lecture 4- laminin and integrins
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
laminin is major component of BM that self assembles into network to present binding sites for cells
laminin is high molecular weight glycoprotein(800kDa)
after collagen IV, laminin is most abundant BM protein
originally isolated from tumour in rodents. made of basement membrane components
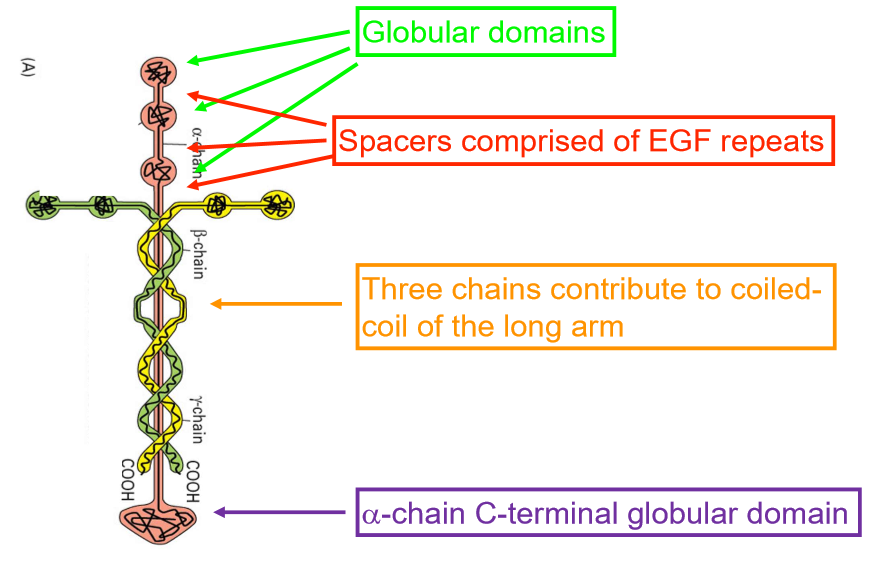
crucible structure

laminin made of 3 chains into crucible structure
3 separate polypeptide chains
alpha c terminal makes globular domain
coiled coil, different from collagen
each chain made of alpha helix
alpha helices wrap together to form long arm
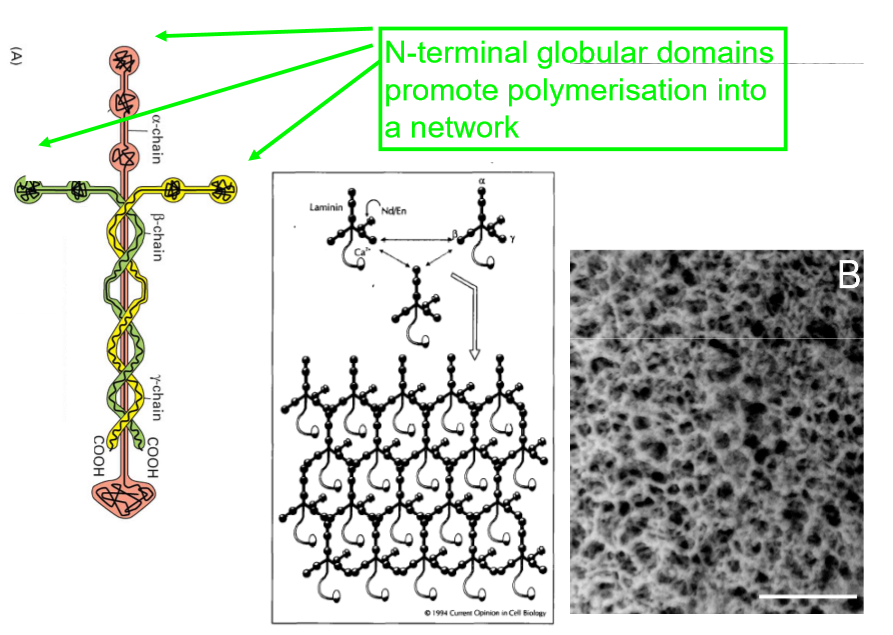
laminin 1 spontaneously forms a network in vitro
self assemble into network of laminin molecules interacting with other laminins
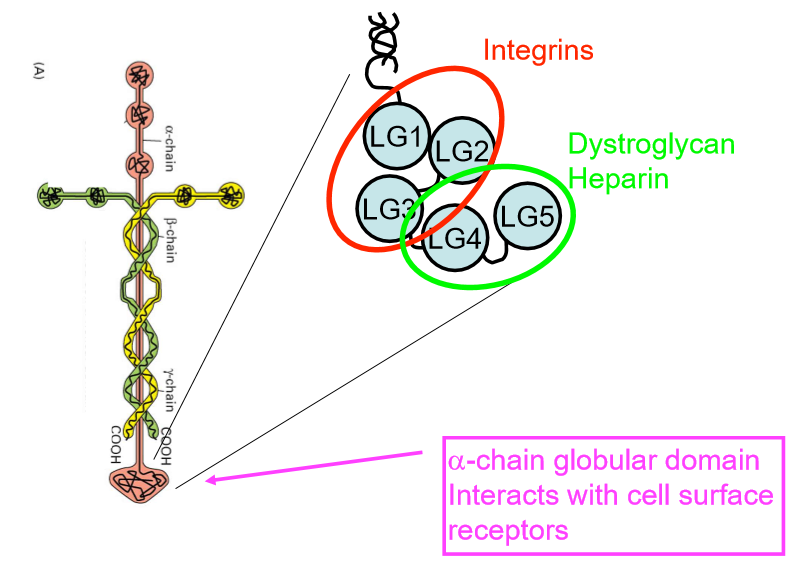
alpha chain golbular domain contains 5 LG domains that interact with cell surface receptors
5 subdomains which are binding sites for different cell surface receptors
