Structure and function of neurons
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is a neuron?
Building blocks of communication within the body, cells inside the nervous system
What do neurones do?
Send electrical and chemical messages around the body to sensory organs and glands, which is then directed to the CNS
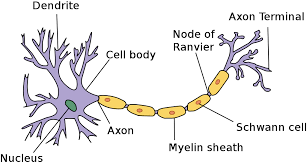
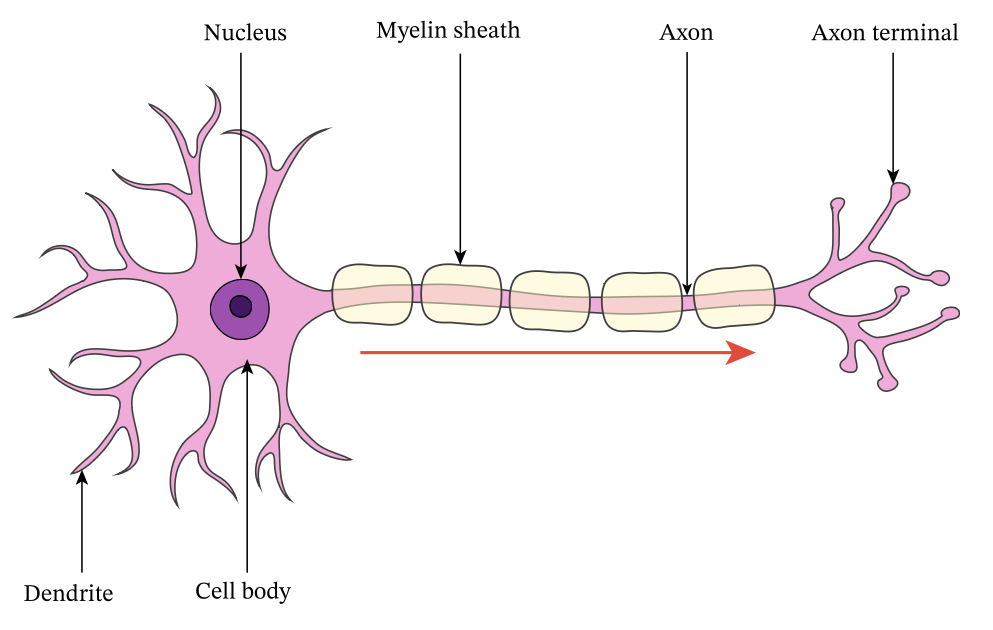
What are the features of a neuron?
Nucleus
Dendrites
Axon
Myelin sheath
Terminal buttons
What is the purpose of the nucleus?
Stores DNA
What is the purpose of the dendrites?
Carries electrical charges from one neurone to the next
What is the purpose of the axon?
Carries electrical charges down the length of the neuron
What is the purpose of the myelin sheath?
Covers the axon to protect it
What are the nodes of Ranvier?
Gaps in the myelin sheath which speed up the message’s transmission
What is the purpose of the terminal buttons?
Located at the end of the neurone, they communicate across the synaptic cleft to the next neurone
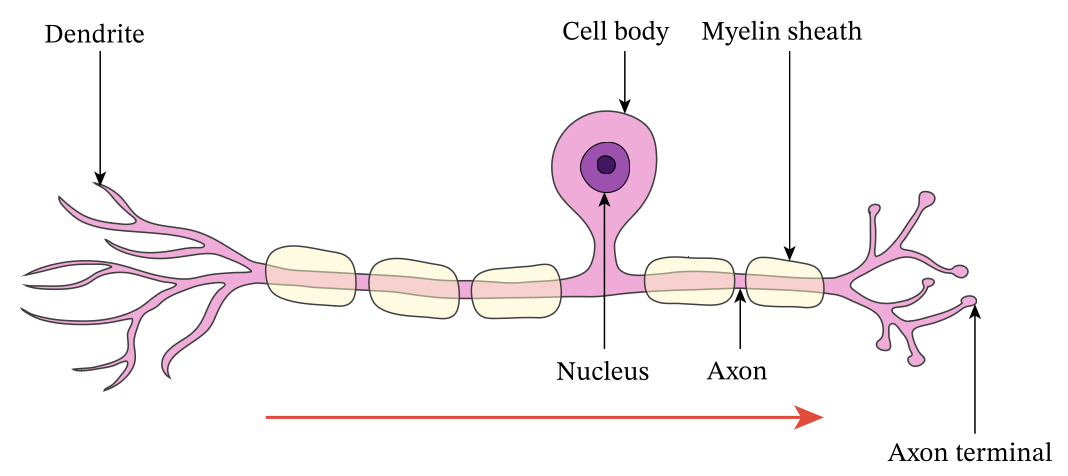
What does the sensory neurone do?
