AP CSP EVRYTHING ON COLLEGEBOARD COURSE DESCRIPTION!! + vocab from practice tests
1/227
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocab for AP test pls excuse any typos i was typing very fast
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
228 Terms
MetaData
Data about data such as author, data created, usage, file size, etc
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
a communications standard that enables application programs and computing devices to exchange messages over a network
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
the foundation of the World Wide Web, and is used to load webpages using hypertext links.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
a protocol used for communication throughout the internet. ( faster, less accurate)
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
the premier standards development organization (SDO) for the Internet.
computing bias
computer systems that systematically and unfairly discriminate against certain individuals or groups of individuals in favor of others.
Heuristic
an algorithim that finds an approximate solution rather than an exact solution
Compiling
the process of converting human-readable code into machine-readable code.
HyperText Markup Language (HTML)
the basic scripting language used by web browsers to render pages on the world wide web. HyperText allows a user to click a link and be redirected to a new page referenced by that link.
Latency
the time it takes for data to pass from one point on a network to another.
Bandwidth
the maximum amount of data that can be sent over a particular computer network in a fixed amount of time
Recursion
a method of solving a computational problem where the solution depends on solutions to smaller instances of the same problem.
Assembler
a computer program that translates assembly language code into machine code, allowing for direct communication with a computer's hardware. It converts human-readable instructions into binary code that the central processing unit (CPU) can execute.
Wide-Area Network
the technology that connects your offices, data centers, cloud applications, and cloud storage together
Commodity Components
computers or components that are readily available, inexpensive and easily interchangeable with other commodity hardware. Example: PCs
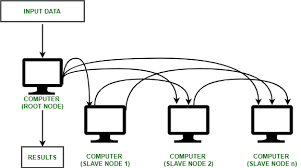
Clustering
a group of servers and other resources that act like a single system and enable high availability, load balancing and parallel processing.
iterative
a process where the design of a product or application is improved by repeated review and testing.
Qualitative (data)
information that cannot be counted, measured or easily expressed using numbers.
Public Key encryptions (Assymetric Key encryptions)
a method of encrypting or signing data with two different keys and making one of the keys, the public key, available for anyone to use. The other key is known as the private key. Data encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key.
Symmetric Encryption
a method of encryption that uses just one key for both encrypting and decrypting
Holistic decision-making
an approach to making great things happen in a way that increases quality of life for all involved.
Boolean Variables
can either be True or False and are stored as 16-bit (2-byte) values
Crowdscourcing
the practice of obtaining input or information from a large number of people via the Internet
Data Abstraction
Filtering out specific details to focus on the information needed to process the data
Abstration
a way of hiding information
Application Program Interface (API)
Specifications for using a library’s procedures and understanding how they behave
Creative Commons License
A not-for-profit organization that has various forms of licenses that can be used to protect the orignal work from being plagarized
Libraries
a collection of precompiled procedures that can be used by other programs
Lossless Compression
a reduction of the number of bits stored or trasmitted that guarentees complete restoration of the orignal data
Lossy Compression
a significant reduction in the number of bits stored or transmitted that only allows for an approximation of the orginal data
Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
Information about a person that can uniquely identify them, such as educational, medical, financial, or employment information
Procedural abstraction
the calling of a function with the concern only for the end result rather than how the code functions
Pseudocode
A way of describing an algorithm that is not the specific code of any language
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP/IP)
An Internet protocol in which packets are repeated sent until reciept is confirmed
A computing innovation includes…
a program as an integral part of its function
A computing innovation can be…
physical (ex: self-driving car), nonphysical computing software(ex:picture editing software), or a nonphysical computing concept )ex: e-commenerce)
Effective collaboation produces..
a computing innovation that refkects the diversity of talents and perspectives of those who designed it
Collaboration tha includes diverse perspectives helps..
avoid bias in the development of computing innovations
Consultion and communcation with users are important aspects of..
the development of computing innovations
Informations gathered from potential users can be used to…
understand the purpose of a program from diverse perspectives and to develop a program that fully incorporates these perspectives
Online tools support collaboration by…
allowing programmers to share and provide feedback on ideas and documents
Common models such as ______ exist to facilitate ____
pair programming, collaboration
Effective collaborative teams practive interpersonal skills, including but not limited to…
communication, consensus building, conflict resolution, negotiation
The purpose of computing innovations is to..
solve problems or to pursue intrests throuhg creative expression
An understanding of the purpose of a computing innovation provides developers with…
an improved ability to develop that computing innovation
A program is…
a collection of program statements that performs a specfic task when run by a computer.