3D structure assemble into network, cell binding sites stick out
laminin network is linked with collagen IV network by accessory molecules
laminin form binding sites
collagen is foundation
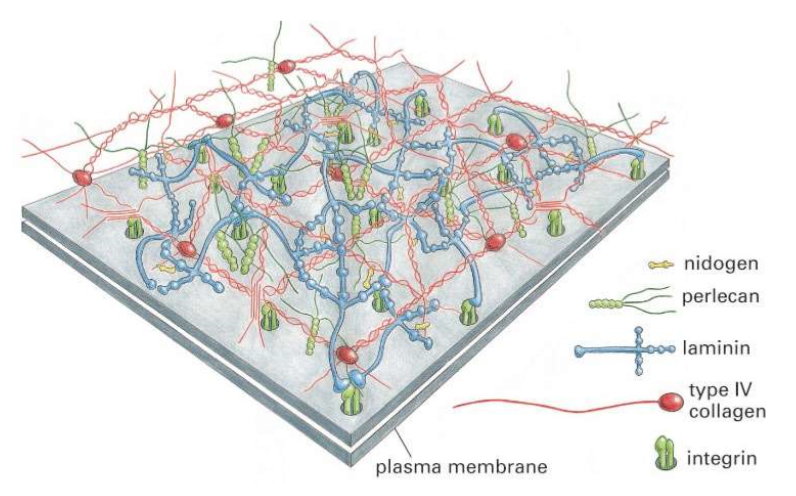
many laminin genes but only limited number of trimers are formed
11 laminin genes form 15 different heterotrimeric combinations
more laminin isoforms than collagen IV isoforms
more variability
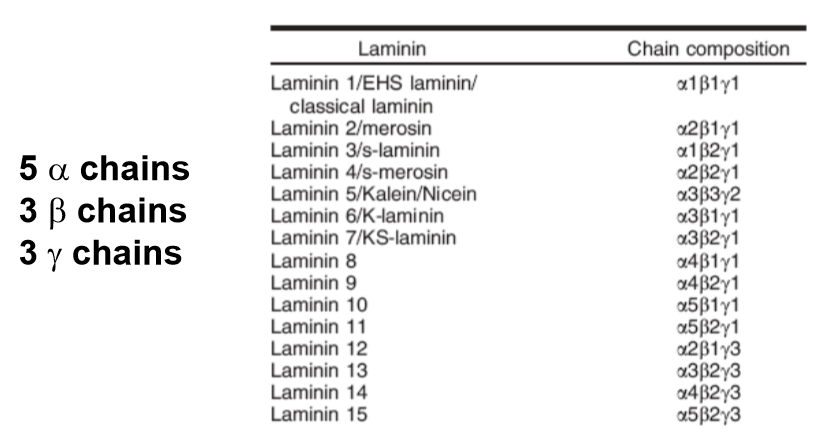
different laminin isoforms show tissue specific expression
some are widely expressed, in early embryos
mice unable to develop where basement membrane forms
other laminin genes show tissue specific defects when they are deleted in mice, phenocopy some human diseases
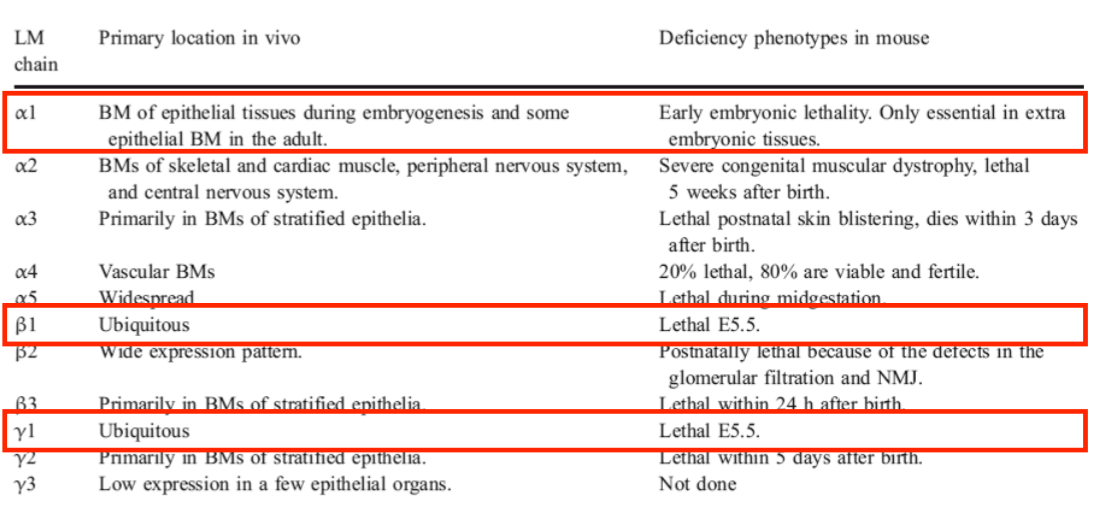
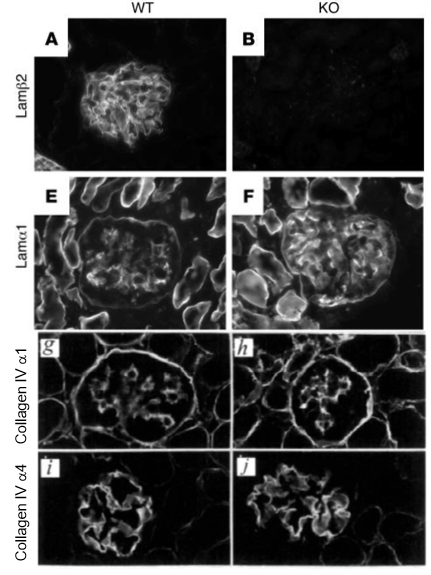
loss of laminin beta 2 isoform leads to similar condition as loss of GBM collagen IV isoforms
pierson syndrome- rare lethal condition
congenital nephrotic syndrome progressing to end stage renal disease
eye abnormalities
sever muscular hypotonia
