AP Euro World War 1
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Suez Canal
provided a passage from Mediterranean Sea to the Indian Ocean built by Egyptians but taken by British
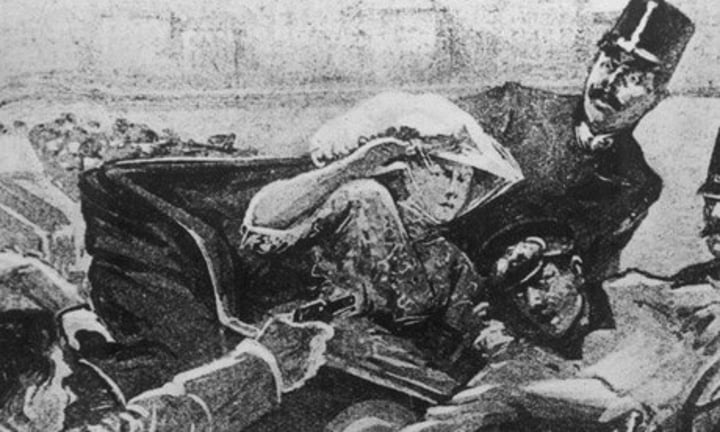
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
The spark that started World War I. The Austrian crown prince, was murdered on June 28, 1914, by a Serbian nationalist while visiting Sarajevo, Bosnia. Germany urged Austria-Hungary to fight and they went to war against Serbia
Woodrow Wilson
American President who led the US into WWI. Later wrote a plan for post-WWI peace known as the Fourteen Points.

Austria-Hungary
This Central Power empire during WWI, started the war with their invasion of Serbia after the assassination of Archduke Ferdinand on June 28, 1914 . It was made up of Austria, Hungary and several other nations and territories. After World War I it split up into several nations.
The Black Hand
Serbian rebel group that assassinated Archduke Ferdinand after several failed attempts.

Kaiser Wilhelm II
This emperor led the Germans during WWI. In 1918 he was forced to step down by German generals.

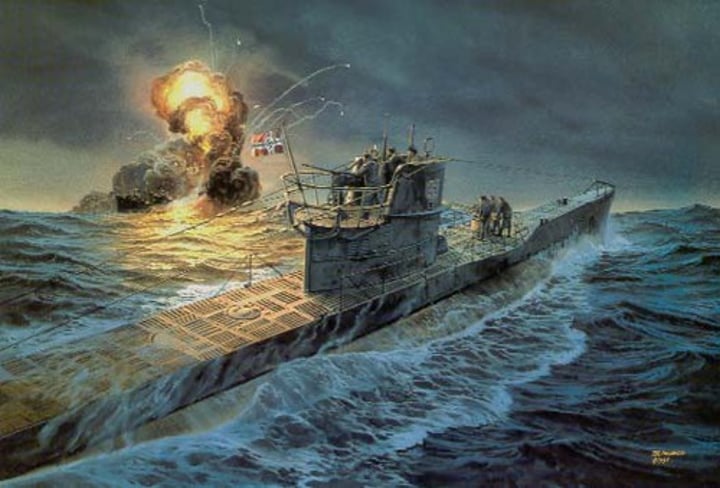
U-boats
Naval weapon used by the Germans to attack British and American supply ships in the North Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.

Nationalism
This cause of World War I was based on an intense pride in one's nation.

Fourteen Points
Plan for post-World War I outlined by President Wilson in 1918; called for self-determination, freedom of the seas, free trade, end to secret agreements, reduction of arms and League of Nations.

Zimmerman Telegram
Intercepted note from the German foreign minister to the Mexican government; confirmed the new policy of unrestricted submarine warfare by Germany against the Allied Powers. This helped turn Americans against Germany in WWI.

Lusitania
This British passenger ship was sunk by German U-boats in 1915, carrying civilians and ammunition to Britain from the U.S. The event turned American opinion against Germany.

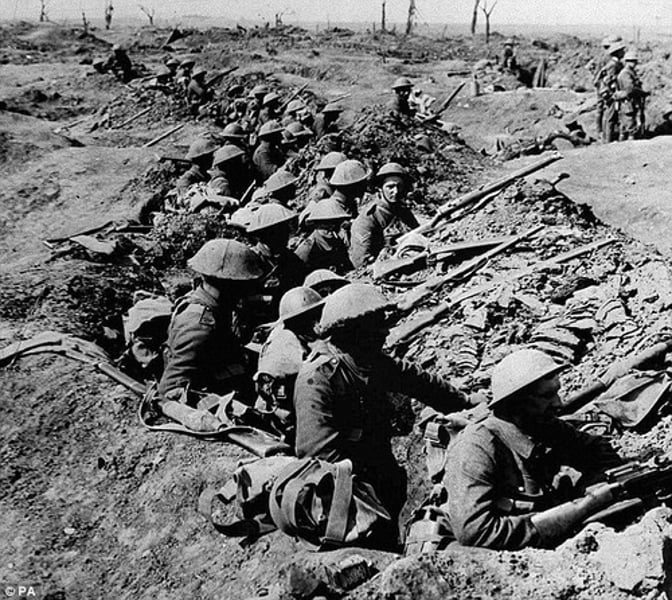
Trench Warfare
Style of warfare was common in WWI, due to the invention of the machine gun and heavy artillery. It included digging long ditches, separated by barbed wire and 'no mans land'.

