Social Psychology 2. Topic 7: Opinion formation in groups. group norms, conformity, groupthink
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Social Norms
accepted ways think, feel, act
mental representations
attitudes
information on appropriateness
tells us what right behavior/opinion/emotion is in the situation
learned by observing, reading guidebooks, etc.
Descriptive social norms
what the group typically does
desired path
seeing what other people do
Action heuristics
through observations → follow their behavior
e.g. red light → others walk → u walk
e.g. hungarian students start filling classroom from the back and international students from the front
has stronger effect if there is a mismatch
Injunctive social norms
what the group should do
written/unwritten rule of behavior
what people believe should be done
requires more cognitive effort: looking it up, read the rule book, …
e.g. red light → don’t walk
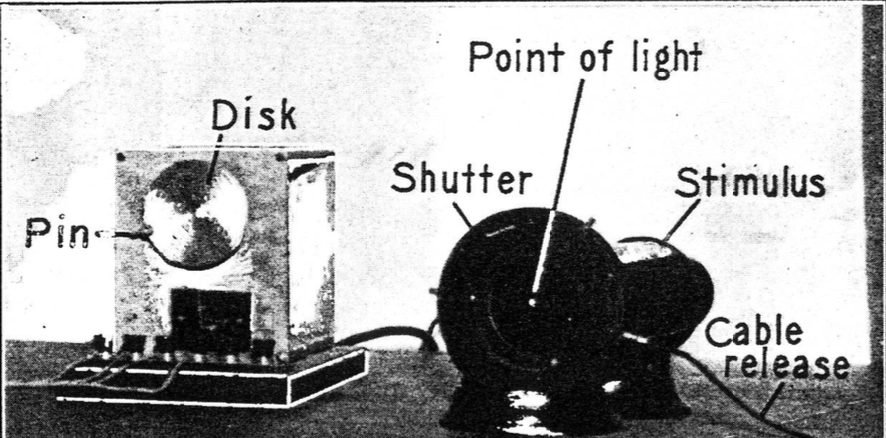
Establishing a group norm (Sherif)
it was a challenge to land a plane in darkness because the light on landing strip was not stable → light is moving → autokinetic effect (illusory motion)
experiment: peopleneeded to judge how much light is moving
individual = a lot of different answers
second person involved = other person got taken into account and judgement was similar
that established group norm → (term=) informational influence
Informational influence (mastery)
agreement of independent judgements made by many people is an idication of correctness → source of informational influence
motivation to be accurate increases reliance on others’ opinions
trusting them they know best
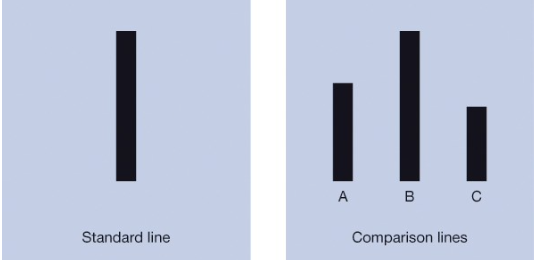
Normative Influence (Ash) (Connectedness)
clear, unambiguous perceptual judgements
confederates posing as participants gave wrong judgements on trials
actual participants frequently went along
not adjusting behaviour out of accuracy but only to not stand out
100% right answer when asked individually
25% right answer when in a group
only 25% never conformed
Conformity
adjusting behavior/opinion/emotion to the rest of the group
convergence of individuals`thoughts, feelings or behavior toward a group norm
normative influence → connectedness: to avoid criticism, ostracism, express group identity
in sitzations where u want to belong and be a good group member
informational influence → mastery: others are correct and i am wrong
especially in situations where u are not really sure like with optical illusions
Private Conformity
informational influence leads to it
convinced that the group is correct
conform when the group is not present
e.g. after sherfis study (autokinetic effect) on a follow up, the individuals still gave groups answer even when group was not present
Public conformity
behave consistently with norm → even tho privately not accepted as coorect
go along to get along
reward and punishment
ash experiment basis → only go with group norm when others are present
Consensus in groups: Is this a good thing?
