Product Design WJEC- textiles key info
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/133
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
1
New cards
What is CAD?
Computer Aided Design
2
New cards
What is CAM?
Computer Aided Manufacturing
3
New cards
What is CNC?
Computer Numerical Control
4
New cards
What does CNC do?
Automated control of machinery.
5
New cards
Name 3 advantages of CAD
- Saves time and improves accuracy.
- Higher quality piece of work produced.
- Can be easily shared.
- Doesn't take up a lot of room.
- Links to CAM.
- Can easily be edited.
- Higher quality piece of work produced.
- Can be easily shared.
- Doesn't take up a lot of room.
- Links to CAM.
- Can easily be edited.
6
New cards
Name 3 advantages of CAM
- Faster and more accurate than manual work.
- Creates complex designs.
- Cost efficient over time
- Can produce identical products
- Eliminates costly errors.
- Creates complex designs.
- Cost efficient over time
- Can produce identical products
- Eliminates costly errors.
7
New cards
Name 3 disadvantages for CAD/CAM
- Can be expensive especially start-up costs
- They can require servicing/maintenance.
- Training will be required in order to use.
- Upgrades may be required.
- Will still need worker watching/doing process.
- They can require servicing/maintenance.
- Training will be required in order to use.
- Upgrades may be required.
- Will still need worker watching/doing process.
8
New cards
What is CIM?
Computer Integrated Manufacturing
9
New cards
What does CIM do?
CIM refers to the use of computers during manufacturing process like CNC.
10
New cards
What are some advantages of CIM?
- Increases pace of manufacturing
- Automates the process (efficient)
- Manufacturing will become less error prone.
- Automates the process (efficient)
- Manufacturing will become less error prone.
11
New cards
What is Digital Technology?
Any form of media that uses electronic devices for distribution.
E.g. Software, Videos, Cookies, Social Media etc.
E.g. Software, Videos, Cookies, Social Media etc.
12
New cards
What is Rapid Prototyping?
The fast fabrication of a physical part, model or assembly using CAD.
13
New cards
Name 3 main methods used in Rapid Prototyping
- 3D Printing
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Stereo Lithography (SLA)
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Stereo Lithography (SLA)
14
New cards
Name 3 advantages of 3D Printing?
- Fast production.
- Easily accessible.
- High-quality, complex shapes can be achieved.
- Easily accessible.
- High-quality, complex shapes can be achieved.
15
New cards
What is SLS?
Selective Laser Sintering
High powered lased used to solidify powdered polymer.
High powered lased used to solidify powdered polymer.
16
New cards
What material can SLS be used in?
- Glass
- Metals
- Ceramics
- Metals
- Ceramics
17
New cards
What are some advantages and disadvantages of SLS?
✓ Very little waste produced
X It can be a time-consuming process
X It can be a time-consuming process
18
New cards
What is SLA?
Stereo Lithography
Laser beam to build up layers or liquid polymer that hardens with the laser light.
Laser beam to build up layers or liquid polymer that hardens with the laser light.
19
New cards
What is 1 advantages and 1 disadvantage of SLA?
✓ Quick method
✓ Complex shapes can be fragile
X Machinery is expensive
X Outcomes can be fragile
✓ Complex shapes can be fragile
X Machinery is expensive
X Outcomes can be fragile
20
New cards
Name some advantages of Rapid Prototyping
✓ Allows functionality testing
✓ Improved and increased use of involvement
✓ Reduced overall product development cost
✓ Shows any flaws of the design of the product
✓ Improved and increased use of involvement
✓ Reduced overall product development cost
✓ Shows any flaws of the design of the product
21
New cards
Name some disadvantages of Rapid Prototyping
X Lack of accuracy
X Requires skilled labour
X Key features can be missed or overlooked
X May be expensive
X Requires skilled labour
X Key features can be missed or overlooked
X May be expensive
22
New cards
What is Anthropometrics?
Study of human body and it's measurements relevant to the human body.
23
New cards
Give me an Anthropometric example using a chair.