Sends information from the PNS to the CNS
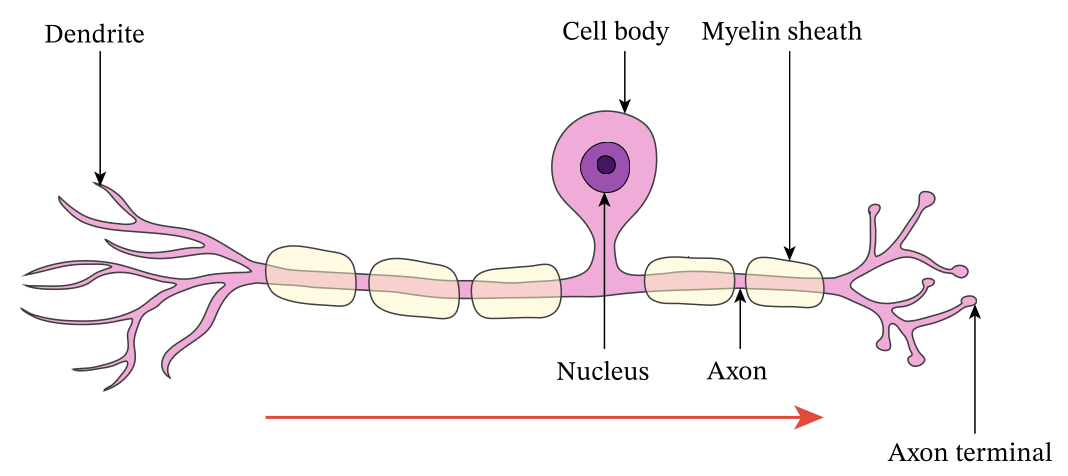
Sensory neurones cannot…
…receive messages, only transmits one way
What are the features of a sensory neurone?
Long dendrites, short axons, cell body at the side of cell
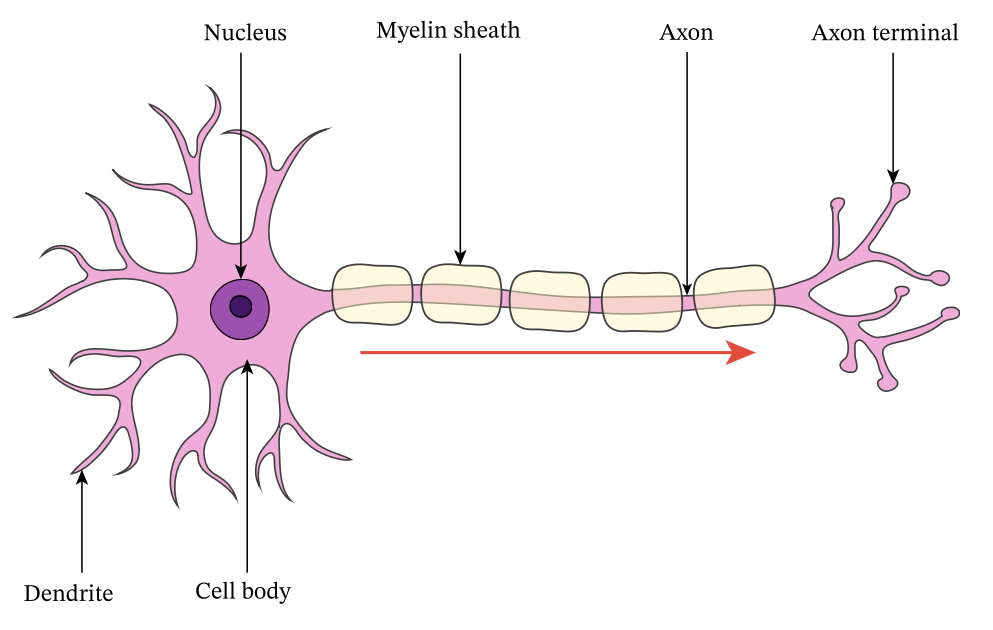
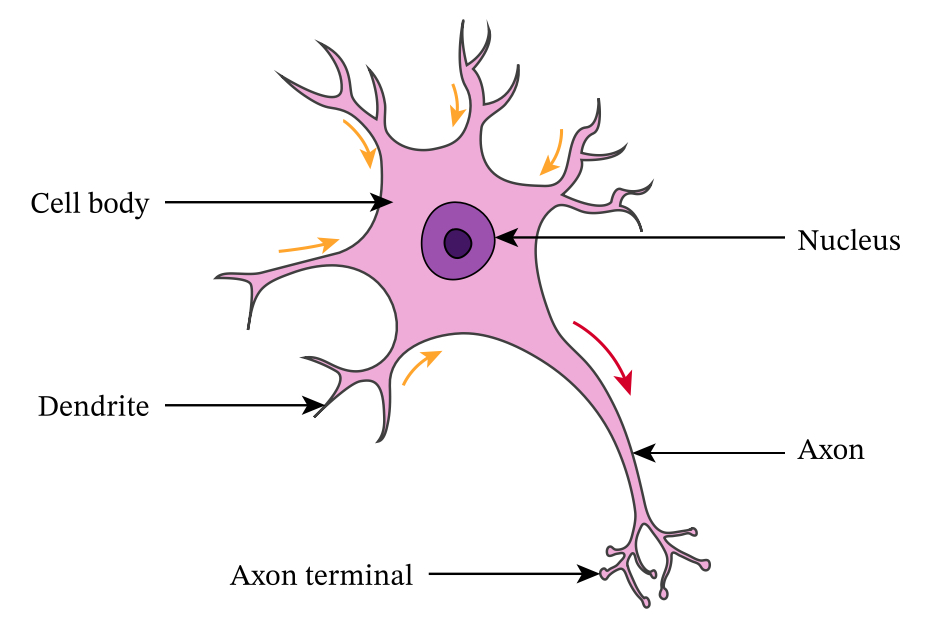
What does the motor neurone do?
Carries signals from the CNS towards PNS (organs, muscles and glands) - controls muscle contraction + relaxation
