ch 1 Psychological Science/Research
1/69
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
overconfidence
tendency to perceive patterns in random events
“I knew it all along” phenomenon
Game show door (you should switch, but it feels better to stay)
“if…, then…”
goal: provide clear, accurate picture of people’s behaviors, thoughts, and attributes
BUT doesn’t provide generalized conclusions
ONLY fruitful ideas on the topic at hand
hawthorne effect
behave differently when you know you are being observed (ruins observation)
survey and interview
examines multiple cases in less depth but allows for more generalizations
wording effect
phrasing of questions could bias answers
random sampling
Taking a random group from a population that represents that population.
correlation is NOT … ?
causation (NOT)
correlation defined
research determining if a relationship between two or more factors exists
positive correlation
(0 to +1.00) Indicates a direct relationship where two things increase or decrease together
Negative correlation
(0 to -1.00) Indicates inverse relationship; as one increases, the other decreases
Correlation coefficient
[r] Provides statistical measure of how closely two things vary together and how one predicts the other
example of correlation coefficient
r = -.37
negative weak correlation
variable
anything that can vary and is feasible and ethical to measure
directionality problem
situation where one knows two factors are related but does not know what is the cause and which is the effect
3rd variable possibility
when two correlated variables can actually be explained by a third unaccounted variable
illusory correlation
perception that a relationship between two variables exists when there is little to no relationship
regression toward the mean
tendency for an extreme or unusual score or event but will later fall back to towards the average
experimentation
when researchers focus on possible causes and effects between factors in several ways. Can manipulate the factors of interest to determine the effect
experimental group
participants who are exposed to independent variable
control group
participants who are NOT exposed to independent variable
double-blind procedure
Procedure to eliminate bias in a study. Neither the participants or those collecting data know which group will receive treatment; only the head researcher will know.
