Behavior and training
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Objective 1: Name the basic of horse behavior
prey animal
fight or flight: will choose to flee vs fight
social or herd animal
Use of dominance hierarchy
Prey animal
their instincts and behaviors are adaptions to avoiding predators
Fight or flight response
horses usually run away (flight) from danger but instead of fighting
social heard animal
horses live in groups (herds) for safety and companionship
dominancy hierarchy
in a herd, some horses are more dominant and control access to food, water or space.
Objective 2: describe common equine body language
ears out to the side: dozing
ears forward and up: alert or curious
ears outward and forward: calm
eyes showing white alarm/concern/fear
ears lying back a bit: annoyed, anxious, or uncomfortable
teeth being shown bare: displeased and confrontational
obejective 3: Describe the ways that horses communicate
whinny
nicker
squeal
snort
blow
sigh
mutual grooming
flehmen
whinny
is a strong,long almost staccato sound that used to contact other horses
nicker
is low, throaty sound , made with the mouth closed
squeal
cry for help, if there is a threat
snort
to communicate a range of feelings and situations, including signaling excitement, happiness, fear, or the presence of danger
blow
through the nostrils, mild warning or clearing the nose
sigh
expressing relief, or bored
mutual grooming
they nibble each other bodies particularly the back and withers
flehmen
It curls its upper lip back, showing its teeth, and also might stretch its neck and raise its head high, to investigate smells

Objective 4: Describe the types of behaviors exhibited by the
horse
REMINDER:
feral→ an animal that once was domesticated but now lives in the wild
domesticated→ an animal that has been bred and adapted by humans
agonistic behavior
allelomimetic
epimeletic
et-epimeletic
ingestive behavior
eliminative
agonistic behavior
dominance hierarchy
ex: kicking, rearing, charging
allelomimetic behavior
definition: when one horse copies the actions of another horse
herd animal: they survive by sticking together
early man (humans) will use this as an advantage to control one horse and the rest often followed because of this specific behavior
epimeletic behavior
giving care and attention
ex: mutual grooming
et- epimeletic behavior
calling for attention upon separation
ingestive behavior
related to eating and drinking
ex:
coprophagy: eating feces
bolting feed: eating food fast
cribbling: biting wood and suck on it to get a natural high
wooding chewing
mane and tail
chewing
digging or pawing
pica: eating non food items
eliminative behavior
territorial marking: urination and defecation
sexual behavior (three horses) Name the horses and what are there sexual behavior?
stallions: biting, striking, rearing, charging, crowding and flemmne and mounting
mares:
estrus: the period when a mare(female) is sexualy receptive)
Leads to→ kicking, winking (opening and closing of the vulva), squatting in estrus, and kick threat if out of estrus
gleddings: a castrated male horse
Proud cut: when a horse is castrated, but some testicular tissue is accidentally left behind, leading to still showing male behaviors
Objective 5: Describe the senses of the horse
Vison
hearing
touch
smell
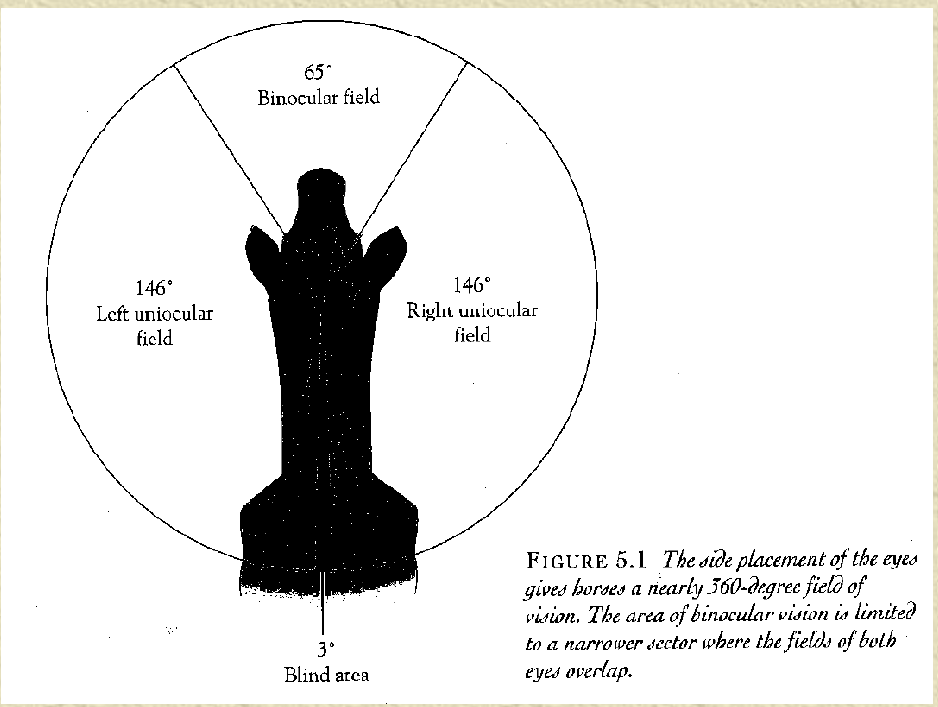
what type of vision does a horse have?
monocular (side)
left 146
right 146
bionuclear (front), which is their blind spot, and also behind
Night vision: Horses see well in low light because they have many rods and a reflective layer (tapetum lucidum).
Depth perception: Limited since eyes are on the side; best when they use both eyes in front. They move their heads to judge distance.
Categorical perception (color): Horses are dichromatic — see blues and yellows but not reds (reds look grayish).
What type of hearing do horses have? What are the primary functions? what can the ear specifically do?
55Hz to 33.5 Hz
0-80 decibels
Functions:
detect sound
determine location of sound
provide sensory information that allows horses to recognize the identity of these sounds
The ear can move 180 degrees using 10 different muscles
describe the different traits of touch of the horse
skin very specialized sense organ
most sensitive in mouth, feet, flanks, neck, shoulder
hard mouth
What are the traits of a horse that have a good sense of smell?
define receptors
more acute than humans
less sensitive than dogs
Definition: the upper part of the nasal cavity within the mucous membrane