Chapter 29 - Between Two Fires (Section Three)
5.0(1)Studied by 15 people
Card Sorting
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Same as all the other sections. It's funny because half of this chapter is literally just the reasons my Grandfather's family fled Italy.
Last updated 1:37 AM on 3/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
Totalitarianism = ?
A form of dictatorship in which the individual is viewed as a servant of the state and is allowed few personal freedoms.
2
New cards
What happened when totalitarian governments came into conflict with each other and the Western democracies during the postwar period?
It set the stage for the beginning of another world war.
3
New cards
Italian nationalists were outraged that the _____ __ _____ treaties had not given Italy huge portions of territory from the defeated Central Powers.
^ Peace of Paris
4
New cards
Which dictator rose to power in Italy?
Benito Mussolini.
5
New cards
Benito Mussolini worked as a __________ during World War I, so he was very well-versed in the art of propaganda.
^ Journalist
6
New cards
Fasci di Combattimento = ?
It means “The Fascist Party” in Italian.
7
New cards
Fascism = ?
A political philosophy that advocates the glorification of the state, a single-party system with a strong ruler, and an aggressive form of nationalism.
8
New cards
Similarities/Differences of Communism and Fascism:
Like communism, fascism gives the state absolute authority. But fascism defends private property (although with some government regulation) and the class structure.
9
New cards
Italy was in a state of chaos and general discontent after World War I. Give some examples of what was going wrong.
* Veterans could not find jobs when they returned home.
* The value of the lira decreased rapidly.
* The price of bread rose. (Don’t take carbs from Italians).
* A coal shortage hampered industry production.
* The value of the lira decreased rapidly.
* The price of bread rose. (Don’t take carbs from Italians).
* A coal shortage hampered industry production.
10
New cards
Workers in ________ and ________ took over factories when their strikes were not effective, peasants seized ____ from wealthy landowners,and tenant farmers refused to pay their ____.
^ Lombardy
^ Piedmont
^ Land
^ Rent
^ Piedmont
^ Land
^ Rent
11
New cards
How did Mussolini gain so much popularity among the starving and destitute Italian people?
In his plans, he gave everyone something they desired.
12
New cards
Give three examples of Mussolini’s broken/empty promises:
1. To appease the landowners, he vowed to end the unrest and protect private property.
2. To woo the workers, he promised full employment and workers’ benefits.
3. He pleased nationalists by pledging to restore Italy to its former glory.
13
New cards
Blackshirts = ?
Mussolini’s followers who did not rely on verbal assaults alone to achieve their goals.

14
New cards
In October of 1922, the Fascists staged a march on ____ with Mussolini (a brave leader who fights on the frontlines) waiting in _____ to see how the government would react.
^ Rome
^ Milan
^ Milan
15
New cards
King Victor Emmanuel III = ?
The absolute dumb@ss who named Mussolini prime minister of Italy after he attacked the capital.
16
New cards
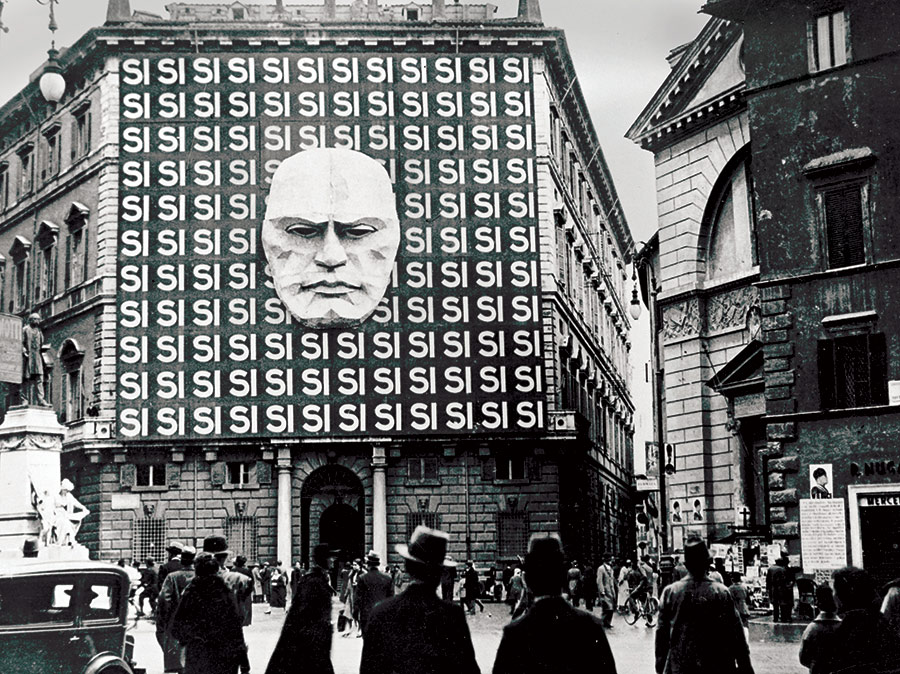

