Core Technical Principles
1/131
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AQA GCSE Design & Technology - Core Technical Principles
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
Input (Automation)
All the materials, tools, and equipment to make the product
Process
All the work required to make the product
Output (production/automation)
The finished product
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)
Factories where a series of machines are put together to make a product. Automated systems process each step from an input to an output.
This system is expensive
Just in time (JIT)
Form of manufacturing which minimizes the waste. Materials are ordered when they’re needed. Saving on storage costs.
Market Pull
Consumers demand a redesign of a product to satisfy a new need
Technology Push
Manufacturers & designers inspire new products or improve old ones
Visual Marketing
Popup advertisements, spam emails, and virtual retailing
Crowdfunding
People invest in the development of products or services
Co-operatives
Groups of people who share their investment & develop products together
Ethical Issues
Deducing whether a product harms the environment or unfairly treats people
Fair Trade
Principle where everyone in the chain is offered a minimum price & good working conditions
Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
Process of making small changes to improve the way a company works
Planned Obsolescence
Products are intended to require repairs and become obsolete quicker than others
Computer Aided Design (CAD)
Process of creating a 2D or 3D design using computer software
Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM)
Manufacturing a part or product from CAD using computer-controlled machinery (E.g. A 3D printer)
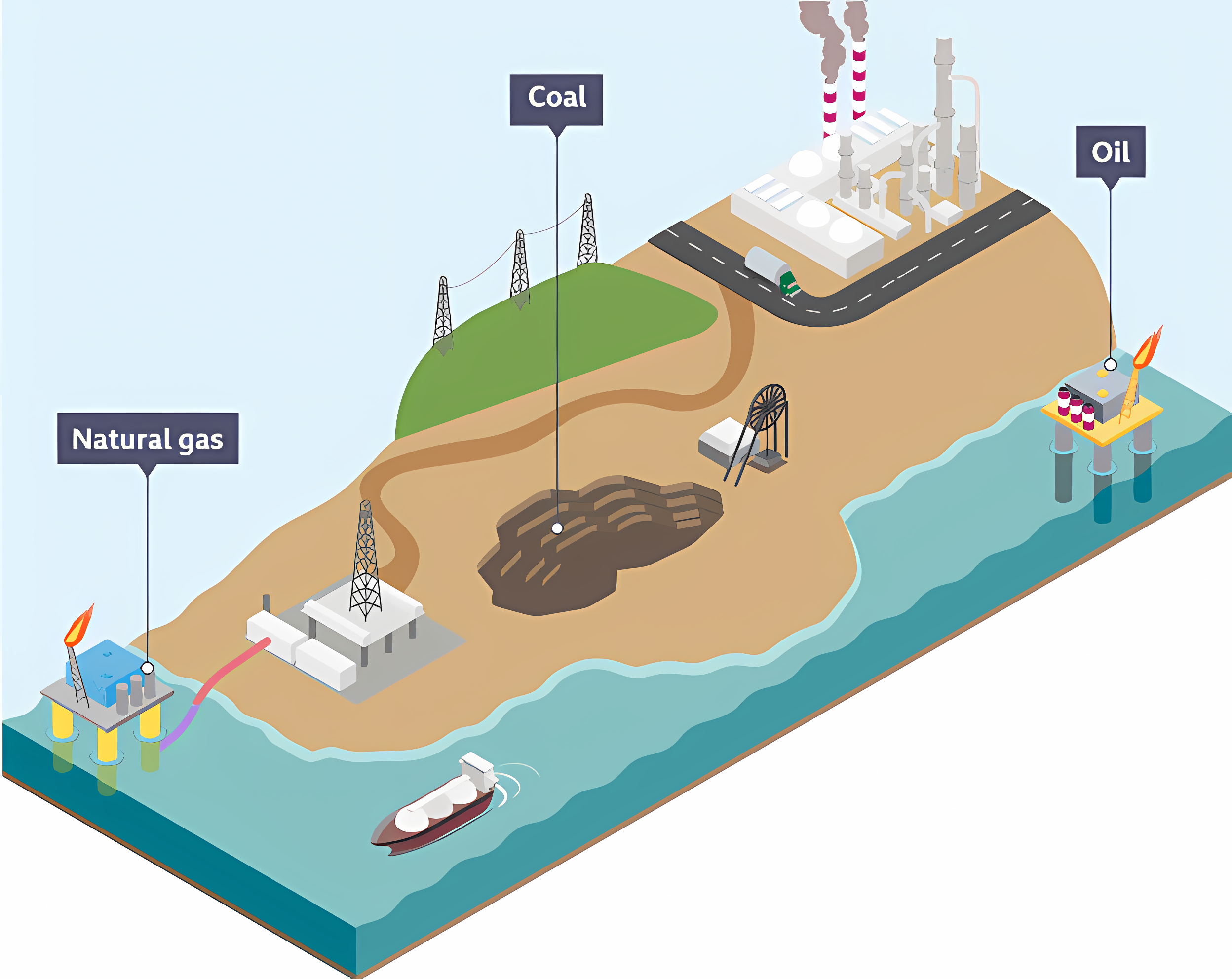
Fossil Fuels
Formed underground over millions of years. They are burnt to generate power by heating water to turn a turbine to generate power.
