Chapter 1: Structure of Organic Compounds
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What is organic chemistry?
Is the study of carbon-containing molecules and their reactions
What elements do organic compounds always contain?
Carbon and a limited number of other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen
Compounds containing sulfur, phosphorus, and halogens are known but less prevalent
Can organic compounds vary in size?
Yes, from small to very large in molecular weight
How are molecules represented?
There are many ways to represent molecules
Often, a compound’s molecular formula is NOT adequate to define it
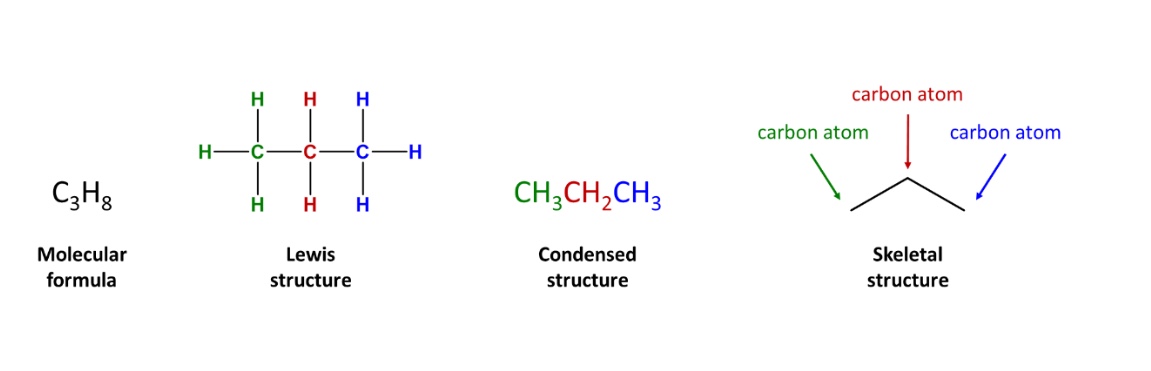
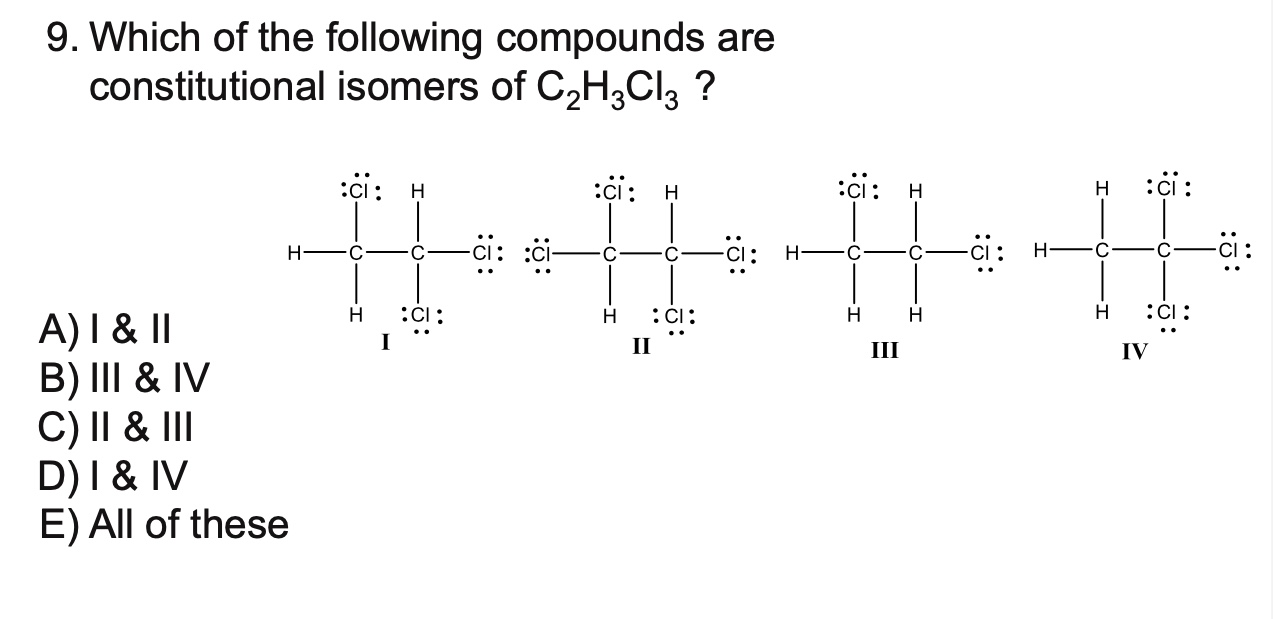
What are constitutional isomers?
are different compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in how the atoms are connected
structural atoms
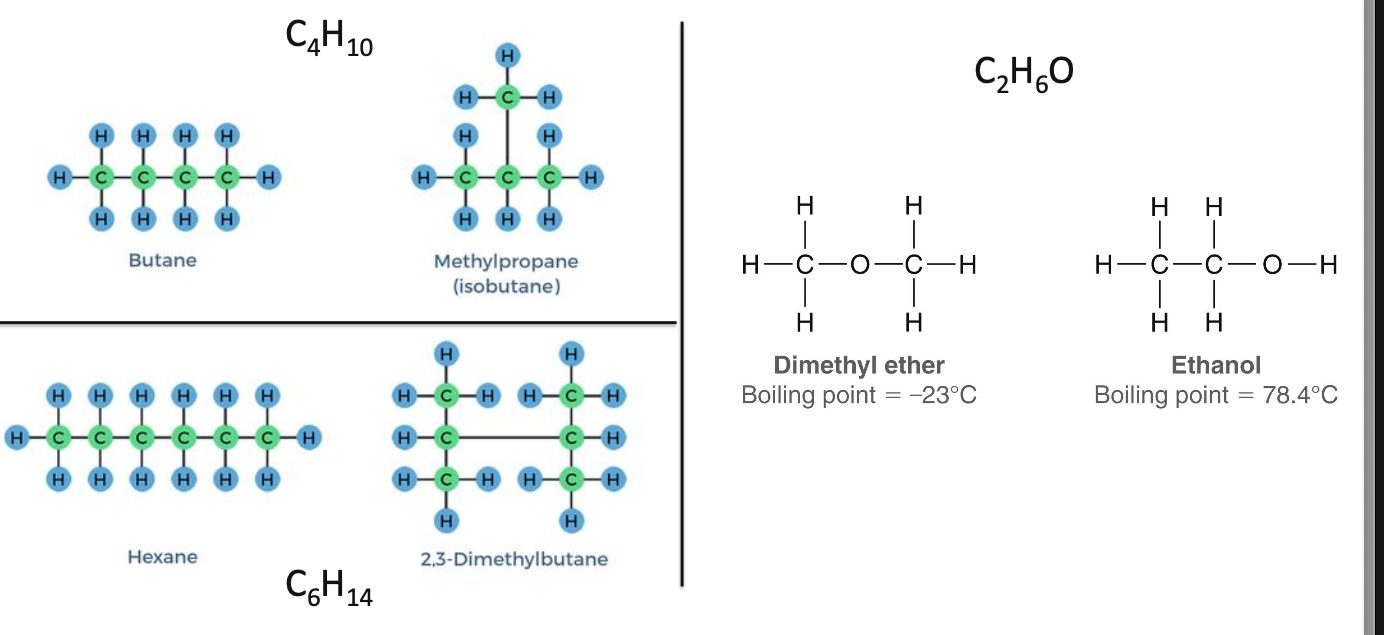
What is the structural theory?
