Unit 3
1/41
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
elastic deformation
temporary change, returns to normal
plastic deformation
permanent change, but doesn’t break
ionic solid
strong inter and intramolecular forces
high melting/boiling point
brittle
not conductive unless dissolved in water
molecular solid
formed by distinct molecules bonded together
strong intramolecular forces, weak intermolecular forces
low melting/boiling point
cannot conduct electricity
covalent network solid
formed by atoms bonded covalently in a 3d network
indicated by presence of B/Si/Ge + element, C + metalloid, or just C
high melting point
does not conduct electricity
metallic solid
sea of electrons keeps metal atoms together
malleable/ductile
good conductors of electricity
dipole-dipole interactions
between polar + polar, increased polarity strengthens
dipole-induced dipole
polar + nonpolar, temporary, electronegative atom of polar molecule repels electrons, creating partial positive charge
London Dispersion Forces
nonpolar + nonpolar, present in all IMFs, stronger with larger molecules b/c more polarizable
hydrogen bonding
H surrounded by F/O/N, type of dipole-dipole, strong
ion-dipole
negative from dipole connects with positive ion + vice versa
stronger IMF effect on boiling point, surface tension, heat of vaporization
boiling point- raised
surface tension- raised
heat of vaporization- raised
volatility
ease of evaporating, stronger IMF lowers
viscosity
resistance to flow, stronger IMF increases
vapor pressure
pressure exerted by a gas when it is at equilibrium with its liquid, stronger IMF lowers b/c liquid doesn’t evaporate as much
relative strength of intermolecular forces
h bonding > dipole-dipole > LDF (when molecules are similar sized); LDF more important when molecules are larger
effect of volume on pressure
as volume increases, pressure decreases; inversely proportional
effect of number of particles on pressure
less particles = less pressure
effect of temperature on pressure
higher temp = higher pressure
ideal gas law
(pressure)(volume) = (# moles)(R)(temp in kelvin)
r
0.08206 atm
8.314 kPa
partial pressure
pressure that each gas would exert if it was the only gas present in the container (mole fraction x total pressure)
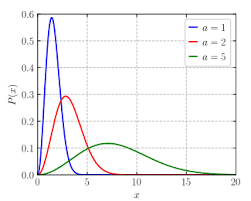
graph with same temperature but different masses
heavier molecules move slower and have a narrower distribution
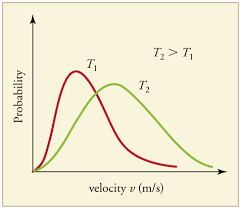
graph with same gas at different temperatures
higher temp = higher velocity = wider distribution
what makes a gas more ideal
higher temperature, lower pressure, weak IMF’s, smaller molecules (more attraction = less ideal)
positive pressure deviation
caused by non-negligible particle volumes (big particles = hit wall more often)
negative pressure deviation cause
stronger interparticle attractions (if they’re attracted to each other, won’t hit wall as often)
molarity
moles solute / liters solution
things to consider when drawing molecules
relative size, orientation (±), number (read directions)
distillate
the liquid that is collected after vaporizing a mixture and then condensing the vapor back into a liquid during the process of distillation (lowest boiling point)
chromatography
substances with similar polarity as mobile phase (liquid) will move further up, substances with different polarity to liquid won’t move as far
higher solubility
stronger interactions between solute + solvent molecules
lower Rf value
spot is lower on the plate/didn’t move as far
gas relationship between temp and solubility
as temp increases, solubility decreases
solid relationship between temp and solubility
temp increases, solubility increases
microwave radiation
rotates molecules
infrared radiation
vibrates molecules (move closer/further from each other)
ultraviolet/visible light
transitions in energy levels of electrons
ultraviolet wavelength
1-400 nm
visible light wavelength
400-750 nm
infrared wavelength
750 nm- 1 mm
microwave wavelength
1 mm- 1 m