energy and voltage in circuits
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
define series circuit
components are connected one after the other
same amount of current flows through each component
if one component breaks the whole circuit breaks
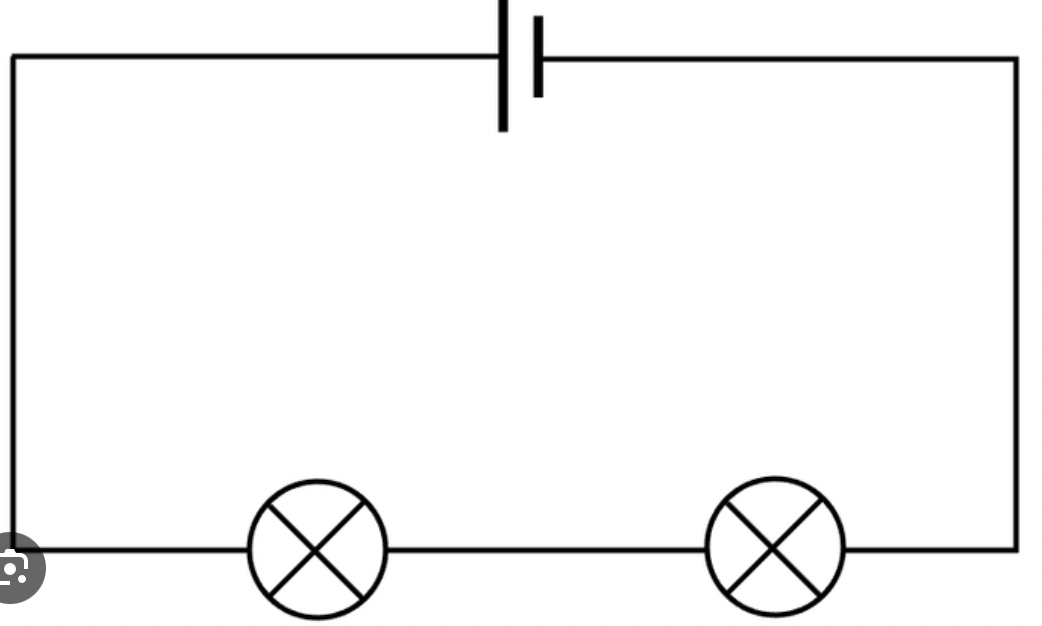
define parallel circuit
components that are connected on different branches
voltage is same
if one component breaks the others can still work
what is the trend between voltage and current
directly proportional (if voltage increases that means the current increases)
what is the formula for current
voltage / resistance.
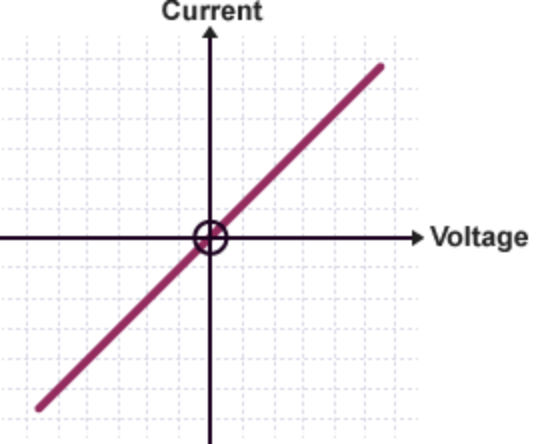
what is the current and voltage characteristic for wires
current is directly proportional to the voltage
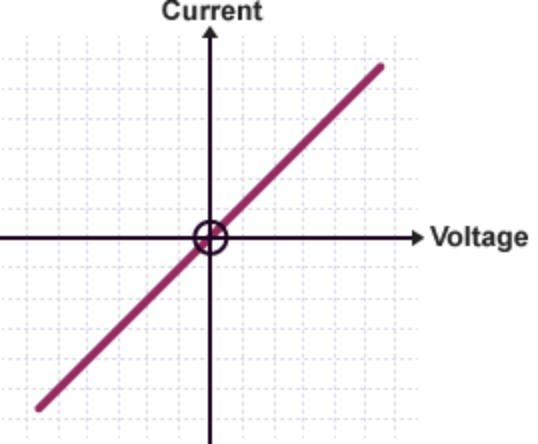
what is the current and voltage characteristic for resistors
current is directly proportional to voltage if the temperature is constant.