states that the properties of a compound depend on how its atoms are connected and arranged within the molecule, not just on the molecular formula
Same formula ≠ same compound
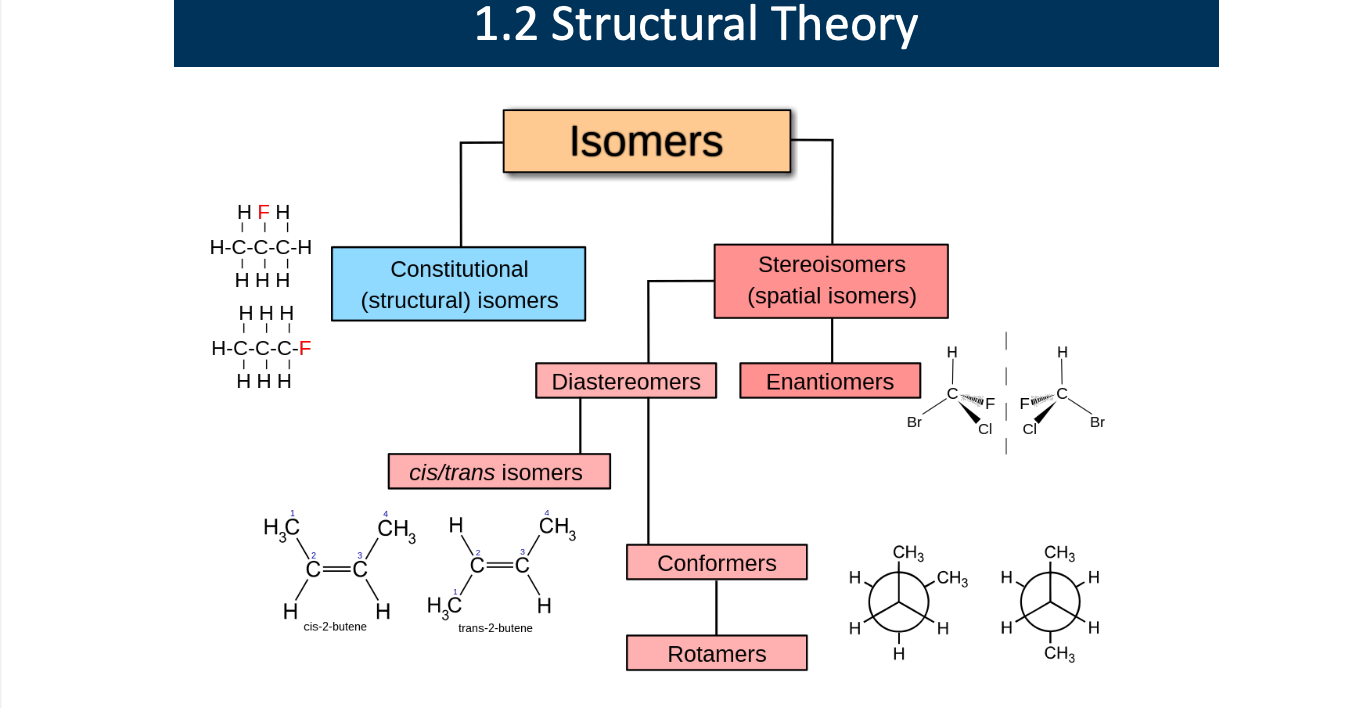
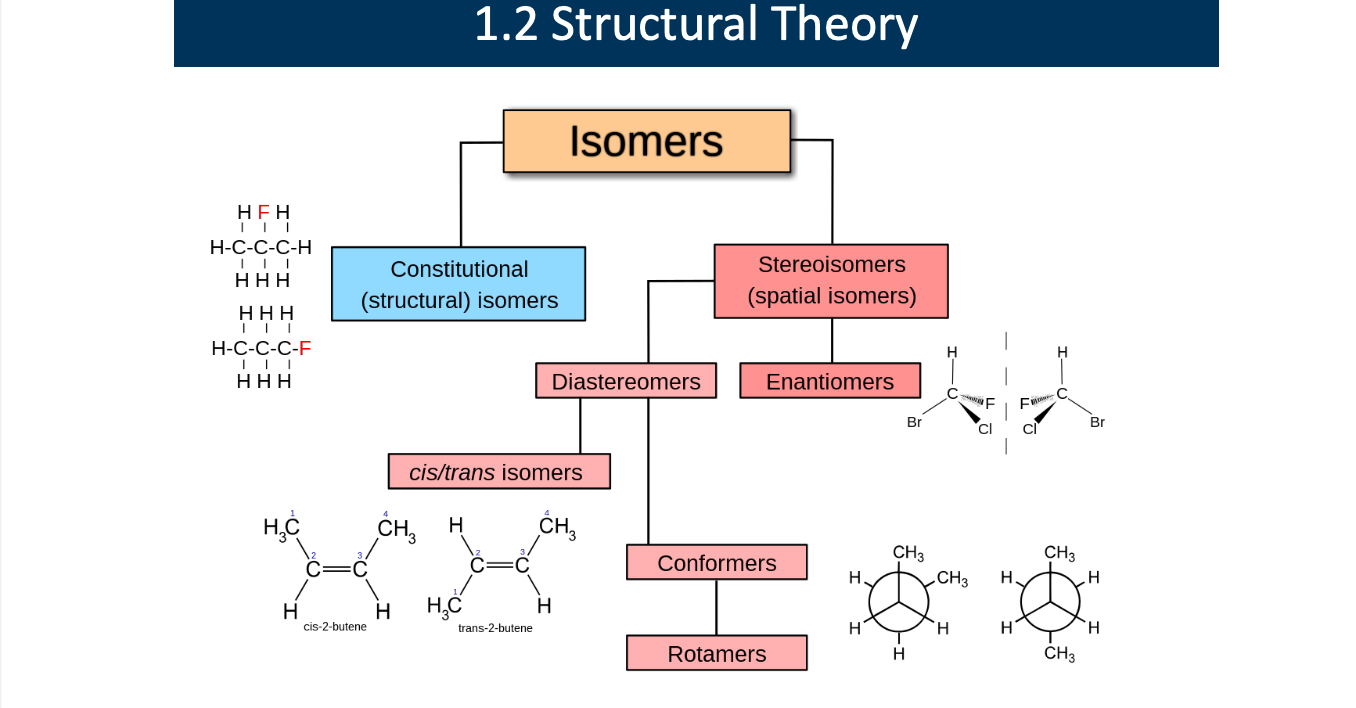
Explain each role
Isomers: different compounds that have the same molecular formula
splits into constitutional (structural) isomers or stereoisomers (spatial isomers)
Consitutional (structural) isomers: compounds that have the same molecular formula but different connectivity of atoms (the atoms are bonded in a different order).
Stereoisomers (spatial isomers): compounds that have the same molecular formula and the same connectivity of atoms, but differ in the three-dimensional (spatial) arrangement of those atoms.
types of stereoisomers:
Diastereomers Not mirror images, Different physical and chemical properties, Include cis/trans isomers
Enantiomers:Mirror images, Not superimposable (left vs right hand), Often differ in biological activity
How can you calculate number of valence electrons?
Look at the group number (this only works for main elements not transition elements)
How many valence electrons does phosphorus have?
5
What are elements are most commonly bonded to carbon?
N, O, H, and halides (F, Cl, Br, I)
Can elements form certain number of bonds?
With some exceptions, each element generally forms a specific number of bonds with other atoms
How many bonds does carbon form?
Four bonds (tetravalent)
How many bonds does nitrogen form?
three bonds (trivalent)
How many bonds does oxygen form?
two bonds (divalent)
How many bonds does halogens and hydrogen usually form?
1 (monovalent)
What are the possible structures for the molecular formula C3H8O
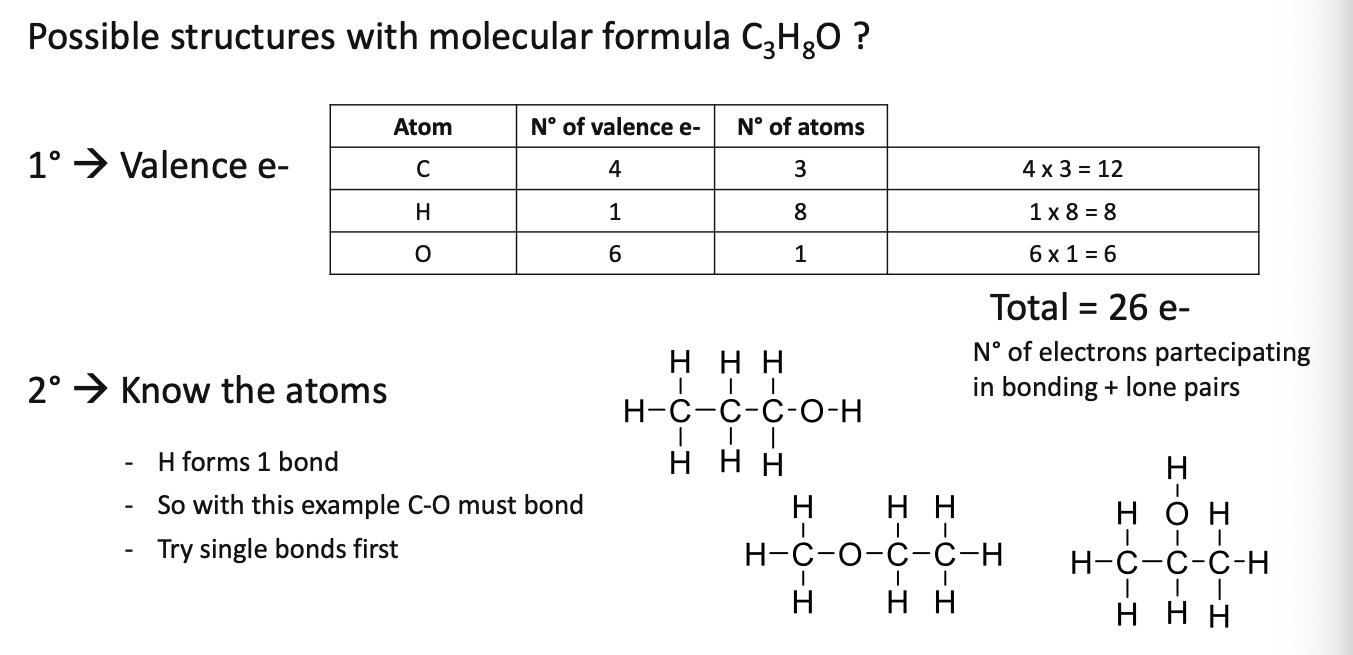
Answer the following question
D
What is an anion?
negatively charged atom
What is a cation?
a positively charged atom
How do you calculate formal charge?
compare the number of valence electrons that should be associated with the atom to the number of valence electrons that are actually associated with an atom
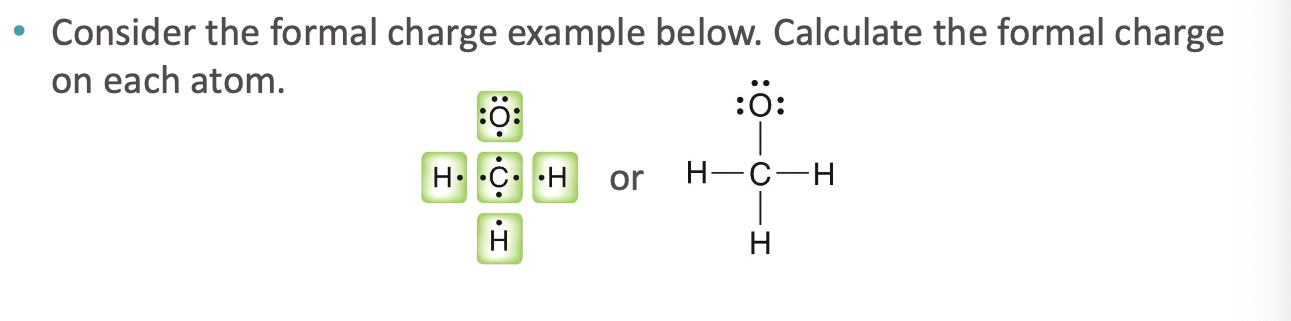
Calculate the formal charge of each atom
Carbon needs four valence electrons to be neutral (Group IV)
Carbon is surrounded by eight electrons here, but it only owns four of them (one
from each of the bonds).
