Physics IGCSE Mock 2025
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
Average Speed Equation
Average speed = Total distance / Total time (s = d/t)
Displacement
The distance moved in a straight line, in a given direction
Velocity
A speed in a stated direction (displacement/time)
Acceleration
The rate of change of velocity
Acceleration Equation
Acceleration = final velocity - initial velocity/ time
(a = v-u/t)
A - Acceleration (m/s2)
V - Final velocity (m/s)
U - Initial velocity (m/s)
t - Time (s)
Uniform Acceleration Equation
a = (v - u)/ 2s
A - Acceleration (m/s2)
V - Final velocity (m/s)
U - Initial velocity (m/s)
S - Distance (m)
Distance travelled in a graph
The area beneath the velocity-time graph
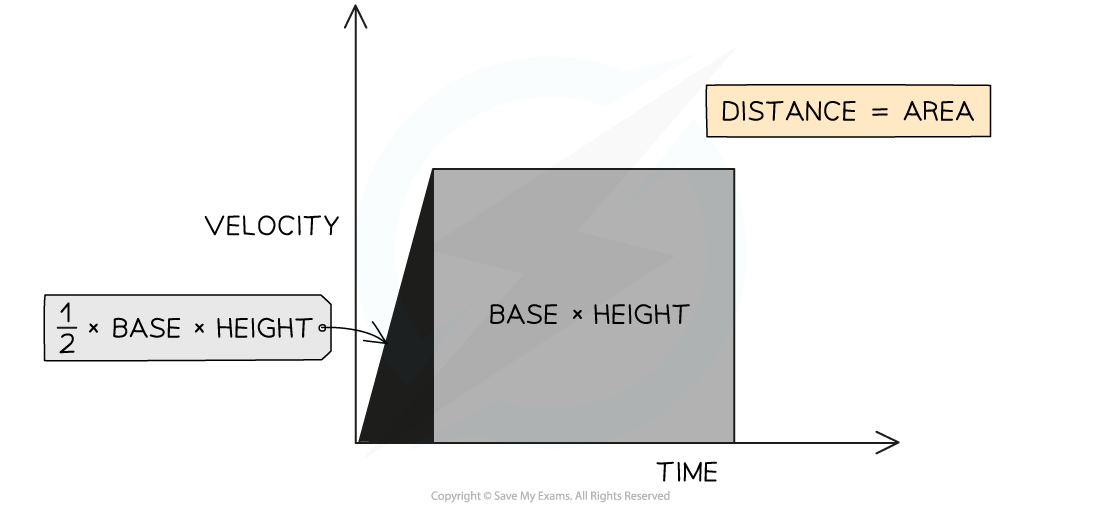
Velocity - Time Graph
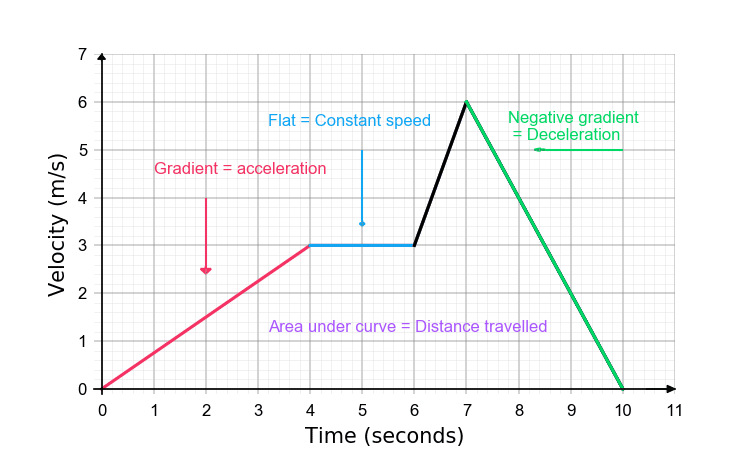
Forces - Acceleration Equation
Acceleration = resultant force/mass (a=F/m)
Weight Equation
Weight = Mass x Gravitational field strength (W = m x g)
Explain the forces acting on falling objects.
When an object falls there is initially one force acting on it, weight. There is a resultant force, so the object accelerates downwards.
Once the object starts to get faster Air resistance begins to act in the opposite direction to weight.
The faster the object falls, the larger the force of air resistance becomes.
