Exam 3 - Plants
5.0(1)Studied by 3 people
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Last updated 1:56 AM on 4/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1
New cards
What was the main challenge that early plant life on land face?
Drying out
2
New cards
What adaptations allowed plants to colonize the land?
They adapted in ways that helped them avoid drying out, structural support, capturing sunlight, and dispersal of reproductive cells.
3
New cards
Identify the main characteristics of seedless nonvascular plants
They have alternating generations, they are often very short, They do not have “real roots” as their roots main function is anchoring the plant not absorption.
4
New cards
What are the three phyla of bryophytes?
\
Hepaticophyta (Liverworts), Anthocerotophyta (Hornworts), and Bryophyta (Mosses)
Hepaticophyta (Liverworts), Anthocerotophyta (Hornworts), and Bryophyta (Mosses)
5
New cards
What are the two different generations seedless plants have?
Sporophyte and gametophyte
6
New cards
What is the ploidy of the Gametophyte generation?
Haploid (n)
7
New cards
What is the ploidy of the sporophyte generation?
Diploid (2n)
8
New cards
What’s the difference between an extinct and existent species?
An extinct species is one that has lost all genetic heritage
9
New cards
What adaptations did nonvascular plants make to transition to vascular plants.
They grew a stem, roots and a vascular system.
10
New cards
What are the benefit of roots?
They help stabilize the plant, they also allow for more water an mineral absorbance.
11
New cards
What are the benefits of a stem?
Allows for the plant to grow taller which can let it get more sunlight, and spread it spores/pollen farther.
12
New cards
What are the main components of a vascular system?
Xylem and Phloem
13
New cards
What does the vascular system do in plants.
Moves water, minerals, and nurturance around the plant.
14
New cards
What is the function of Xylem?
Conduct water and minerals from soil up to the shoot.
15
New cards
What is the function of phloem?
Transport products of photosynthesis throughout the entire plant.
16
New cards
What are some examples of seedless vascular plants?
Horsetails and ferns
17
New cards
What are the two major innovations that allowed seed plants to reproduce in the absence of water?
Pollen and fruits
18
New cards
What is the propose of pollen?
It is the male gamete, and it is dispersed by pollinators or wind.
19
New cards
What is the poupous of seeds?
It is an embryo that is protected by a seed coat.
20
New cards
What are the two types of seeding plants?
Angiosperms and gymnosperms
21
New cards
What is significance of gymnosperms?
“naked seeds”, they lack flowers but they keep their seed exposed on a scale.
22
New cards
What is significance of angiosperms?
They are flowering plants.
23
New cards
What are the two types of angiosperms?
Monocots and eudicots
24
New cards
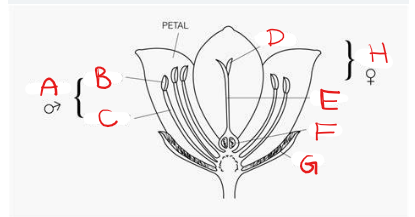
What is A?
Stamen
25
New cards
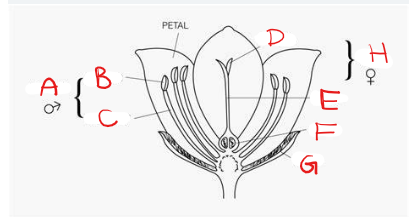
What is B?
Anther
26
New cards
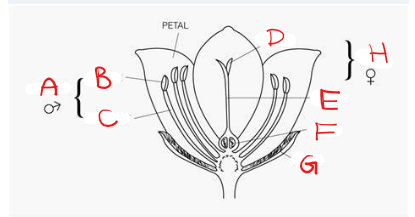
What is C?
Filament
27
New cards
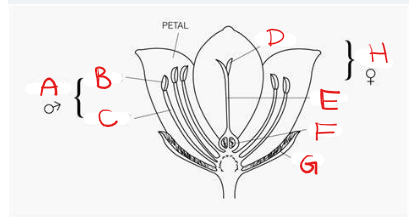
What is D?
Stigma
28
New cards
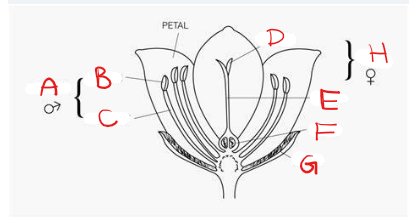
What is E?