Since carbon owns four electrons, and needs four electrons to be neutral, it does
not have a formal charge.
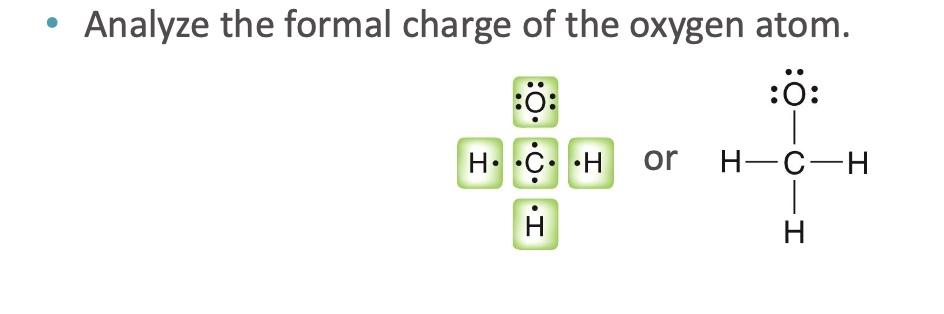
Analyze the formal charge of the oxygen atom
Oxygen needs six valence electrons to be neutral (Group VI).
• Oxygen is surrounded by eight electrons here, but it only owns seven of them (one from
the bond, plus three lone pairs ).
• Since oxygen owns seven electrons here, and needs 6 electrons to be neutral, it has an
extra electron, and therefore has a −1 charge.
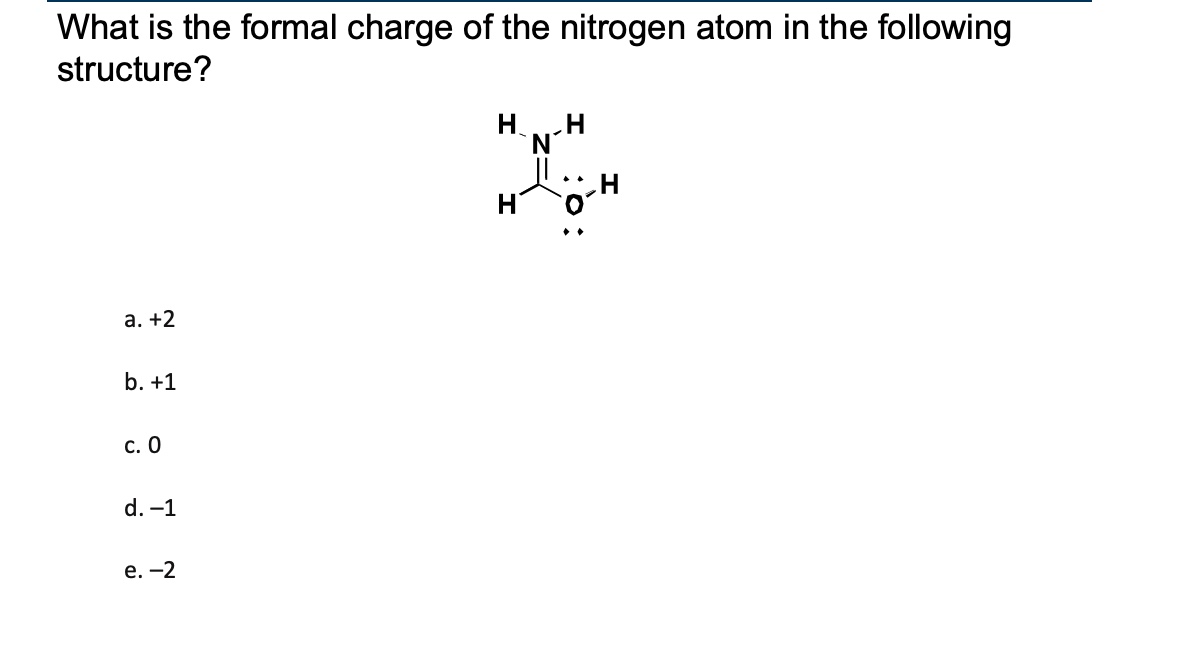
What is the formal charge of the nitrogen atom in the following structure?
b) +1
What is valence bond theory?
A bond shared electron density
What is molecular Orbital (MO) theory
Atomic orbital wavefunctions overlap to form MOs
that extend over the entire molecule
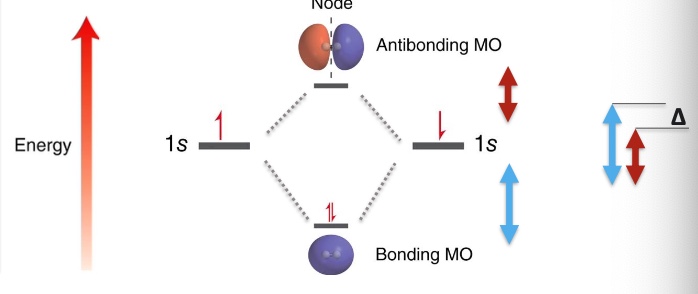
Describe sigma bond
Is the strongest type of covalent chemical bond
The greater the overlap between atomic orbitals (valence bond theory), the stronger the bond formed between the two atoms
it is symmetrical with respect to rotation about the bond axis
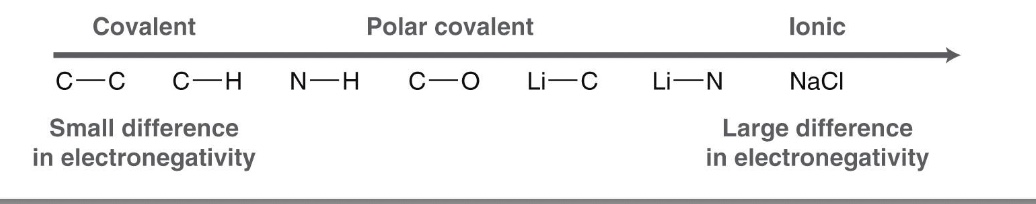
What is a covalent bond?
It is the sharing of electrons between atoms
they are either polar or nonpolar
What is a nonpolar covalent bond?
bonded atoms share electrons evenly
the electronegativity difference is less than 0.5
What is a polar covalent bond?
one of the atoms attracts electrons more than the other
the electronegativity difference is between 0.5 and 1.7
What is electronegativity?
how strongly an atom attracts shared electrons
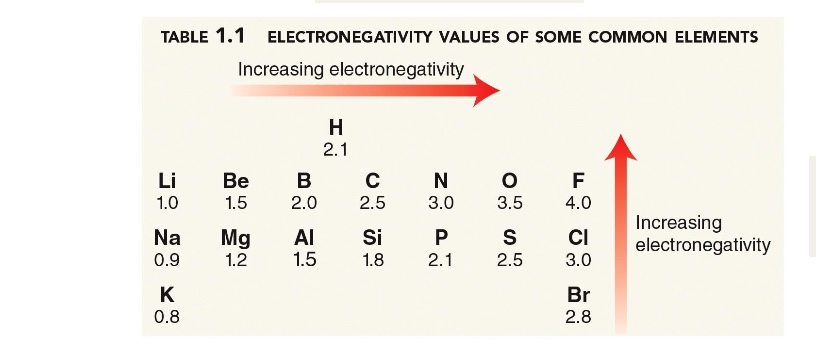
What is an ionic bond?
The electrons are not really shared, the two atoms differ in electronegativity by more than 1.7, and so the more electronegative atom owns the electrons
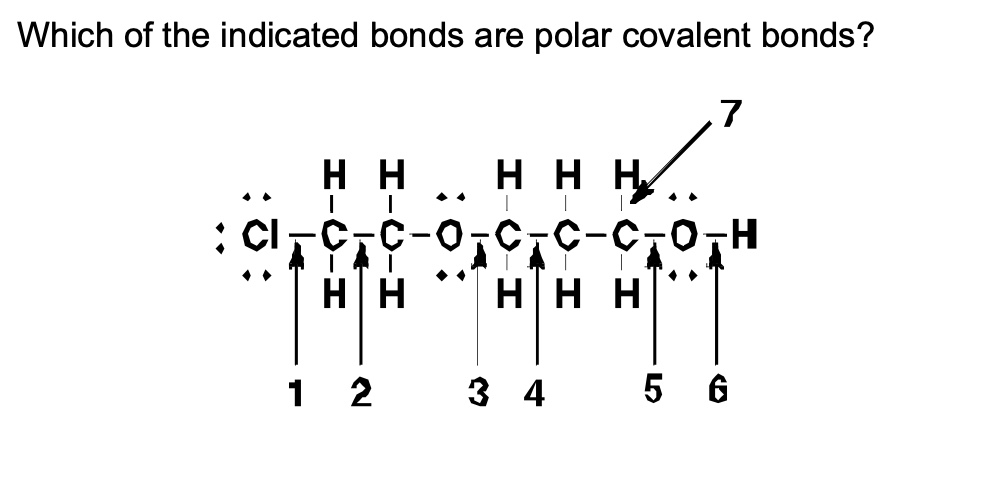
Which of the indicated bonds are polar covalent bonds?