Aside from the empty promises we discussed earlier, how did Mussolini gain power once he became dictator?
He used intimidation, force, and the fear of communism to his advantage as any tender man would.
17
New cards
Il Duce = ?
It means “The Leader” in Italian.
18
New cards
Corporate State = ?
* Established to end the political quarreling that Mussolini associated with a democratic party system.
* When Mussolini banned non-Fascist parties and ordered that syndicates be formed in each industry.
* When Mussolini banned non-Fascist parties and ordered that syndicates be formed in each industry.
19
New cards
Syndicates = ?
Corporations of workers and employers.
20
New cards
The _______ of Italians believed that Mussolini had done Italy a great service by preventing a communist revolution and that he “made the trains run on time.”
^ Majority
21
New cards
Mussolini rekindled the feelings of __________ and ___________ lain dormant in the Italian people by stating that it was Italy’s destiny to recapture the glory of ______ ____.
^ Patriotism
^ Nationalism
^ Ancient Rome
^ Nationalism
^ Ancient Rome
22
New cards
The _____ __ _________ limited the size of Germany’s armed forces and required the Germans to form a democratic government.
^ Treaty of Versailles
23
New cards
Meeting in _______, delegates elected to the national assembly drafted a constitution for Germany establishing a democratic republic called the _______ Republic.
^ Weimar (x2)
24
New cards
Claiming that the Weimar leaders had betrayed the nation by accepting the terms of the Treaty of Versailles, nationalist army officers staged an unsuccessful ____ _’____
^ Coup d’Etat
25
New cards
Great Britain and France promised their citizens that the German government would pay ___________ covering the full cost of the war.
^ Reparations
26
New cards
How much money did the Allies demand from Germany?
$35 billion, a very unrealistic amount that Germany, of course, could not come up with.
27
New cards
After the German government announced that it could not meet such lofty obligations due to its preexisting financial difficulties, French troops marched into Germany’s industrial ____ ______ and took control of the coal mines and steel mills there.
^ Ruhr Valley
28
New cards
To meet expenses, the German government ________ more and more paper money. What did this create?
^ Printed
Very terrible inflation.
Very terrible inflation.
29
New cards
Among the political parties challenging the Weimar Republic was the ________ ________ ______’_ ____, or the Nazi party.
^ National Socialist Worker’s Party
30
New cards
One of the Nazi party’s first recruits was an undercover German agent and WWI veteran sent to investigate the party, named what?
Adolf Hitler.
31
New cards

Brownshirts = ?
Formed by Hitler, it was a private party of young veterans and street thugs.
32
New cards
What happened in a Munich beer hall?
Hitler made a half-@ssed attempt to seize power. He jumped up on a table and announced that the revolution had begun. Of course, the police intervened and arrested Hitler.
33
New cards
Mein Kampf = ?
An autobiography written by Hitler during his stint in prison that has 3.6 stars on Goodreads.
34
New cards
What are some of Hitler’s very invalid opinions?
* The Jews and the Communists were responsible for the German defeat in World War I.
* The Germans were a “master race” whose destiny was to rule the world.
* He was the leader who would unite all German-speaking people into a new empire that would dominate other groups.
* The Germans were a “master race” whose destiny was to rule the world.
* He was the leader who would unite all German-speaking people into a new empire that would dominate other groups.
35
New cards
During the Great Depression, Hitler appealed to workers and industrialists alike with what?
His promise to end unemployment and restore Germany’s military might.
36
New cards
Reichstag = ?
A legislative body that the Nazi party won a large number of seats in.
37
New cards
President Hindenburg = ?
Another tremendous dumb@ss who named Hitler chancellor, allowing Hitler to rise to power 100% legally.
38
New cards
Nuremberg Laws = ?
Stripped Jews of their citizenship and their right to hold public office, barred Jewish students from schools, and destroyed Jewish businesses.
39
New cards
The Gestapo = ?
Hitler’s secret police (not to be confused with his ragtag army of small-time criminals).
40
New cards
Concentration Camps = ?
Large prison camps where people were confined under harsh living and working conditions.
41
New cards
Kristallnacht = ?
* November 9th and 10th, 1938 when Nazis attacked Jews on the streets and vandalized Jewish property.
* 1,350 Jewish synagogues were burnt to the ground.
* 30,000 Jews were thrown into concentration camps.
* 1,350 Jewish synagogues were burnt to the ground.
* 30,000 Jews were thrown into concentration camps.
42
New cards
Star of David = ?
What Jewish people were required to wear on their person and display in the windows of their stores for easy identification.
43
New cards
Der Führer = ?
It means “The Leader” in German.
44
New cards
The Third Reich = ?
It means “The Third Empire” in German.
45
New cards
Hitler ignored the provisions of the Treaty of Versailles by doing what?
Ordering the army to recruit more soldiers and ordering German factories to churn out guns/ammunition/airplanes/tanks/etc.
46
New cards
By 1936, Germany occupied the ________.
^ Rhineland