Chapter 3: Motion in Two or Three Dimensions
0.0(0)Studied by 6 people
Card Sorting
1/5
Last updated 2:10 PM on 3/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
1
New cards
what is the composition of the position vector (r)?
\
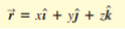
2
New cards
average velocity
the difference of the position vectors divided by the time vectors.
3
New cards
instantaneous velocity vector projectile is any body that is given an initial velocity and then follows a path determined entirely by the effects of gravitational acceleration and air resistance.
it is the limit of the average velocity as the time interval approaches zero, and it equals the instantaneous rate of change of position with time.
4
New cards
projectile
it is any body that is given an initial velocity and then follows a path determined entirely by the effects of gravitational acceleration and air resistance.
5
New cards
trajectory of a projectile
The path followed by a projectile is called its trajectory
6
New cards
formula for a(rad) with uniform acceleration
The formula for acceleration in uniform circular motion is `a = v^2/r`, where `a` is the acceleration, `v` is the velocity, and `r` is the radius of the circular path.