Depression (George Hales)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
How to measure depression
With diagnostic tools: summarises emotions, behaviours, distress that typically occur together
What are the four D's
distress
dysfunction
danger
deviance from norms
DSM-5 definition of depression
Clinically significant disturbance in an individual’s cognition, emotion regulation, or behaviour that reflects dysfunction in the psychological, biological, or developmental processes underlying mental functioning. Mental disorders are usually associated with significant distress or disability in social, occupational, or other important activities.
DSM-5 approach
Committee of experts define the diagnosis
Diagnostic categories are made up of’criteria’
Criteria are symptom clusters that are grouped together based on intuition to bring reliability and to produce validity
Every diagnosis has one or several criteria which contains one or several possible symptoms
What is the rule that is needed to meet a specific criteria
A number of symptoms must be present to meet a number of specifc criteria
Defining mental illness based on logical rules has
high reliability, but limited validity
DSM-5 major depression criteria (core symptoms)
feeling of sadness or low mood
loss of interest in usual activity
How long do core symptoms have to last
at least two weeks
What are the other common symptoms of depression
change in appetite, losing or gaining weight
sleeping too much or not sleeping well
fatigue and low energy most days
feeling worthless, guilty, and hopeless
inability to focus/concentrate that may interfere with daily tasks
movements that are unusually slow or agitated (a change noticeable to others)
thinking about death and dying; suicide
How many symptoms should at least be present
five symptoms
WHO - “Globally, the total number of people with depression was estimated to exceed…
300 million in 2015”
Prevalence varies by country and gender, from a … among males in the Western Pacific Region to … among females in the African Region
2.6% among males
5.9% among females
Depression was the … most common reason for consulting a doctor or GP (Singleton et al., 2001)
third
Prevalence estimates of adolescent depression symptoms by region what is the percentage in the Middle East (Shorey et al., 2022)
64%
Prevalence estimates of adolescent depression symptoms by region what is the percentage in Africa (Shorey et al., 2022)
45%
Prevalence estimates of adolescent depression symptoms by region what is the percentage in Asia (Shorey et al., 2022)
40%
Prevalence estimates of adolescent depression symptoms by region what is the percentage in North America (Shorey et al., 2022)
20%
Prevalence estimates of adolescent depression symptoms by region what is the percentage in Europe (Shorey et al., 2022)
16%
Prevalence estimates of adolescent depression symptoms by region what is the percentage in South America (Shorey et al., 2022)
15%
Prevalence estimates of adolescent depression symptoms by region what is the percentage in Oceania (Shorey et al., 2022)
14%
The number of incident cases of depression worldwide increased of … (Liu et al., 2019)
50% from 172 million in 1990 to 258 million in 2017
Prevalence of elevated depression symptoms among adolescents increased from … (Shorey et al., 2022)
24% in 2001-10 to 37% in 2011-20
estimated higher for females (32%) compared to males (24%)
Despite efforts to raise public awareness about mental health problems to reduce/prevent distress, prevalence has
increased
What is the polygenetic risk scores studies (Halldorsdottir et al., 2019)
estimates the effects of many genetic variants
strongly associated with depression diagnosis, severity of symptoms, and age of onset
What is the study by Mandelli et al., 2015?
reviewed and meta-analysed studies that evaluated childhood traumas
depression must have been assessed by clinical or structured interview, or self-report questionnaires
What did Mandelli et al., 2015 find?
Emotional abuse strongest association with depression (OR = 2.78) followed by neglect (OR = 2.75) and sexual abuse (OR = 2.42)
significant associations also found for domestic violence (OR = 2.06) ad physical abuse (OR = 1.98)
What did Kraaij et al., 2002 do?
meta analysis of 25 studies of specific types of negative life events and depression in old age
grouped negative life events into categories:
severe illness of self or significant others
sudden unexpected events
negative events in relationships
daily hassles
abuse
Total number of negative life events and the total number of daily hassles had strongest relationship with
depression
abuse, negative events in relationships, and severe illness all associated with depression
sudden unexpected events not related to depression
Not all individuals who experience negative life events will develop depression because
resilience is a common response to negative life events (Masten, 2001)
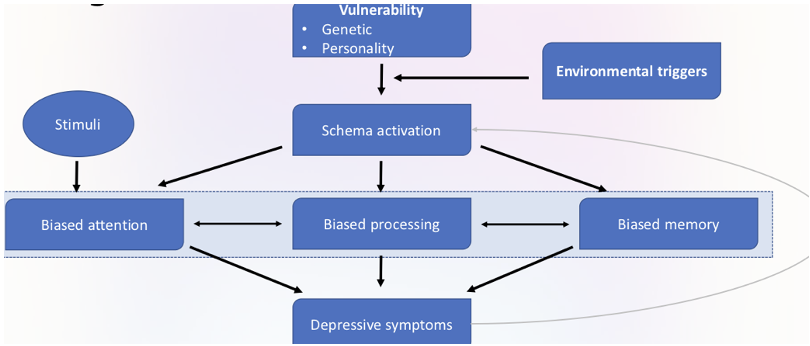
Most influential theory ‘negative Triad Theory’ (Beck, 1967) states that depression arises from:
negative schemas
results in information processing biases (e.g. over sensitive to criticism)
dysfunctional attitudes leading to absolute negative beliefs
Psychological risk factors: the cognitive model
Gender differences in depression, (Salk et al., 2017)
women are twice as likely as men to have depression, not due to men under-reporting depression (Parker & Brotichie, 2010).
Gender differences in depression possible factors (Salk et al., 2017)
girls are more likely to be abused
women more likely to be exposed to chronic stress (e.g. caregiving)
women tend to provide more social support to others facing stress (dubbed the ‘cost of caring’)
social roles
Treatment for depression
antidepressants in combination with CBT
Cognitive behavioural therapy
schemas and coping strategies
i.e challenge dysfunctional thoughts and replace with rational beliefs
What did Lopez-Lopez et al., 2019 state
CBT yields larger decrease in depression scores to TAU
Psychoanalysis
depression a response to loss
symbolic loss, e.g. losing a job
What did Zimmerman et al., 2014 state
more use of psychoanalytic techniques and greater number of sessions associated with better outcomes compared to CBT
Acceptance and commitment therapy
aims to increase psychological flexibility
What did Ruiz (2012) state
initial studies indicated ACT outcomes were comparable to CBT