laminin 11(alpha5beta2gamma1) expressed in GBM, eye and synaptic BM, explains disease phenotype
frame shift mutation
glomeruli don’t filter properly, similar to alports
affecting tissue where laminin trimer has key role
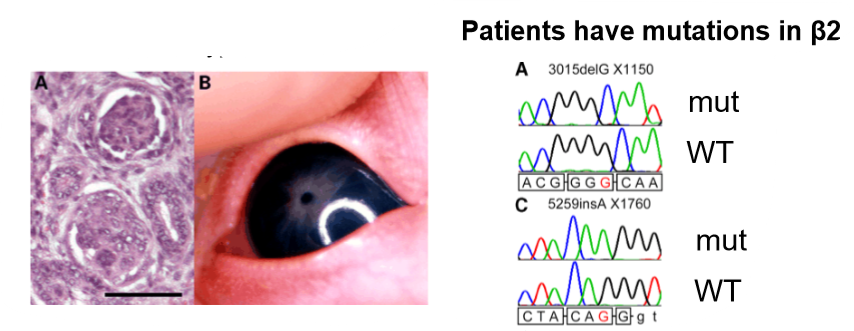
mice deficient for laminin beta 2 gene phenocopy pierson syndrome
beta 2 deficiency GBM shows beta 1 chain expression
GBM contains wrong laminin isoform, can’t form effective filtration barrier
collagen IV not affected
laminin in glomerular BM doesn’t provide filtration barrier
need to be in right isoform to have functional filtration
specific laminin isoforms in epidermis link to underying collagen in dermis
epidermis is attached to underlying dermis via basement membrane
mechanically strong
epidemolysis bullosa- group of conditions where skin blisters following mechanical trauma, mutations affect mechanical strength of dermal/epidermal junction, position of the break depends on genetic defect
3.5kg of skin held on by laminin sticking to integrin
severity of blistering depends on where it happens