1,3,5,6
How to determine molecular geometry?
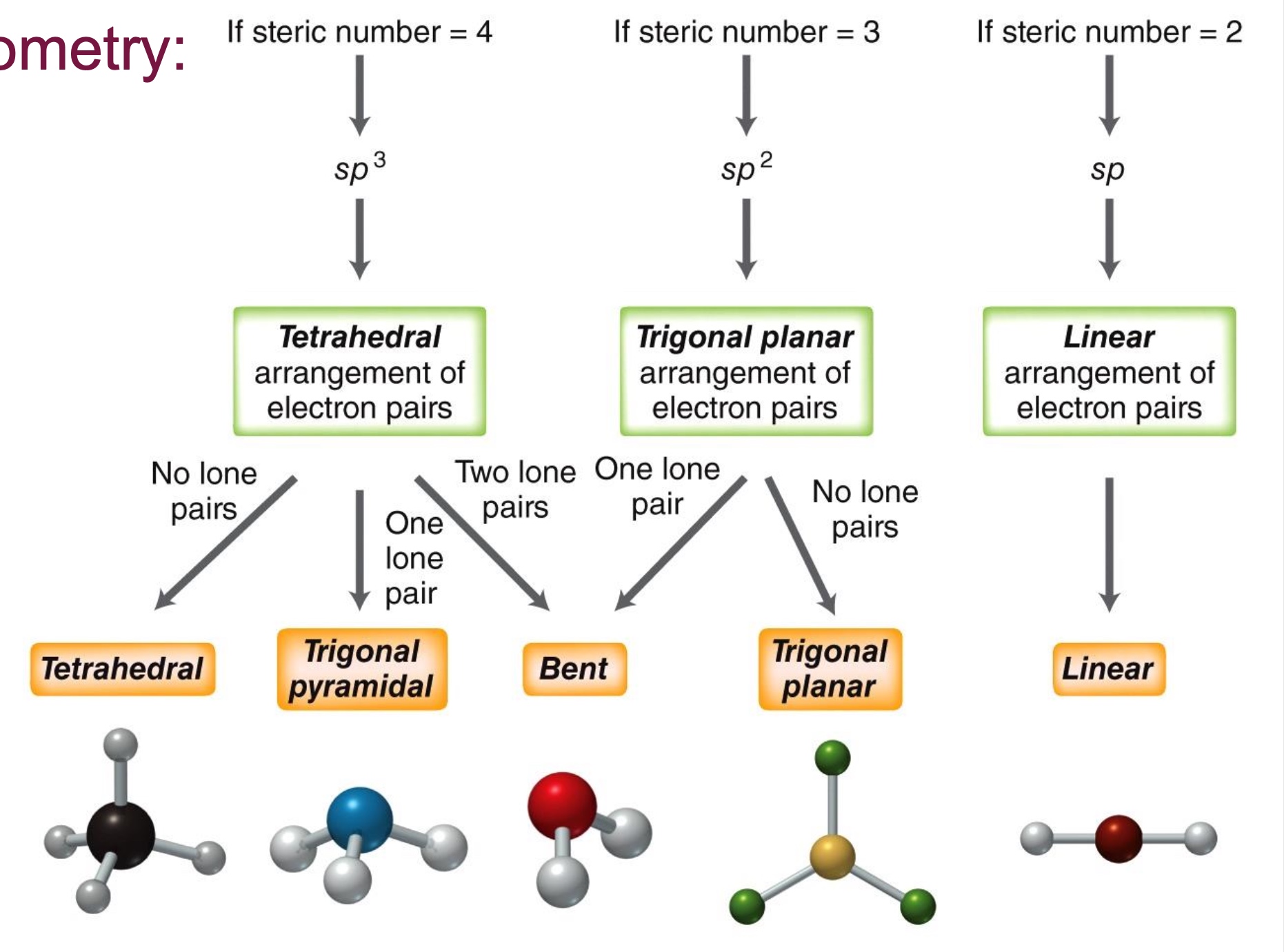
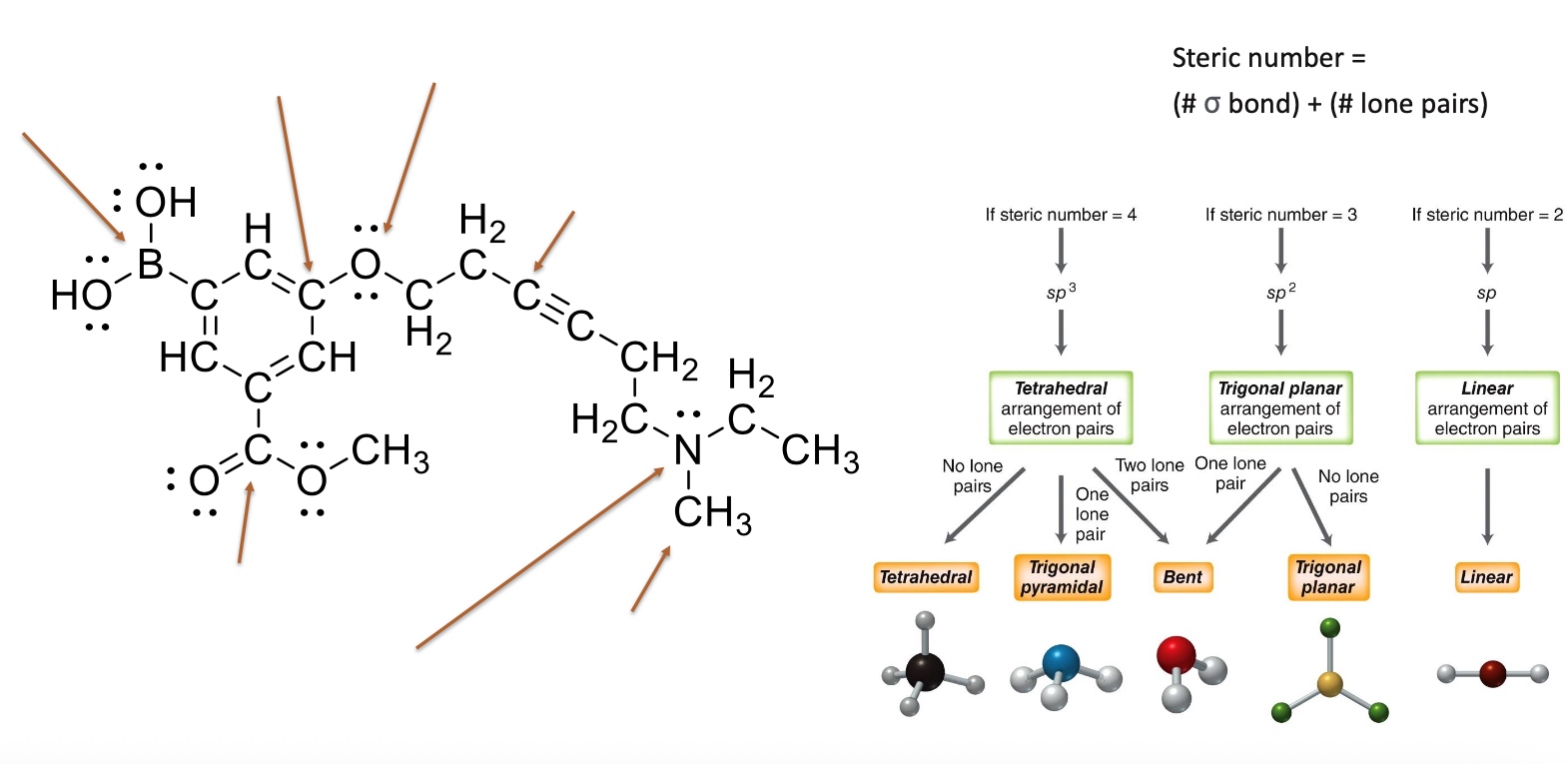
Determine the steric number and molecular geometry
d
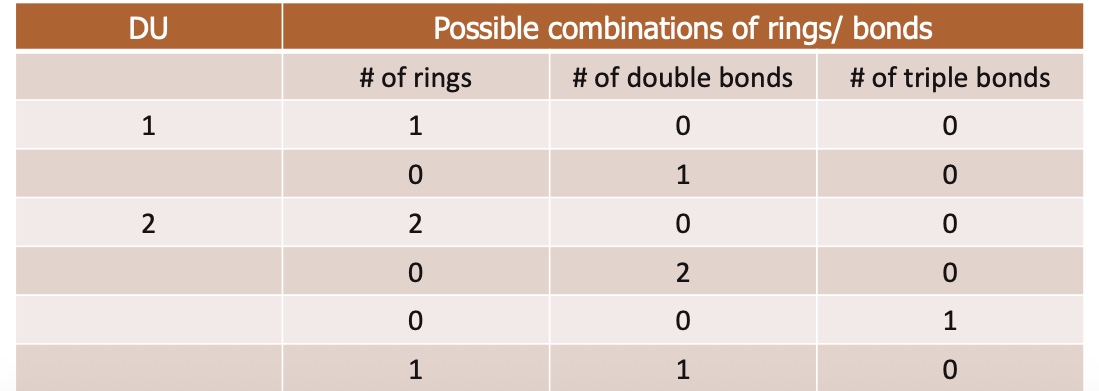
What is degrees of unsaturation?
tells you how many rings and/or multiple bonds (pi bonds) are present in a molecule
What is the calculation of degrees of saturation?