placebo
sugar pill
Placebo effect
When people have an expectation that something will bring a certain effect or response
Example of placebo effect
giving someone advil, a well known medicine that helps relieve pain. Patient will immediately exclaim how they feel much better but advil doesn’t work until 20 minutes after consumption. They had the expectation that the drug would make them feel better.
independent variable
factor that is manipulated and being studied
dependant variable
The item is being measured. This changes when the independent variable is manipulated.
confounding variable
factor other than the independent variable that might produce an effect
example of confounding variable
When studying the ability to improve grades with study guides, a confounding variable may be the intelligence of a person and that they do not need study guides to have good grades
random assignment
in order to lessen the effects of a confounding variable in the participants (example: age, gender, beliefs, etc.), researchers can take the participants and mix them up and put each participant into a control or experimental group.
Ethics code of the American Psychological Association (APA) and British Psychological Society (BPS)
obtain potential participants informed consent
Protect participants from harm/discomfort
Keep participant’s information confidential
Fully debrief people (explain)
informed consent
giving a potential participant enough information about a study to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate
debriefing
Post experimental explanation of a study, including its purpose and descriptions and deception to participants
mode
most frequently occuring scores in a distribution
mean
arithmetic average of a distribution obtained by adding scores and then dividing by number of scores
median
middle scores in a distribution
range
difference between the highest and lowest scores
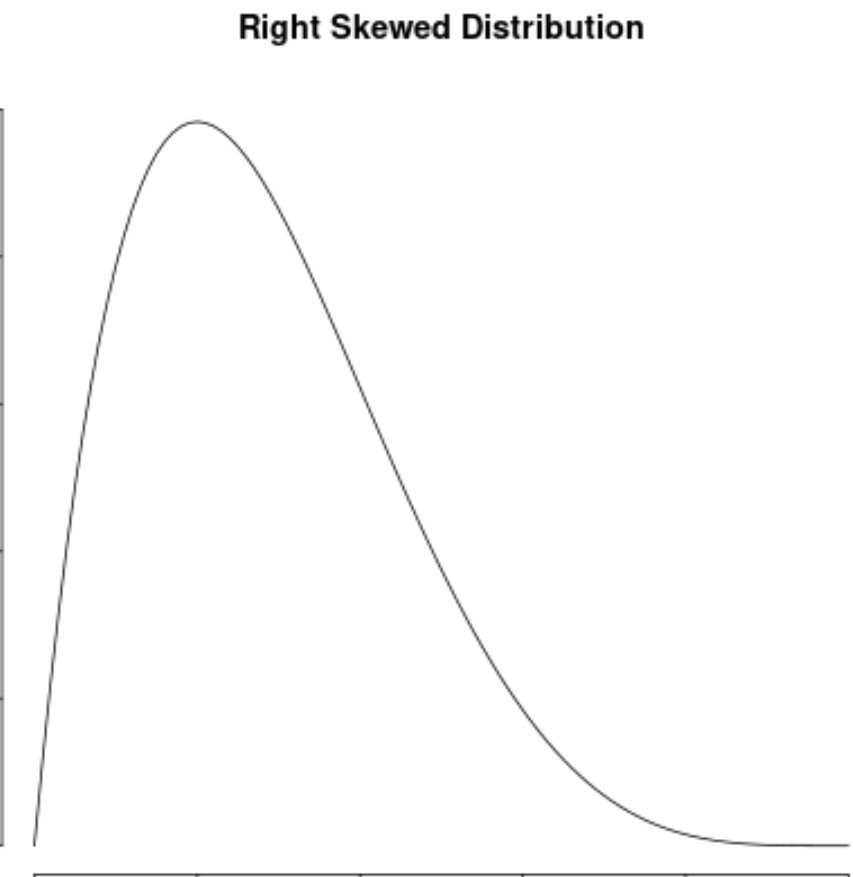
positive skewed distribution
when the outlier of data is on the right
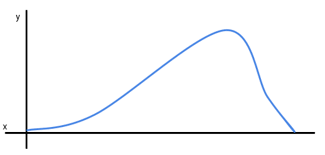
negative skewed distribution
when the outlier of data is on the left
standard deviation
computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean
example of standard deviation
If the IQ of a group’s standard deviation is 10 units, then most of the group will have an IQ about 10 units from the mean