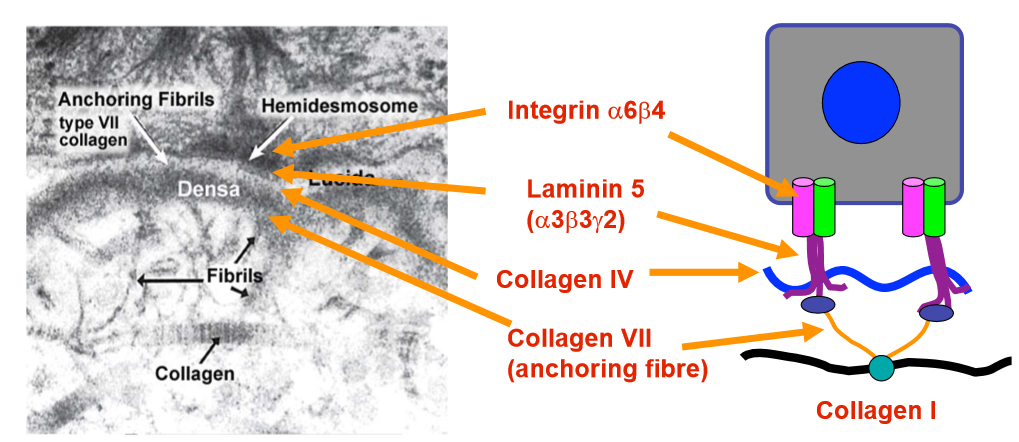
laminin 5(alpha3, betas3, gamma 2) in skin BM
links cell surface adhesion proteins in structures called hemidesmosomes to underlying collagen
collagen VII are anchoring fibres that link BM to the collagen I network in dermis
collagen VII is specific to basement membranes
collagen VII is out of BM, links to collagen I fibres in dermis
hemidesmosomes- dense patches, cell surface receptors are clustered, attach to cytoskeleton
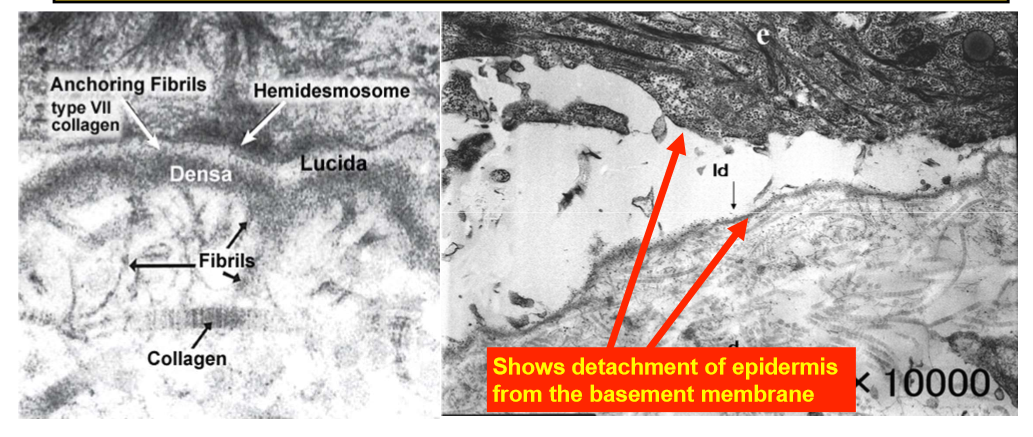
laminin 5(a3, b3,y2) mutations cause junctional EB
complete loss of any laminin V chain leads to herlitz type JEB, lethal within the first few months after birth
other mutations with pertubed laminin 5 function leadws to milder forms of condition
autosomal recessive conditions
no laminin in epidermis, skin has no mechanical strength, lifts off dermis
non-herlitz is partial loss of function mutation, can survive but severe blistering
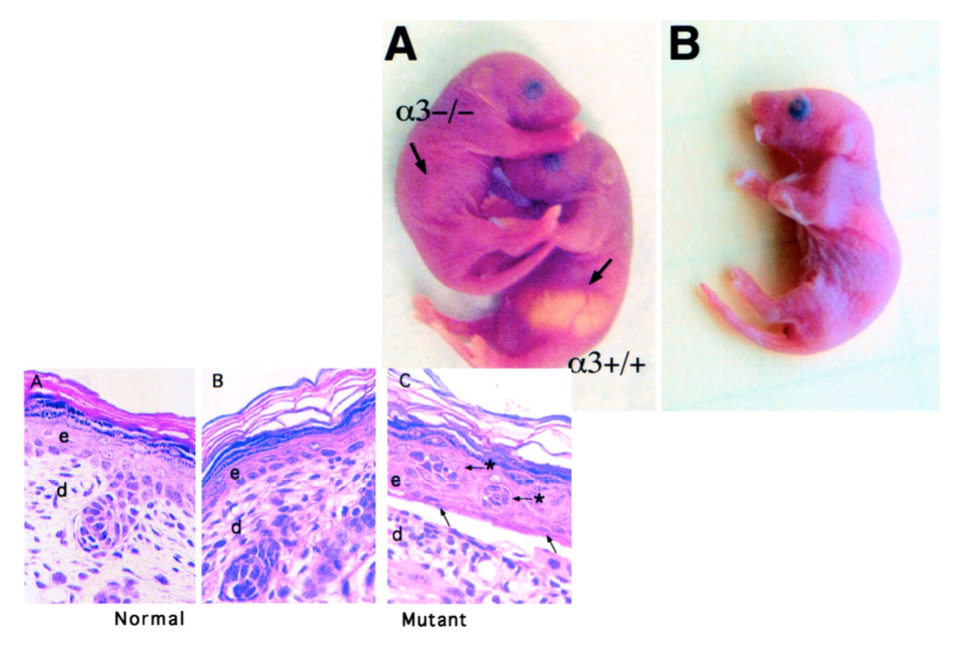
genetic models in mice prove that loss of laminin 5 causes junctional EB