Reparations
This term refers to the payments and transfers of property that Germany was required to make under the treaty of Versailles.

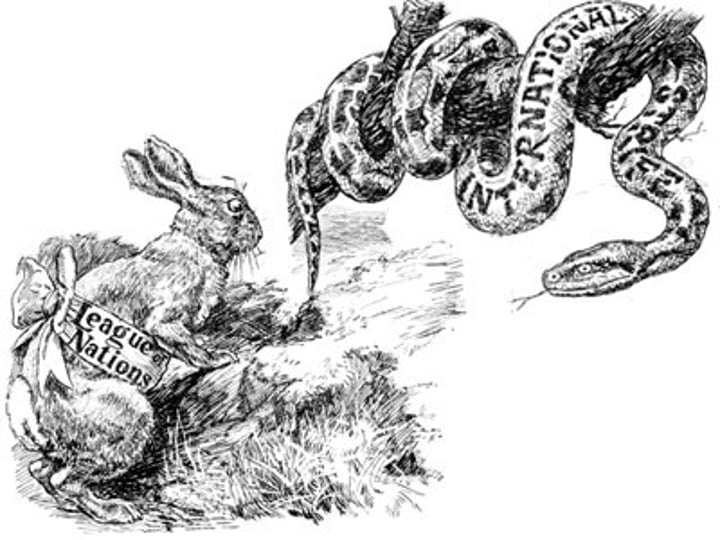
League of Nations
Organization that lasted from 1919-1946, was founded after the Paris Peace Conference. It did not work effectively to prevent WWII, U.S. did not join

War Guilt Clause
Article 231 of the Treaty of Versailles placed all blame for WWI with Germany and its allies. This forced Germany to pay reparations for World War I.

