Language acquisition 1
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
what are the skills involved in learning a language?
association
generalisation/extension
recognition
retrieval
in what ways is language acquisition learning patterns?
look for which sounds fit together to make a word
look for which word-types fit together in which order
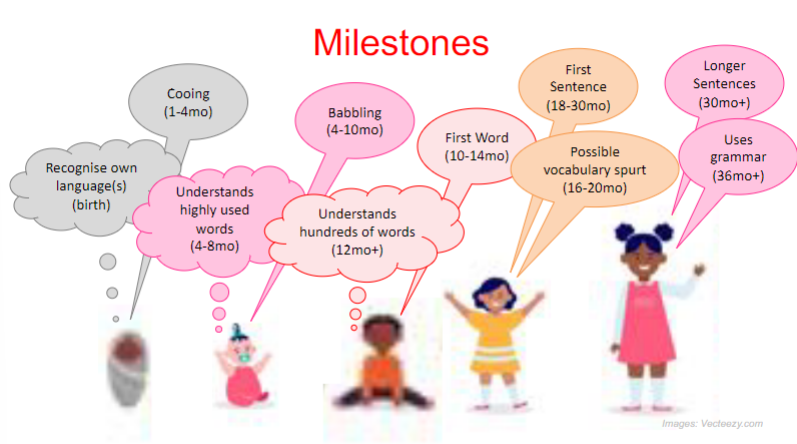
what are the key milestones for language acquisition?
recognising own language (birth)
understands highly used words (4-8 months)
first word (10-14 months)
first sentence (18-30 months)
what is comprehension?
understanding what others say (or sign or write)
precedes production
what is production?
speaking (or signing or writing) to others
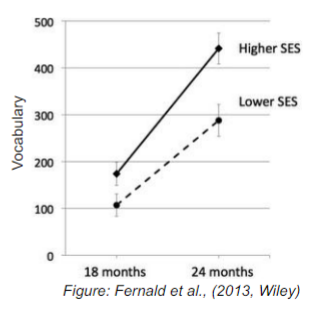
how does socio-economic status affect early vocabulary growth?
at 18 months, children from low SES backgrounds produce fewer words (word gap)
children from low SES backgrounds produce less complex sentences
by 24 months there is a 6 month language gap between SES groups
what is the Matthew effect?
“the rich have become richer, and the poor have become poorer”
term was popularised by Stanovich
gaps between groups will widen over time
key aspects of prenatal language recognition
foetuses can hear from 15-18 weeks
sounds are muffled in the womb → later, infants prefer muffled sounds
which voices and languages to infants prefer?
prefer their mother’s voice
parents over strangers
own language(s) over another
describe the results of study by DeCasper & Spence (1987)
foetus and infants can learn and recall cadence (and learn contingencies)
how do infants know where the breaks are between words?
pitch
pauses
adults talk slower to infants
sounds that occur together often are more likely to be from the same word (transitional probability - patterns)
statistics??
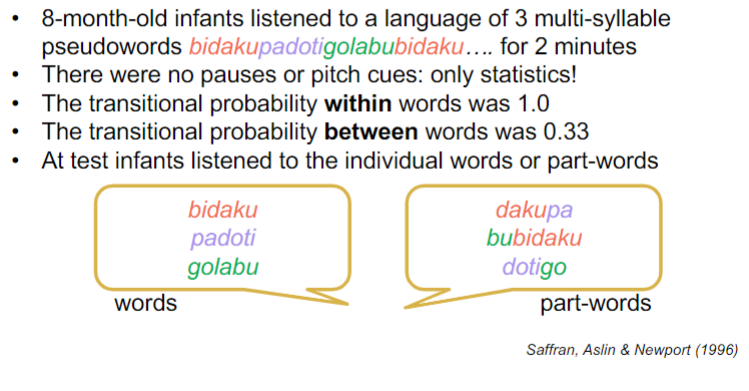
describe the results of Saffran, Aslin, and Newport (1996)
infants can segment speech
infants preferred the part-words
they could distinguish between words and part-words
they can use statistical regularities/patterns to learn language
what is infant directed speech (IDS)?
speech that has characteristics that help children isolate words
what are the characteristics of infant directed speech?
higher pitch (observed across languages)
wider range of pitch
exaggerated intonation
simple structure
highly grammatical
slower speed
lots of repetition
exaggerates differences between vowels (this is observed across languages)
what is the effect of infant directed speech on segmentation?
aids segmentation
when presented with identical speech streams, 7 month old infants learned words significantly better if IDS was used (Thiessen, Hill & Saffran, 2005)
effects of child directed speech
Children who hear more CDS have larger
vocabularies (Schwab & Lew-Williams, 2016)Parents adjust their speech based on words they
think their children do not know (Leung, Tunkel & Yurovsky, 2021)5yrs understand sentences better in CDS (Foursha-
Stevenson et al., 2017)CDS even helps adults learn words in a new
language (Ma et al., 2020)
key milestones in infant word recognition
4.5 months - recognise their own names
6 months - understand the words ‘mummy’ and ‘daddy’
6-9 months - show understanding of some words for familiar objects
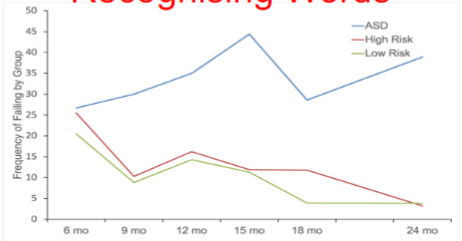
describe the results of the study by Miller et al. (2017)
orient name task - children with more repeated failures were diagnosed with ASD earlier than other children with ASD
differences in monolingual and bilingual children in language acquisition
develop similarly
macrostructure shows flexibility and robustness of language acquisition
microstructure may give insights into how children learn language?
how does categorisation influence language?
most of the input children hear is for categories (nouns)
most early vocabularies are words for solid, shape-based categories with count noun syntax
describe the results of the study by Samuelson (2002)
children trained on shape categories developed a precocious shape bias
children trained on shape categories even over-generalised the shape bias to non-solid substances
children trained on material categories did not develop any bias
shape-bias is a product of word learning