laminin 5 deletion in mice phenocopies herlitz JEB
no difference at birth
develop blisters post natal
die by day 3
knockout one critical gene for mice
shortly after birth, mouse dies, dehydrates
important to have mechanical connection
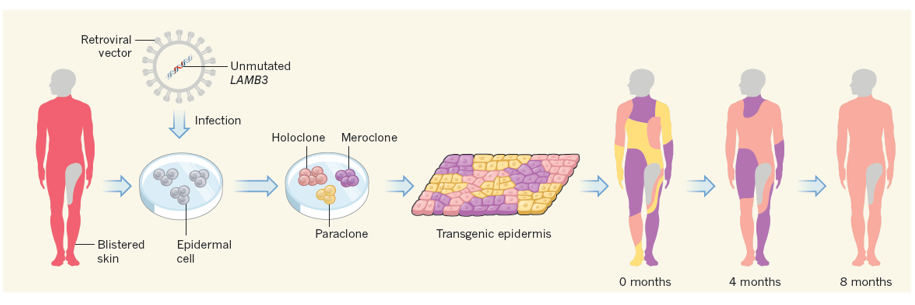
gene therapy for laminin beta 3 chain mutations
7 year old with splice site mutation in exon 14 of LAMB3
suffered severe blisters since birth, presented at hospital following S aureas infection, loss of 60% of epidermis
used retrovirus to deliver functional LAMB3 gene to patients own keratinocytes
holoclones are proliferative and contain stem cells
after 8 months skin was almost entirely derived from holoclones
skin repopulated by holoclones(stem cell regions)
replaced defective laminin with functional gene
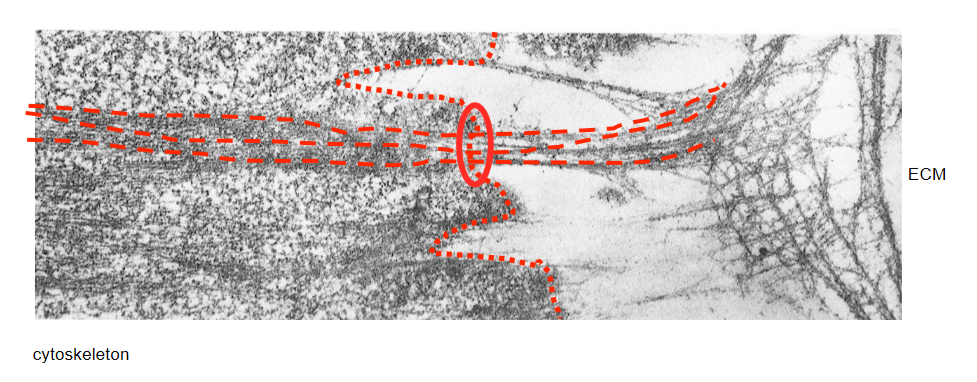
cell surface receptors for laminin link epidermal cells to BM
cell-ECM junctions in skin
structural links between cytoskeleton and matrix
provides physical strength to tissues
continual linkage
everything in cell mechanically connected
