molecular bio test 1 (1-4)
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
what is biology?
the study of life
what is biology’s 10 organizations?
biosphere
ecosystems
communities
populations
organisms
organ systems and organs
tissues
cells
organelles
molecules and atoms
a type of research that involves fundamental truths on how the world works. researching to find out things, not to fix issues. finding out the “what” and “why” of issues.
eg. discovering that COVID exists.
basic research
a type of research that uses information to fix an issue or improve already existing systems in place using evidence and solidified already existing research.
eg. finding the cure to COVID.
applied research
what is reductionism?
breaking down complex systems by studying their smaller component parts.
a smaller simple cell, such as bacteria
prokaryotic cells
complex larger cells, such as plants, animals or fungi
eukaryotic cells
part of what considers something alive
the way in which cells are structured and how they function together to create living organisms
cellular organization
part of what considers something alive
not random, but organized, like DNA
ordered complexity
part of what considers something alive
maintaining certain regulations or internal/external conditions
eg. sweating to keep you cooler or goosebumps to keep you warmer
homeostasis
part of what considers something alive
the way a living thing responds to stimuli
eg. an allergic reaction
sensitivity
part of what considers something alive
increase in size, structure, function, behavior, change and creating offspring
growth, development and reproduction
part of what considers something alive
the term for converting nutrients or sunlight
energy utilization
part of what considers something alive
organisms develop traits through natural selection over generations that helps them adapt better to their environment
evolutionary adaptation
describe evidence for evolution
fossil record - shows how organisms change over time
genes being passed down through generations, showing similar traits and physical features
darwins observations on birds and how they adapted and evolved to their environments
a theory that describes the organizations of living systems
the theory includes:
- all organisms are composed of cells
cells are life’s basic units
all cells come from preexisting cells
cell theory
what is molecular basis of inheritance
how genetic info in DNA is stored, encoded, replicated and passed down from parents to offspring
how something is shaped directly affects what it does.
once involves shape, the other does a job
eg. insulin-binding site
structure and function
what are the 3 domains of life?
bacteria (single celled prokaryote)
archaea (single celled prokaryote)
eukarya (both single and multicellular prokaryote/eukaryote)
what is a nonequilibrium state?
a constant supply of energy that living systems need to maintain organizations
all matter is composed of…
atoms
what are the 3 components of an atom?
protons
neutrons
electrons
energy type of a proton?
positive charge
energy type of a neutron?
neutral charge
energy type of an electron?
negative charge
term for a positive ion?
(more protons than electrons)
cation
term for a negative ion?
(fewer protons than electrons)
anion
what is an atomic number?
how many protons there are in an element
what is atomic mass?
the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom
what is an isotope?
atoms of a single element that possess different numbers of neutrons
what happens when electrons are farther from the nucleus?
they gain energy
what is oxidation?
(hint, OIL RIG)
O xidation
I s
L osing electrons
what is reduction
(hint, OIL RIG)
R eduction
I s
G aining an electron
most of the human body consists of what 4 elements?
hydrogen
oxygen
carbon
nitrogen
what 2 elements make something considered organic?
carbon and hydrogen
what are the 4 major biological macromolecules?
nucleic acids
proteins
lipids
carbohydrates
the attraction of oppositely charge ions are….
an ionic bond
the gain or loss of electrons forms what?
ions
a group of atoms held together in a stable association
molecules are
molecules containing more than one type of element are…
compounds
what is an organic compound?
things that are made up of carbon based molecules
a cell is made up of what substance primarily? what is the rest made up of?
water and carbon based molecules
what are macro molecules?
