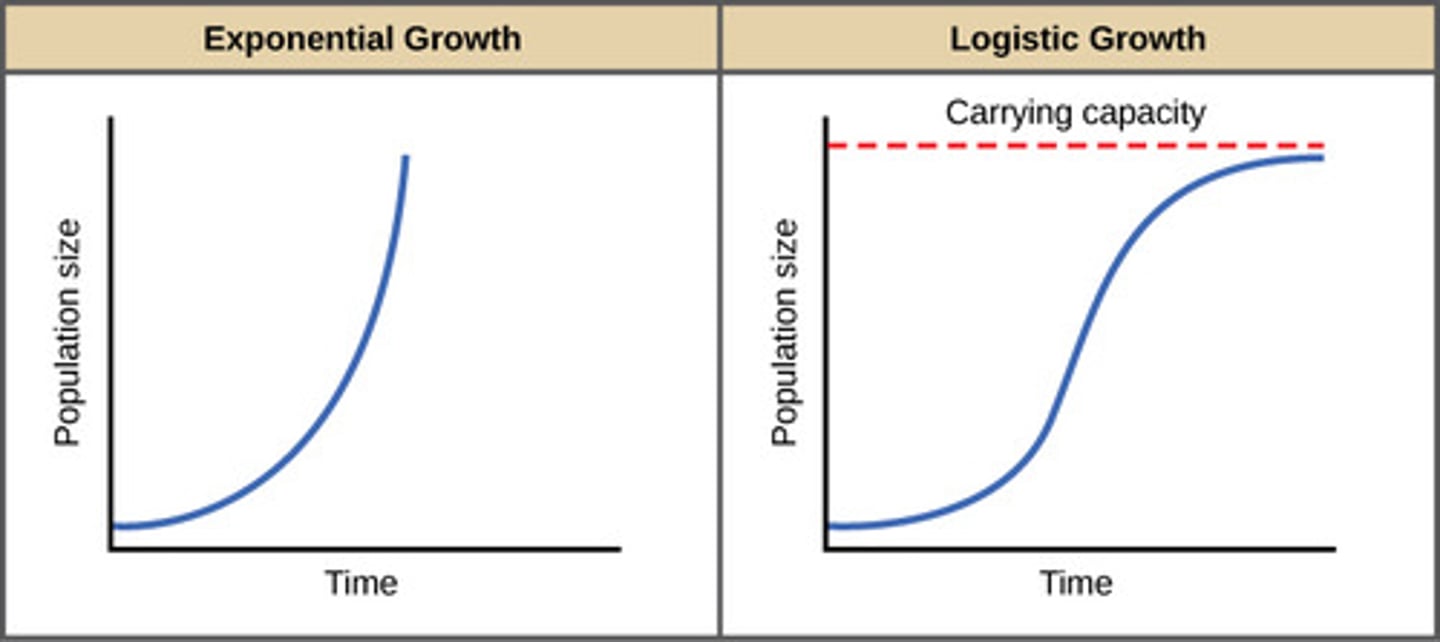
Exponential Growth
Exponential- J Curve, rapid growth without limits
Related to: population growth, ideal conditions
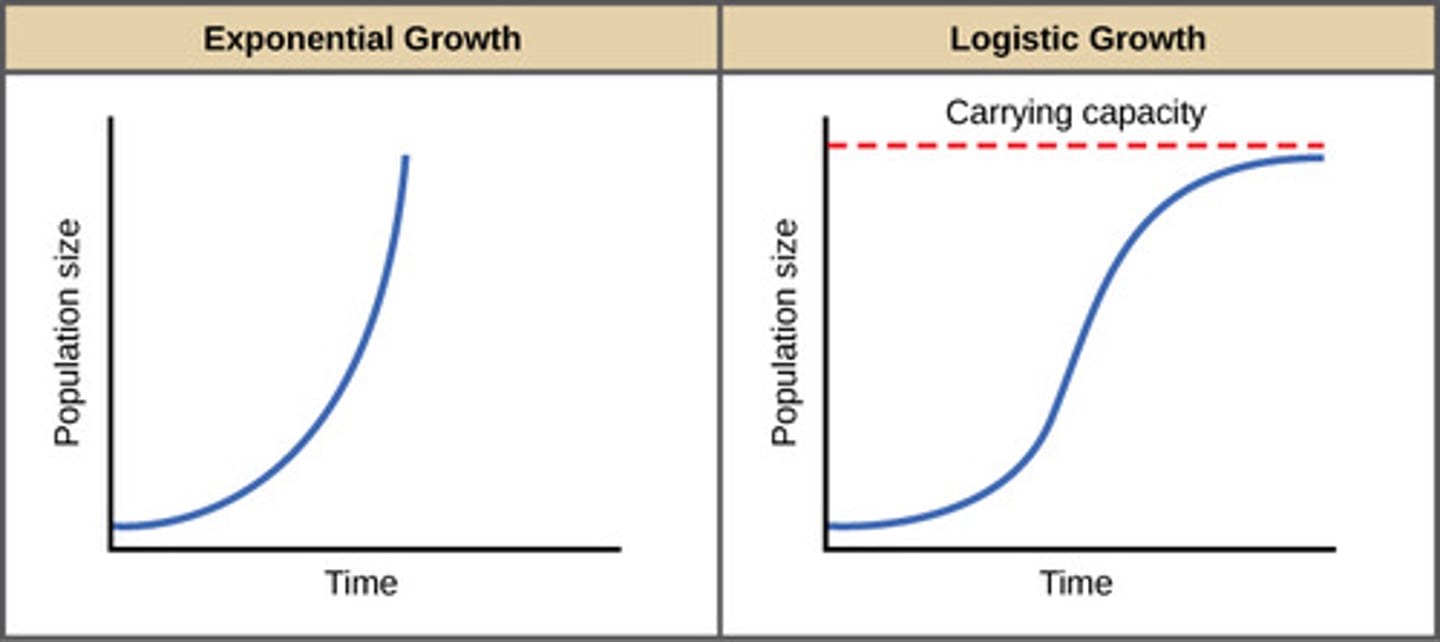
Logistical Growth
Logistic- S Curve, steady growth with limits
Related To: Carrying Capacity, limiting factors
