AP Psych Total Review
1/444
Earn XP
Description and Tags
an entire review of the AP Psych 2025 curriculum
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
445 Terms
Likert Scales
rating system for participants, typically ranging from 1 being strongly disagree, to 5 strongly agree. This helps us quantify qualitative data.
Mode
The most frequently occurring data points. There can be no mode or multiple modes.
Range
The difference between the highest and lowest data points, (sensitive to outliers).
Standard Deviation
The avg distance of each data point from the mean. It tells us how much the points differ from the avg. Larger SD means the points are more spread out.
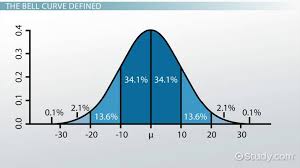
The Normal Curve (Bell Curve)
A graph where the mean, median, and mode, are all located at the center of the curve. Follows the Empirical Rule
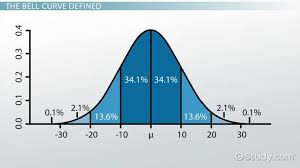
Empirical Rule
States that for a normal distribution, 68% of data falls within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% within two, and 99.7% within three.
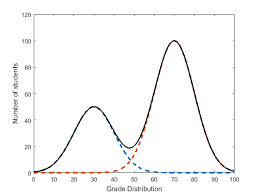
Bimodal Distribution
A distribution with 2 peaks. Reasons: 2 groups are combined in the data, or there are 2 processes influencing the data.
p-value
The p-value helps determine the significance of results. It represents the probability of observing the data, or something more extreme, assuming the null hypothesis is true. However, if the p value is less than 5% (p< 0.05), the results are considered statistically significant.
Effect Size
Measures the strength of the relationship between variables. Tells us how meaningful the effect is.
Standard Deviation Calculations
Subtract the mean of the set from each data point then square. Add all of these together. Then divide by either the number of data points (population) or the sample size minus 1 (sample). Then, sq root the answer.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Made up of brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
all the other nerves in you body that are not your brain or spinal cord.
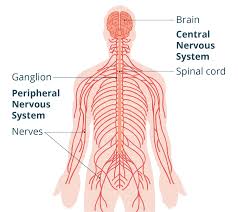
Somatic Nervous System
A function of the PNS that controls all voluntary movement.
Autonomic Nervous System
A function of the PNS that controls all involuntary movement.
Eugenics
A controversial social philosophy advocating the improvement of human populations through selective breeding and sterilization.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Part of the Autonomic NS, responsible for fight or flight functions.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Part of the Autonomic NS, responsible for pumping the breaks after fight or flight response. Rest and Digest.
Interneurons
Nerve cells that connect sensory and motor pathways within the central nervous system, facilitating communication between them.
Reflex Arc
A neural pathway that mediates a reflex action, consisting of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. ie: pulling your hand from a hot stove.
Cell Body / Soma
The part of a neuron that contains the nucleus and organelles, responsible for maintaining the cell's life and function. Has genetic info. Controls the activities of the neuron.
Dendrite
The branched projections of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons and transmit them to the cell body.
Axon
The long, slender projection of a neuron that sends electrical impulses away from the cell body toward other neurons. Where the train leaves the station.
Nodes of Ranvier
Small gaps in the myelin sheath of an axon that facilitate the rapid conduction of nerve impulses by allowing the axon to depolarize.
Myelin Sheath
A fatty layer that insulates axons, increasing the speed of electrical impulse transmission between neurons.
Glial Cell
Supportive cells in the nervous system that assist neurons by providing structural support, nutrition, and protection, aiding in signal transmission.
Threshold
The minimum level of stimulus required to trigger an action potential in a neuron.
Action Potential
A rapid electrical impulse that travels down the axon of a neuron, caused by the movement of ions across the cell membrane.
Resting Potential
The state of a neuron when it is not actively sending a signal, characterized by a higher concentration of potassium ions inside the cell and sodium ions outside.
Resting Period
The neurons state of recovery following an action potential where it prepares to fire again.
Refractory Period
The brief time after an action potential during which a neuron cannot fire another impulse, as it re-establishes ion distribution.
All-or-nothing principle
The concept that a neuron either fires completely or not at all, it cannot, “half-fire,” It needs to hit the threshold
Synapse or Synaptic Cleft
The passing of an electrical signal from neuron to neuron.
Reuptake
The process by which neurotransmitters are taken back into the firing neuron after communicating with receptors on the receiving neuron.
Negative Correlation
As class absences increase, test scores decrease
Positive Correlation
As the number of books read increase, the persons vocabulary also increases.
Correlation Coefficent
A statistical measure that describes the direction and strength of a relationship between two variables, ranging from -1 to +1. -1 Indicates a very negative correlation while +1 indicates a very strong correlation. 0 indicates no correlation at all.
Illusory Correlation
The perception of a relationship between two variables when it doesn’t exist.
Regression Towards the Mean
A statistical phenomenon in which extreme values on a variable tend to be closer to the average on subsequent measurements.
Single-blind procedure
An experimental design where participants do not know what group they have been assigned to,.
Double-blind procedure
An experimental design where neither the participants nor the experimenters know which group participants are in.
Case Study
an in-depth investigation of an individual or group. Ex. studying a person with a rare brain condition.
Correlation Study
Examining the relationship between 2 or more variables, does not manipulate them.
Meta-analysis
Combining the results of multiple studies on the same topic. Not doing your own personal research.
Natural Observation
Observing the behavior in its natural setting. Ex. Jane Goodall with the gorillas.
Population
The entire group the researcher is studying. Ex. All college students in the US.
Sample
A smaller group of the population the researcher is studying, should be representative of the population.
Convenience Sample
A sample taken due to its ease of study, easy but risky. Ex. A professor only testing on her students.
Social Desirability Bias
Occurs when respondents sway data in order to conform to societal norms.
Self-report bias
When a participant provides inaccurate information about themselves.
Institutional Review Board (IRB)
A committee that hears research proposals and determines if they are ethical or not.
Informed Consent
When a participant agrees to participate in a study after hearing the risks.
Informed Assent
When a legal guardian provides consent for participation from a minor or incapacitated person.
Debriefing
A process that occurs after a study, where researchers inform participants about the study's purpose, procedures, and any deception involved.
Research Confederates
Members of the research team that act as participants. Used sometimes in deception studies.
Cognition
mental action if process of acquiring knowledge through thought, experience, and the senses.
Sensation
The process of detecting physical energy from the environment and encoding it as neural signals, essential for perception.
Perception
The process of selecting, organizing, and interpreting sensory info.
Top-down processing
Bottom-up processing
Analysis that begins with sensory info and works up to the brain’s integration. Ex. trying to learn a new word with no previous reference points to the word.
Schema
A collection of basic knowledge about a concept or entity that serves as a guide to perception, interpretation, imagination, or problem solving. Ex. abandonment, dependence, failure, entitlement.
Perceptual set
Mental predisposition to perceive stimuli in a particular way. Ex. every time I am home alone, there is a serial killer in my house.
Selective Attention
the act of focusing on a specific object and ignoring distractions.
Divided Attention
paying attention to multiple things at once.
Cocktail party effect
the ability to focus ones listening attention on a single speaker among a mixture of conversation or background noise.
Inattentional Blindness
The failure to notice the existence of an unexpected item. Ex. the gorilla and the basketball.
Change Blindness
Failure to notice obvious change.
Gestalt
perception emphasizes processing entire patterns, not each thing individually.
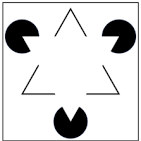
Closure
The tendency to perceive an incomplete figure as whole.
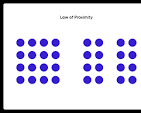
Proximity
The tendency to organize objects close to each other into groups and a single identity.
Similarity
Organizing objects with similar characteristics into a group.
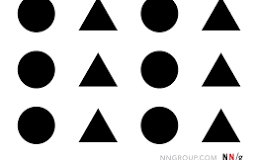
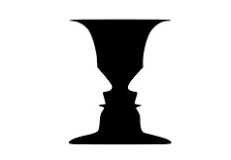
Figure ground
The idea that perceptions have 2 parts, a figure and a homogenous background.
Retinal Disparity
The slight difference between right and left retinal images. (Binocular Depth
Convergence
Rotation of the 2 eyes inward toward a light so the image points on the fovea. (Binocular Depth Cue).
Interpostiton
When a closer object eclipses a further one. (Monocular Depth Cue)