DoU=2C+2+N-X-H/2
C is the number of carbons
N is the number of nitrogens'
X is the number of halogens (F, Cl, Br, I)
H is the number of hydrogens
If DU> 4 or greater → likely benzene ring
Calculate the degrees of unsaturation of C5H11N
DoU=1
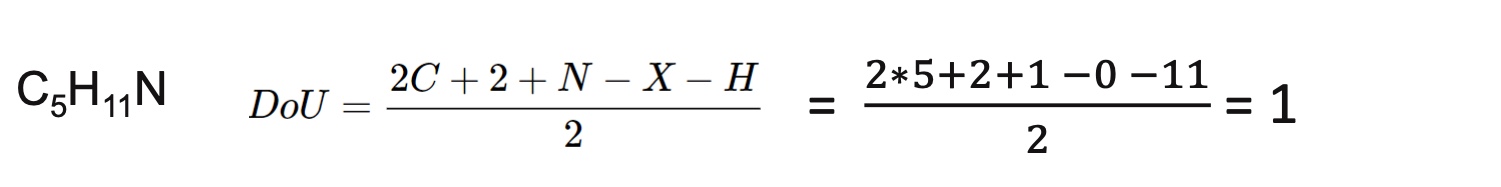
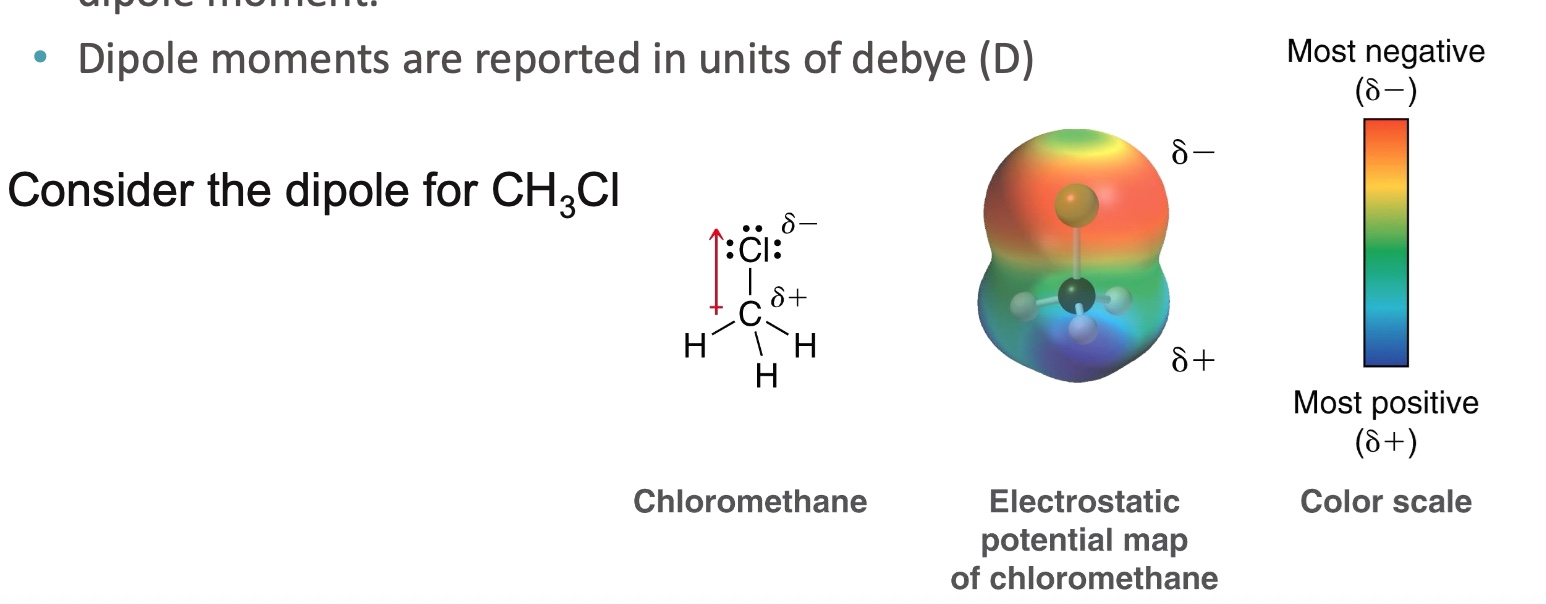
What does electronegativity differences cause?
induction
What is induction?
The shifting of electrons within their orbitals
results in a dipole moment (dipole moments are reported in units of debye (D)
Consider the dipole of CH3Cl
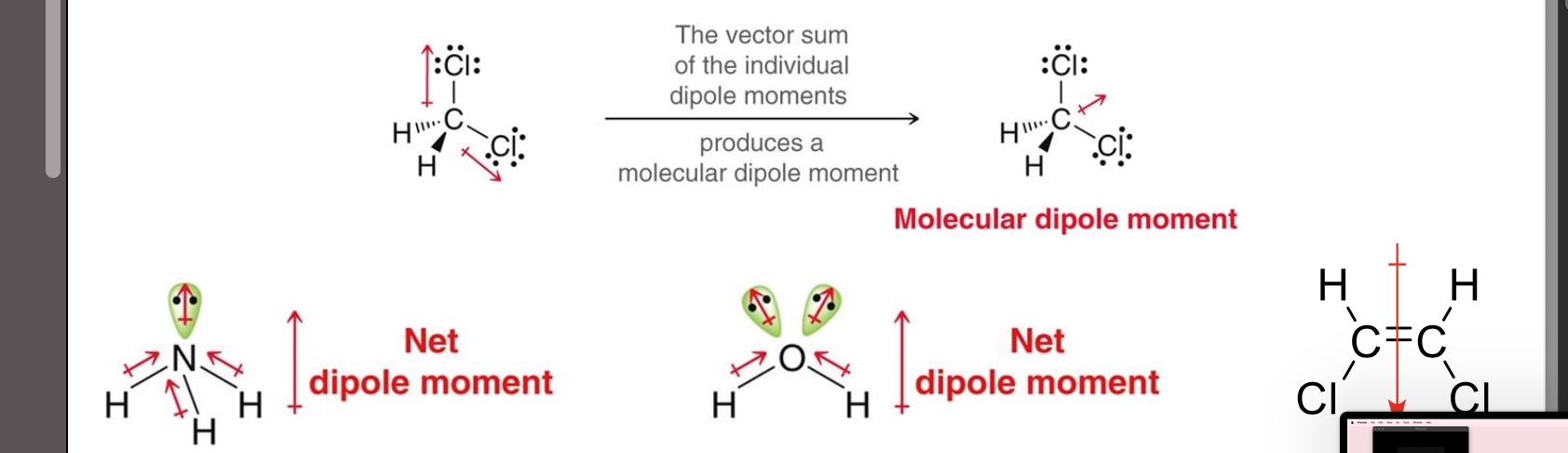
How do you analyze polarity in molecules with multiple polar bonds?
The dipole moment is the vector sum of all of the individual bond dipoles
It is important to determine a molecule’s geometry FIRST before analyzing its polarity
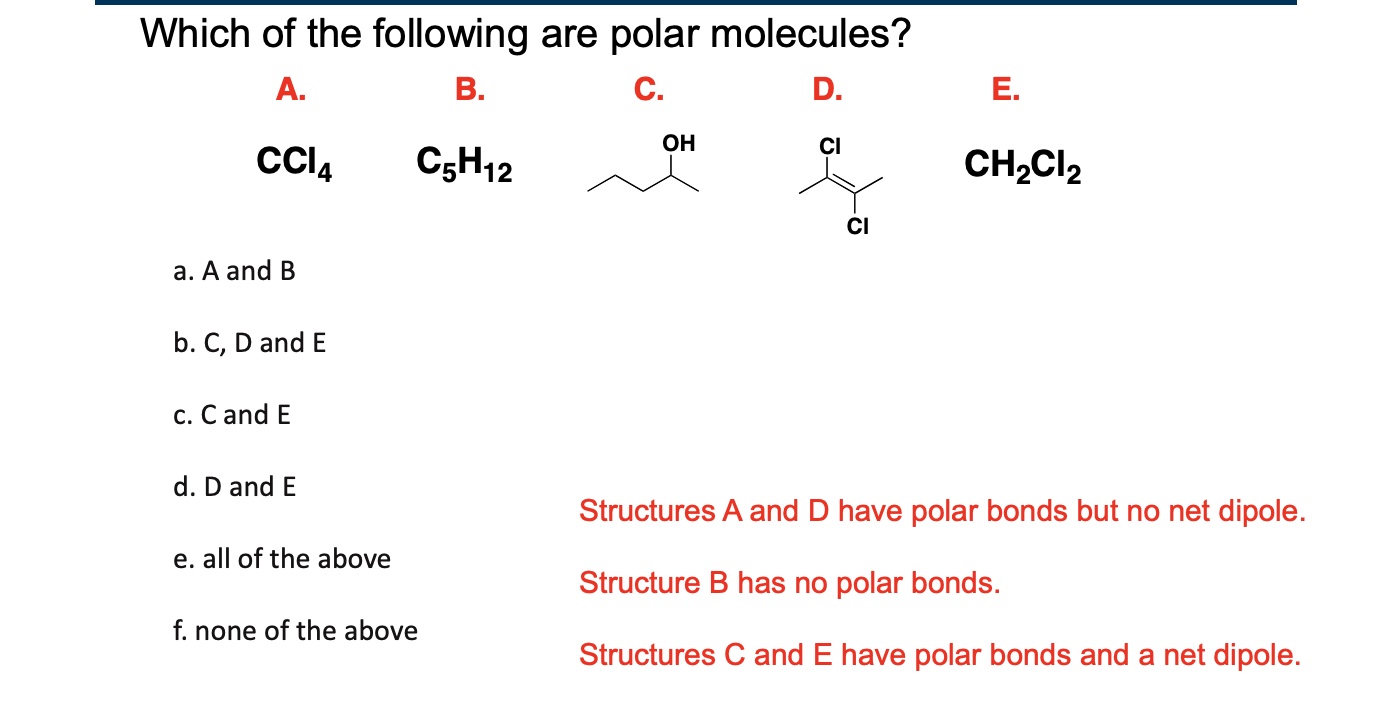
C and D
How does dispersion force affect boiling point
Weakest IMF
Only force in nonpolar molecules
Bigger molecules → stronger dispersion → higher BP
how does dipole-dipole forces effect boiling point?