When air resistance gets so large that it's equals to Weight, there is no net force. The object stops accelerating, Terminal velocity is reached.
Effects of opening a Parachute?
Before parachute opens the air, resistance and weight are equal.
After parachute opens the weight stays the same, air resistance becomes very high due to the surface area increase so the parachutist decelerates.
Eventually air resistance and weight are equal and falls at a new slower velocity.
What is Terminal Velocity?
The Maximum velocity for an object in freefall when the forces of weight and air resistance become balanced.
What is Hooke's Law?
Extension is Proportional to Force
Hooke's Law with Springs (Experiment)
Set up apparatus (Weight stand, Masses, Spring, Clamp)
Measure the springs length when no load is applied
Add 1 mass at a time and allow the spring to come to rest, then measure the springs new length.
Repeat experiment till you have enough measurements
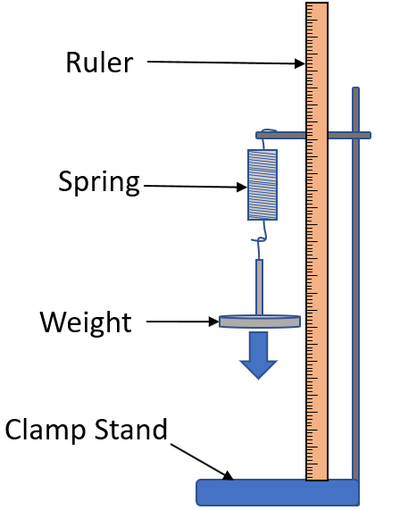
What is Elastic Behaviour?
The ability of a material to recover its original shape after forces causing deformation have been removed.
Force Equation
Force(N) = Spring constant(N/m) x extension(m)
F = K x e
What is Power?
The amount of energy transferred per second (Units: Watt (W))
Power Equation
Power = Current x Voltage (P = I x V)
Energy Transfer Equation
Energy transfer = Current x Voltage x Time (E = I x V x t)
AC & DC Power Supply
Mains electricity supplies AC, which switches direction 50x a second, which powers household appliances. DC comes from a cell/ battery & flows consistently in 1 direction, its used in portable devices (e.g. flashlights & electronic gadgets).
Series Circuit
A one loop circuit (E.g. fairy lights)
Current is the same at all points in a series circuit
Voltage supplied by the battery is shared between each component
Series Circuit - Advantage.
All components can be controlled by a single switch
Series Circuit - Disadvantage.
If a component in the circuit breaks the others won't work
Parallel Circuit
A circuit with more than one loop (E.g. lights at home)
In a parallel circuit the total current is shared between each loop
The total voltage in each loop is the same as the voltage of the battery
Parallel Circuit - Advantages.
If a component in the circuit breaks the others will still work
Parallel Circuit - Disadvantage.
Sometimes you don't want each component to have the same voltage & this is harder to control
What is Ohms Law?
Voltage and current are directly proportional (only if temperature of component stays constant)
What is resistance in conductors caused by?
Resistance in conductors is caused by electron-metal ion collisions, causing metal ions to vibrate faster, causing ⬆️ temperature. As an object becomes hotter, the number of collisions ⬆️, resulting in resistance. Resistance ⬆️ with temperature.
An I-V Graph for a Wire or Fixed Resistor
Resistance of a Wire or Fixed Resistor is constant, so the gradient is constant (linear)
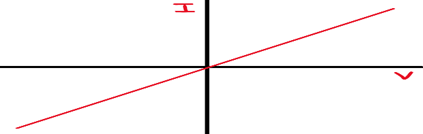
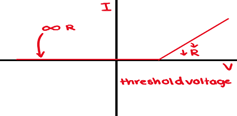
An I-V Graph for a Filament Lamp
At higher voltages, the filament lamp gets hot so its resistance ⬆️. So, there is less current & the graphs slope ⬇️
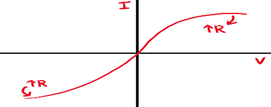
An I-V Graph for a Diode
Diode lets current flow in 1 direction, in the reverse direction resistance is large and current is 0. In the forward direction, the line curves towards the I axis as resistance ⬇️
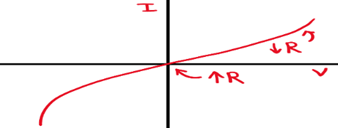
An I-V Graph for a Thermistor
Its resistance ⬇️ with ⬆️ temperature as its made of a semiconductor, & more mobile electrons are released as the components get warmer
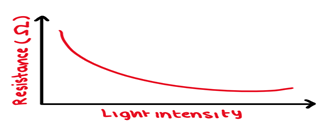
An I-V Graph for a LDR
Resistance ⬇️ with ⬆️ light intensity as extra mobile electrons are released
What is Current?