different people coming to the same conclusion → the conclusion is more likely to be valid
group processes do not garantee that consensus is reached through careful consideration of evidence
Similarity-difference paradox
more trustful to people similar to us → e.g. peace treaty
but we trust more when more different people have the same opinion
renovating isabella utca → it is good idea said by bilers, school, students, people living there and drivers => sounds like an excellent idea
Dark side of consensus
often used on how to make a decision
without consideration
based on heuristics
not based on well-considered arguments
without interdependence
group members share a bias → convergence is not trustworthy
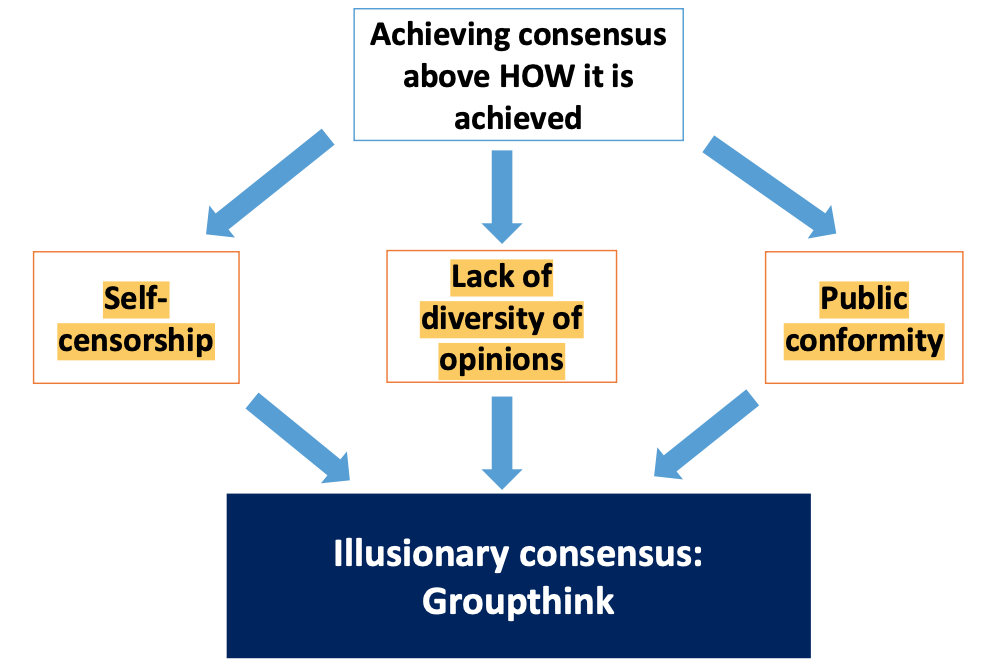
Groupthink (Janis: Bay of Pigs Invasion → perfect failure)
how did they make such a bad decision to sacrifice these soldiers in cuba?
consensus achieved without considering all available evidence
members suppress their doubts
consensus contaminated by members’ shared backgrounds
public conformity without private acceptance
happens in groups with members of high status/power
-> leader says something and even tho they do not share the same opinion they agree; because they think he is a great leader and a trusted source
-> happens in groups that feel extremly importent themselves
spaceship challenger which blew up within a minute after launching; knew the problem beforehand -> group of engeneers and they had 1 hour to say yes or no to the launch; they knew the problem; felt the pressure -> they agreed to launch -> belief in inner greatness of group
False consensus effect
Overestimating the extent to which others agree with us
we don’t really accounter the people who disagree → politics
most people think like me
what we think is the right way to think
Pluralistic Ignorance
most members of a group privately reject a norm or belief, but incorrectly assume that everyone else accepts it, so they go along with it even though they personally disagree
fairy tale -> sewer says textile will only be seen for people who are honest -> doesn’t say that he doesn’t see the dress
Cures of faulty group decisions
Open enquirery
Encourage dissenting
members selected for diversity
reduce pressure for conformity
democratic leadership
devil’s advocate role
Risk taking in groups
Rsik shift (Stoner, 1961)
individuals take more risks when in group then when alone
study was about judgement of carrer either individually or in group
one job low promotion, no risk, stable lower income
one job highr promotion, higher risk, higher income
at which chance would you suggest Mr. A to take the risk
people made more risky decisions in groups
Group polarozation (Moscovici)
groups position bevomes more extreme as a result of discussion and the group’s influence
Superficial processing
Normative influence
heuristics
others follow the norms
desire to be the best group member
Systematic Processing
Informational influence
more people - more arguments
more compelling
more confident
more discussion