Style
29
New cards
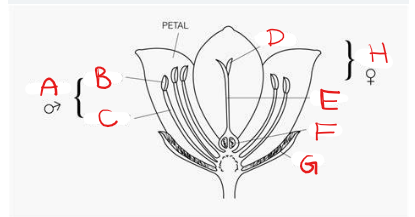
What is F?
Ovary
30
New cards
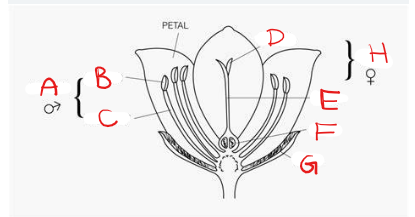
What is G?
Sepal
31
New cards
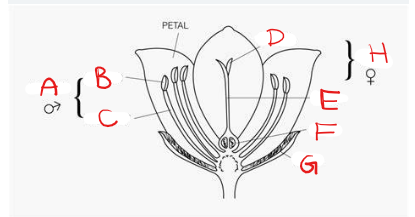
What is H?
Pistil
32
New cards
What is the difference in seed in monocots and eudicot?
Eudicots have multiple cotyledons while Monocots only have one.
33
New cards
What is the difference in leaf vascular system in monocots and eudicot?
Monocots have parallel vein structures, while eudicots have a network structure.
34
New cards
What is the difference in vascular systems in monocots and eudicot?
Monocots have scattered vascular systems while eudicots have a ring like structures.
35
New cards
What is the difference in petals in monocots and eudicot?
Monocots have sets of three petals, while eudicots have sets of four petals.
36
New cards
Dermal tissue
Involved in protection and gas/ion exchange
37
New cards
Vascular tissues
xylem and phloem
38
New cards
Ground tissues
metabolism, storage, and support \n activities
39
New cards
Where does primary growth (taller) occur?
Apical meristems (tips of root and stem)
40
New cards
Where does secondary growth (wider) occur?
Lateral meristems
41
New cards
What is the function of the stem?
supports the leaves, conduct water, and transports minerals from roots.
42
New cards
Nodes
Points of attachment for leaves, aerial roots, and flowers
43
New cards
Internodes
regions between two nodes
44
New cards
Petiole
stalk that extends from the stem to the base of the leaf
45
New cards
Axillary bud
usually found in the axil—the area between the base of a leaf and the stem—where it can give rise to a branch or a flower
46
New cards
Apical bud
The apex (tip) of the shoot contains the apical meristem
47
New cards
What are the functions of roots?
To anchor plants, absorb water and dissolved minerals, and storage
48
New cards
What are the two types of root systems?
Tap, and fibrous roots
49
New cards
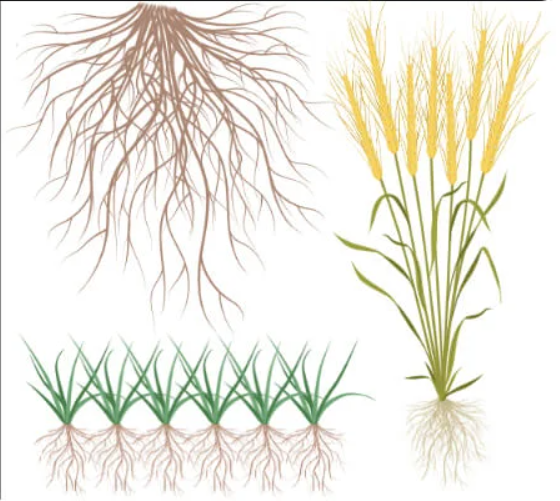
What type of root is this?
Fibrous Root
50
New cards
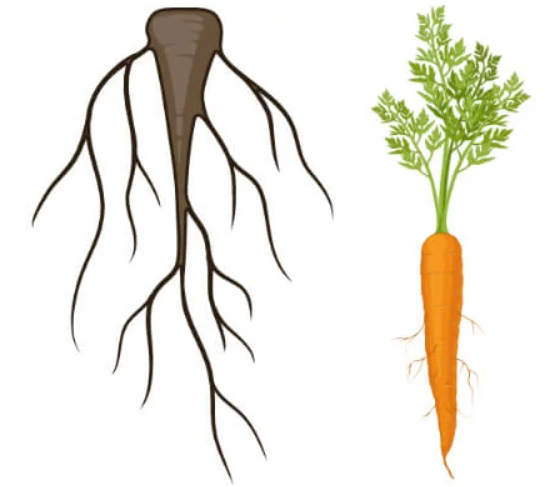

What type of root is this?