Rate of flow of charge
What is Voltage?
The energy transferred per unit charge passed (The volt is a joule per coulomb)
What happens if you increase the voltage?
The current also increases.
What is Resistance?
Hindrance of flow of electrons along a conductor
Voltage Equation
Voltage = Current x resistance (V = I x R)
Charge Equation
Charge = Current x Time (Q = I x t)
Current Equation
Current = Charge/ time (I = Q/t)
What happens if you increase the resistance in a circuit?
The current will decrease.
What are conductors?
Metals (E.g. Copper, Aluminium, Silver, Gold, Iron, Brass & Bronze)
What are Insulators?
Plastics (E.g. Polyethylene, Polypropylene, PVC, Teflon & Nylon)
What happens when an atom becomes charged?
Atoms have a 'neutral charge', but when an atom becomes charged, it becomes an ion. To make a ➕ charged ion you remove an electron, to make it ➖ you add electrons.
How does Static electricity occur?
Static electricity stays put on objects which are all insulators and occurs by friction of an insulator.
What happens when you rub and insulator with a cloth?
When you rub an insulator with a cloth the insulator may gain a positive charge by losing electrons. The cloth gains the opposite charge by gaining electrons.
What happens if a negatively charged object is brought near to a wall?
If a negatively charged object is brought near to a wall, electrons nearest the object would be repelled, leaving the front of the wall positive. The object can stick.
Longitudinal Waves
The vibrations are parallel to the direction of wave travel (E.g. sound waves & ultrasound waves)
Transverse Waves
The vibrations are at right angles to the direction of wave travel (E.g. Water surface ripples, electromagnetic waves, seismic S-waves)
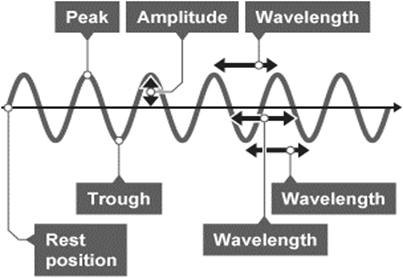
What is wavelength?
The distance between two peaks (M)
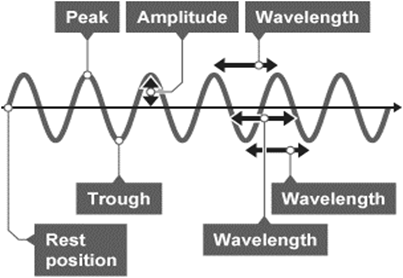
What is amplitude?
The maximum displacement of the wave from the equilibrium position
What is frequency?
The number of waves passing a point each second (Hz)
What is Time Period?
The time taken for one wave to pass a point (s)
What is a Wavefront?
An imaginary surface drawn to represent the vibrating part of a wave
Wave Speed Equation
Wave speed (m/s) = Frequency (Hz) x wavelength (m)
v = f x λ
What is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
A range of similar behaving waves. Their all transverse waves & travel at the same speed in a vacuum, they can all be reflected and refracted.
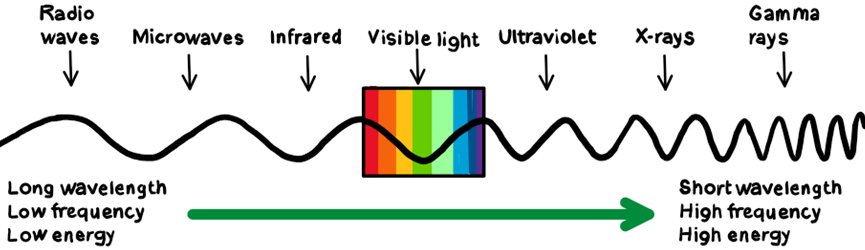
How do light waves travel?