- Ensure the back of the chair supports the spine
- Ensures adequate leg space
- Ensures adequate leg space
24
New cards
Why is Anthropometrics important to the Designer?
Knowing of the measurements, allows the designer to ensure the product fits target market.
25
New cards
Why is Anthropometrics important to the Manufacturer?
Products can be made effectively and efficiently ensuring the end product will be suitable for the market.
26
New cards
Why is Anthropometrics important to the User?
Product will be well received and not sent back.
27
New cards
What is Ergonomics?
The study of how equipment and furniture can be arranged in order for people to do various things more efficiently + comfortably.
Aimed to ensure design of product optimise performance, safety of user etc.
Aimed to ensure design of product optimise performance, safety of user etc.
28
New cards
What is a Softwood?
Include some examples
Include some examples
They come from coniferous trees and are fast to grow.
e.g. Pine, Cedar, Spruce
e.g. Pine, Cedar, Spruce
29
New cards
What are some advantages and disadvantages of Softwoods?
✓ Readily available
✓ Lightweight
X Not as durable
X Can warp
✓ Lightweight
X Not as durable
X Can warp
30
New cards
What is a Hardwood?
Include some examples
Include some examples
They come from deciduous trees and have a long grow back time.
e.g. Oak, Beech, Mahogany
e.g. Oak, Beech, Mahogany
31
New cards
What are some advantages and disadvantages of Hardwoods?
✓ Very durable
✓ Good natural finishes
X Expensive
X Difficult to work with due to its density
✓ Good natural finishes
X Expensive
X Difficult to work with due to its density
32
New cards
What are Manufactured boards?
Include some examples
Include some examples
Man-made materials also known as regenerated materials due to them being made from recycled materials.
e.g. MDF, Plywood, Chipboard
e.g. MDF, Plywood, Chipboard
33
New cards
What are Polymers and what 2 sections are they split into?
Plastic
1. Thermoforming Plastics
2. Thermosetting Plastics
1. Thermoforming Plastics
2. Thermosetting Plastics
34
New cards
What is a Thermoforming Polymer?
Include 2 examples.
Include 2 examples.
It can be reshaped when heat is applied multiple times.
e.g. Polypropylene, Polystyrene
e.g. Polypropylene, Polystyrene
35
New cards
What is a Thermosetting Polymer?
Include 2 examples
Include 2 examples
It can be reshaped when heat is applied ONCE.
e.g. Epoxy Resin, UF
e.g. Epoxy Resin, UF
36
New cards
What is a Ferrous Metal?
A metal that contains iron, is magnetic, and lacks resistance to corrosion.
37
New cards
What is a Non-Ferrous Metal?
A metal that doesn't contain any iron, is not magnetic, and is resistant to corrosion.
38
New cards
What is an Alloy?
A mixture of metals with an element to improve it's properties or aesthetics like Brass.
39
New cards
What are Stock Forms?
Standardised shapes and sizes that materials are bought and sold in e.g. Plywood being 1200x2400
40
New cards
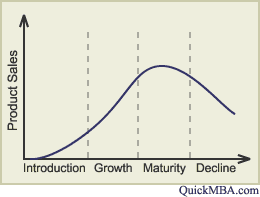
What are the 5 stages of the Product Life Cycle?
1. Introduction
2. Growth
3. Maturity
4. Decline
5. Obsolesce
2. Growth
3. Maturity
4. Decline
5. Obsolesce
41
New cards
What is the term used to extend a products life and describe it.
Extension Strategy - Product developed further to keep in market e.g. iPhone 13
42
New cards
What is a FAD Product?
Very short life, fast growth + fast decline e.g. fidget spinner.
43
New cards
What is Product Diffusion?
When a new product is introduced to different people and they will buy it over time.
44
New cards
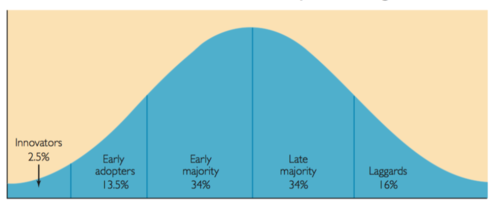
What are the 5 stages of Product Diffusion?