Limiting Factors
Any factor that stops population growth
Related To:
Independent: Natural disasters, weather, flood
Dependent: disease, parasites, competition for food
Roots: Limits= Stops

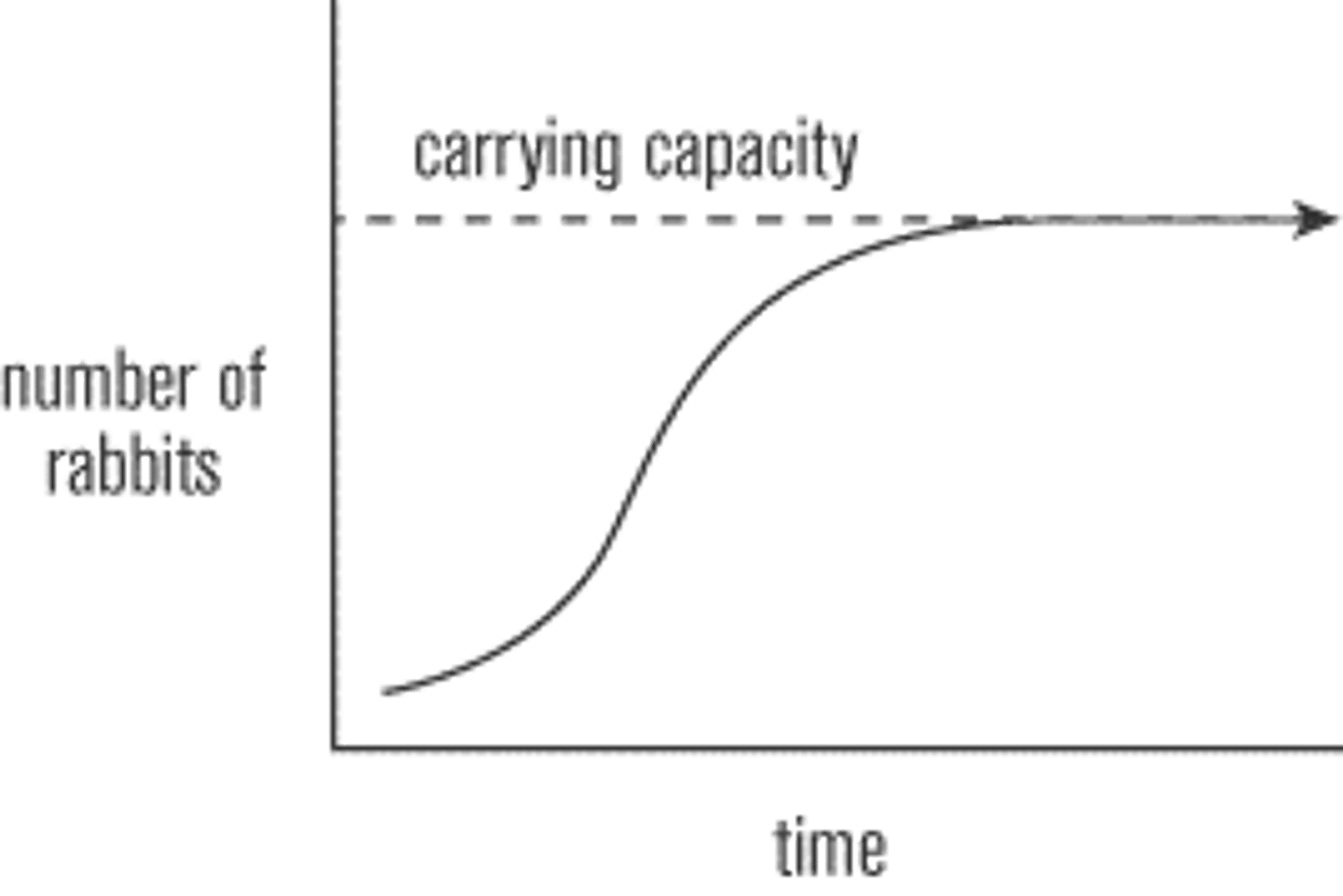
Carrying Capacity