They travel as transverse waves, and they can be reflected and refracted
Refractive Index Equation
Refractive index = Angle of incidence/ Angle of refraction
n = sin i / sin r
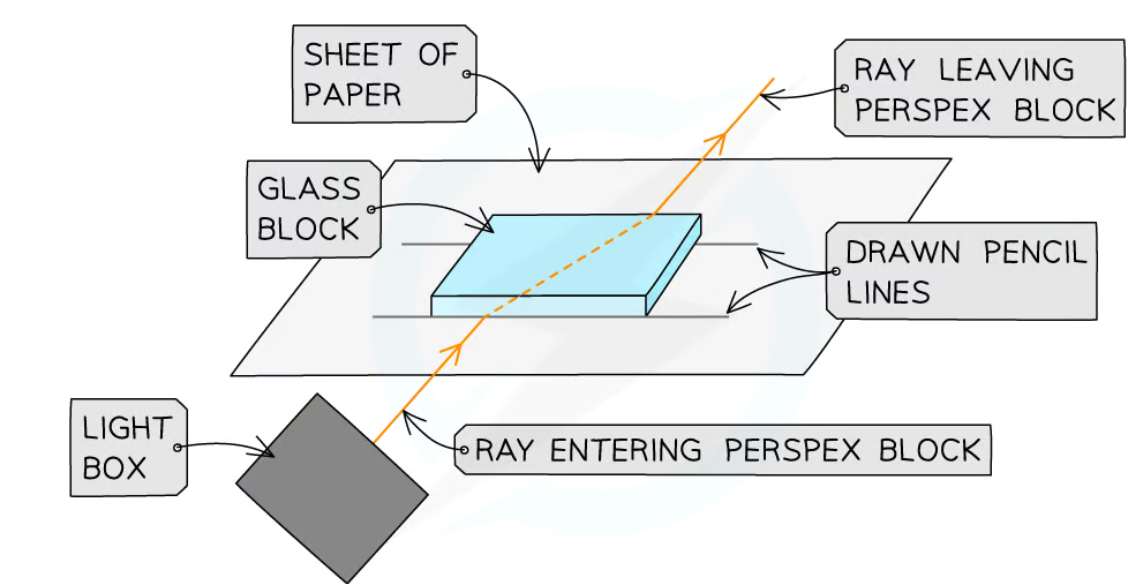
How to find the Refractive Index of glass
Place rectangular block in centre & draw round it
In the middle of one of the long sides mark a target
Remove the glass block and draw the normal passing through the target
With protractor measure 1st angle of incidence (predetermined angle) & with draw the incident ray
Direct beam along the ray drawn using a laser board
Replace the glass block
Mark points along the beam that exits the block
Remove the block again and draw in this ray. Draw the ray within the glass block by joining the rays together
Measure the angle of refraction
Calculate the refractive index of glass
What is the human hearing range?
20Hz - 20,000Hz
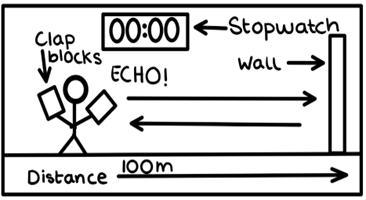
Describe an experiment to find the speed out sound?
Stand 100m from wall, measure distance with tape measure.
Clap 2 wooden blocks together & listen for echo.
Synchronize clapping of blocks with echo.
Measure time for 10 claps using stopwatch.
Repeat 3x and calculate the average.
Use speed = distance/ time to calculate sounds speed
What does a microphone do?
A microphone converts sound energy into electrical signals, which an oscilloscope displays to show the soundwaves changes in amplitude & frequency.
How to use an Oscilloscope?
The horizontal line axis on the oscilloscope displays time
Adjust the time scale till the display shows at least 1 wavelength
Read of the period - the time taken for 1 wavelength
Frequency(Hz) = 1/ period

What does a sound having fast vibrations mean?
Fast vibrations (i.e. high frequency) cause high pitch sounds. Low frequency vibrations cause low pitch sounds.
What does a sound being loud mean?
The louder a sound, the greater the amplitude of vibration.