Describe them including %
Describe them including %
1. Innovators 2.5% = Well informed willing to take a risk and buy it 1st.
2. Early Adopter 13.5% = Wait a bit to ensure product sells and performs, still well informed.
3. Early Majority 34% = Product widely seen + tested, rely on communication.
4. Late Majority 34% = Product fairly common, they seem to be skeptical and will only but if needed.
5. Laggards 16% = Only adopt product if absolutely necessary.
2. Early Adopter 13.5% = Wait a bit to ensure product sells and performs, still well informed.
3. Early Majority 34% = Product widely seen + tested, rely on communication.
4. Late Majority 34% = Product fairly common, they seem to be skeptical and will only but if needed.
5. Laggards 16% = Only adopt product if absolutely necessary.
45
New cards
What are the 4P's?
Describe them
Describe them
Product = Includes design, packaging, quality
Price = Costs, discounts, margins
Place = Retail, market, distribution
Promotion = Advertising, sales, publicity
Price = Costs, discounts, margins
Place = Retail, market, distribution
Promotion = Advertising, sales, publicity
46
New cards
What is Market Pull?
When user wants a product to be improved or developed.

47
New cards
What is Technology Push?
When a new material is introduced which brings about a new product.

48
New cards
How have products developed over time?
Include some examples
Include some examples
The idea of improving certain products drastically.
Kettle:
1. Heated via a cooker
2. Now heated via a power supply (plug)
TV:
1. Had a massive box on the back
2. Now developed to thin flat screen
Kettle:
1. Heated via a cooker
2. Now heated via a power supply (plug)
TV:
1. Had a massive box on the back
2. Now developed to thin flat screen
49
New cards
What is a Standardised Part?
Parts used in production of products which are standard across a range of products (as well as manufacturers and even internationally)
50
New cards
What are some examples of Standardised Parts?
- Screws + bolts
- Hinges + handles
- Knock-down fittings
- Electronic components
- Hinges + handles
- Knock-down fittings
- Electronic components
51
New cards
What are 3 advantages of Standardised Parts
✓ Easily available/replaceable
✓ JIT - for deliveries
✓ Cheap - mass produced by someone else.
✓ JIT - for deliveries
✓ Cheap - mass produced by someone else.
52
New cards
What are 3 disadvantages of Standardised Parts?
X Reliant on other company - JIT doesn't work
X Restriction on possibilities of design
X Ethical issues - made abroad = air miles/working conditions
X Restriction on possibilities of design
X Ethical issues - made abroad = air miles/working conditions
53
New cards
What is a bought-in components?
A component for a product or manufacturing process that's bought in from another company.
It has the same ads + disads as standardised parts.
It has the same ads + disads as standardised parts.
54
New cards
What is an Adhesive?
Used for permanent joints between similar + dissimilar materials
55
New cards
Name 3 different Adhesives and what they're used for?
1. Tensol Cement - Used for glueing acrylic to acrylic.
2. PVA - Used for glueing wood on wood.
3. Epoxy Resin - Two-part thermosetting plastic glue used for dissimilar properties.
2. PVA - Used for glueing wood on wood.
3. Epoxy Resin - Two-part thermosetting plastic glue used for dissimilar properties.
56
New cards
How have adhesives effected the automotive industry?
They use adhesives instead of welding because it can further improve the stiffness and strength of the vehicle.
57
New cards
Name 3 different types of Joining Methods.
- Welding
- Brazing
- Soldering
- Brazing
- Soldering
58
New cards
Name 3 different types of Fixing Methods.
- Nailing
- Extrusion
- Tube bending
- Extrusion
- Tube bending
59
New cards
What is Laminating?
Layers of material added together.
60
New cards
What is Combining?
Mixing a material together to form a composite material.
61
New cards
What are the 2 reasons for using surface finishing?