The motor neurone can…
…transmit AND receive messages
What are the features of motor neurones?
Short axons, long dendrites
What does the relay neurone do?
Connects sensory neurones to motor neurones, carries messages across the CNS
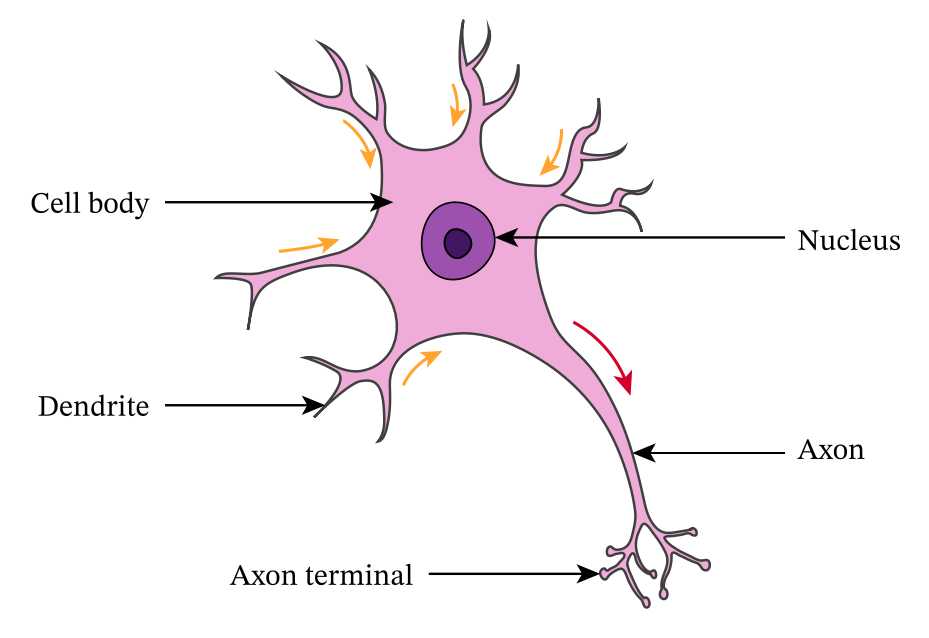
Where are the relay neurones located?
CNS and visual system
Relay neurones can…
…transmit AND receive messages
What are the features of the relay neurone?