A program is often referred to as…
software
A code segment is….
a collection of program statements that is part of a program
a program needs to work for..
a variety of inputs and situations
the behavior of a program is how…
a program functions during execution and is often described by how a user interacts with it
A program can be described broadly by…
what it does, or in more detail by both what the program does and how the program statements accomplish this function
Program inputs are…
data sent to a computer for processing by a program. Input can come in a variety of forms, such as tactile, audio, visual or text.
an event is associated with…
an action and supplies input data to a program.
Events can be generated when….
a key is pressed, a mouse is clicked, a program is started or any other defined action occurs that affects the flow of execution
Inputs usually affect the….
output produced by a program
In event-driven programming, program statements are executed when….
triggered rather than throught the sequential flow of control
input can come from a…
user or other programs
Program outputs are..
any data sent from a program to a device.
Program output can come in a variety of forms such as…
tactile, audio, visual, or text
Program output is usually based on…
a program’s input or prior state (ex: internal values)
There are multiple development processes. What are the most commonly used phases when developing a program?
Investigating and reflecting, designing, prototyping, testing
A development process that is iterative requires…
refinements and revision based on feedback, testing, or reflection throughout the process. This may require revisting earlier phases of the proess
A development process that is incremental is..
one that breaks the problem into smaller pieces and makes sure each piece works before adding it to the whole
Investigation in a development process is useful for…
understanting and identifying the program constraints, as well as the concerns and interest of the people who will use the program.
Some ways investigation can be performed are…
collecting data through surveys, user tetsing, interviews, and direct observations
Program requirements describe…
how a program functions and may include a description of user interactions that a program must provide
A programs specifications defines the..
requirements for the program
In a development process, the design phase outlines..
how to accomplish a given program specification
The design phase of a program may include…
brainstorming, planning and storyboarding, organizing the program into modules and functional components, creation of diagrams that represent the layouts of the user interface, and the development of a testing stregy for the program.
Program documention is a…
written description of the function of a code segement, event, procedure, or program and how it was developed. ( Programmers should document a program throughout its development)
Comments are…
a form of program documentation written into the program to be read by people and do not affect how a program runs.
Program documentation helps in….
developing and maintaining correct programs when working individually or in collaborative programming enviroments
A logic error is…
a mistake in the algoithm or program that causes it to behave incorrectly or unexpectedly
A syntax error is a….
a mistake in the program where the rules of the programming language are not followed
A run-time error is…
a mistake in the program that ccurs during the execution of a program.
An overflow error is…
an error that occurs when a computer attempts to hanfle a number that is outside of the defined range of values
What are effective ways to find and correct errors…
test cases, hand tracing, visualizations, debuggers, and adding extra output statements
Data values can be stores in…
variables, lists of items, or standalone constants and can be passed as input to (or output from) procedures
Computing devices represent data digitally meaning that the lowest- level of any value are …
bits
Bit is short hand for..
binary digit
Bit is either which numbers?
0 and 1
A byte is
8 bits
Abstration is…
the process of reducing complexity by focusing on the main idea. By hiding details irrelevant to the question at hand and bringing together related and useful details, abstraction reduces complexity and allows one to focus on the idea
Bits are grouped to represent…
Abstractions… These absractions include, but are not limited to, numbers characters, and color
Analog Data…
has values that change smoothly rather than in descrete intervals, overtime. Some examples of analog data include pitch and volume of music, colors of a painting, or position of a sprinter during a race.
The use of digital data to approximate real world analog data is an example of…
abstraction
Analog data can be closely approximated digitally using a sampling technique which means…
measuring values of the analog signal at regular interval called samples. The samples are measured to figure out the exact bits required to store sample
In many programming languages, integers are represented by a fixed number of bits which limits the range of integer values and mathmatical operation on those values. This limitation can result in what types of errors?
overflow or other errors
In programming languages, the fixed number of bits used to represent real numbers limits the range and mathmatical operations on these values; this limitation can result in what type of errors?
Round-off and other errors?
Number bases are used to represent what ?
data
Binary (base 2) uses what numbers
0 and 1
Decimal (base 10) uses what numbers
0-9
Data compression can…
reduce the size ( number of bits) of transmitted or stored data
fewer bits do not nessearily mean less…
information
The amount of size reduction from compression depends on ….
the amount of redundancy in the original data representation and the compression algorithm applied
Lossless data compression algorithms can usually…
reduce the number of bits stored or transmitted while guaranteeing complete reconstruction of the original data
Lossy data compression algorithms can…
siginificantly reduce the number of bits stored or transmitted but only allow reconstruction of an approximation of the original data
Lossy data compression algorithms can usually
reduce the number of bits stored or transmitted more then lossless compression algorithms
In situations where quality or ability to reconstruct the original is maximally important, which compression algorithm is tyically chosen
Lossless compression
In situations where minimizing data size or transmission time is maximally important, what style of compression algorithms are typically chosen?
Lossy compression