1. Improving the aesthetics of the product colour, shape.
2. Preservation and protection of the product from things like corrosion, fading.
2. Preservation and protection of the product from things like corrosion, fading.
62
New cards
What is Galvanising/Plating?
Explain why this is used
Explain why this is used
Process of immersing iron or steel in a bath of molten zinc to produce a corrosion resistant, multi-layered coating of zinc-iron alloy and zinc meta
63
New cards
What is Anodizing Aluminium?
1. Submerge metal in sulphuric acid, when electric current passes through oxygen forms creating 'anodic layer'.
The thicker the layer the longer resistance.
The thicker the layer the longer resistance.
64
New cards
What is Hot Blackening?
Where is this used.
Where is this used.
Oil motor oil + hot steel in a can, then let cool down.
Commonly used in automotive parts, tools and firearms
Commonly used in automotive parts, tools and firearms
65
New cards
What finish is suitable for Manufactured Boards?
Before any finish can be applied a primer needs to be applied as they will absorb the finish damaging the material.
66
New cards
What does a Varnishs do?
- Applied to give a shiny finish
- Increases durability on material
- Increases durability on material
67
New cards
What does Paints do?
Provides thick layer to protect material with a solid or transparent colour.
68
New cards
What do Enamellers do?
Layer of metal glass that, once heated it will fuse to metal surface.
69
New cards
Name 5 properties of materials and explain them.
1. Elasticity = Ability to return to its original shape once the forces deforming it are removed.
2. Durability = Ability for a material to withstand wear or damage.
3. Malleability = Ability to be formed or shaped without breaking.
4. Compressive Strength = Ability to withstand a compressive force without breaking.
5. Tensile Strength = Ability to withstand a pulling force without stretching.
2. Durability = Ability for a material to withstand wear or damage.
3. Malleability = Ability to be formed or shaped without breaking.
4. Compressive Strength = Ability to withstand a compressive force without breaking.
5. Tensile Strength = Ability to withstand a pulling force without stretching.
70
New cards
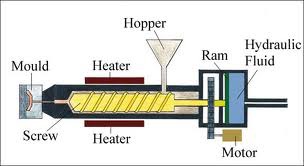
What is Injection Moulding explain the process?
Shaping of a product by injecting a heated material into a mould.
71
New cards
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Injection Moulding?
✓ Very high quality finish
✓ Suitable for mass production
X Expensive to setup
✓ Suitable for mass production
X Expensive to setup
72
New cards
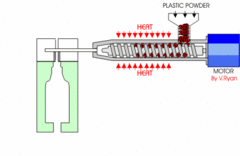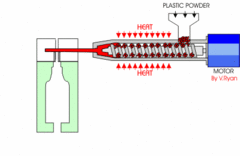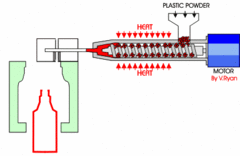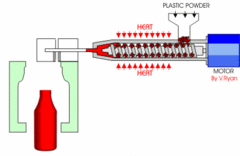
What is Blow Moulding explain the process and where it is used?
Often using HDPE the mould forms the bottle and the thread to which the lid screws on is...
73
New cards
What is Injection Blow Moulding?
1. Perform injection moulding for thread (full size) and small bottle sector.
2. Use blow moulding to put bottle into shape.
2. Use blow moulding to put bottle into shape.
74
New cards
What is Extrusion?
Include examples
Include examples
Melted plastic forced through a shaped hole (die) to produce long pieces of material with a consistent cross section.
e.g. Gutter, Piping
e.g. Gutter, Piping
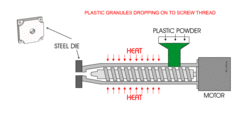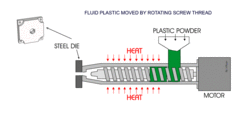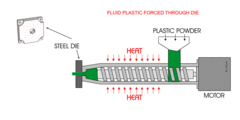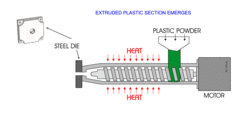
75
New cards
What is a JIG?
