Chapter 14: Conjugated Compounds (Maybe Ultraviolet Spectroscopy)
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Richards Class and things you need to know for this chapter about Dienes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is a diene?
compound w/ 2 C=C groups.
What are the 3 types of dienes?
Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated
What is a isolated diene?
A diene where the two double bonds are separated by at least two alkyl groups.
What is a cumulated diene?
A diene where the two double bonds are next to each other (sharing a carbon, also known as a allene)
What is a conjugated diene?
A diene where the double bonds are separated by a single bond, allowing for resonance and stability.
What type of reaction do conjugated dienes do?
Electrophilic addition
What is a nucleophile and what are it’s characteristics?
electron pair donor, electron rich
What is an electrophile and it’s characteristics?
electron pair acceptor, electron deficient
What is an allylic carbon?
the carbon attached to the C=C
What is thermodynamic control?
ensuring that a rxn reaches equilibrium (Long rxn time, high temps = 100C, lowest E prod. expected)
What is Kinetic Control?
ensuring that the rxn is irreversible (short rxn times, low temps = 0C, fasted formed prod expected)
What is the proximity rule?
The halogen group generally doesn’t want to leave the bond it’s already near (next to the H that was added due to Markovnikov’s Rule)
Draw the mechanism for H-X of the conjugated diene CH2=CH-CH=CH2 and HBr
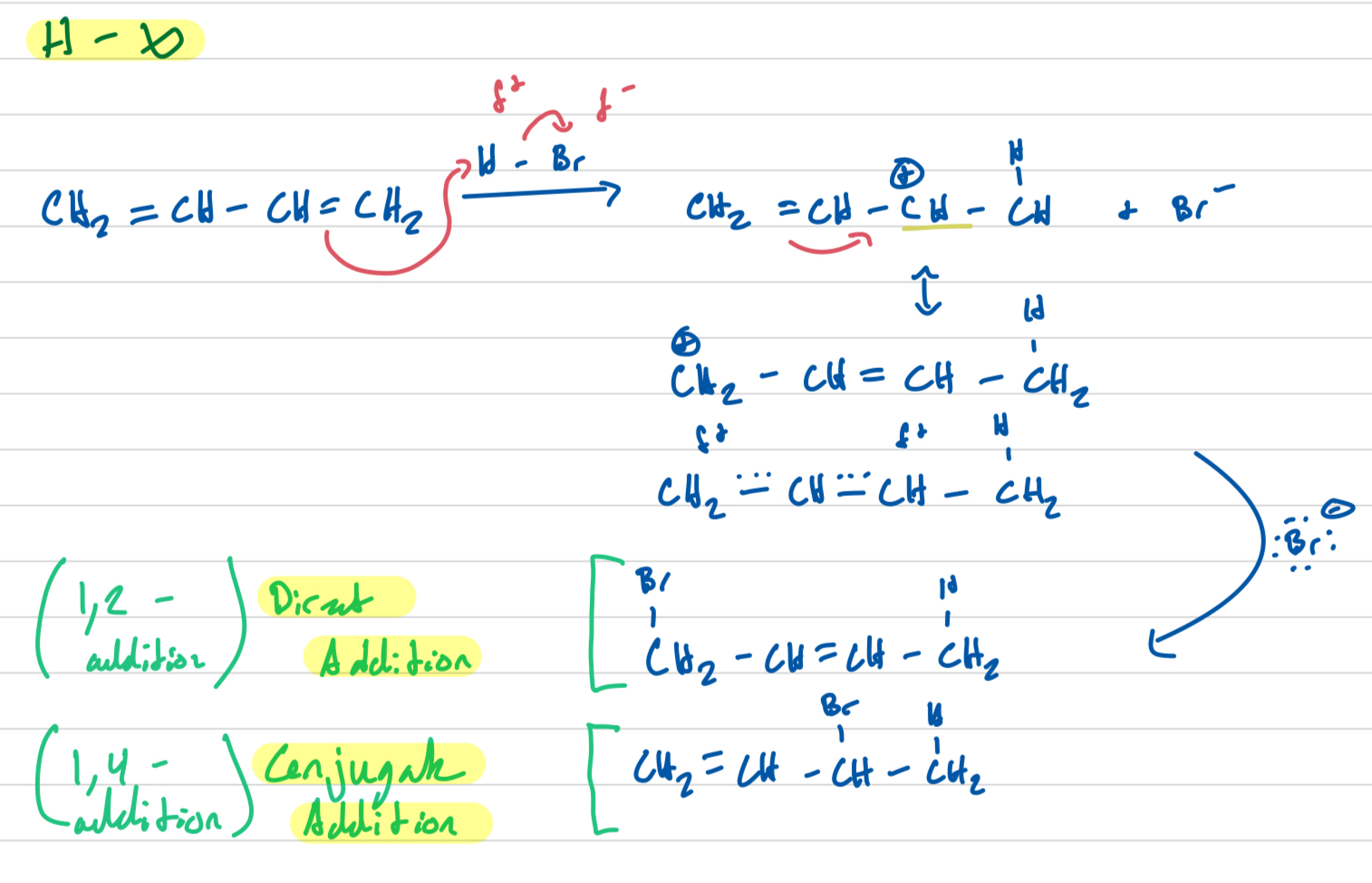
Why are we able to get two different results from electrophilic addition of a conjugated diene?
Because of resonance