Tap root
51
New cards
What happens in the area of maturation?
Root hairs are grown
52
New cards
What happens in the area of elongation?
Cells in the root elongate
53
New cards
What happens in the area of cell division?
cell division and growth occurs here
54
New cards
What is the function of leaves?
photosynthesis, exchange of gasses, and transpiration
55
New cards
Lamina/leaf blade
widest part of the leaf
56
New cards
Petiole
The small stem that attaches the leaf to the stem.
57
New cards
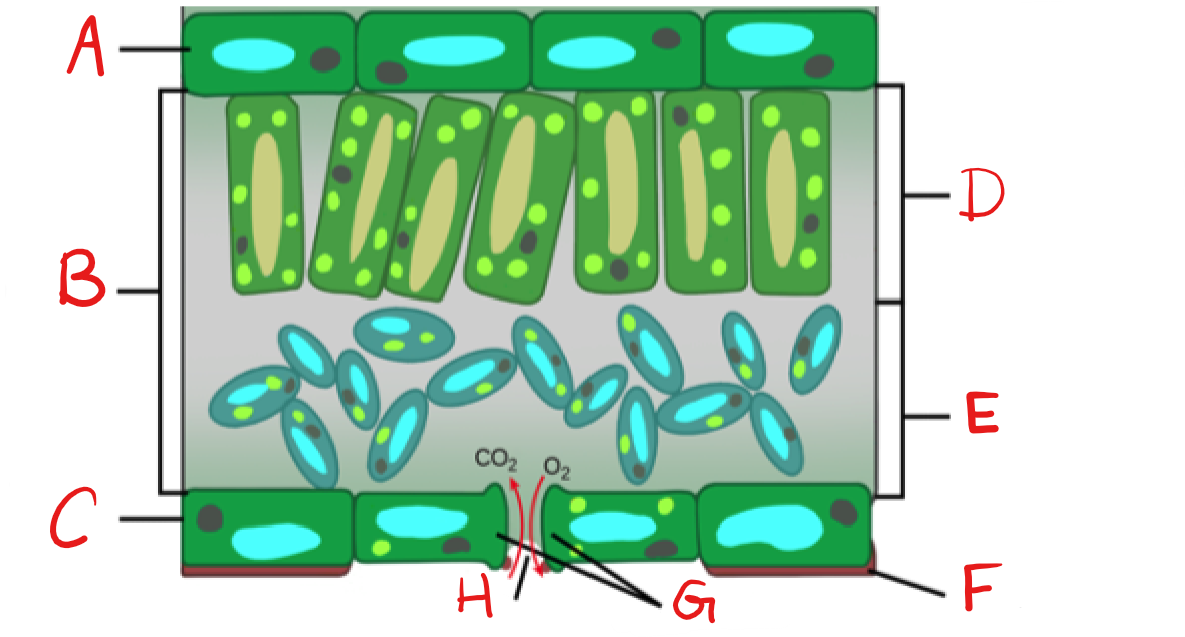
What is A?