The max # of a population a environment can support, the LIMIT of an environment
Related to: Logistic, S-Curve, Population Growth
Roots: Capacity=MAX
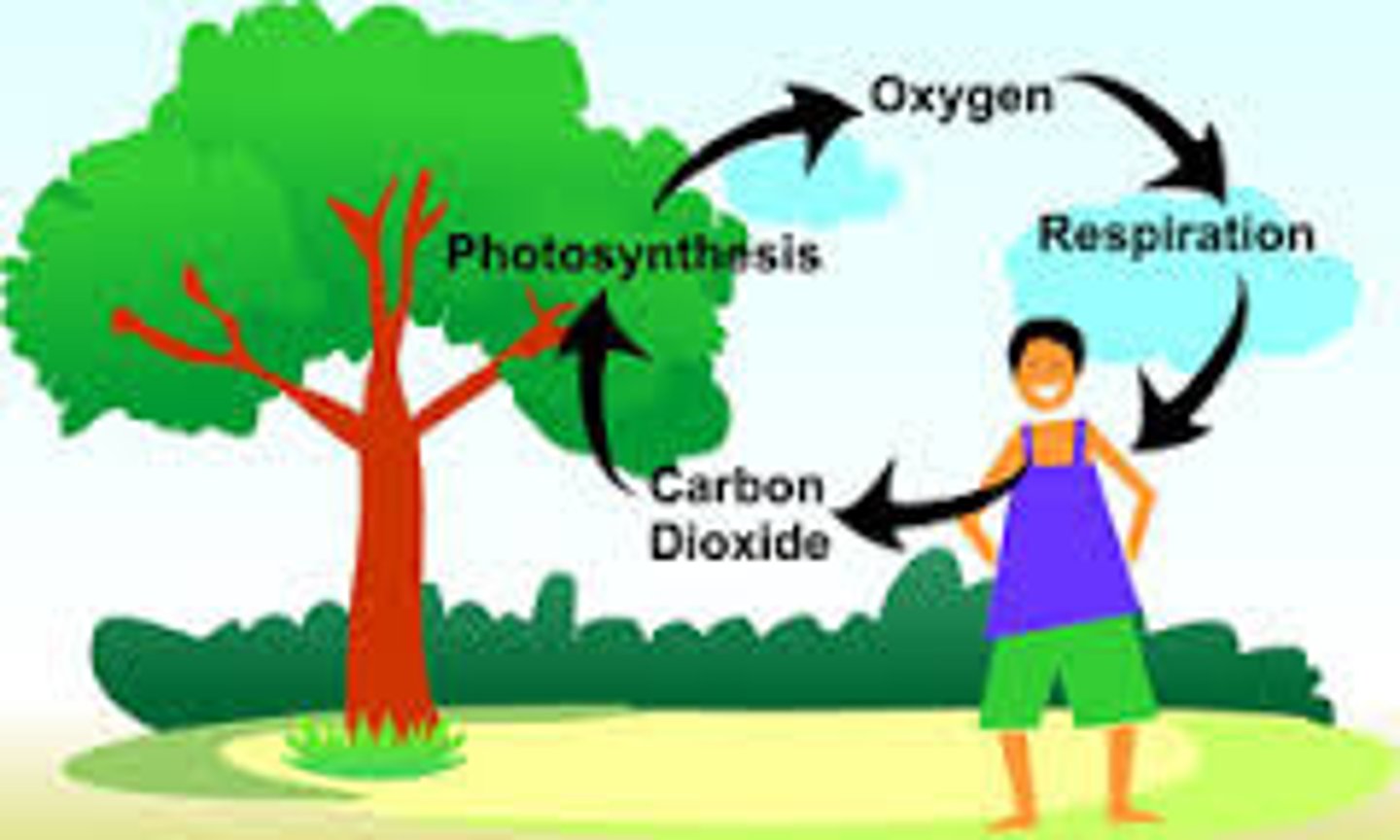
Carbon Cycle
Plants remove Carbon with photosynthesis, Animals d add carbon through respiration, HUMANS SUCK and add EXTRA carbon by burning fossil fuels and more.
