Bone Anatomy and Structure Terms
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
1
New cards
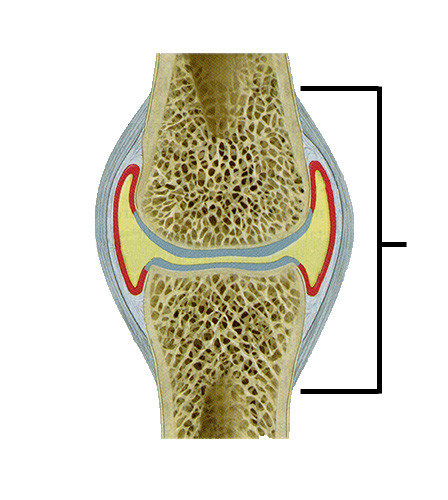
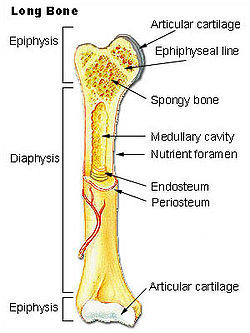
epiphysis
the end of a long bone; proximal or distal depending on where it is attached to the body
2
New cards
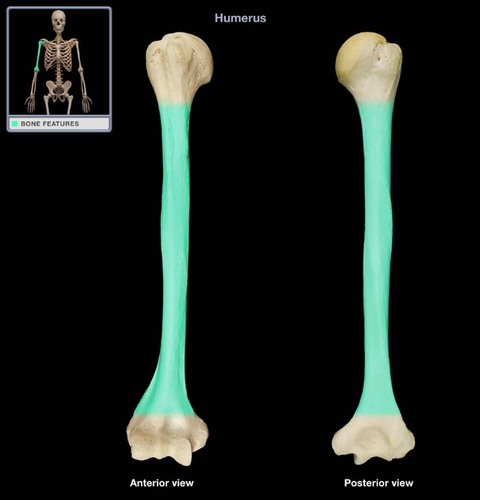
diaphysis
the shaft of a long bone
3
New cards
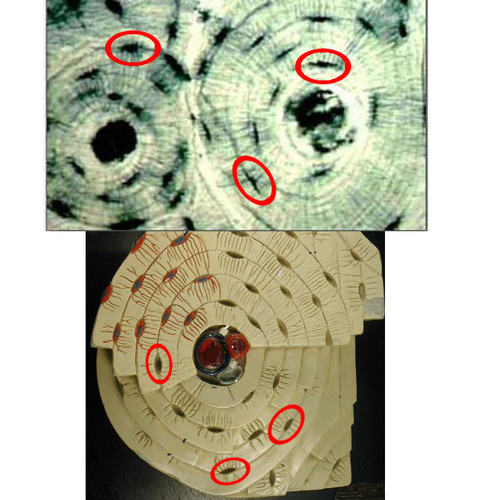
osteocytes
mature bone cells that are found in the web of the bone matrix
4
New cards
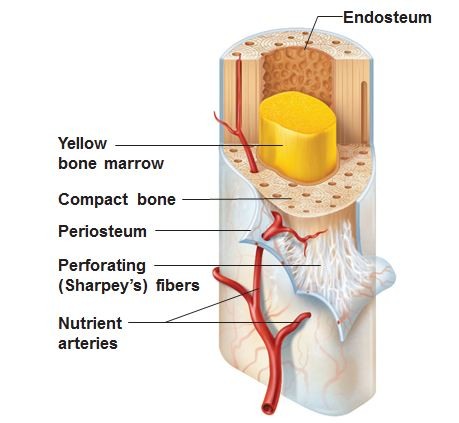
endosteum
lines the medullary cavity
5
New cards
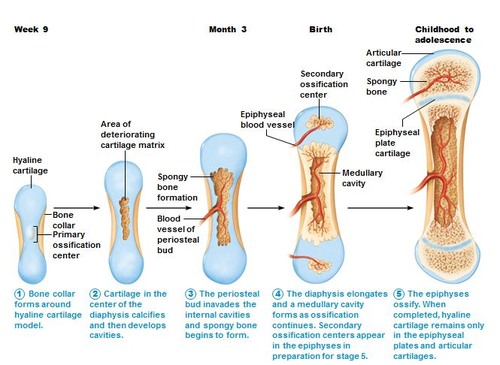
hyaline cartilage
Forms much of the fetal skeleton and covers the articular surfaces of long bones
6
New cards
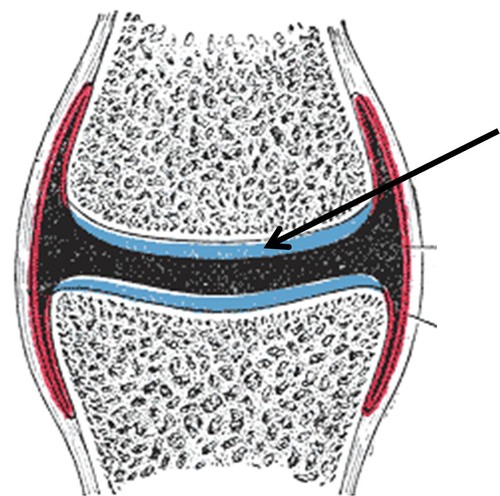