Upper Epidermis
58
New cards
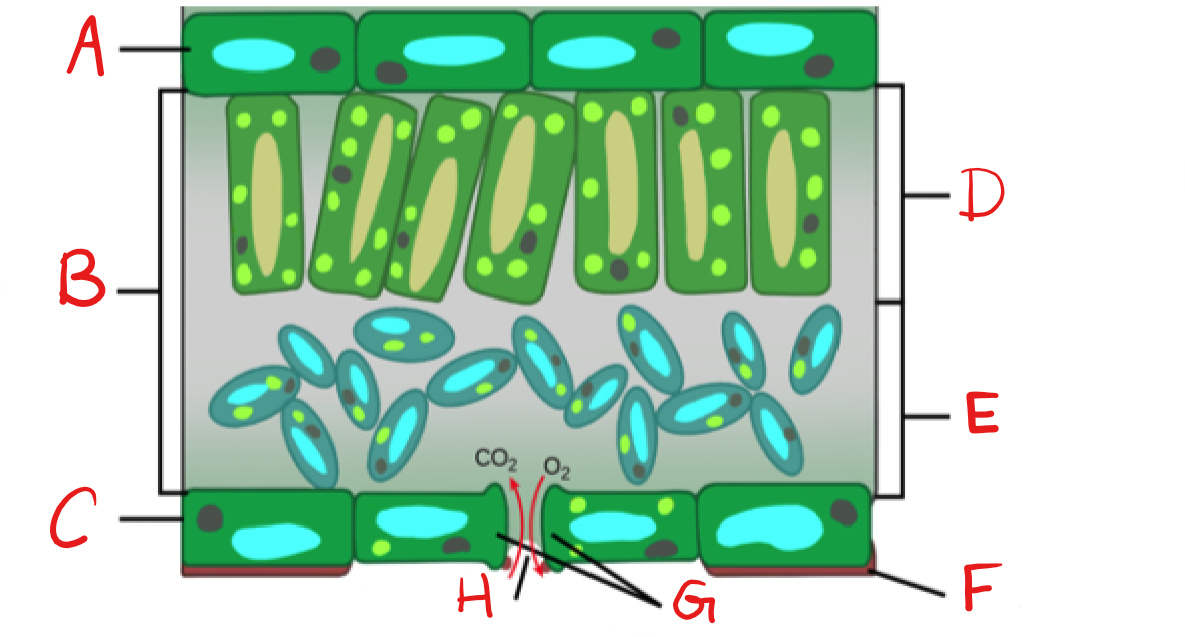
What is B?
Mesophyll
59
New cards
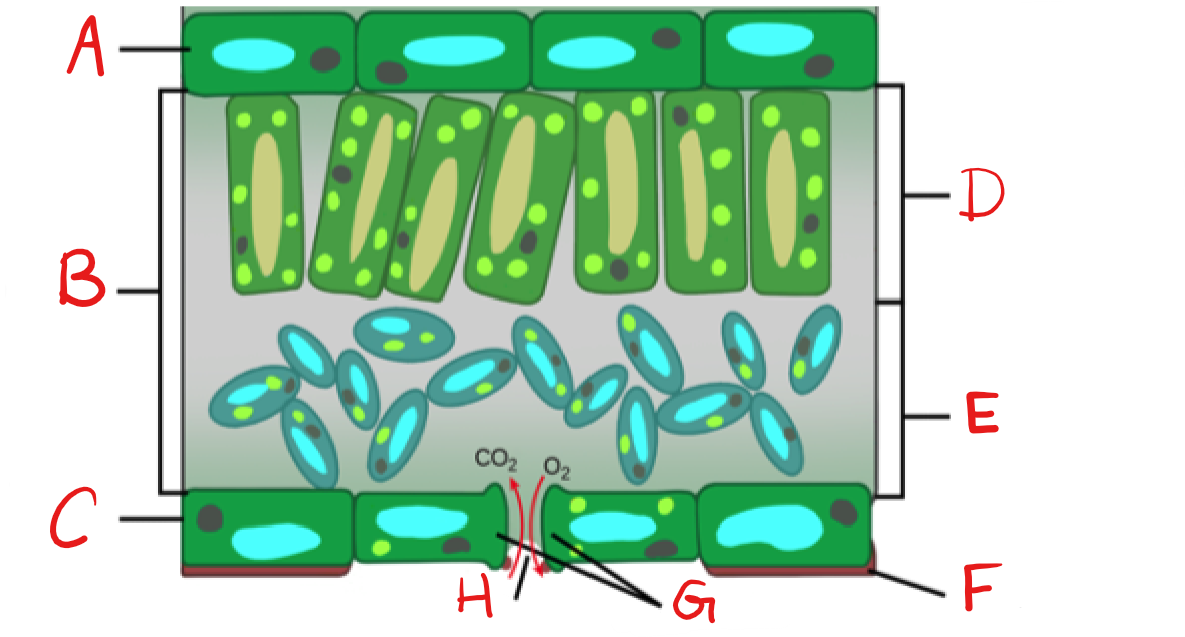
What is C?