Related to: Fossil fuels, Ozone depletion, CFC's
Roots: None
Nitrogen Cycle
How nitrogen cycles through the environment, bacteria needed for nitrogen fixation
Related to: nitrogen fixation, bacteria,
Roots: Nitrogen
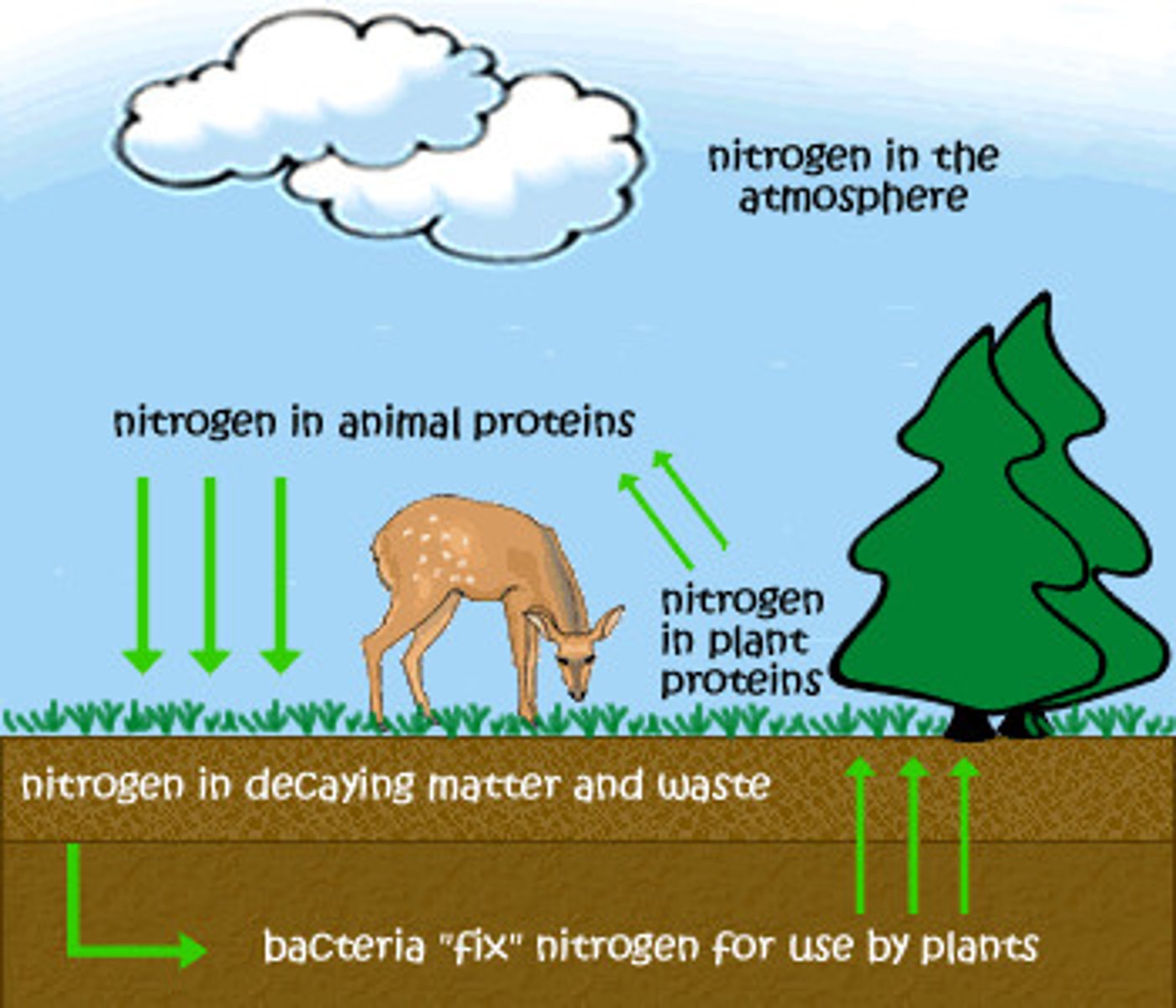
nitrogen fixation