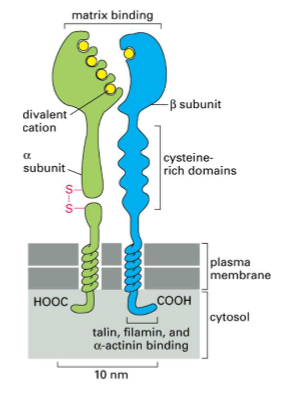
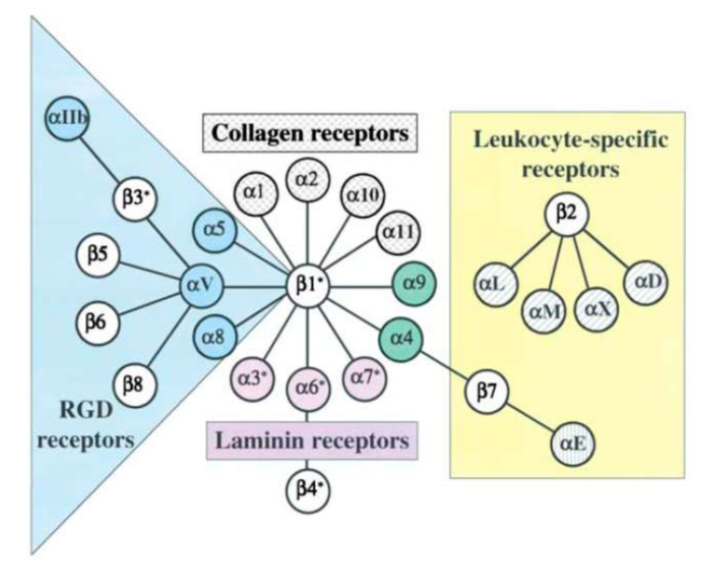
integrins
they are cell/ECM adhesion receptors on most cells
heterodimers of alpha and beta subunits
large extracellular domain
single transmembrane spanning domain
short cytoplasmic domain( exception in beta 4)
2 legs go to plasma membrane
alpha and beta subunits specifies what integrin it will bind to
very short tail that will connect to cytoskeleton
alpha and beta subunits
numerous alphabeta heterodimers
distinct and overlapping specificity for different ECM
RGD(Arginylglycylaspartic acid) receptors interacts with ECM glycoproteins
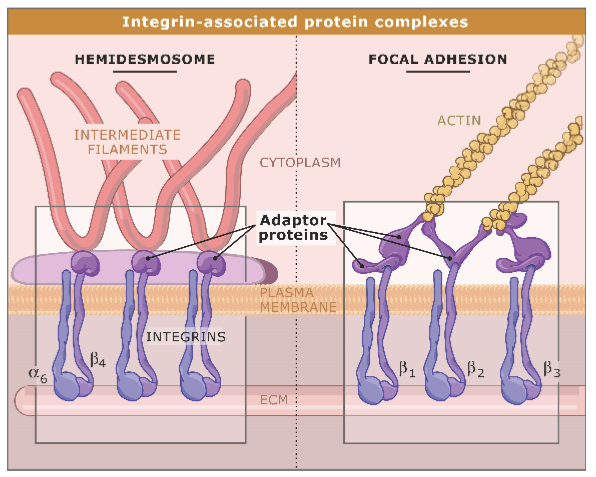
integrin cytoplasmic domain and cytoskeleton
most integrins associate with actin
in hemidesmosomes, link to intermediate filaments made of keratin
keratin is imporant for epidermolysis bullosa
connect ECM with cytoskeleton
integrin binds to actin
keratin fibres used to resist mechanical force
tissue specific distribution of beta integrin isoforms
integrin is tissue specific
beta 1 expressed in early embryos

