Genetics: Linkage, Recombination, and Chromosomal Mutations
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
What is Progeria?
A genetic condition that causes premature aging which typically leads to death in the early teens.
What are linked genes?
Genes that do not sort independently because they are physically near each other on the same chromosome.
Who discovered exceptions to the principle of independent assortment?
Morgan.
Which organism was used to discover the principles of linkage and recombination?
Fruit flies.
What process exchanges alleles between homologous chromosomes?
Genetic recombination.
What can be said about genes a, c, and b if they have certain recombination frequencies?
They are linked genes.
Why is the total distance between genes a and b less than the distance between a and c plus c and b?
Double crossovers between a and b decrease recombinants.
What is recombination frequency?
A measurement used to create linkage maps.
What is the expected phenotype ratio from a testcross of RrTt x rrtt?
1 red-eyed with thumbs : 1 yellow-eyed with thumbs : 1 red-eyed without thumbs : 1 yellow-eyed without thumbs.
What is the expected phenotype ratio if two genes are completely linked?
1 red-eyed with thumbs : 1 yellow-eyed without thumbs.
If two genes are linked on the same chromosome, what occurs?
The less crossing-over occurs between them.
What is a recombinant phenotype?
A different combination of the traits seen in either parent.
A recombinant phenotype is
a different combination of the traits seen in either parent
What is another name for map unit?
centimorgan
What is the order of the four linked genes A, B, C, and D based on given map distances?
ADBC
When two genes on the same chromosome are located 10 map units apart, what percentage of offspring should have a recombinant phenotype?
about 10%
When two genes are located on different chromosomes, what percentage of offspring should have a recombinant phenotype?
about 50%
What is recombination frequency for two genes a function of?
distance between the two genes on a single chromosome
What is the best representation of the map distance between the genes for red eyes and gray body in Drosophila?
6.0 map units
What is the best representation of the map distance between the genes for long wings and gray body in Drosophila?
25.0 map units
What result indicates that gene c lies between genes a and b if the map units between a and b are 7.4 and between b and c are 5.7?
2.0 map units
What do genetic map units represent?
relative positions of genes with respect to one another
Which process results in the production of recombinant offspring for two genes on the same chromosome?
crossing over between homologous chromosomes
What are sex-linked genes?
located on sex chromosomes
Which statement correctly describes the inheritance of sex chromosomes?
A woman will pass on an X chromosome to all of her children.
What is only found on the Y chromosome?
SRY gene
What generally determines sex in humans?
Presence of the Y chromosome
What does the X chromosome carry?
Many genes that are not involved in sex determination
What is an autosome?
A chromosome other than a sex chromosome
In birds and butterflies, what are the sex chromosomes for males and females?
ZZ for males; ZW for females
In humans, what are the sex designations for males and females?
Males are heterogametic; females are homogametic
What triggers development toward maleness during embryonic development?
Presence of a Y chromosome
Who may be a carrier for a recessive X-linked trait in humans?
A heterozygous female
What are the genotypes of the parents if only red-eyed females and both red-eyed and white-eyed males are present in Drosophila?
Xw+Xw; Xw+Y
What are the genotypes of the parents if both red-eyed and white-eyed females and males are present in Drosophila?
Xw+Xw; XwY
What are the genotypes of the parents if only red-eyed females and white-eyed males are present in Drosophila?
XwXw; Xw+Y
What are the genotypes of the original parents if only red-eyed females and red-eyed males are present in Drosophila?
Xw+Xw+; XwY
What is the prediction for children of a woman with normal blood clotting and a man with hemophilia?
Half of the boys and half of the girls will have hemophilia
What is the likelihood that half of the boys and none of the girls will have hemophilia if a woman with normal blood clotting mates with a man with normal blood clotting and their first child has hemophilia?
Half of the boys and none of the girls will have hemophilia.
What mechanism equalizes expression of sex-linked genes in placental mammals?
Inactivating one of the two X chromosomes in most female somatic cells.
What is the sex chromosome combination of a male calico cat?
XXY
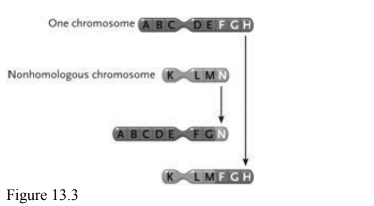
the change in the chromosomes depicted between the top and bottom in the accompanying figure represents
Reciprocal translocation.
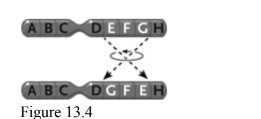
What change is this in the accompanying figure
Inversion.
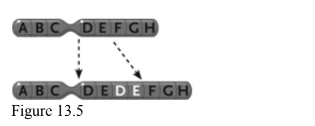
What change does this look like
Duplication.

What does this change look like
Deletion.
What disorder is caused by a deletion from chromosome 5 leading to severe mental retardation and a malformed larynx?
Cri-du-chat syndrome.
What happens if a hypothetical human female of genotype XX has no Barr body in her cells?
The genes on both X chromosomes would be expressed.
What is the evidence of duplication of genetic material in mammals?
The presence of genes that encode many types of hemoglobin.
What happens to deleted genes in individuals with therapy-related myeloid neoplasms (t-MN)?
They are expressed at lower levels due to haploinsufficiency.
What can chemical compounds released during tobacco use cause?
