Biol 111 - Ghosh final exam
1/184
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All 3 midterm exams with some important concepts sprinkled in, all post midterm 3 content as well. (basic chemistry questions taken out)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
185 Terms
Which of the following order is correct in terms of hierarchy of organization from largest to smallest
Biosphere-ecosystem-community-population-organism
How are amino acids connected in a polypeptide?
peptide bond
When a lipid is liquid at room temp it possibly has
a high number of cis double bonds
Difference between saturated and unsaturated fats
saturated - single bonds - solid at room temp
unsaturated - double bonds - liquid at room temp if cis
Two types of unsaturated fats
cis - hydrogens on same side of double bond (kink) = good - cannot be packed tightly
trans - hydrogens on opposite side of double bond (no kink) = bad - can be packed tightly
Carl Woese created the phylogenic tree of life using data from:
Genetic evidence using 16s rRNA (only)
What is amylopectin’s structure?
Branched polysaccharide containing alpha 1-4 and alpha 1-6 glycosidic bonds
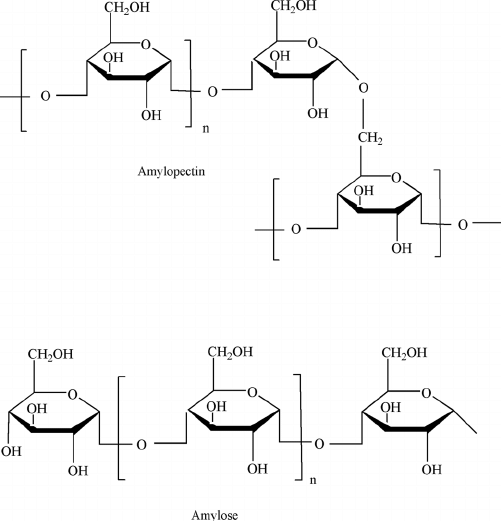
What is amylose’s structure?
unbranched glucose monomers in alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds (straight)
which 2 monosaccharides make up sucrose
glucose and fructorse
Which polysaccharide is made with modified sugar…
chitin
natural selection is one of the mechanisms by which evolution of life occurs
true
What is a theory?
a hypothesis that has been repeatedly tested and not yet falsified
What type of bond is a weak chemical bond?
Van der Waals interactions
To act as an effective coolant in a car’s radiator….which table would you check first?
specific heat
Which statement is true for cohesion? Adhesion?
cohesion is attraction between water molecules due to hydrogen bonds
adhesion is the attraction of a water molecule with a different type of molecule due to hydrogen bonds
Cohesion - surface tension
Adhesion - capillary action
Adhesion is stronger than cohesion
four most common elements in organisms
carbon oxygen nitrogen and hydrogen
Which functional group can pick up protons and raise the pH of the surrounding solution?
-NH2 (it can pick up a proton)
The amiphatic nature of which macromolecules makes it curucial for plasma membranes in cells
phospholipids
What is true for sickle cell anemia
Caused due to a single amino acid substitution in beta hemoglobin
Why does ice float in a glass of water
ice has stable hydrogen bonds keep water molecules of ice farther apart than water molecules of liquid water
Prokaryotes are classified as belonging to which two domains
bacteria and archea
Valence shell of most atoms is full when they have how many electrons
8
When a general conclusion is drawn from a number of observations it is called
inductive reasoning
Deductive is when a theory is used to explain observations
Atoms that vary in the number of neutrons in their nucleus are called
isotopes
Within a single molecule of water, two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a single oxygen by
polar covalent bonds
Not hydrogen, not nonpolar covalent, not ionic
A covalent bond is likely to be polar when
there is unequal sharing of electrons b/w atoms
Whcih two functional groups are always present in an Amino acid
Amino and carboxyl (NH2 and COOH)
which of the following types of cells utilize DNA as genetic material but do not have a well-defined nucleus
archaea (prokaryotes)
Which bond type exists in one carbon and four hydrogen bonds in methane
nonpolar covalent
Enantiomers are
non-superimposible mirror images of each other
Types of isomers (compunds w/ same number of elements but are arranged differently)
Structural isomers: Different covalent arrangement entirely
Geometric isomers: Same covalent bond places but different types of bonds in those places
Enantiomer isomers: non-superimposable images (mirror but not exact same placement of elements)
what functional group is nonpolar
methyl
Which of the following is NOT strictly classified as a polymer?
