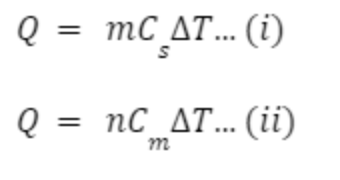AP Chemistry Exam Review
1/98
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Boyle’s Law
Pressure is inversely proportional to Volume
P1V1=P2V2
Charle’s Law
Volume is proportional to temperature
V1/T1=V2/T2
Gay-Lussac’s Law
Pressure is proportional to temperature
P1/T1=P2/T2
Avogadro’s Law
mole is proportional to volume
N1/V1=N2/V2
ideal gas law
PV=nRt
molar mass
mass of sample/moles of sample
density of ga gas
(p*m)/(R*temperature at K)
kinetic molecular theory
gases are in constantly random motion, elastic, volumes are small, attractive forces are negligible, kinetic energy is proportional to temperature
as volume decreases what hawppens to collisions
collisions increase, inversely proportional
as pressure decreases what happens to the collisions
collisions decrease, proportional
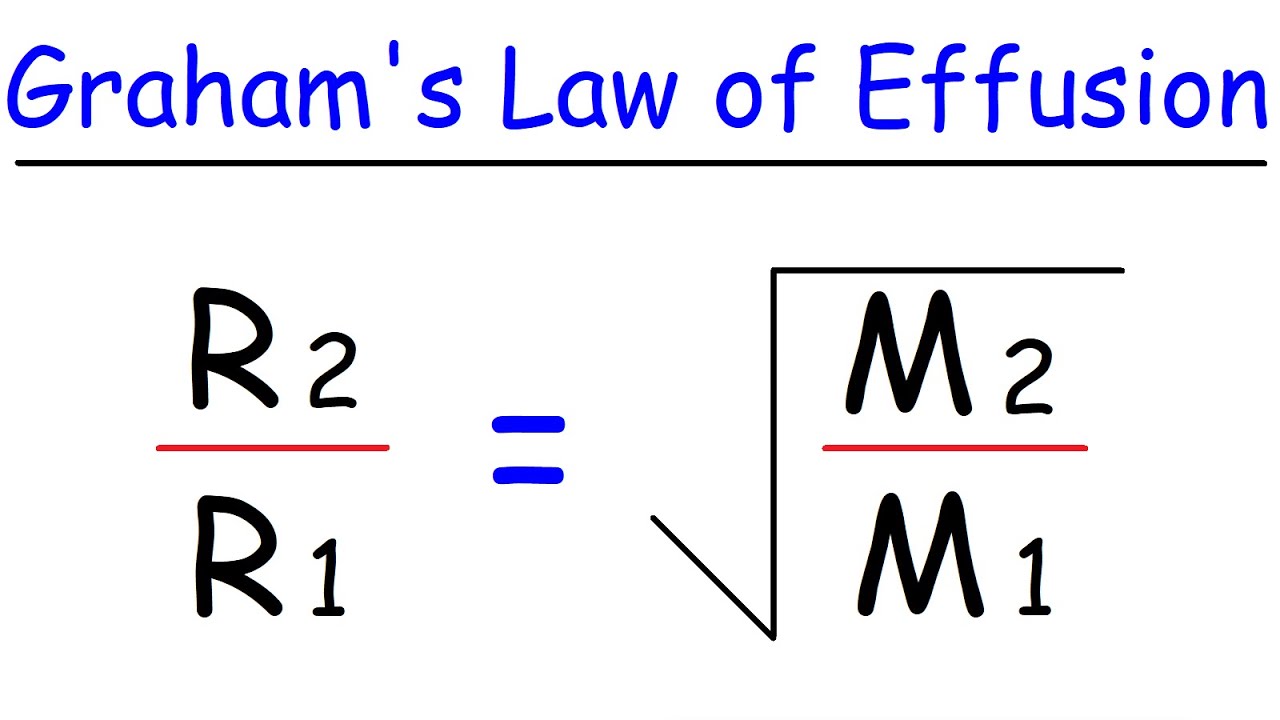
graham’s law of effusion
kinetic energy formula
KE=1/2mv²
effusion
movement of gas molecules into a tiny hole
diffusion
gas move into another container filled with gas
dalton’s law of partial pressure
Pi=Xi*Pt
Xi
Xi/Xt
element/total moles
dipole-dipole
think of like a magnet
polar molecules
coulomb’s law
K(+)(-)/r²
as attractive forces increase in coulomb’s law
the distance decreases
as pressure increases in coulomb’s law
kinetic energy decreases
london dispersion forces
present in all molecules, nonpolar and then becomes polar for an instant
how to tell what compound has a higher boiling point
if they have the same intermolecular forces, check on moles
hydrogen bonds
H with NOF, strongest intermolecular forces
surface tension
increased attractive forces at surface of a liquid compared to center of liquid
evaporation
liquid to gas
vaporization
liquid to vapor
condensation
gas to liquid
visosity
liquid’s resistance to flow
ex. ionic compounds are viscous because of their structure and can’t move freely
vapor pressure
pressure of gas above a liquid → evaporation does happen but can’t escape a container
dynamic equilibrium based on vapor pressure
liquid molecules and gas molecules are start colliding with each other until the rates are equal to each other
metallic crystals
rigid structure and are alloys
substitutional alloy
replace ions
interstitial alloy
go in between ions because so small
ionic crystals
positive and negative ion structure
based on coulomb’s law
molecular crystals
covalent and nonmetals
held by any intermolecular force
<ionic, softer and low melting point
comparing compounds based on certain thing
whichever has the greater attractive force will have the higher boiling point and vaporization and a lower evaporation and vapor pressure
network crystal
structure filled with covalent bonds in empirical formulas
amorphous
soft and cannot form crystals
heating curve order
solid heating solid melting liquid heating liquid boiling (this is where superheating can happen) and then gas heating
cooling curve order
gas cooling, gas condense, liquid cooling, liquid crystallize, solid cooling
saturated solutions
maximum amount of solute dissolved in the solvent
unsaturated solution
some of solute dissolved in solvent
supersaturated solution
more than maximum amount of solute dissovled in the solvent
how to tell if two compounds are soluble with each other
similar interactive forces interact and can be soluble with each other
dissasociate
molecules break apart after dissolving with water