Magnetic Energy Store
Energy stored when repelling poles are pulled closer or when attracting poles are pulled further apart
Internal (thermal) Energy Store
Total kinetic & potential energy of particles in an object, in most cases this is vibrations of particles. Hotter objects, particles have ↑ internal energy & vibrate faster
Chemical Energy Store
The energy stored in chemical bonds, such as those between molecules
Kinetic Energy Store
The energy of a moving object
Electrostatic Energy Store
The energy stored when repelling charges move closer together or when attracting charges have been pulled further apart
Elastic Potential Energy Store
The energy stored when an object is stretched or squashed
Gravitational Potential Energy Store
The energy of an object at height
Nuclear Energy Store
The energy stored in the nucleus of an atom
Pathways for transferring energy - Mechanical Work
A force moving an object through a distance
Pathways for transferring energy - Electrical Work
Charges moving due to a potential difference
Pathways for transferring energy - Heating
Due to temperature difference caused electrically or by chemical reaction
Pathways for transferring energy - Radiation
Energy transferred as a wave (e.g. light & infrared)
What is Renewable Energy?
Energy sources that won't run out (e.g. solar energy, wind energy & hydropower).
Wind Energy - Wind Turbines
Wind turbines are installed in exposed locations (e.g. sea) to generate electricity from the kinetic energy store of moving air by turning blades which turn a generator inside.
Energy Transfer of Wind Turbines:
Kinetic energy of the Air (wind) ➡Kinetic energy of Turbine ➡ Electrical Energy
Advantages of Wind Turbines
Highly Efficient
Low maintenance
Renewable
Disadvantages of Wind Turbines:
Unreliable
Noise Pollution
Visual Pollution
Tidal Power
Tidal barrages are dams built across river estuaries, with turbines. Tide comes in & fills up the estuary. This water is then allowed out through turbines at a controlled speed whilst driving turbines on the way in.
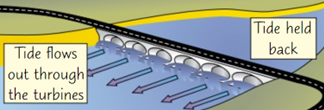
Energy Transfer of Tidal Power:
Gravitational Potential Energy of water ➡️ Kinetic Energy ➡️ Electrical Energy
Advantages of Tidal Power:
Durable
Renewable
Zero carbon emission
Disadvantages of Tidal Power:
Expensive
Energy demand
Geographical Limitations
Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric power involves flooding a valley by building a dam. Rainwater is captured & released through turbines, transferring energy from the water's gravitational potential to its kinetic energy stores as it falls, generating electricity
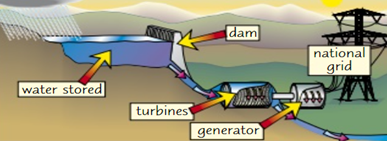
Energy Transfer of Hydroelectric Power:
Gravitational Potential Energy of water ➡️ Kinetic energy of water ➡️ Mechanical Energy of turbine
Advantages of Hydroelectric Power:
Renewable
Reliable
Highly Energy Efficient
Disadvantages of Hydroelectric Power:
Initially expensive
Environment Impact
Occasionally unsafe
Solar Energy - Solar Cells
Uses energy from the Sun to directly generate electricity. They generate direct energy in your home.
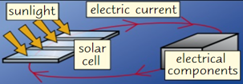
Solar Energy - Solar Heating Panels
The glass allows energy from the Sun in, which is then absorbed by the black pipes and heats the water.

Energy Transfer of Solar Energy:
Electromagnetic Energy (light) from Sun ➡️ Electrical Energy
Advantages of Solar Energy:
Renewable
Low maintenance
Zero carbon emission
Disadvantages of Solar Energy:
Initially Expensive
Sunlight dependant
Limited Resources
Geothermal Power
Energy is generated by the decay of radioactive elements, such as uranium, in hot rocks near the Earth's surface. Water is pumped in pipes down the hot rocks & forced up due to pressure to turn a turbine that drives generator.
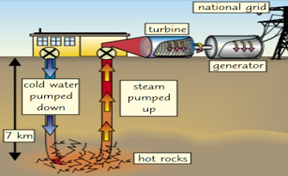
Energy Transfer of Geothermal Power:
Thermal Energy store of rocks ➡️ Mechanical Energy ➡️ Kinetic Energy ➡️ Electrical Energy
Advantages of Geothermal Power:
Renewable
Environmentally Friendly
Little Maintenance Required
Disadvantages of Geothermal Power:
Generates Waste
Initially Expensive
Location Specific