The 3 types include:
1) Coal
2) Oils
3) Gas
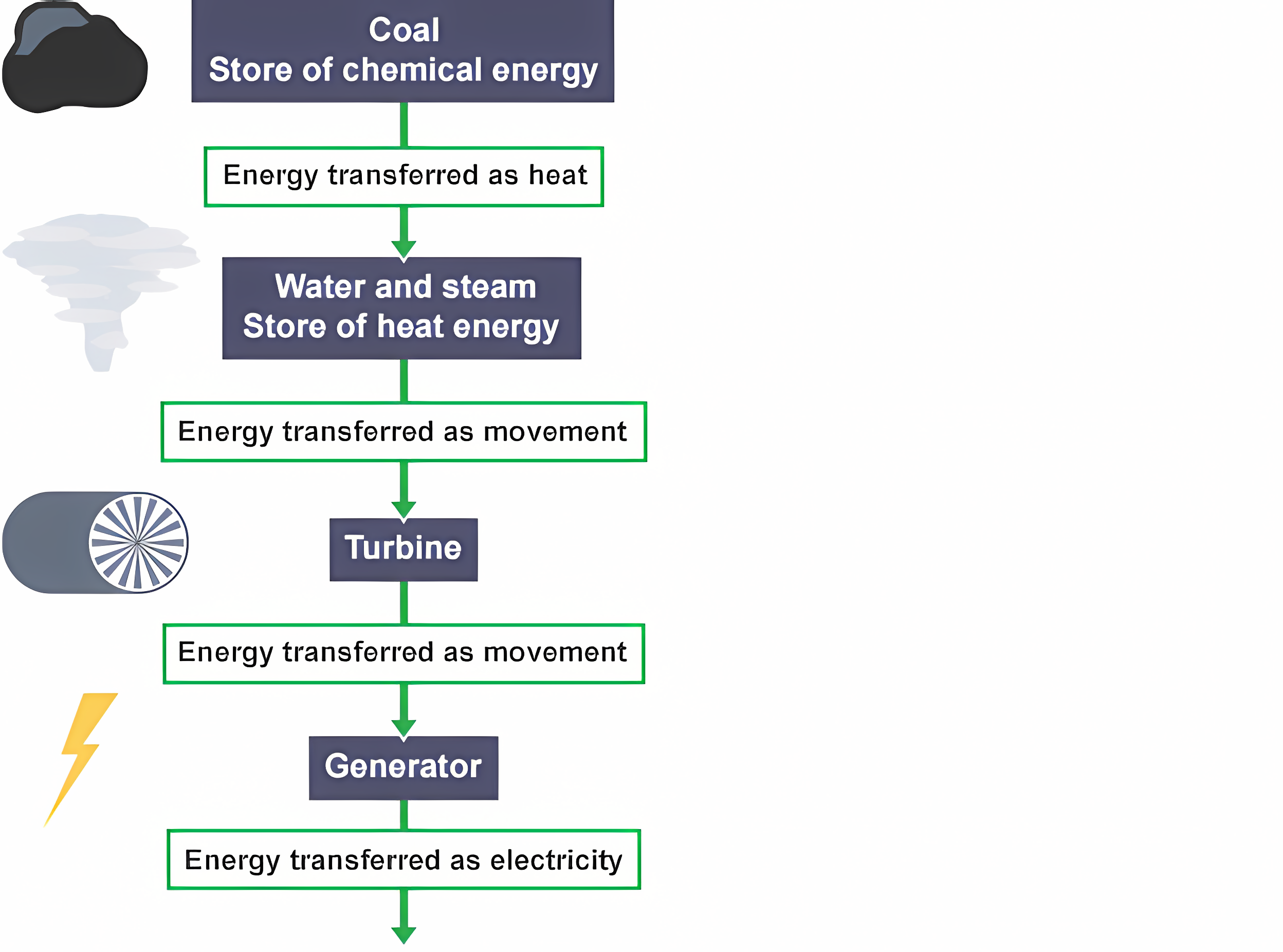
Coal
Energy generated as the coal is burned, the hot coal heats water turning it into steam. The steam builds a high pressure which spins a turbine. The turbine is connected to an electrical generator, creating electricity
Advantages of Coal
Enough coal on Earth to last hundreds of years
Produces high amounts of energy
Disadvantages of coal
Produces carbon dioxide when burned, contributing to global warming
Damage is caused to natural land when mining takes place
Natural Gas
Used for heating & cooking. Produced off-shore & transported through pipelines to a gas-powered electricity station.