Lower Epidermis
60
New cards
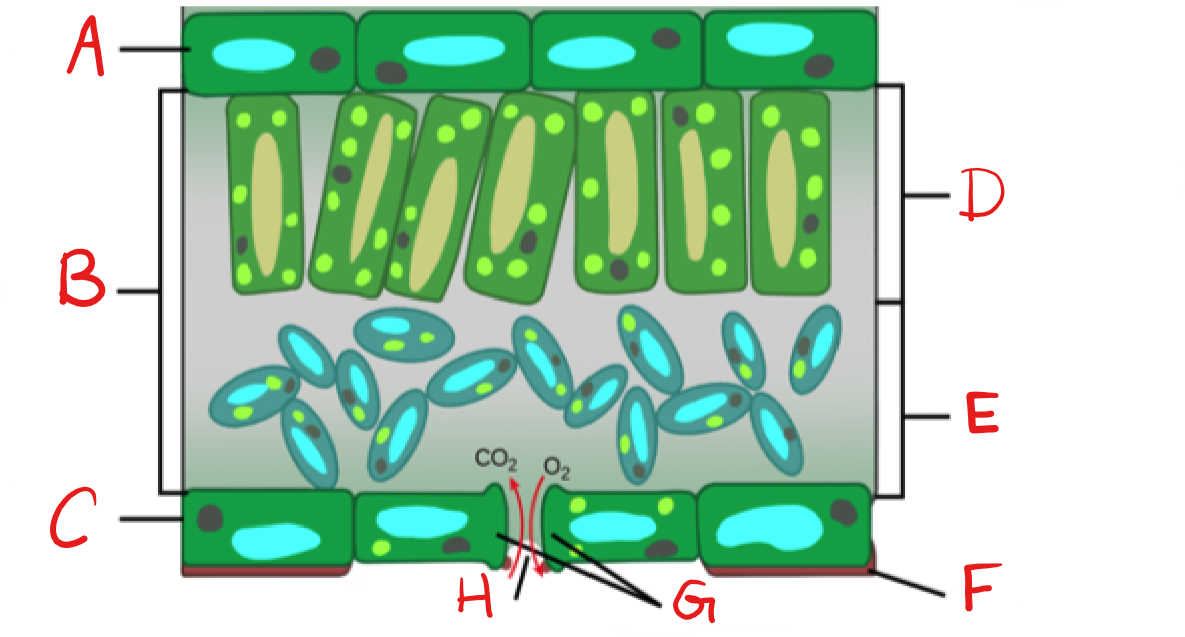
What is D?
Palisade mesophyll/Parenchyma
61
New cards
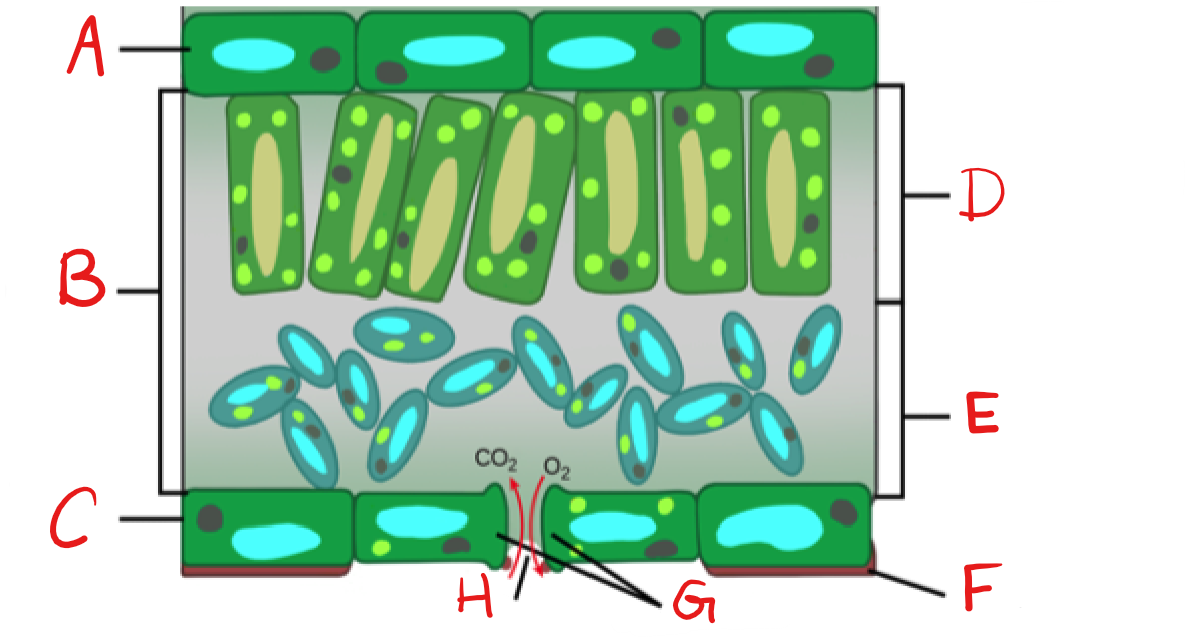
What is E?