Molecules have partial charges
Stick together more than nonpolar molecules
Higher BP than similar-sized nonpolar molecules
How does hydrogen bonding effect boiling point?
Strongest IMF
Requires H bonded to N, O, or F
Causes very high boiling points
How do you know which IMF has the highest boiling point?
Identify the strongest IMF present
Strongest IMF = higher boiling point
If same IMF → compare size & shape
What is the difference between protic and aprotic solvents?
Protic solvents: engage in H-bonding
Aprotic solvents: do not H-bond
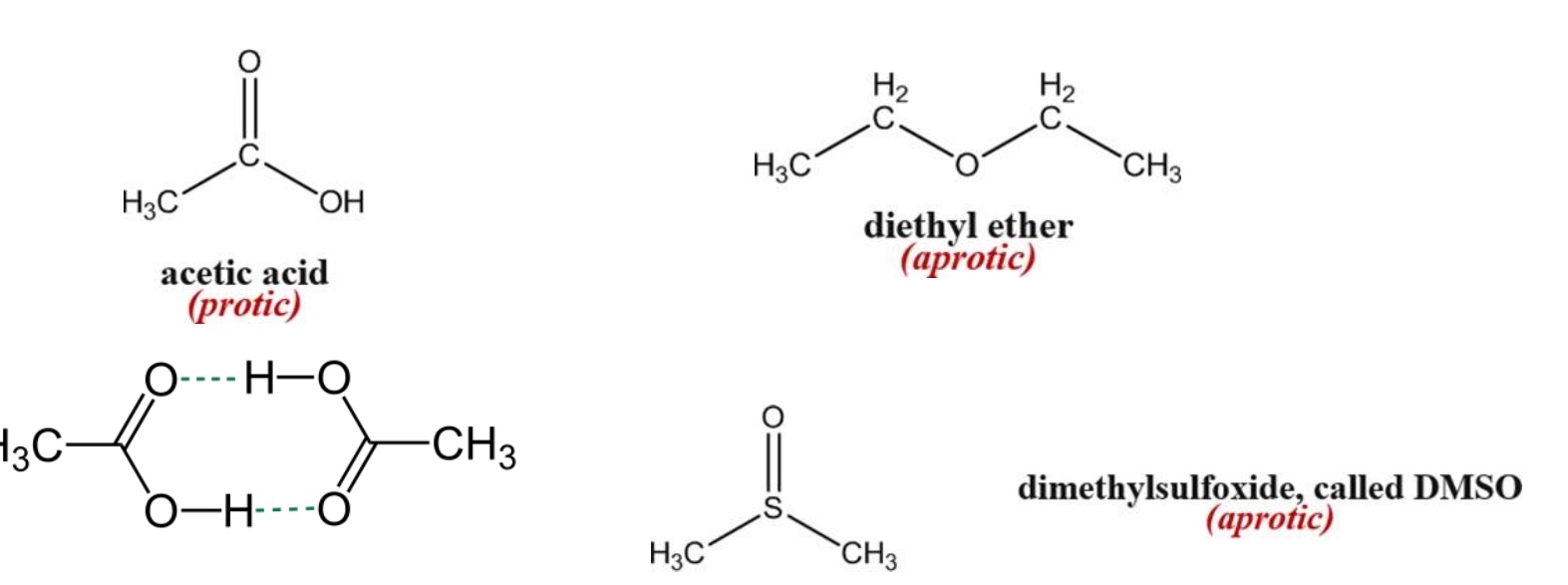
What is isomer effect?
Different shapes → different intermolecular attractions → different boiling points
If IMF’s are the same how do you identify which one has a higher boiling point?
Less surface area = lower boiling point
More branching = less surface area and a lower boiling point
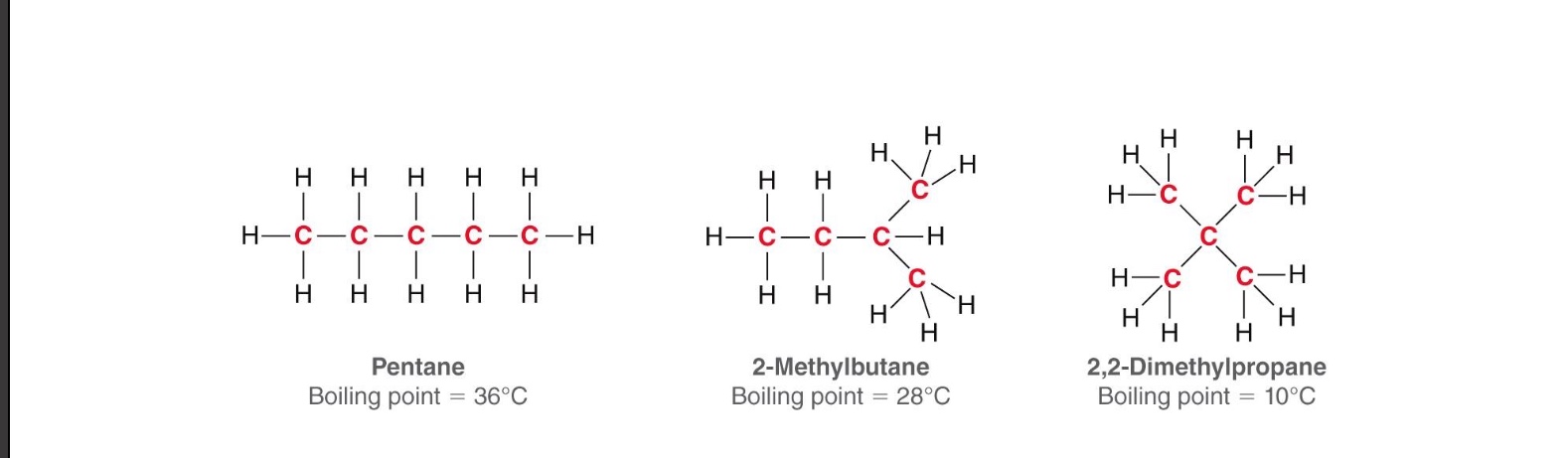
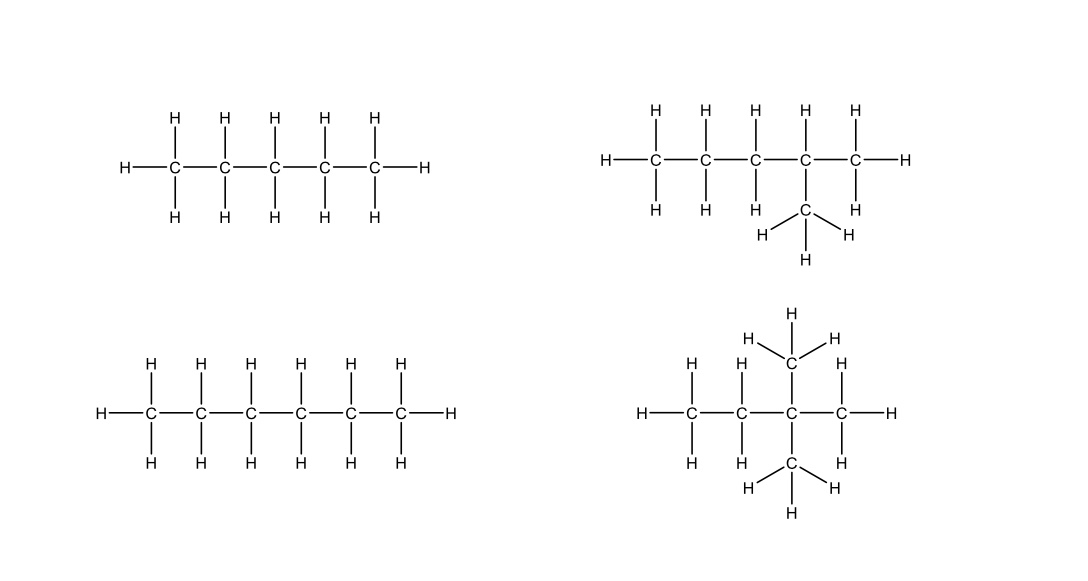
Rank the following molecules in order of highest to lowest boiling point
answer
What principle is used for solubility?