articular cartilage
padding between bones; at the ends of the bones
7
New cards
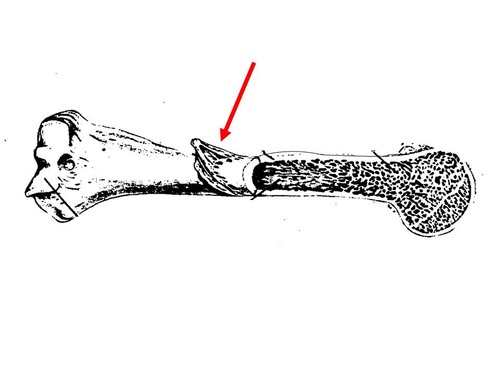
periosteum
membrane that covers entire bone
8
New cards
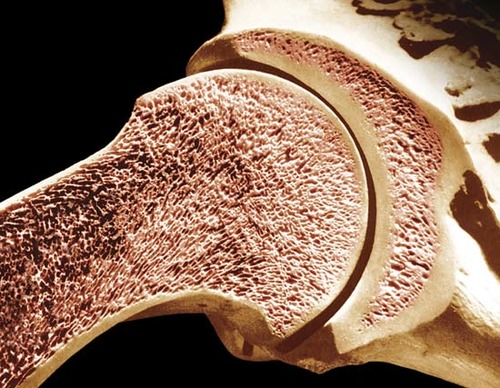
spongy bone
type of bone found in the epiphysis; also called cancellous bone
9
New cards
Hematopoeisis
formation of blood cells and occurs in the bone marrow
10
New cards
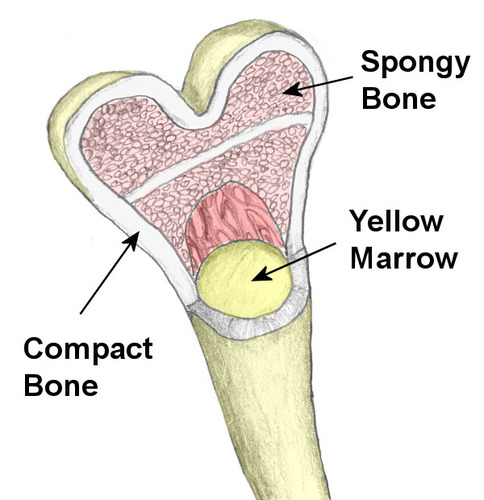
Compact bone
dense, hard layers of bone tissue that lie underneath the periosteum membrane; contains calcium and phosphorus minerals
11
New cards
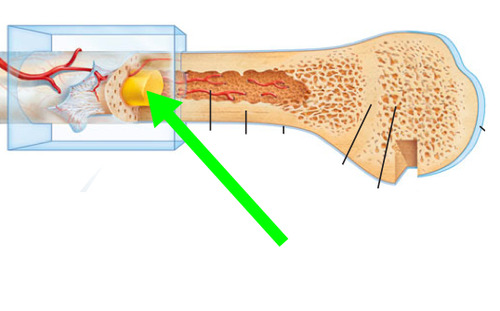
Yellow marrow
soft, fatty material found in the medullary cavity of long bones
12
New cards
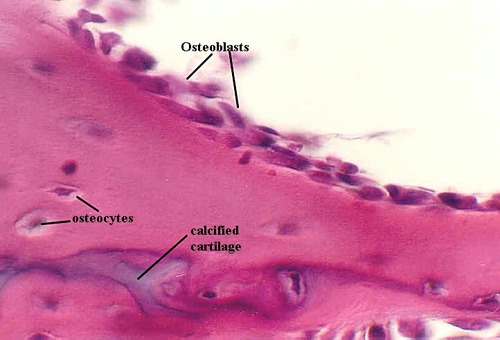
Osteoblasts