they are carbon forms, large, complex and diverse molecules necessary for life’s functions
list the 4 main macromolecules
carbohydrates
nucleic acids
proteins
lipids
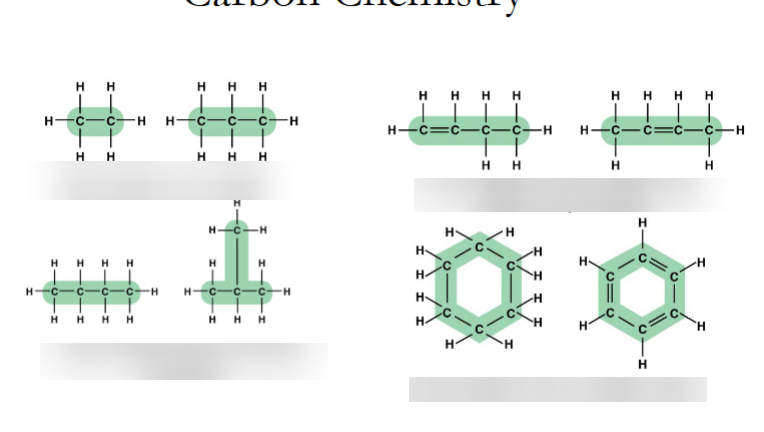
explain how carbon skeletons can look
they can vary in lengths
they may have double bonds which can vary in locations
they may be unbranched OR branched
they may be arranged in rings
what is a hydro carbon?
they are the simplest organic compound, only containing carbon and hydrogen atoms
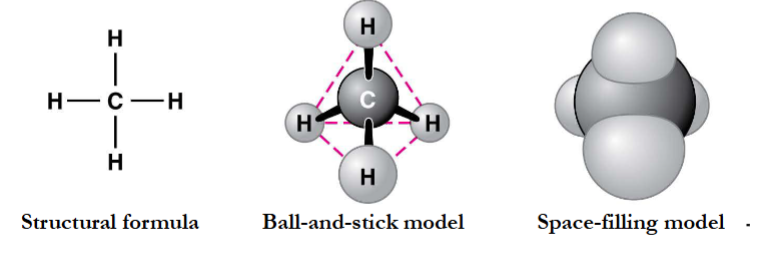
what is the simplest hydrocarbon?
methane, only 1 carbon with 4 hydrogens
what are hydrocarbons good at?
they’re good fuel, both for bodies as energy and for literal fuel too.
what polarity are hydrocarbons?
non polar
are macromolecules polymers?
yes they are polymers
difference between monomers and polymers in terms of their visual
monomers are the smaller piece while the polymers are the bigger, strung together pieces
what is something a polymer can do and is unique to them?
be broken down and built back up again
what is a dehydration reaction?
dehydration is removing H2O and links 2 monomers together
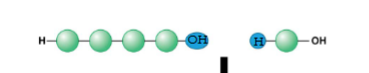
what is the product of dehydration (what was removed?)
H2O
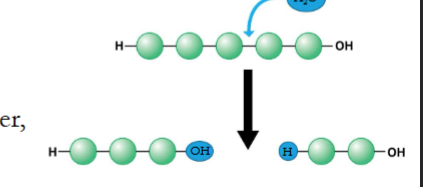
What happens in hydrolysis? (hint; -lysis is to break, like hemolysis)
breaks bonds between monomers, adds a H2O molecule back, reverses the dehydration reaction
what is a nucleic acid and what does it do?
stores genetic information, provides directions for building proteins and includes both DNA and RNA
where does DNA chill at ?
inside of chromosomes
what is a gene?
specific stretch of DNA that encodes the amino acid sequence of a protein

whats this (DNA, RNA, OR AMINO ACID?)
DNA

WHAT THIS (DNA, RNA OR AMINO ACID)
RNA
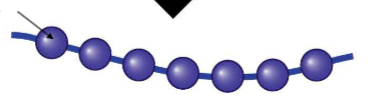
WAHT THIS (DNA, RNA, OR AMINO ACID)
AMINO ACID
in what order does the neucleic acids go?
DNA, RNA, Amino Acid
are neucleic acids polymers or monomers? what are they made out of?
polymer, made from monomers called nucleotides
what are the 3 parts that a nucleotide has?
a 5 carbon sugar
a phosphate group
nitrogen containing base
what is the nitrogen containing base of DNA?