Process of bacteria converting nitrogen gas into ammonia
Related to: BACTERIA roles, Biogeochemical Cycles
Roots: Fixation- Making Nitrogen usable for organisms
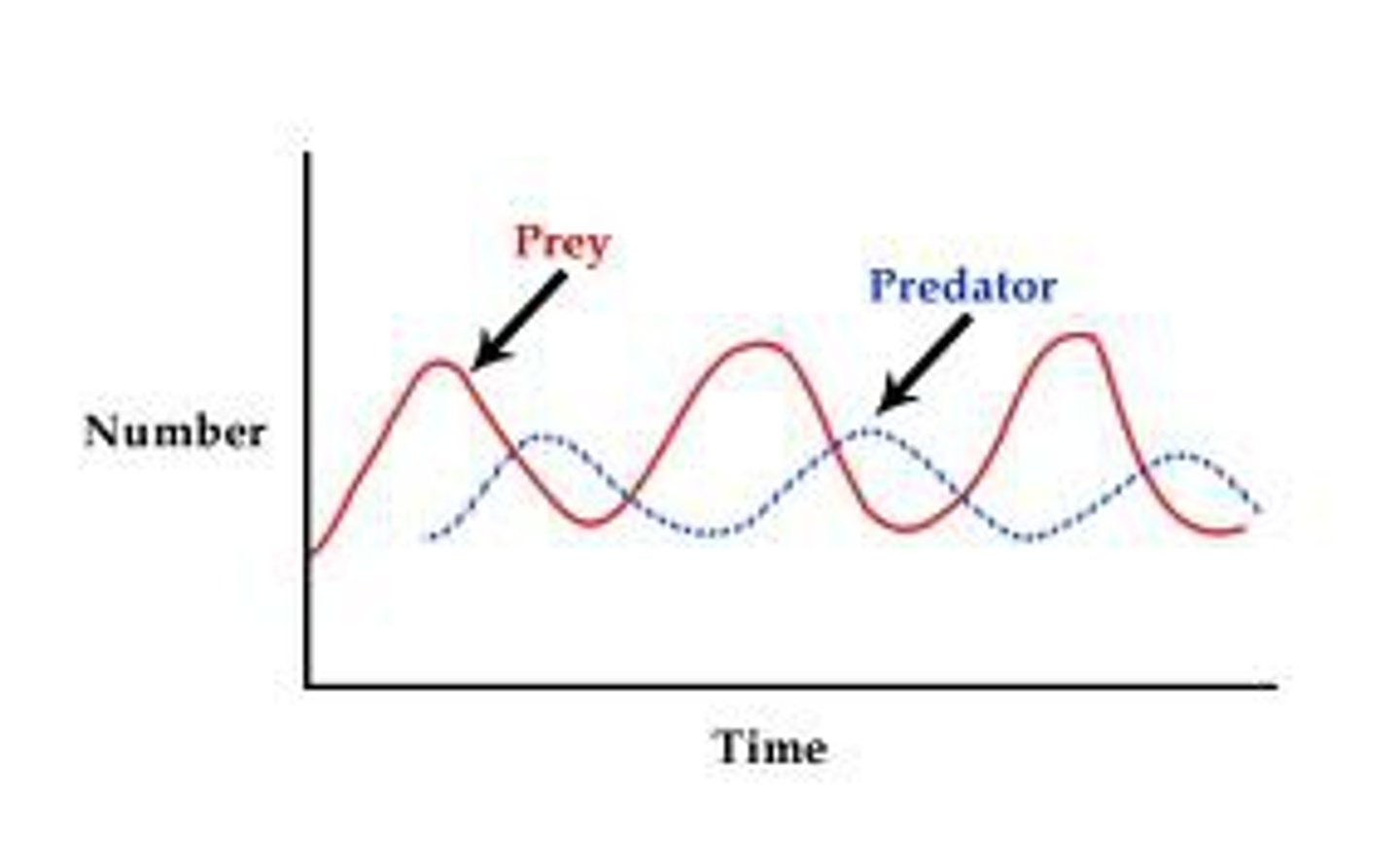
Predator Prey Cycles
populations of the predators and prey fluctuate in size according to one another