ionization
molecules break apart into ions after dissolving with water
strong electrolyte
conduct electricity, ionizable and dissociate
ionic compounds mainly but HI, HBR, HCL
weak electrolyte
slightly ionizable and dissociate
weak acids and bases
molarity
moles of solute/liters of solution
as temperature increases what happens to gases in liquid
decrease
which state of matter is easiest to compress
gas
henry’s law
solubility of gas = k * pressure of gas
intermediate
cannot be present in rate law
present in first and second steps
what is the criteria for a reaction to happen
colliding
proper orientation
sufficient energy
what step do you use to determine the rate law
slow
how many steps will the addition of a catalyst be
>=2
how to tell if activation energy diagram will be endothermic or exothermic
reactant>product exothermic
reactant<product endothermic
single elementary step
molecules collide at the same time
first order units
1/s
zero order units
m/s
second order units
1/ms
as temperature increases what happens to the reaction rate
increases
as concentration increases what happens to the reaction rate
increases
as a catalyst is added what happens to the reaction rate
increases
as volume increases what happens to the reaction rate
decreases
as surface area increases
reaction rate increases and particle size decreases
beer’s law
absorbance is proportional to concentration
base
loses a proton (H+)
acid
gains a proton (H+)
stoichiometry steps
balance equation
convert to moles
mole ratio
convert back to grams of question element
how to convert to another element if needed and have the right information
use mole ratios
titration problems on finding moarlity
to find moles of solute → convert to liters the moles then mole ratio
then divide that answer by solution (probably given(
precipitation reaction
synthesis
redox reaction
includes OH- and H2O
acid-base reaction
can clearly tell the acid and bases
beer lambert law formula
absorbance = molar absorptivity * path length * concentration
if the rate of forward > rate of reverse
favors reactants
products increase and reactants decrease to make equal
if the rate of reverse > rate of forward
favors products
products decrease and reactants increase to make equal
reaction quotient
products/reactants
when to use q
determine direction of reactant
when to use k
determine if there are more reactants or products at equilibrium
k>1
prod>react num>den
k<1
react>prod den>num
k=0
prod=react num=den
le chatelier’s principle
adding stress can knock out of equilibrium
if reactant increases
consumes reactants and creates more products
reactant decreases
consumes product and create more reactants
when evaporating or adding
whatever side added will consume and other side will create more
goes onto the lowest side
pressure increases and volume decreases
goes onto the highest moles
pressure decreases and volume increases
solvent increases what happens to molarity
decreases, inversely proportional
addition of catalysts equilibrium
increases both sides
what side does heat favor
endothermic side → reactants
what happens to temperature surroundings in endothermic forces
temperature decreases
what happens to temperature surroundings in exothermic forces
temperature increases
enthalpy
delta H
exothermic or endothermic
endothermic
break forces
unfavorable
exothermic
form forces
favorable
specific/molar heat