Short dendrites, short axons
How does electrical transmission work?
When a neurone is in resting state, the inside of it is negatively charged, outside positive.
When a neurone is activated by a stimulus, the inside of the cell becomes positively charged for a split second - causes action potential to occur.
Action potential create an electrical impulse that travels down the axon towards the end of the neurone.
Signals within neurones are transmitted…
…electrically
Signals between neurones are transmitted…
…chemically across the synapse
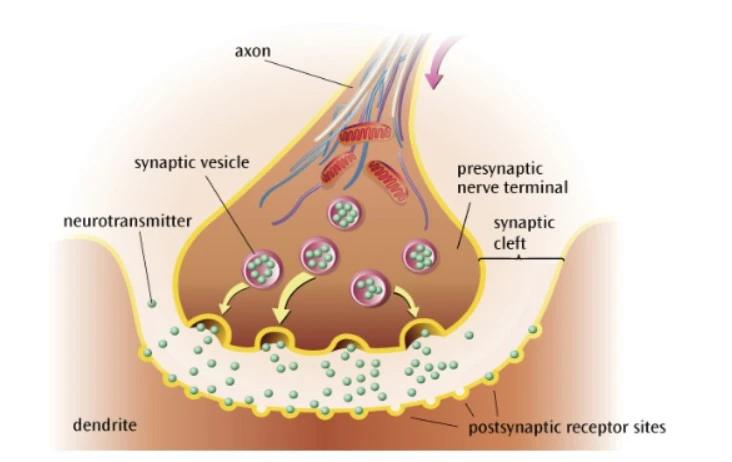
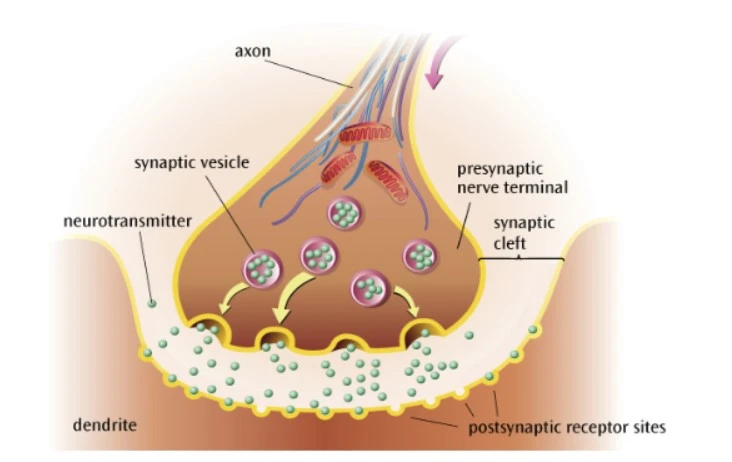
What happens before chemical transmission?
Action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal
This triggers the release of neurotransmitter from synaptic vesicles
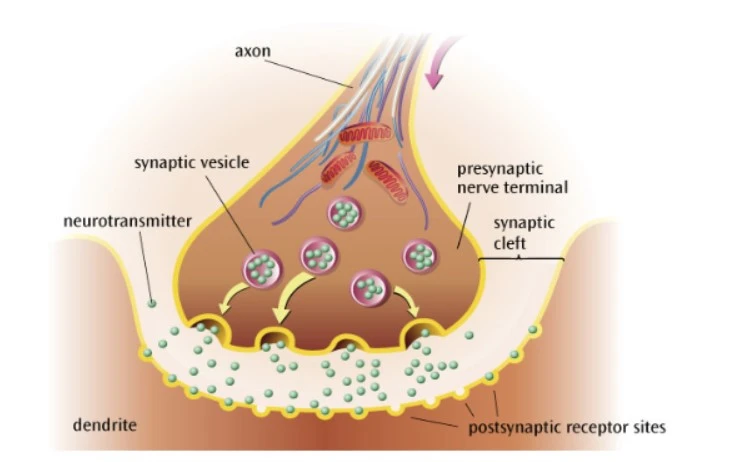
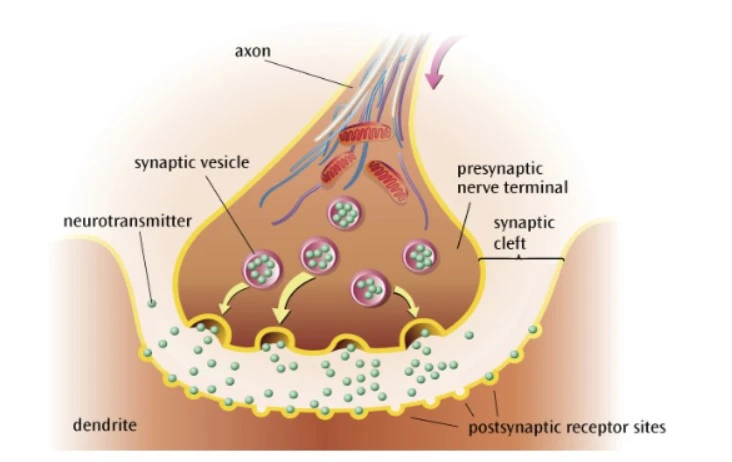
What happens during chemical transmission?
