APPSYCH Unit 1 Words to Review
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:22 AM on 9/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
1
New cards
empiriscm
the idea that knowledge is the result of experience and that scientific knowledge is developed through observation and experimentation
2
New cards
behavioral perspective
how learned and observable behaviors impact behavior and mental processes
3
New cards
biological perspective
how biological (genetics, neural, hormonal) and physiological processes impact behavior and mental processes
4
New cards
cognitive perspective
interpretation of a situation & mental processes (thoughts, memories, problem-solving) impact behavior and mental processes
5
New cards
evolutionary perspective
natural selection of traits has promoted the survival of genes
6
New cards
humanistic perspective
a way of evaluating an individual as a whole, rather than looking at them only through a smaller aspect of their person
7
New cards
psychodynamic perspective
encompasses a number of theories that explain both normal and pathological personality development in terms of the dynamics of the mind.
8
New cards
social-cultural perspective
behavior and thinking vary across situations and cultures
9
New cards
biopsychosocial approach
systematically considers biological, psychological, and social factors and their complex interactions in understanding health, illness, and health care delivery
10
New cards
basic research
scientific inquiry that aims to increase psychology's knowledge base
11
New cards
applied research
scientific inquiry that aims to use psychology to solve practical problems
12
New cards
human-factors psychology
how people interact with machines and technology
13
New cards
central tendencies
a statistic that identifies a single value as representative of the entire distribution of data
14
New cards
standard deviation
a measure which shows to what extent the values in a data set deviate from the mean

15
New cards
normal curve

16
New cards
statistical significance
helps quantify whether a result is likely due to chance or to some factor of interest
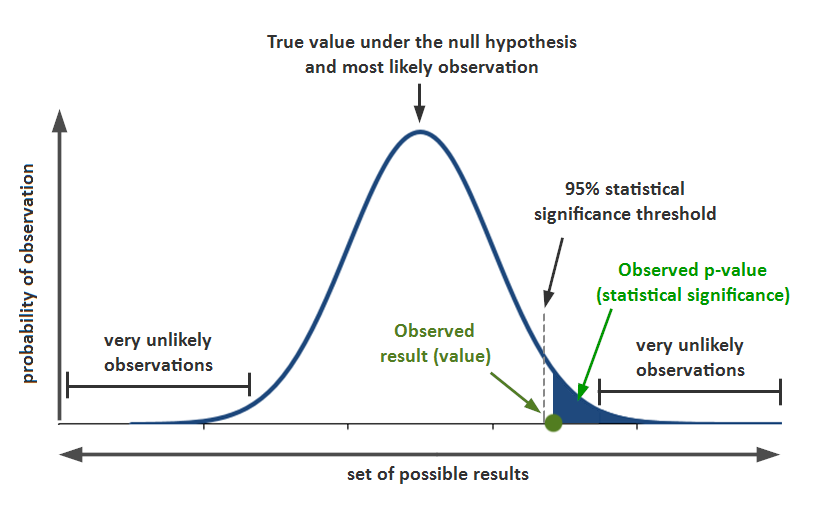
17
New cards
Wilhemn Wundt
established the first psychology law in 1879
18
New cards
William James
Introduced funtionalism