Bone building cells; lay the bone matrix
13
New cards
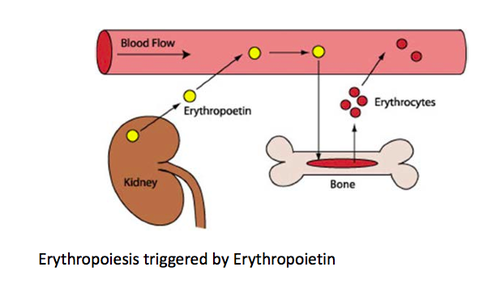
Erythropoietin (EPO)
hormone secreted by the kidney to stimulate the production of red blood cells by bone marrow
14
New cards
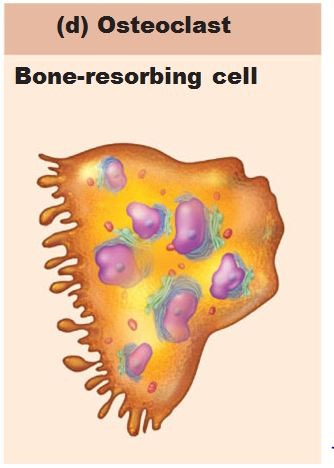
osteoclasts
break down bone to release calcium into the bloodstream
15
New cards
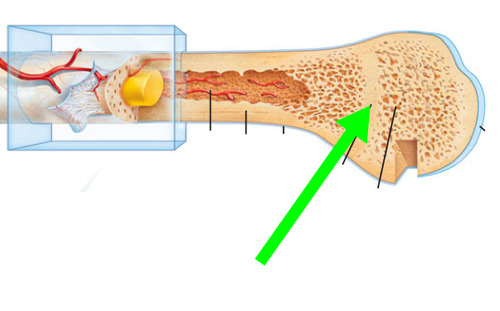
epiphyseal line/plate
between diaphysis and epiphysis of an adult bone. A disc of hyaline cartilage that grows during childhood to lengthen bone.
16
New cards
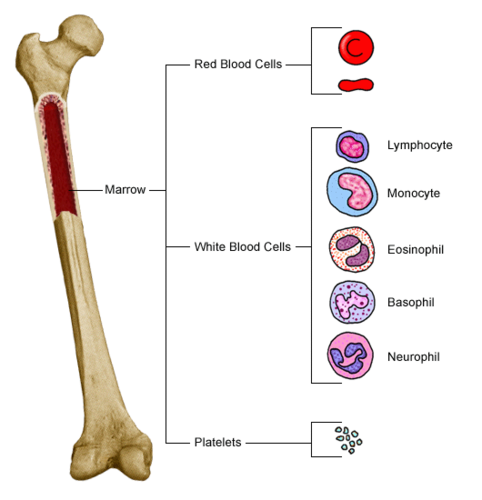
Red marrow
found in the epiphysis of long bones; where red blood cells are produced.
17
New cards
What are the inorganic and organic components of bone? Which one provides strength and which provides flexibility?