Relative Clarity
Clarity of objects under varying atmospheric conditions. Nearer=clearer. (Monocular Depth Cue)

Relative Size
If separate objects are the same size, the nearer one appears larger. (Monocular Depth Cue)
Texture Gradient
When the details in a texture degrade over distance. (Monocular Depth Cue)

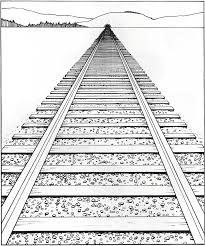
Linear perspective
When 2 parallel lines appear to converge in the distance. (Monocular Depth Cue)
Perceptual Constancy
when you percieve an object at a constant, size no matter the distance from which it is viewed.
Apparent Movement
When something appears as if it is moving, when no moving is occurring. Ex. Carnival lights.
Concept
A basis of thought or mental representation
Prototype
the most typical or representative example of a category, concept, or object. Ex: house, panda, fruit,
Schema
a mental framework or set of beliefs and expectations about something, such as a person, place, object, or event Ex: your idea of what a job at mcdonalds looks like
Assimilation
The cognitive process of incorporating new information into existing schemas or frameworks without changing them. Ex: this animal must be a dog too because it has 4 legs.
Accommodation
Altering existing categories to fit the new definition." Ex: this animal has 4 legs but is not a dog, so not all animals with 4 legs are dogs.
Algorithm
A system in which every possible option is attempted and a solution is guaranteed. Ex: I will check everywhere I went yesterday to find my lost keys.
Heuristic
A shortcut system that may or may not lead to a solution. Ex: only checking the last place you went for your keys.
Representativeness Heuristic
Judging a particular thing by how well it could assimilate to other members of the same group.
Availability Heuristic
A system of which judgements are made using info that particularly stands out, like recent, vivid, or memorable events.
Mental set
A temporary readiness to perform certain psychological functions or solve problems based on past experiences, often leading to an inability to see new solutions. Applying a solution that previously worked on a similar problem. Ex: turning the computer off and on again.
Priming
The activation, often unconsciously, of memory associations.
Framing
Defining context or issues in a way that serves to influence how the context or issues are perceived and/or evaluated. Ex:
Gambler’s Fallacy
The belief that independent events are connected.
Sunk-Cost Fallacy
The tendency to continue an action when one has already lost time, money, or effort.
Executive Function
The ability to generate, organize, plan, carry out actions, and think critically.
Divergent thinking
Starting from the problem and brainstorming solutions from there
Convergent thinking
Starting with a solution and finding problems to apply it to.
Functional Fixedness
The inability to consider a new use for an item.
Automatic processing
the unconscious encoding of incidental info. well-learned information
Effortful Processing
encoding information through conscious intent and effort