Cancer.
What does nondisjunction refer to?
Failure of homologous pairs or sister chromatids to separate during meiosis.
What is the failure of homologous pairs to separate during mitosis called?
Nondisjunction
Individuals with extra or missing copies of one or more chromosomes are called what?
Aneuploid
What are individuals with three or more copies of each of their chromosomes called?
Polyploids
What is the most likely outcome for a human polyploid?
Natural abortion
In cells of human individuals with three or more X chromosomes, what happens to the X chromosomes?
One X chromosome remains active and the others are inactivated
What disorder is typically caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21?
Down syndrome
Which condition would most likely lead to an apparently normal human female?
Triple-X syndrome
What genetic condition is revealed in the karyotype display shown in the accompanying figure?
Down syndrome
About half of all flowering plant species, including many important crop plants, are what?
Polyploids
What correctly describes autosomal recessive inheritance?
Individuals who are homozygous for the recessive allele display the trait.
About 10-15% of African Americans in the US are carriers for which autosomal recessive genetic disorder?
Sickle-cell anemia
Carriers of the sickle-cell allele have a genetic advantage because they have what?
Increased resistance to malaria
About 4% of individuals of Northern European descent are carriers for which autosomal recessive genetic disorder?
Cystic fibrosis
What does it mean to be a carrier of a genetically inherited disease?
Does not have the disease but may have offspring with the disease
What autosomal recessive disorder is routinely tested for in newborns?
Phenylketonuria
What autosomal dominant genetic trait causes dwarfing due to defective cartilage formation?
Achondroplasia
Which genetic condition has an X-linked recessive inheritance pattern?
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
If a woman is a carrier for cystic fibrosis and the man is not, what is the chance their child will be a carrier?
50% chance of being a carrier
If both parents are carriers for sickle-cell anemia, what is the chance their child will have the condition?
25% chance of having sickle-cell anemia
What is the purpose of prenatal diagnosis techniques like amniocentesis?
To test for the presence of mutant alleles or chromosomal alterations
What mutation is responsible for achondroplasia?
Mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR)
Where are cytoplasmic inheritance genes found?
Mitochondria and chloroplasts
Why are mitochondrial genes inherited in a non-Mendelian pattern?
They are not separated by meiosis
From whom are mitochondria inherited in most multicellular eukaryotes?
Only from the mother
What phenomenon occurs when one parental allele is expressed and the other is silenced?
Genomic imprinting
What mechanism silences an allele by DNA?
Methylation
What is haploinsufficiency?
Occurs when a diploid organism has only one functional copy of a gene
What refers to the loss of a whole set of chromosomes?
Aneuploidy
Which inheritance pattern is most likely correct if individuals affected by the genetic condition are indicated by filled squares or circles?
X-linked recessive
Which inheritance pattern is indicated if the answer is autosomal dominant?
X-linked dominant
If a couple has a child and the man has X-linked recessive hemophilia while the woman is not a carrier, how should they be advised?
None of their children will have hemophilia, but all of their daughters will be carriers.
If a woman has X-linked recessive hemophilia and the man does not, how should they be advised?
All of their sons will have hemophilia, and all of their daughters will be carriers.
If neither parent has hemophilia but the woman's father did, how should they be advised?
Each of their sons will have a 50% chance of having hemophilia, and each of their daughters will have a 50% chance of being carriers.
What is the mode of inheritance for Down syndrome?
Aneuploidy
What is the mode of inheritance for achondroplasia?
Autosomal dominant
What is the mode of inheritance for sickle-cell anemia?
Autosomal recessive
What is the mode of inheritance for hereditary enamel hydroplasia?
X-linked dominant
What is the mode of inheritance for phenylketonuria?
Autosomal recessive
What is the mode of inheritance for Duchenne muscular dystrophy?
X-linked recessive
What is the mode of inheritance for cystic fibrosis?
Autosomal recessive
What is the mode of inheritance for red-green colorblindness?
X-linked recessive
What is the mode of inheritance for progeria?
Autosomal dominant
What crosses should you perform to determine if a new mutant trait in Drosophila is recessive or dominant?
Cross a male with the mutant phenotype and a female without the mutant phenotype.
What should you do to determine if a mutant phenotype is X-linked recessive or dominant?
Cross a male with the mutant phenotype and a female without it. If none of the offspring have the mutant phenotype, it is likely X-linked recessive. If half of the male and female offspring have it, it may be X-linked dominant. If none of the male offspring and all female offspring have it, it is likely X-linked dominant.
What does it indicate if crossing over occurs between two genes every time meiosis occurs?
The genes are unlinked, as linkage means two genes do not assort independently.
What is the difference in meiotic products when nondisjunction occurs during the first versus the second meiotic division?
If nondisjunction occurs during the first division, all meiotic products are aneuploid. If it occurs during the second division, half are normal and half are aneuploid.
Why is isolating fetal cells from a pregnant woman's blood useful for genetic testing?
It is less invasive than chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis.
What are two possible modes of inheritance for a genetic disorder inherited from mother to child?
Maternal inheritance via mitochondrial DNA mutation or epigenetic inactivation of the paternal gene.
What should you tell a cousin who is a carrier for phenylketonuria (PKU) and whose husband's mother has PKU about their potential children?
Each child has a 25% chance of having PKU, and they should ensure their child is tested at birth and follow dietary guidelines if diagnosed.