The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse to the postsynaptic neurone
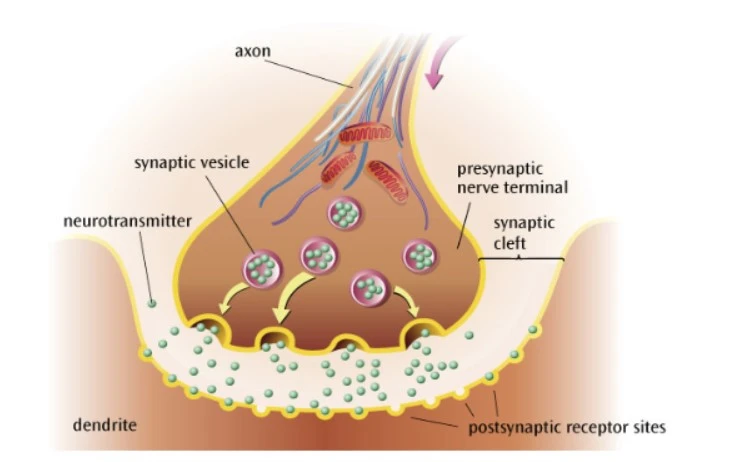
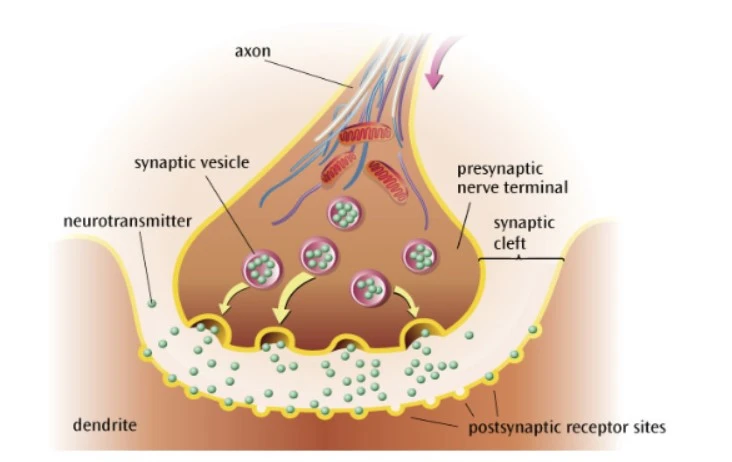
What happens after chemical transmission?
The neurotransmitter binds to postsynaptic receptor sites through a lock-and-key mechanism
This enables excitation or inhibition of the postsynaptic neurone.
Any leftover neurotransmitters in the synapse may be broken or reuptaken by the presynaptic neurone.
What is excitation?
When a neurotransmitter increases the positive charge of the postsynaptic neurone, this increases the likelihood that the neurone will fire (eg adrenaline).
A potential caused by an excitatory charge is called an EPSP (excitatory post-synaptic potential).
What is inhibition?
When a neurotransmitter causes the postsynaptic neurone to become negatively charged, this decreases the likelihood that the neurone will fire (eg serotonin).
A potential caused by an inhibitory charge is called an IPSP (inhibitory postsynaptic potential)
What is summation?
Whether or not a neurone fires depends on the sum of the excitatory and inhibitory influences on it.
A postsynaptic cell receives EPSPs and IPSPs of different strengths at the same time.
Summation is the addition of positive and negative postsynaptic potentials.
If the net effect on the postsynaptic neurone is inhibitory, the neurone will less likely fire, and if the net effect is excitatory, the neurone will be more likely to fire.