Significance: Maintains ecosystem stability, type of limiting factor
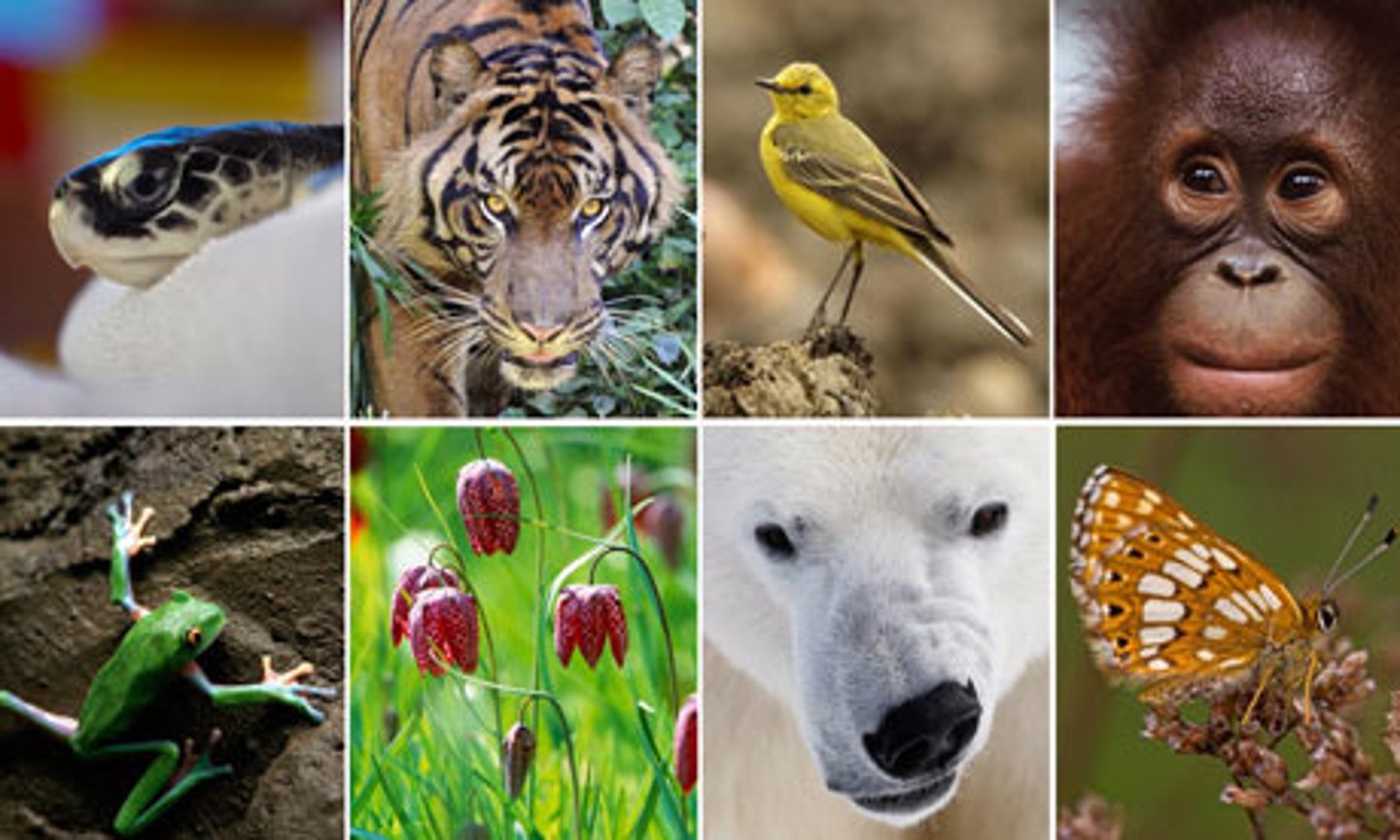
Biodiversity
the variety of life in an ecosystem
Significance: human impacts threaten biodiversity

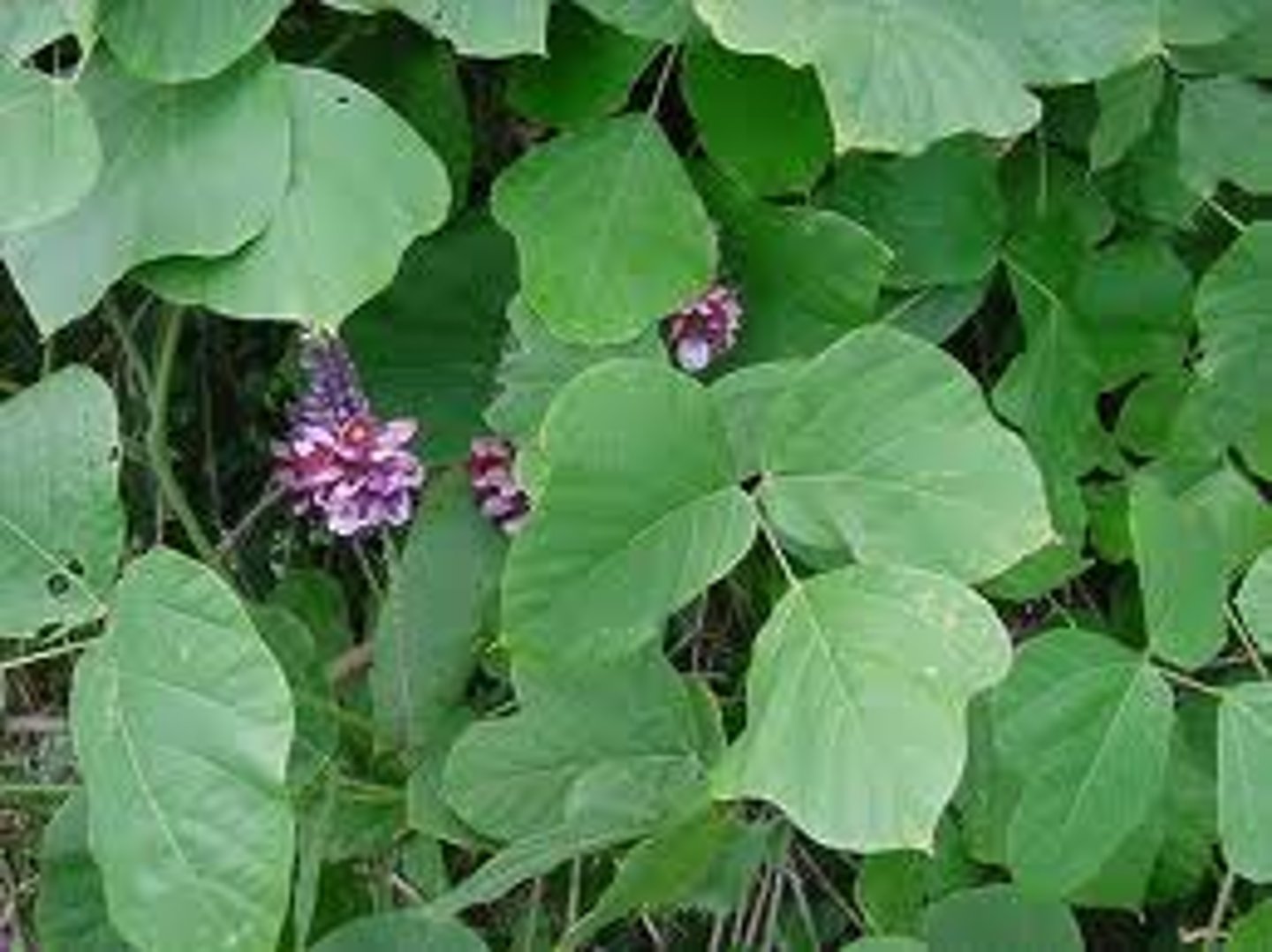
Non-Native Species