Lipids (all other 3 are connected by a special bond)
3 main polymers/organic macromolecules and their bonds
Carbohydrates/sugars - glycosidic bonds/linkages
Proteins - polypeptide bonds (of amino acids)
Nucleic acids - phosphodiester bonds
Aliphatic vs aromatic hydrocarbons?
Ali - Straight chain
Aroma - ring structure
Which disease can be possibly caused by excess levels of iron in the human body
polycythemia vera (anemia is too low iron)
all three aromatic amino acids (closed ring side chain)
Pheynlaline tyrosin and tryptophan
maltose is formed a _____ bond between glucose and ____
glycosidic ; glucose
a helix and b pleated sheet tell us about the _ sturcture of proteins
Secondary
What is true for G = H - TS
enthalpy is the energy available to do work
All types of passive transport
Facilitated diffusion - uses a protein that doesn’t require energy (channel/carrier proteins)
diffusion - high to low concentration of small molecules (not for ions/polar molecules)
Osmosis - water diffusion across semi-permeable membrane
During photosynthesis how many CO2 molecules are needed for 1 glucose
6
Carbs found on a plasma membrane's exterior side when connected to proteins are called ___, and when connected to lipids are called ____.
glycoprotein, glycolipids
Whcih 5-carbon sugar is present RNA (ribonucleic acid)
Ribose (has OH compared to DNA’s H)
During photosynthesis, during which phase is glucose actually synthesized
Second phase or Calvin cycle
During ETC, NADH feeds electrons to ___ and FADH2 feeds its electrons to __
Complex 1, complex 2
Which phase doesn’t require oxygen directly or inderectly
glycolysis
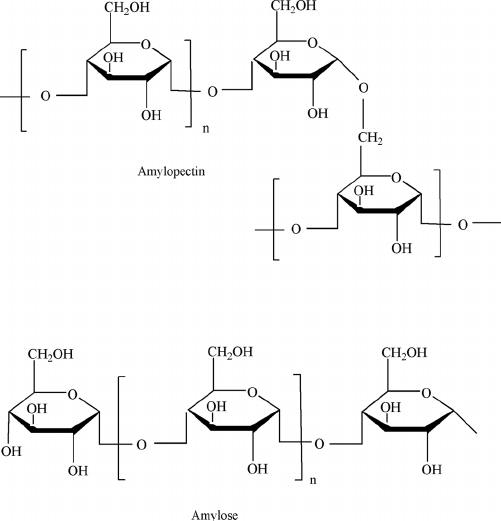
In nucleic acids, which bond connects nucleotides to form a polynucleotide
phosphodiester bonds
Plant cells are turgid and generally the healthiest when place in a ___ environment
hypotonic
Hyper vs hypo tonic solutions
prefix refers to the amount of solute in environment and water follows the higher solute
hyper - more solute outside the cell - water flows out
hypo - less solute outside the cell - water flows in
iso - equilibrium - rbcs
In metabolism, ___ pathways break down compelx foods into simpelr substances, while ___ pathways build molecules
catabolic ; anabolic
In glycolysis for each molecule of glucose oxidized to two pyruvate molecules,
2 ATP used, 4 ATP produced
Which bonds are hydrolyzed in ATP to provide energy?
Phosphoanhydride bonds, (terminal gamma phosphate lost)
One molecule of glycose needs two rounds of citric acid cycle during cell respiration, What is the output at the end of two rounds
4CO2, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2ATP/GTP, H2O
When an animal cell is placed in a hyptonic solution, the cell will _ in water
gain water
In bulk transport, which process is responsible for moving contents outside the cell into the extracellular space
exocytosis
Types of bulk transport
exocytosis - exporting via vesicles that fuse with membrane
phagocytosis - cell eating, package and kill
pinocytosis - cell drinking, package into smaller vesicles and put in cytoplasm
receptor mediated endocytosis - specific receptor for substance that takes in through coated layer vesicle
What affect does cyanide poisoning have on cell resp
Complex 4 affected and inhibits the ETC
In active transport, which type of carrier proteins carry two different molecules or ions in the same direction
symporters
Carrier proteins types (active transport)
uniporters - carry 1 molecule or ion
symporters - carry 2 different molecules or ions in same direction
antiporters - carry 2 different molecules or ions in different directions (sodium potassium pump)
In facilitated diffusion, substances move from a high concentration to low concentration w help of channel and carrier proteins (T/F)
true
___ is a regulatory mechanism in which the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an upstream enzyme
Feedback inhibition
Types of allosteric regulation of enzymes
Allosteric inhibition: inhibitor binds to active site and prevents substrate
Allosteric activators: activator binds to locations away from active site that increases the affinity for substrate
Cooperativity - amplify enzyme activity; one binds to active site of one subunit that locks all subunits in active conformation.