Spongy mesophyll/Parenchyma
62
New cards
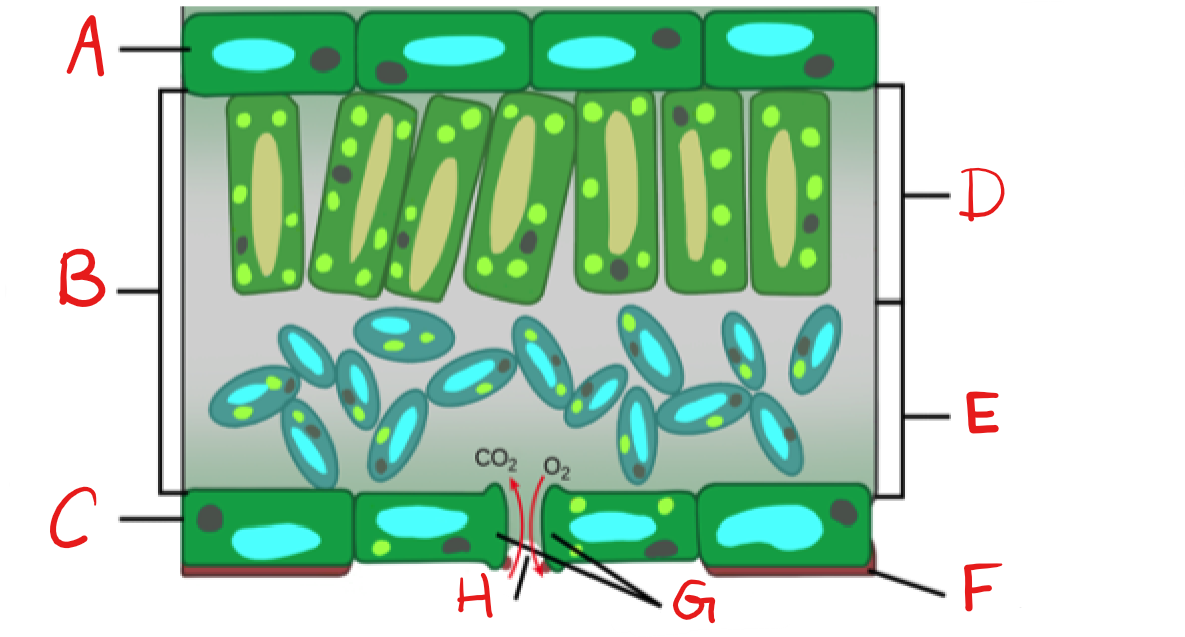
What is F?
Cuticle
63
New cards
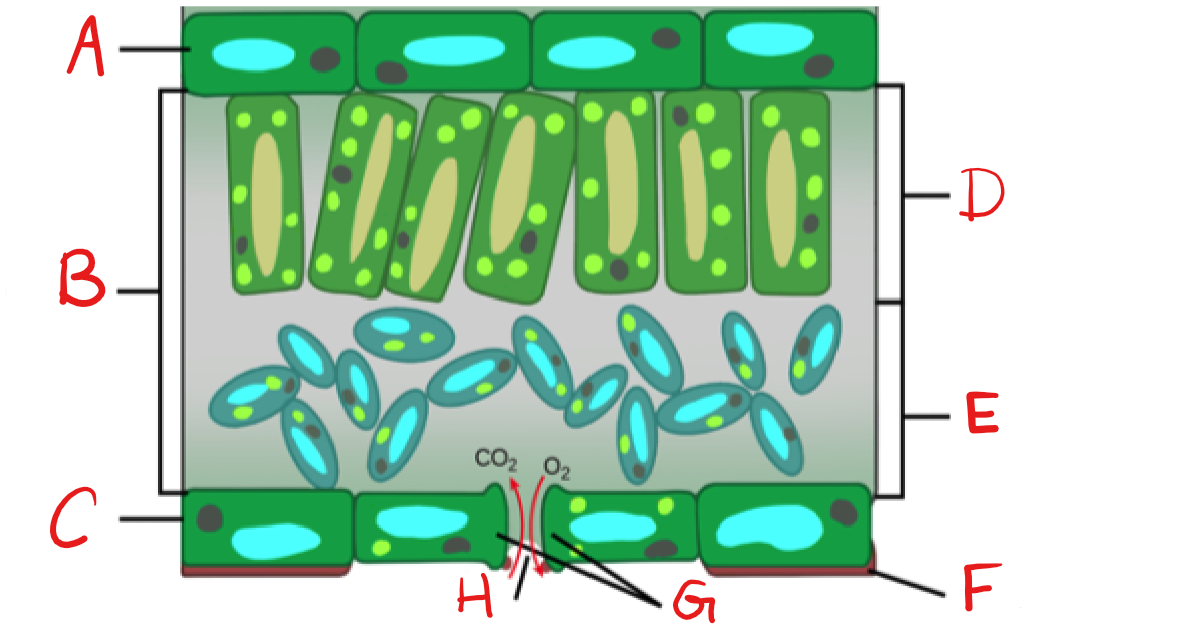
What is G?