small Standard Deviation
scores a concentrated and less scattered
variants
average of the squared difference from the mean
rad(variants) = Standard deviation
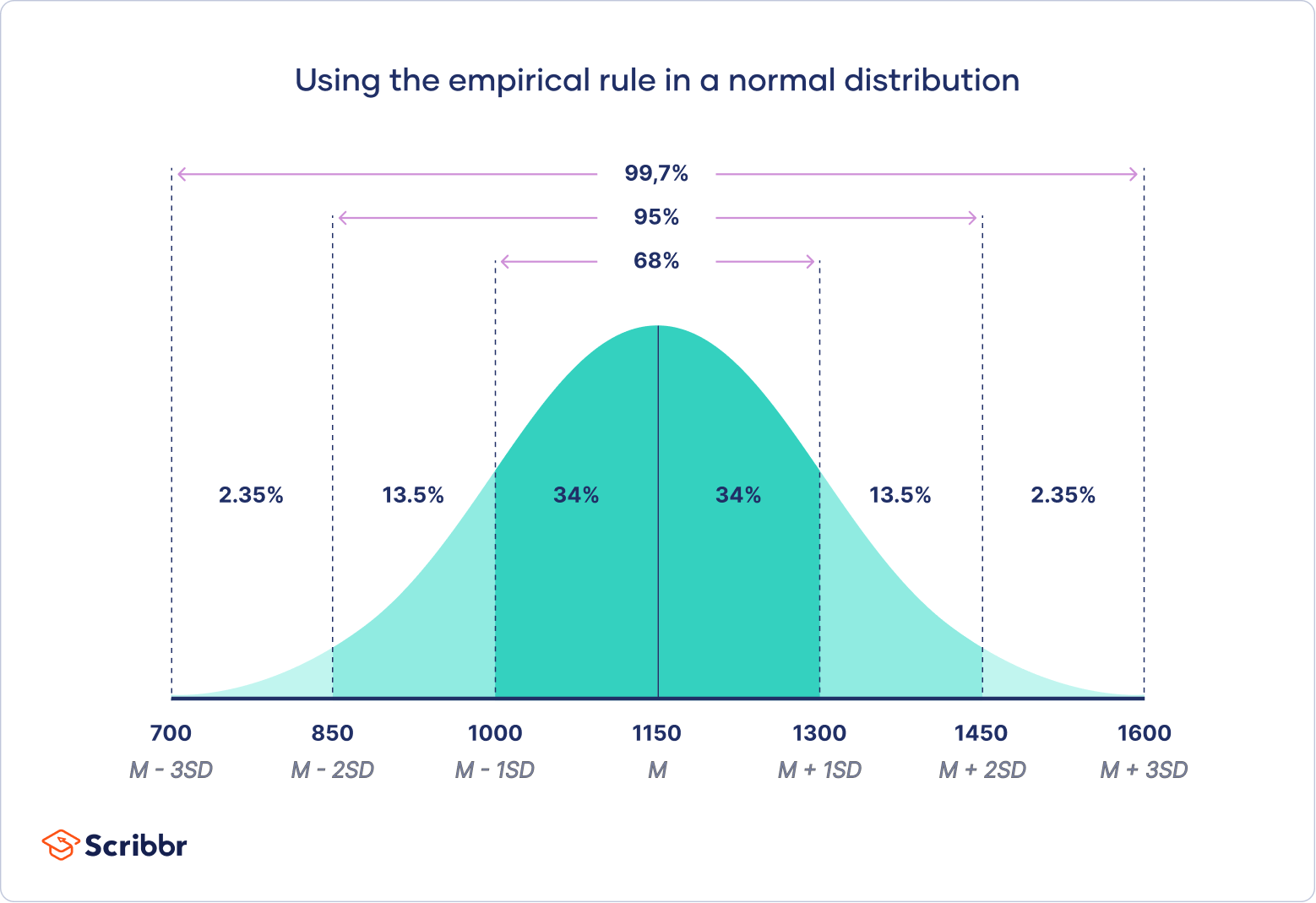
normal curve distribution
symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that described the distribution of data; most scores are near the mean with very few extremes
(68% fall within one standard deviation)
Normal distribution curve example: exam scores
mean = 80
standard deviation = 90-80 = 10
z scores
the number of standard deviations a value is from the mean of a given distribution.
normal distribution percentages
68%, 95%, 99.7%
When is an observed difference reliable?
people are proper representatives
small standard deviation (concentrated)
More cases can allow for generalization
Generalizations based on a few unrepresentative cases are ___________
unreliable
When is an observed difference significant?
when the sample averages are reliable and difference between them is relatively large
(experimental and control results contrast a lot)
statistical significance
likelihood that results happen by chance;
statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained results occurred by chance
research beyond a reasonable doubt means that the odds of an outcome’s occurrence by chance are less than ________
5% or .05
Example of statistical significance
When testing a new speech therapy to an established technique (control), the p-value was 0.032. This statistical statement shows how likely results occurred by chance.
statistical significance does not equal
practical significance
what is practical significance
the likelihood of something to occur in real life.
Example of stat. sig. not being practical sig.
Study on aspirin: It can lower the chances of heart attacks (statistically proven). But people still got heart attacks. Just because the numbers say taking aspirin will lower chances of heart attack, other factors play a role like sleep, exercise, and minimizing stress.
Type 1 error
concluding a difference when there is none (false positive)
Type 2 error
conclude no difference when there is one (false negative)
example of type 1 error
when taking a pregnancy test, a couple believes they are pregnant when they are actually not
example of type 2 error
After a COVID test, it states that a person does not have COVID when they actually do.