species that enter a ecosystem that DO NOT BELONG and they harm the native species and environment
Related to: AKA Invasive Species, KUDZU Vine in NC
Roots: Non- No, Native- Local

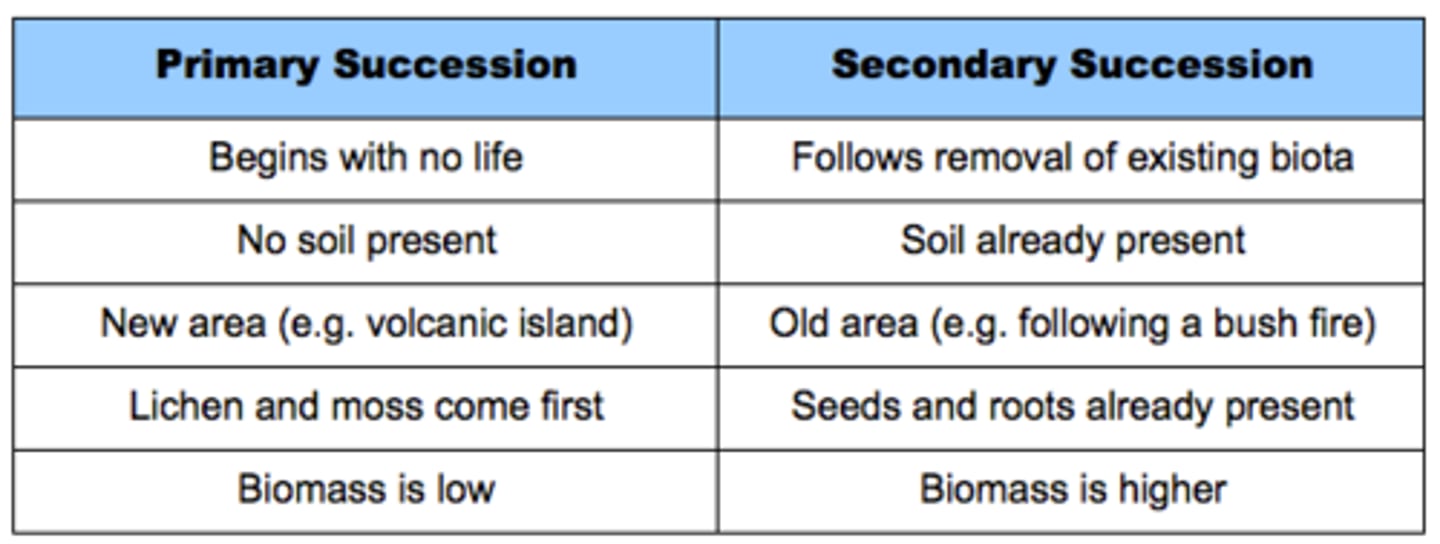
Ecological Succession
gradual recovery in an ecosystem that follows a major disturbance which harmed the environment
2 Types: Primary (barren soil) vs Secondary (soil in tact)
Human impacts
As human population increases, its damaging/depleting earths resources
Example: greenhouse effect, ozone depletion, acid rain, desertification, deforestation, pollution, reduction in biodiversity