ATGC
What is the nitrogen containing base of RNA?
AUGC
what can bond with what in dna? (ACGT)
A=T
C=G (3bonds)
what can bond with what in RNA? (AUGC)
A=U
C=G (3 bonds)
what kind of storage does DNA use?
long term genetic storage
what kind of storage does RNA use?
short term storage, not as stable, stores how to make protiens
is a protein a polymer or a monomer?
a polymer constructed from amino acid monomers
what do proteins do?
they perform most of the tasks required for life
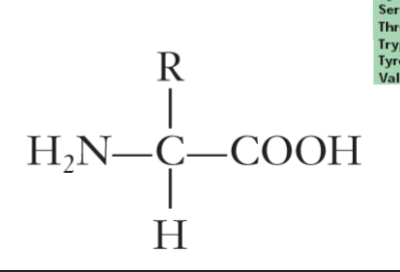
wghat kind of structure is this?
amino acid structure
what are the major categories of macromolecules
carbs
nucleic acids
lipids
proteins
how are amino acids joined together?
through dehydration (peptide bond)
why is structure important to proteins?
it determines their function
what is a primary structure in protiens?
a sequence of animo acids
what is the secondary structure in proteins?
has the a helix: the the curly part of a protein structure
has the b sheet : the ribbons of the strucutre
what is the tertiary structure of proteins?
the extra space, final folded shape for proteins.
what is a quaternary structure in proteins?
when the full protein comes together, like in COVID
what are carbohydrates?
include sugars, and polymers of sugar
what do carbs do?
they store sugar, and are used for energy storage
they are also structural in plants
what is the monomer of a carb?
monosaccharide
what is a disaccharide?
a double sugar formed by a dehydration reaction is a…
what is a polysaccharide?
long chains of monosaccharides linked through dehydration
what is a defining characteristic of lipids?
they are hydrophobic
what are some lipids?
fat, wax, oil, some vitamins and hormones
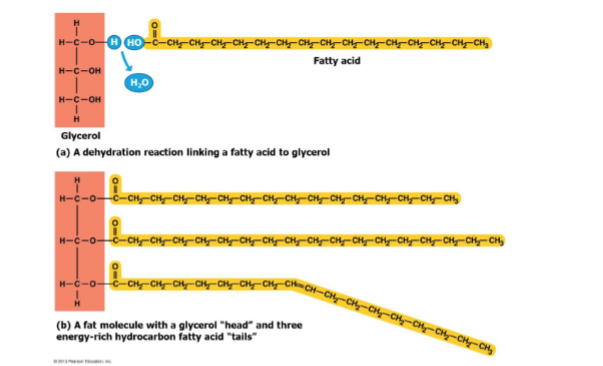
what does typical fats/triglycerides consist of?
a glycerol molecule that is joined with three fatty acid molecules from a dehydration reaction
how can you tell a saturated from an unsaturated fat?
if there is the max amount of hydrogens then it is saturated, if it is not, then it is unsaturated
saturated fats also have no double bonds
what is cell theory?
the organization of living systems
also says that
-all organisms are composed of cells
-cells are lifes basic units
-all cells come from preexisting cells
who founded cell theory and when was it established?
in the 1800’s by robert hooke (first cells) and anton van leeuwenhoek (first microorganisms)
what does a transmission electron microscope do?
it transmits electrons through the materials (seeing inside a cell)
what does a scanning electrom microscope do?
transmits electrons onto the specimen surface (seeing the outside of a cell)
what are the basic structural similarities of a cell?
dna
plasma membrane (phospholipid bilayer and is selectively permeable)
cytoplasm
ribosomes
what is a prokaryotic cell?
simplest organisms
lack of a nucleus, DNA is in the nucleoid
cell wall is on the outside of plasma
what is a eukaryotic cell?
has a membrane nucleus
more complex than prokaryotic cells
compartmentalization
has a cytoskeleton to maintain structure