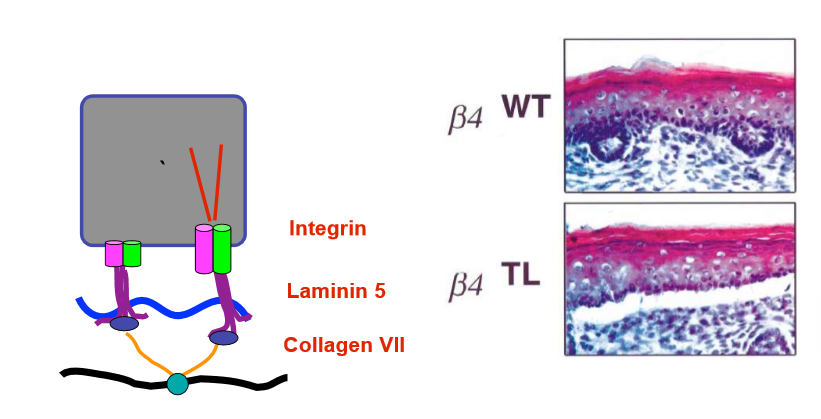
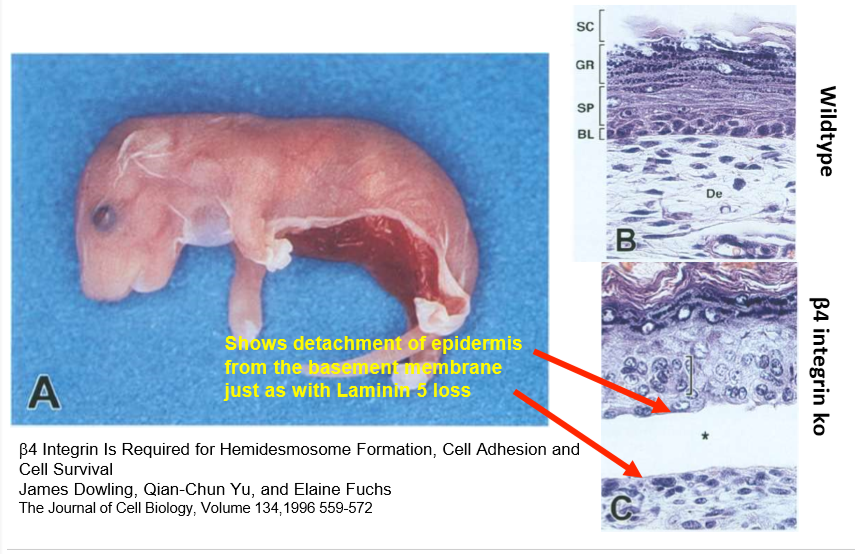
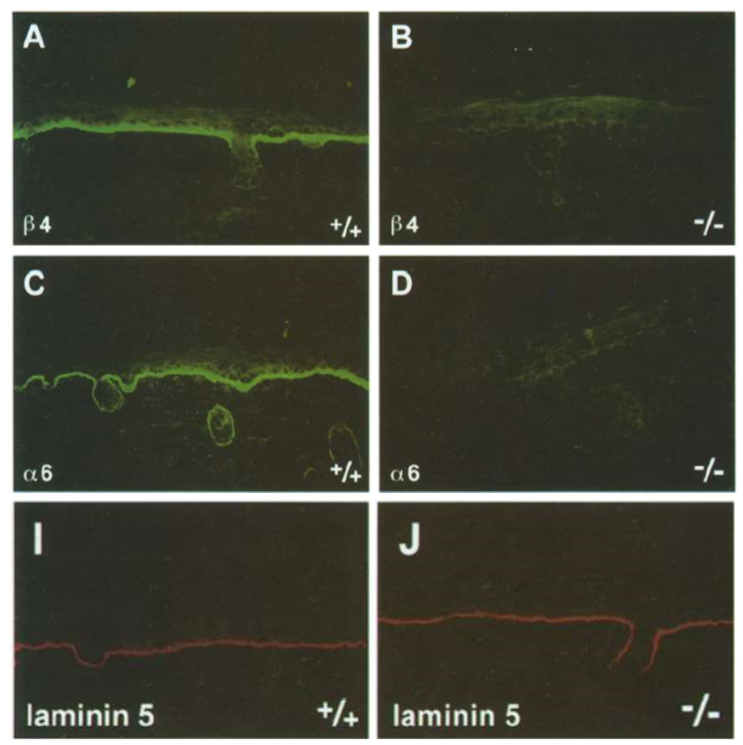
hemidesmosome specific beta 4 integrins are required for integrity of the skin
deletion of beta 4 integrins leads to same phenotype, like laminin 5 deletions
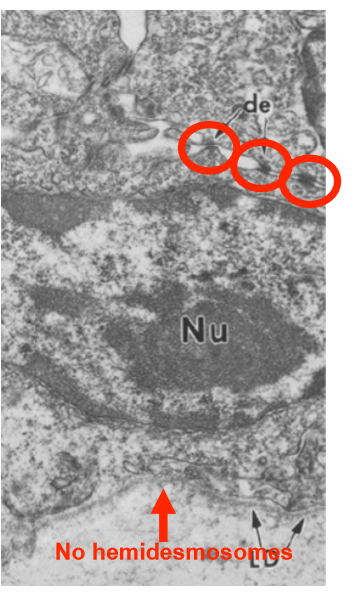
loss of beta 4 integrin in mice
leads to loss of hesmidesmosomes, but not cell/cell adhesions that link to IF
not attaching to basement membrane, whole sheet comes off
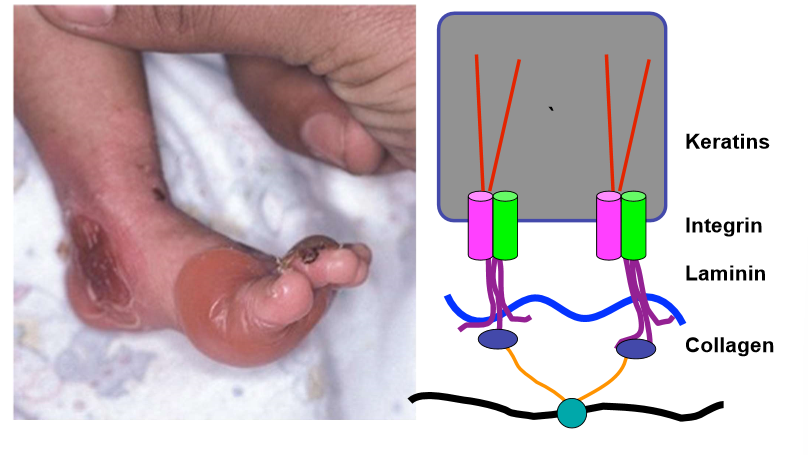
junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia (PA-JEB)
rare autosomal recessive condition associated with loss of a6b4 integrin
neonatal mucocutaneous blistering and gastric outlet obstruction through loss of function in GI, genitourinary and respiratory epithelium
can also lead to atresia- problem with digestive tract
disease is fatal
PA-JEB patient with 2 distinct mutations in beta 4 integrin alleles
paternal mutation leads to shift in open reading frame, downstream premature termination codon
maternal mutation leads to donor splice site, in-frame exon skipping
loss of beta 4 can lead to absence of alpha 6 integrin subunit
loss of alpha 6 integrin expression
formation of basement membrane still occurs, presence of laminin 5
able to make basement membrane, but unable to attach
tissue specific distribution of alpha integrin isoforms

deletion of alpha 6 integrin has same affect as loss of beta 4 in mice and humans
loss of chain, same as loss of lamina
EB simplex has milder phenotype than other forms of EB
usually restricted to blisters on regions subject to mechanical stress
can deal without significant scarring
compare with JEB, has 40% mortality in first year
mostly associated with mutations in keratin 5 and 14
deletion of beta 4 cytoplasmic tail in mice results in EB simplex
cells are weakened internally, but BM is intact
cells rip apart leaving part still attached to BM via integrin
49 year old with heterozygous 2bp deletion in ITGB4 leads to skipping exon, leads to 50 amino acid deletion in cytoplasmic domain, integrin binds to IF cytoskeleton