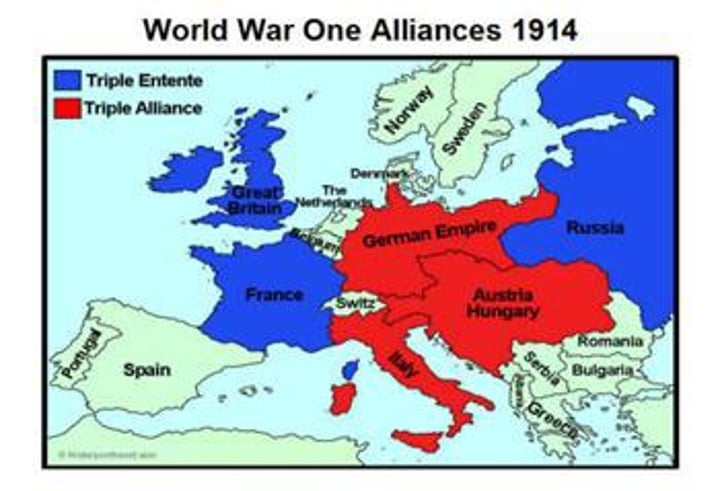
Triple Alliance
This alliance was made Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy in the years before WWI. IN RED ABOVE
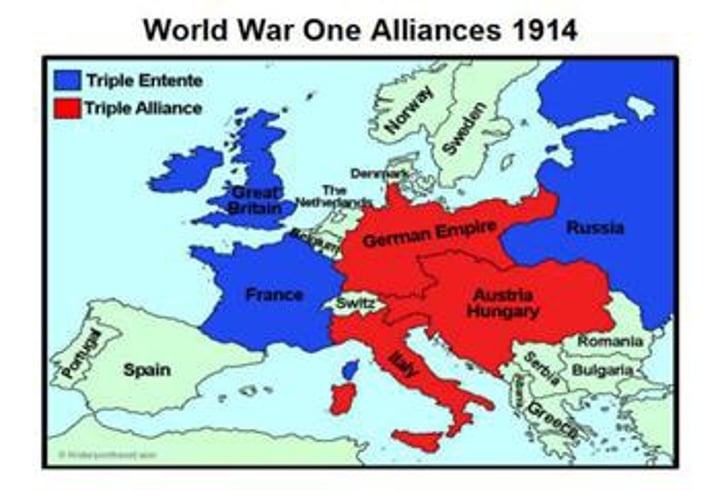
Triple Entente
This alliance between Great Britain, France and Russia in the years before WWI. IN BLUE ABOVE
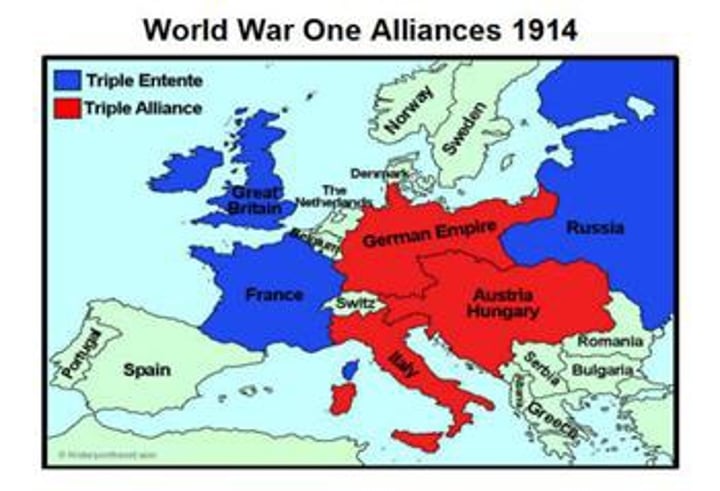
Balkan Region
Slavic Region of intense nationalism and imperial domination in mountains of south/eastern Europe - spark to set off powder keg of Europe.
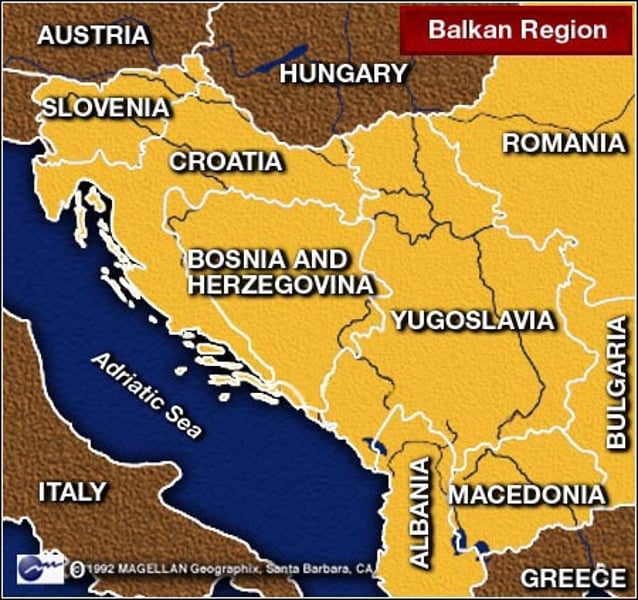
Central Powers
This was a major alliance at the 'center' of Europe during World War I, made up of Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and Ottoman Empire. It was formerly known as the Triple Alliance before the war. (RED)
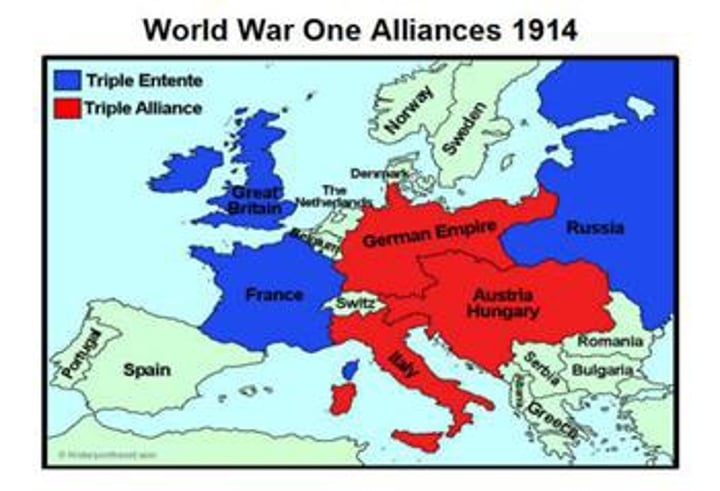
Allied Powers
This was a major alliance during World War I made up of Britain, France, Russia, and the United States. It was known as the Triple Entente before the war. (BLUE)
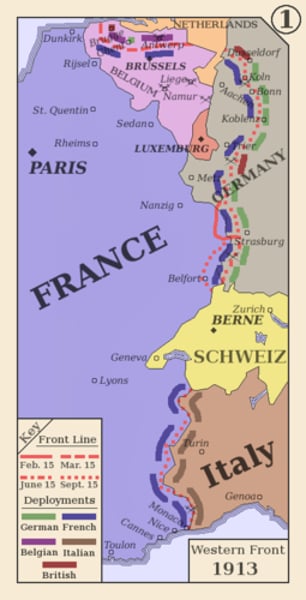
Western Front
Main area of fighting in World War I; line of trenches and fortifications that stretched from Switzerland to the North Sea.
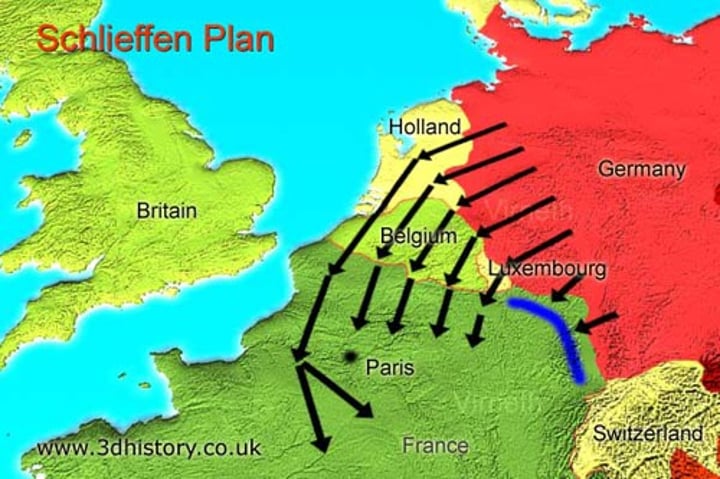
Schlieffen Plan
Germany's military plan at the outbreak of WWl. The failed plan was for troops to rapidly defeat France and move east to defeat Russia.
Eastern Front
The region of fighting happened along the German-Russian Border where Russians and Serbs battled Germans, Austrians, and Turks.
Gallipoli Campaign
A British military attack in 1915 during World War I against the Ottoman Empire at Dardanelles to bring supplies to Russia. The mission failed with high casualties by the British.
Unrestricted Submarine Warfare
This was the policy that the Germans announced on January 1917 which stated that their submarines would sink any ship in the British waters.
Rationing
Restricting the amount of food and other goods people may buy during wartime to assure adequate supplies for the military
Propaganda
These are ideas or information that usually designed by a government to influence public opinion, often to persuade a people to go to war.
Armenian Genocide
When the government of the Ottoman Empire (Turks) killed 1 million Armenians in suspicion that they were working for Russia.
Militarism
This cause of World War I was a policy of building up strong armed forces to prepare for war.
Vladimir Lenin
Russian founder of the Bolsheviks and leader of the Russian Revolution and first head of the USSR
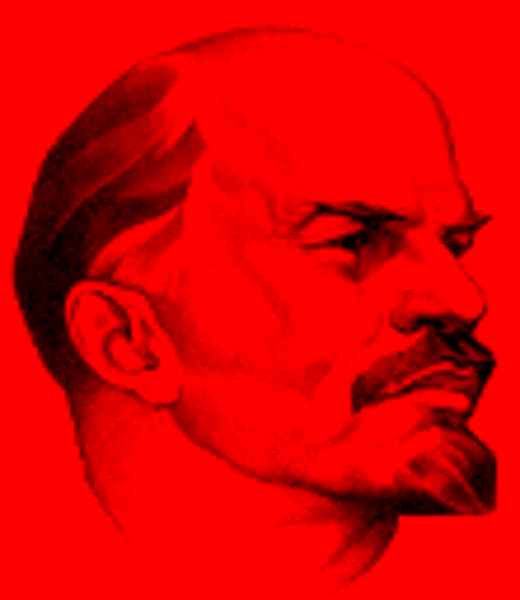