Feedback inhibition - The end product of the metabolic pathway shuts down the pathway; (upstream enzyme)
Which organelle in plants is major site of photosynthesis
chloroplast
Plants are ___, utilizing sunlight to make complex organic molecules from carbon dioxide and water
photoautotrphs
not in DNA
Uracil
What components make up a complete nucleotie
nitro base, 5-C sugar, phosphate group
When a prokaryote can switch between aerobic respiration and fermentation depending on availability of oxygen it’s a
facultative anaerobe
What happens to reactants in the light independent reaction?
CO2 is reduced and H2O is oxidized
According to the first law of thermodynamics, energy _____ be created or destroyed
cannot
Enzymes help reactants reach the _____ state by lowering the _____ energy.
transition; activation
Which energy source fuels the sodium-potassium pump
ATP
In active transport, for every ATP hydrolyzed, the sodium potassium pump can move ____ out the cell and ____ in the cell.
3 Na+; 2K+
In alcohol fermentation, pyruvate is ultimately converted to
Ethanol (acetaldehyde is intermediate)
Which amphipathic molecule is abundantly present in a plasma membrane?
Phospholipids
What is the special type of diffusion where water moves across a semipermeable membrane?
osmosis
What’s the accurate description for oxygen consumed in cellular respiration?
It serves as the final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain
When the free energy change is negative the reaction is
exergonic (spontaneous)
In plasma membranes what increases fluidity at low temperatures and decreases fluidity at high temperatures
cholesterol (fluid mosaic model)
In thermodynamics, in an open system, energy and matter can be transferred between the system and its surroundings
True
What are the coenzymes in their oxidized forms?
FAD+
NAD+
NADP+
Using X-ray crystallography, who took “Photo 51” of a DNA molecule that served as one of the key data for understanding the DNA double helix?
Rosalind Franklin
During photosynthesis, how many turns of the Calvin cycle is required to synthesize one molecule of glucose?
6
In Labradors, B gene locus controls the color of the coat but the E gene locus has an effect on the B locus, what is this an example of?
Epistasis
Stages of calvin cycle in photosynthesis
Carbon fixation stage, Reduction stage, and Regeneration stage
What enzyme prevents over-winding of DNA (supercoiling) ahead of the replication fork when DNA double helix is unwinding?
Topoisomerase
Types of DNA repair mechanisms?
Proofreading by DNA polymerase, Mismatch repair, and Nucleotide excision repair (NER-UV light)
What is required during binary fission in bacteria
FtsZ protein
What phase of the cell cycle is occupied by non-dividing cells permanently or temporarily?
G0
During mitosis, by the end of which phase does the two poles of the cell have equivalent collection of chromosomes?
Anaphase (telophase is once nucelus is already developing around each cell)
Calvin cycle occurs in ___, is light ____, and uses ______
stroma of the chloroplast; independent; ATP and NADPH from light rxns
During DNA replication primase synthesizes RNA primers that primes the replication in both strands of DNA. (T/F)
True
During DNA packaging, when DNA is wound around histone protein, it is referred to as
nucleosomes
In the mitochondria, ATP is synthesized in the ___, whereas in chloroplast ATP synthesis takes place in the ___
inner mitochondrial membrane; thylakoid membrane
What is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes producing what type of chromosomes during prophase 1 of meiosis 1
Crossing over; recombinant
In Mendel’s experiments, the parental P0 generation always consisted of what types of plants?
True breeding plants (homo dom and homo rec)
In Frederick Griffith’s experiments, what happened to the mice when injected with a mixture of heat-killed S cells and live R cells of Streptococcus pneumonia
The mice were dead (transfection/transforming)
Both red and white petals being expressed in Camelia flowers is an example of
Codominance
What enzyme catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres in germ cells?
telomerase
Humans have a _____ life cycle where only haploid cells are the ____
diploid dominant; gametes