Like dissolves like
Polar compounds generally mix well with other polar compounds
Nonpolar compounds generally mix well with other non polar compounds
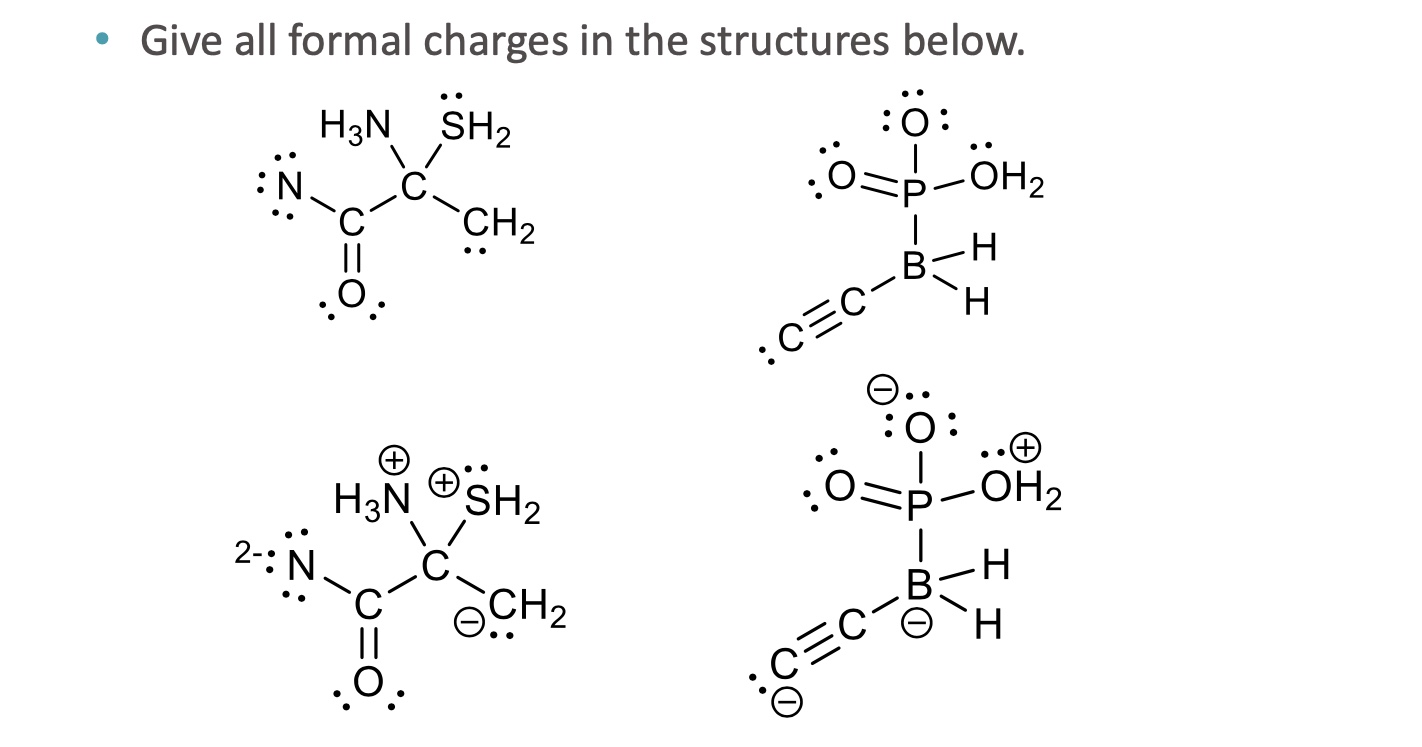
Give all formal charges in the structure below