Otto von Bismarck
German statesman under whose leadership Germany was united (1815-1898)
Georges Clemenceau
French prime minister who wanted to ensure that Germany would never again threaten France; at the Paris Peace Conference.
Vittorio Orlando
Prime Minister of Italy in WWI; represented Italy at the Paris Peace Conference.
Czar Nicholas II
Russian Czar during WWI; unpopular with Russian people; overthrown in March 1917; executed by Bolsheviks after November Revolution (1917)
total warfare
In wartime, when all of a nation's resources go towards the war effort (money, food, clothes, etc.)
Battle of the Somme
(1916) Battle between German and British-French forces. Ending in a stalemate, the bitter three-month conflict is notable for the high number of casualties and the first use of tanks in warfare.
Battle of Verdun
(1916) the longest battle of World War I; ended with German withdrawal
Battle of Jutland
an indecisive naval battle in World War I (1916)
Mandate System
Allocation of former German colonies and Ottoman possessions to the victorious powers after World War I; to be administered under League of Nations supervision.
Russian Revolution
Prompted by labor unrest, personal liberties, and elected representatives, this political revolution occurred in 1917 when Czar Nicholas II was murdered and Vladimir Lenin sought control to implement his ideas of socialism.
Bolsheviks
Led by Vladimir Lenin, the Russian communist party that took over the Russian government during WWI