Physics Electricity & Magnetism
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is static electricity?
A buildup of charge where electrons move between materials and jump back to a positive surface.
Static Electricity: Def
is the result of the imbalance of electrons on a surface
Magectic
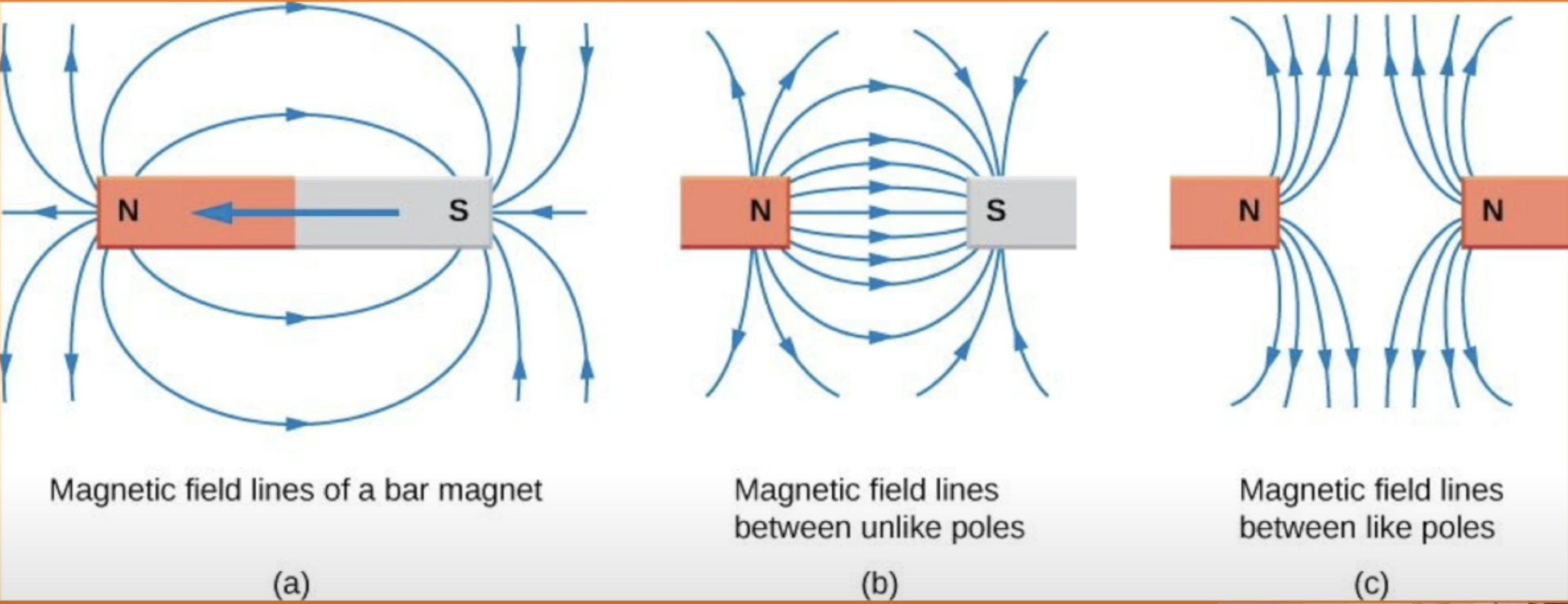
all magnets have a south and north pole
opposite poles attract each other
same poles repel each other
permanent magnets have a permanent magnetic field surrounding them
field lines show the direction of the force at any point on an imaginary single north pole that is placed near the magnet
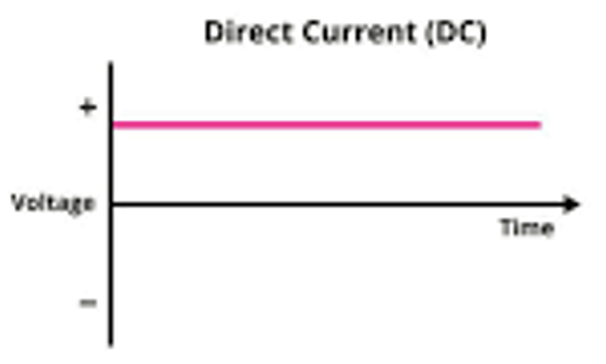
DC
Direct current the electrons always travel in the same direction
Examples:
Electronics (Computers, phones, etc) use DC
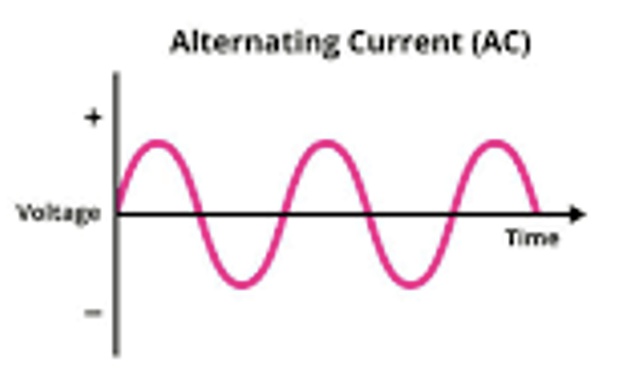
AC
Alternating current the direction the electrons travel alternates direction 50 times every second
Examples:
Household appliances (Fridges, toasters, kettles) use AC
electromagnets
a current carrying wire produces its own magnetic field - called electromagnetism
if you place a compass near a current carrying wire, it will line up with the electric field
no current = no electric field
current flowing = coil has a magnetic field similar to that of a bar magnet
Electromagnets How its created
created by moving electric charges — electric currents produce magnetic fields, and changing magnetic fields induce electric fields.
generators
a device that converts movement energy into electricity
generators are found in steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines
A Basic Generator has
a wire loop, being rotated
a permanent magnet
a slip ring communicator
rotating the wire inside a magnetic field induces a current in the wire
generators use kinetic energy to create electrical energy
fuses
High Resistance wires that have a low melting point. The wire will melt if to much current flows, breaking the circuit.
Circuit Breakers
A switch that flips to break the circuit if to much current is flowing through a circuit
Safety Switch
A device that shuts off the supply to a circuit when a different current is measured on the active and neutral lines.