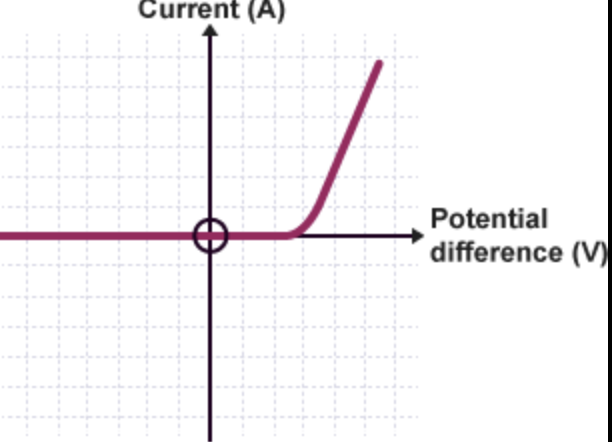
what is the current and voltage characteristic for diode
there is no current until the voltage is 0.6 or above.
what is the current and voltage characteristic for metal filament lamp
the temerpature increases the resistance increases making the current change (that’s why there is a curve)
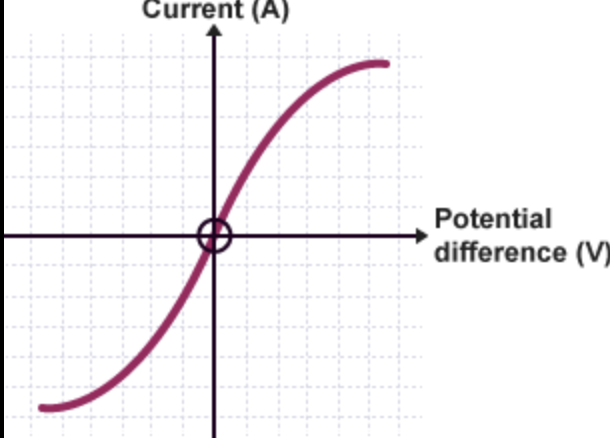
how would you investigate the current-voltage characteristic
use variable resistor (changes the voltage)
voltemeter (measures voltage)
ammeter (measures the current)
use them in a circuit, ammeter in the series and voltmeter In the parallel circuit. and the variable resistor in the series. And component that you are testing in series. Then measure the readings.
if resistance is higher what does that mean for the current
current would decrease
define LDR
(light dependant resistor)
when light shows = lower resistance = more current
when light doesnt show = more resistance = lower current
used in street lights
define thermoister
a resistor that decreases or increases based on temperature.
when at higher temperature = lower resistance = more current
when at lower temerpature = higher resistance = lower current
used in thermostats
how would you know if current Is present in a circuit
When a filament Lamp or LED lights up, it shows that current is flowing throughout the circuit and also shows that it is complete.
what is the ohms law
if resistance increases, the current and voltage will decrease.
what is the formula for ohms law
V = I x R
V = voltage
I = Current
R = resistance
what is current the rate of
charge, current shows you how much charge passes at a point per second.
what is the formula for charge
charge = current x time
what happens to the current when it goes through a metal wire
the current gets carried by the negatively charged electrons
what happens to the current when it meets a junction (when a wire splits into two)
current is conserved, meaning you cannot lose or create current. So if a wire has 5A and it splits into two, one wire might be 3A and the other might be 2A. In total it will be 5A
is the voltage in each branch of a parallel circuit the same or different from the voltage supply
the voltage in each branch is the same from the voltage supply in a parallel circuit.
For example if the voltage supply is 6V, each branch will receive 6V
define voltage
voltage is the amount of energy transferred of a charge as it moves through a component.
since voltage = energy of charge
1V = 1J per C
what is the formula for energy transferred
E = Q X V
E= energy transferred
Q= charge
v = voltage