Organic: Collagen fibers- provide flexibility
Inorganic: Calcium salts- provide strength
Inorganic: Calcium salts- provide strength
18
New cards
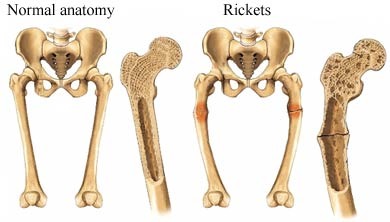
Rickets (osteomalacia of children)
during bone development (usually seen in kids), a lack of calcium and/or vitamin D can lead to a deficiency in calcium in the bone. Osteomalacia is the general term for soft bones.
19
New cards
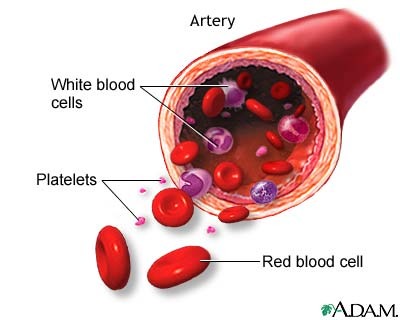
Purpose of bone marrow
Hematopoiesis - blood cell production (RBC, WBC, Platelets) occurs in the red bone marrow. Also serves as
Fat storage (yellow bone marrow)
Fat storage (yellow bone marrow)
20
New cards
Hormone that stimulates red blood cell formation
erythropoietin
21
New cards
Hormone that stimulates growth plate to divide and bones to lengthen?
Growth Hormone
22
New cards
What is another name for the growth plate?
epiphyseal plate
23
New cards
What type of tissue is the growth plate made of?
hyaline cartilage
24
New cards
What is the growth plate called after the tissue ossifies (hardens) and lengthens when adult height is reached?
Epiphyseal line
25
New cards
Where do osteoblasts originate?
osteoprogenitor (stem) cells in the periosteum
26
New cards
How do osteoblasts become osteocytes?
osteoblasts get trapped in the bone matrix they secrete (or lay down)
27
New cards
Why do osteoclasts break down bone?
to reabsorb bone and release calcium minerals back in the bloodstream
28
New cards
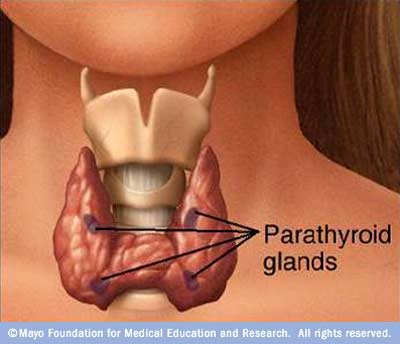
Name the hormone that stimulates osteoclasts.
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) stimulates osteoclasts to break down bone when the body senses blood calcium levels are too low.
29
New cards
What type of feedback mechanism is the regulation of blood calcium levels?
Negative Feedback
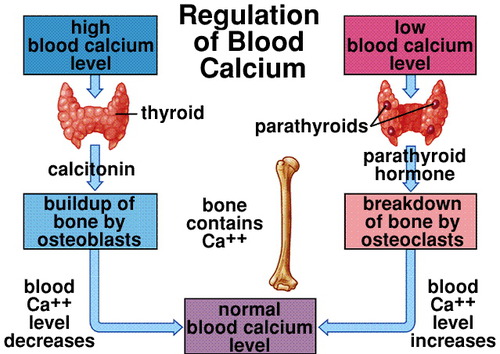
30
New cards
What happens to the bone matrix, over time, if blood calcium levels are always low? Name the condition.
The body will stimulate osteoclasts to break down the compact bone to release calcium leading to osteoporosis (porous bone).
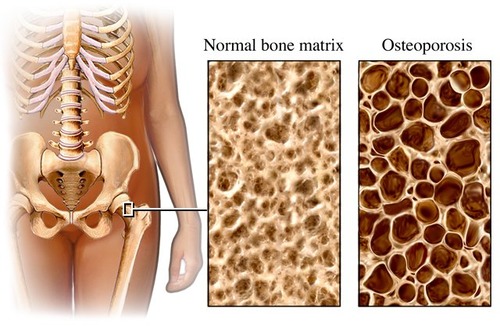
31
New cards
The joint capsule is continuous with which membrane?
periosteum