a
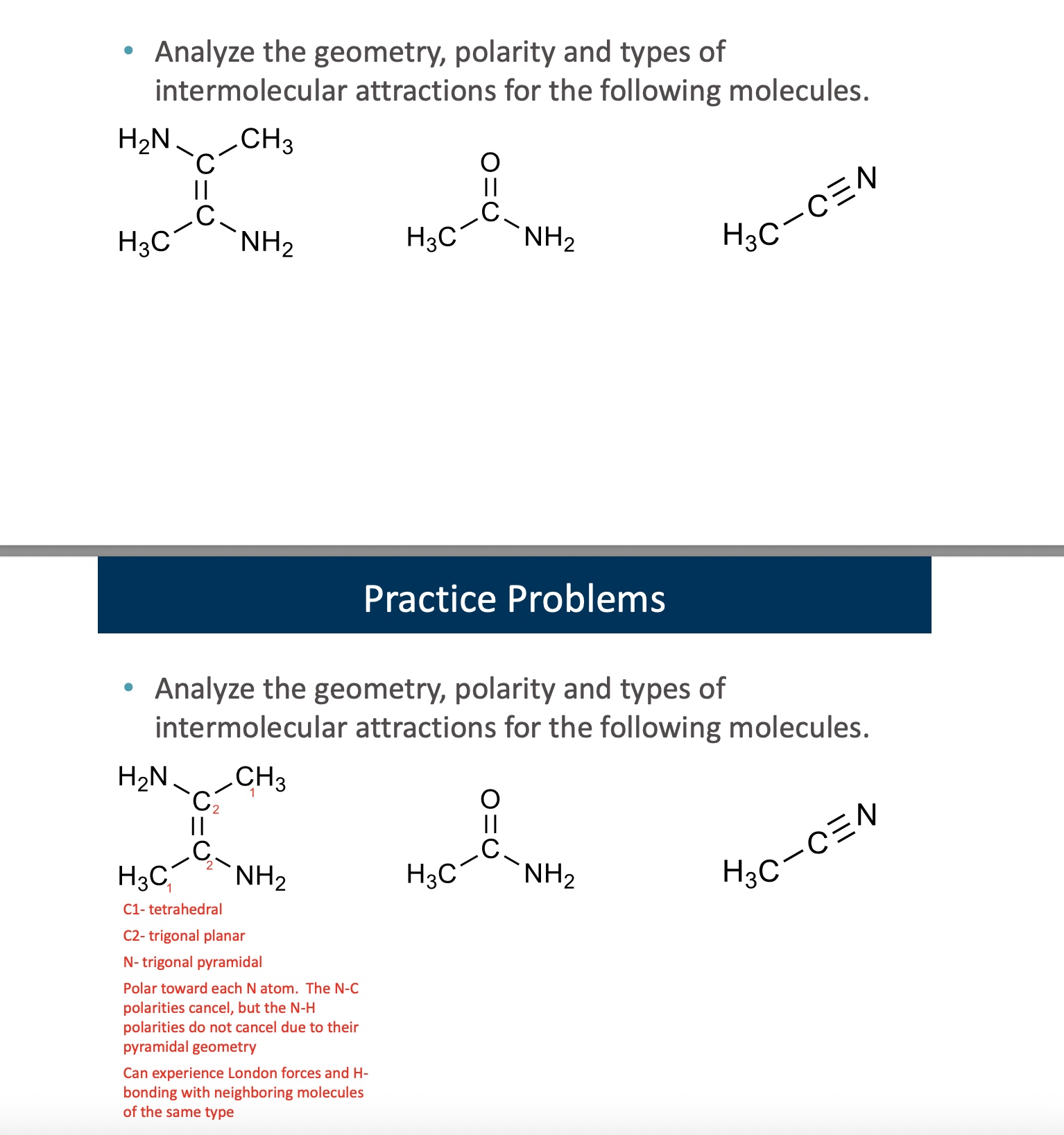
answer both
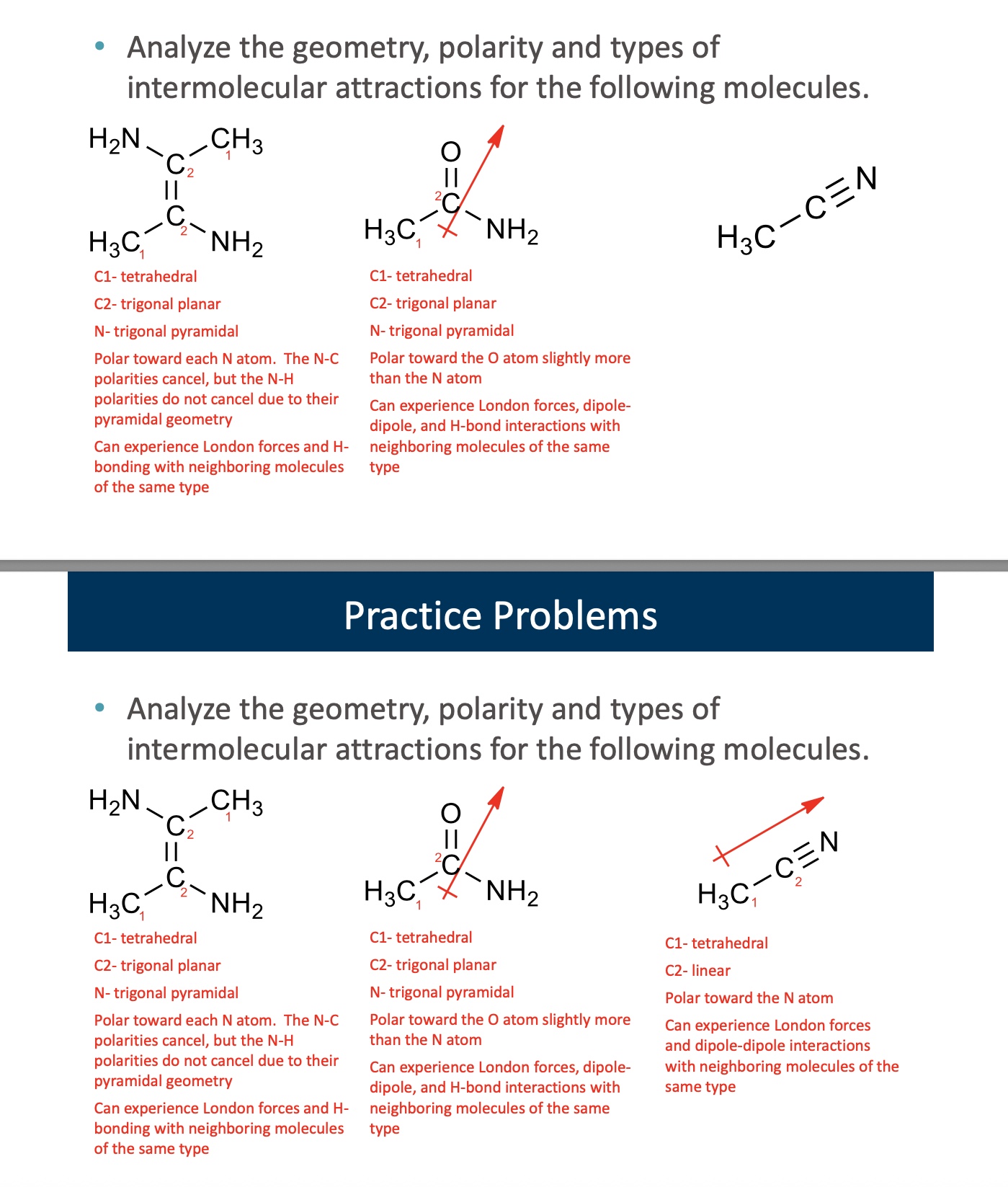
answer both
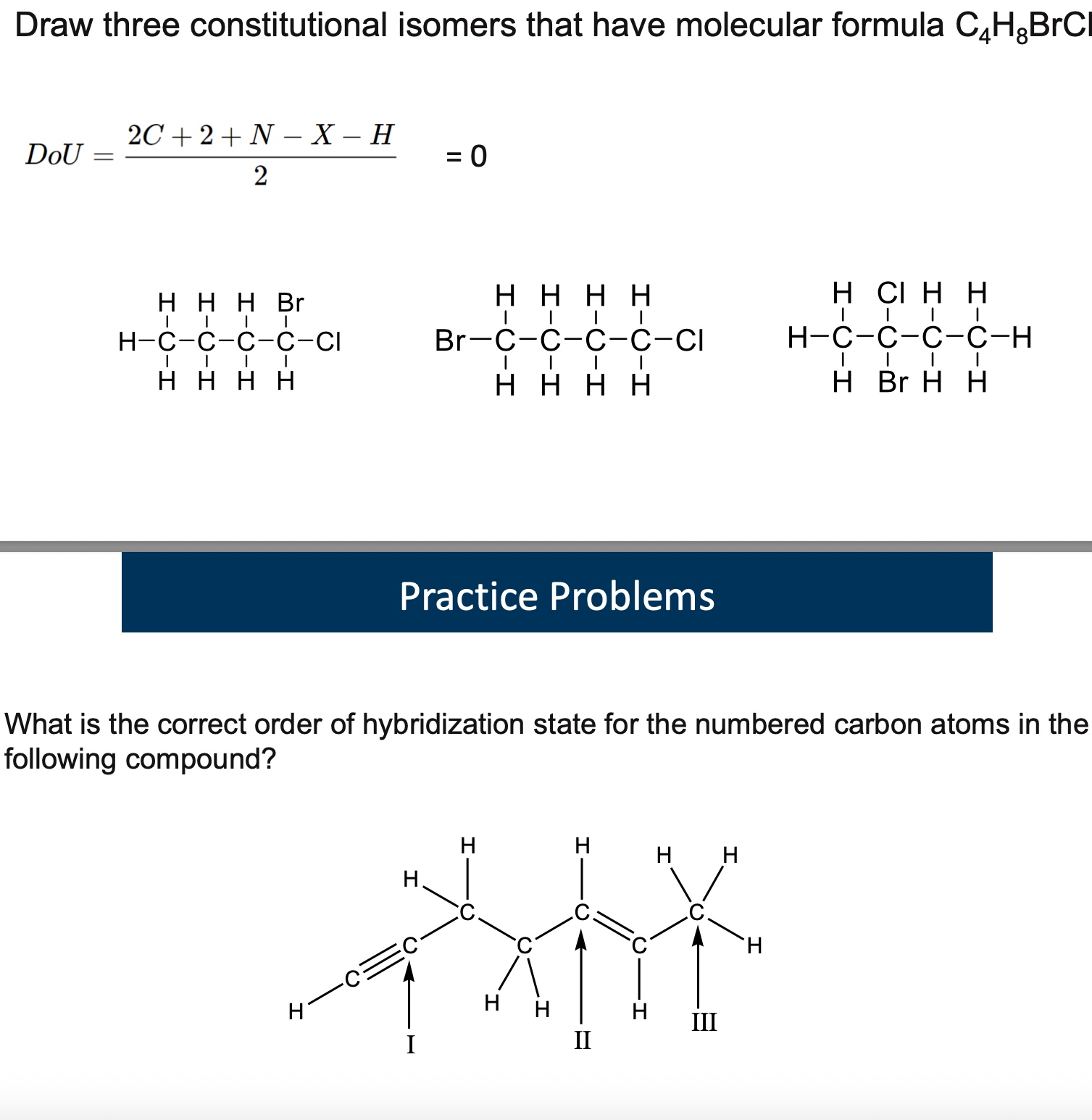
answer both
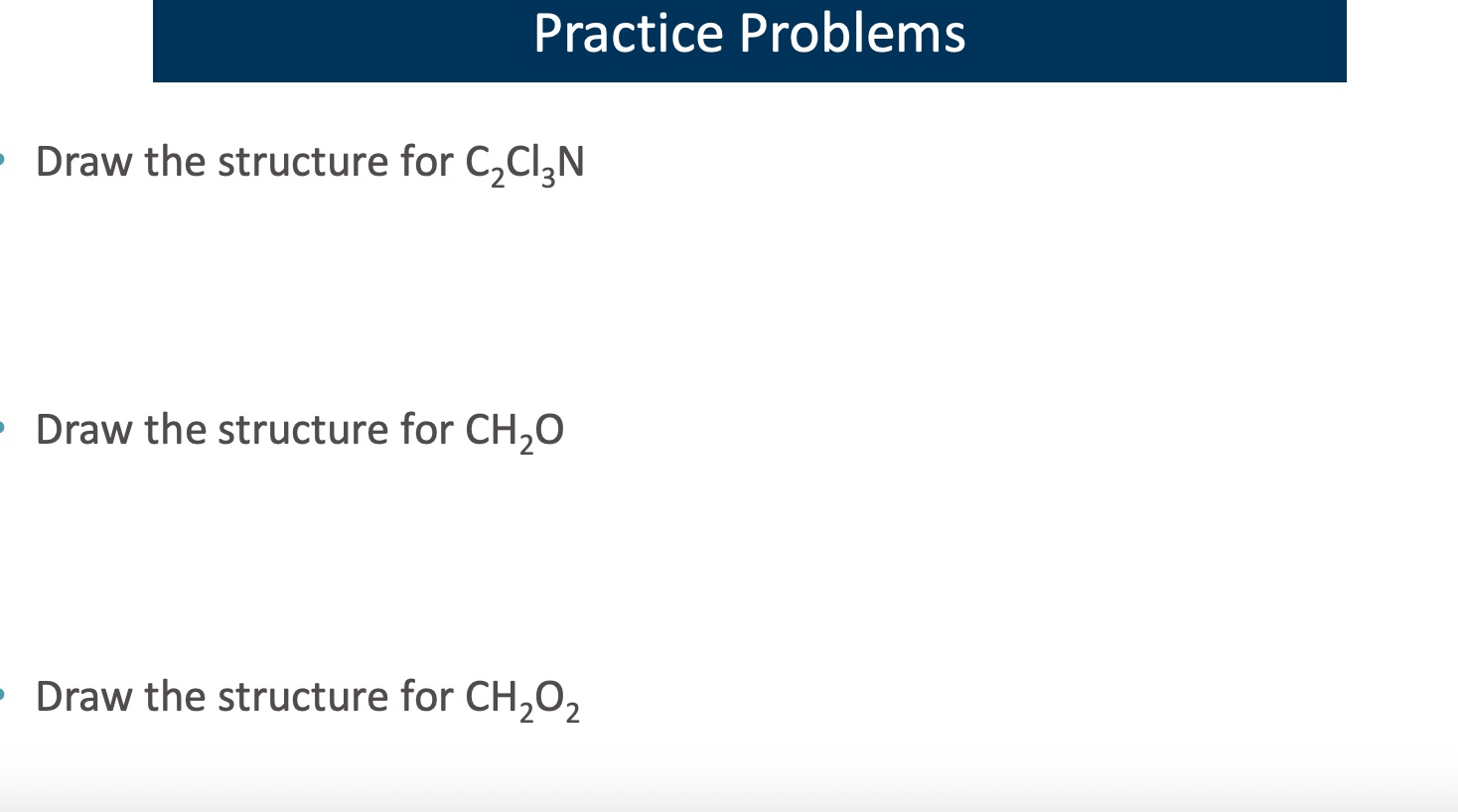
answer all questions