Guard Cell
64
New cards
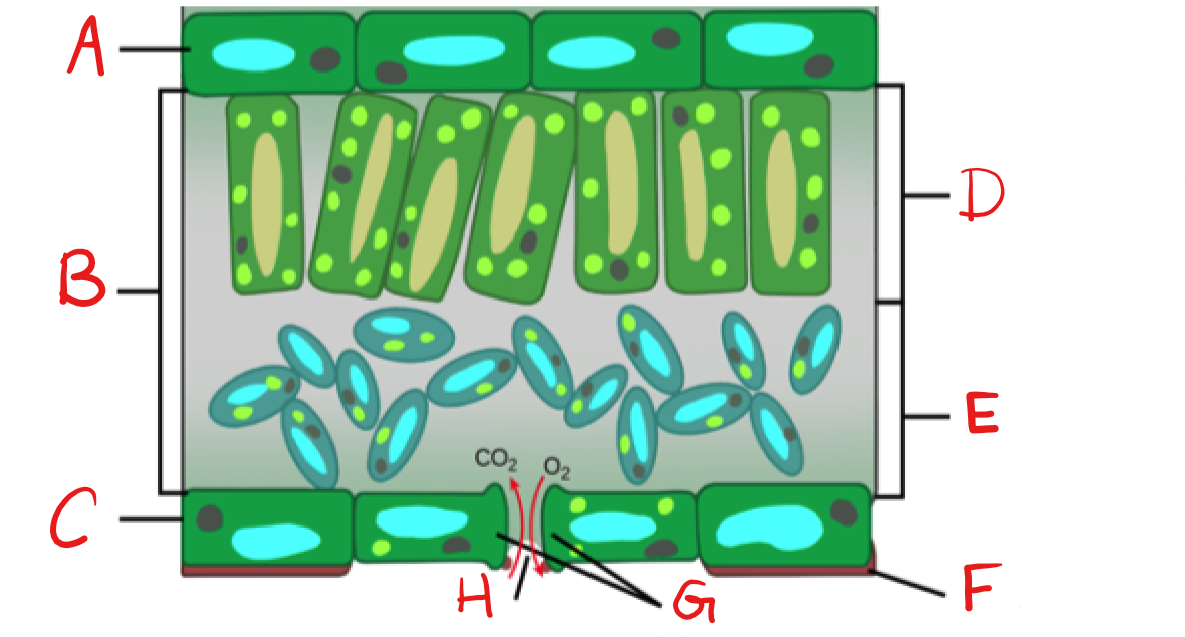
What is H?
Stoma
65
New cards
Epidermis
on top and bottom of leaf, usually one cell-layer thick.
66
New cards
Palisade mesophyll
upper layer of photosynthetic cells, just below upper epidermis
67
New cards
Spongy mesophyll
lower layer of photosynthetic cells, below the palisade cell layer
68
New cards
Water potential
potential energy of water
69
New cards
Phototropism
Is a directional response that allows plants to grow towards, or even away from, light.
70
New cards
Gravitropism
Negative: Shoot grows against gravity
Positive: Roots grow with gravity
Positive: Roots grow with gravity