A device that guides a tool to a specific position.
76
New cards
What is Morphological Analysis?
Explores all possibility's to a problem or new idea.
77
New cards
What is the process of Innovation?
Introducing new and useful ideas and products to market place to add value.
78
New cards
What is Inversion?
Design strategy for turning problems around and approaching it from a different point of view.
79
New cards
What is Reverse Engineering?
Taking apart products to see how they work
80
New cards
What is Product Analysis?
Analyse and learn from existing/competitors products. Things include form, function, style, components.
81
New cards
What must Employees do in the workplace?
- Ensure that dangerous machinery/tools are stored away after use.
- Ensure workplace is clean and risk free to others.
- Ensure workplace is clean and risk free to others.
82
New cards
Why are there Safety Guards on some machines?
- Prevent employees from potential serious injury.
- Ensure that there are emergency stop buttons too.
- Ensure that there are emergency stop buttons too.
83
New cards
Why do workshops have Extractors?
To protect the employees or other people from the harmful dusts or fumes being extracted from the machines.
84
New cards
What is the Health and Safety at Work act (HASAW)?
To ensure all employees are safe and protected in their workplace.
85
New cards
What effect does this act have? (HASAW)
- Employees are obligated to use and supply safety equipment
- Employees could be criminally liable if don't follow regulations.
- Employees could be criminally liable if don't follow regulations.
86
New cards
What do some of these roles include (HASAW)?
- Wearing PPE
- Ensure all tools and securely put away after use
- Safe working environment
- Ensure all tools and securely put away after use
- Safe working environment
87
New cards
What is the Control of Substances Hazardous to health act (COSHH)?
This act states that all hazardous materials should be stored and used correctly and should form part of the company's risk assessment.
88
New cards
What is PPE?
Personal Protection Equipment
e.g. goggles, high-visibility jacket, helmet
e.g. goggles, high-visibility jacket, helmet
89
New cards
What is the electricity at Work Regulations Act?
The act states that fray cables should be replaced immediately (by professionals).
90
New cards
What is the point of Feasibility Studies?
They will determine whether or not a product is commercially viable.
91
New cards
What is the point of producing and testing prototypes?
- If product meets all spec points
- Check if the production process works
- Discuss with client
- Find physical employees
- Check if the production process works
- Discuss with client
- Find physical employees
92
New cards
What are some factors that can effect material costs?
- Ease of transportation
- Aesthetic values
- Durability
- Strength
- Aesthetic values
- Durability
- Strength
93
New cards
What are 3 environmental factors that companies try to do with their products?
1. Reduce their carbon footprint.
2. Selecting materials that are sustainably sources = recycled
3. Green energy = solar panels
2. Selecting materials that are sustainably sources = recycled
3. Green energy = solar panels
94
New cards
What is One-Off Production
A single unique product made by skilled workers
95
New cards
What is Batch Production?
Limited number of similar products manufactured using machinery.
96
New cards
What is Mass Production?
The production of goods in large quantities.
Very quick but high start up costs.
Very quick but high start up costs.
97
New cards
What is Continuous Flow Production?
24/7 mass production with quality control occuring.
98
New cards
What is an Intellectual Property?
The ownership of an idea or design that a person created.
99
New cards
What are the 4 different types of Intellectual Properties?
Explain each.
Explain each.
1. Trademarks = For brand, protecting distinctive reputations in names + logos.
2. Patents = For inventions, protecting function of new products and processes.
3. Registered Designs = For appearance, protecting unique look of parts or articles.
4. Copyright = For creative works, protecting literacy, musical and artistic works.
2. Patents = For inventions, protecting function of new products and processes.
3. Registered Designs = For appearance, protecting unique look of parts or articles.
4. Copyright = For creative works, protecting literacy, musical and artistic works.
100
New cards
Why are Intellectual Properties important?
Protect people from others stealing their work.