Advantages of Natural Gas
It emits less carbon dioxide than coal or oil
The UK has shale gas deposits
Disadvantages of Natural Gas
Gas is highly flammable - if there is a gas leak, an explosion can easily happen
Extracting gas might cause the pollution of water
Oil
Used for fuel or turned into plastics.
Advantages of Oil
A small amount of oil can produce a lot of energy
It is relatively easy to store and transport
Disadvantages of Oil
Creates significant air pollution when burned
Considerable impact on water, land use and disposal
Nuclear Fission
Uranium generates heat to power turbines in the same way as fossil fuels.
Advantages of Nuclear Power
No harmful gases are released in the process
More efficient than fossil fuels
Disadvantages of Nuclear Power
Nuclear power stations have to close after around 40 years of use when the uranium becomes less efficient at heating the water
Disposal of uranium is difficult and costly
Cost of nuclear power stations is very large
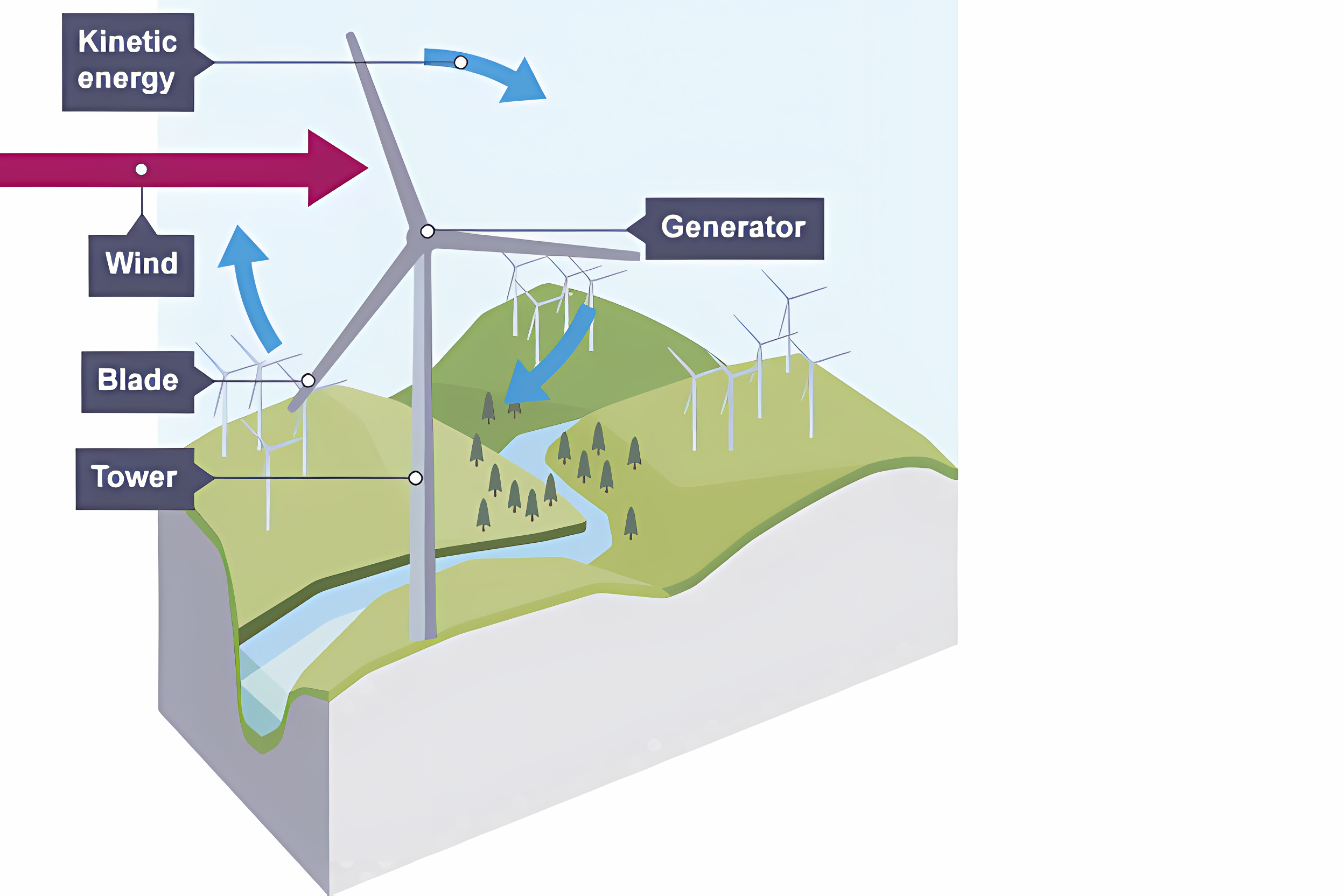
Wind Power
Harnesses the wind to turn a turbine to generate power.
Solar Power
Photovoltaic cells harness the sun’s light energy & convert it into electricity
Photovoltaic
Converting light energy into electrical current
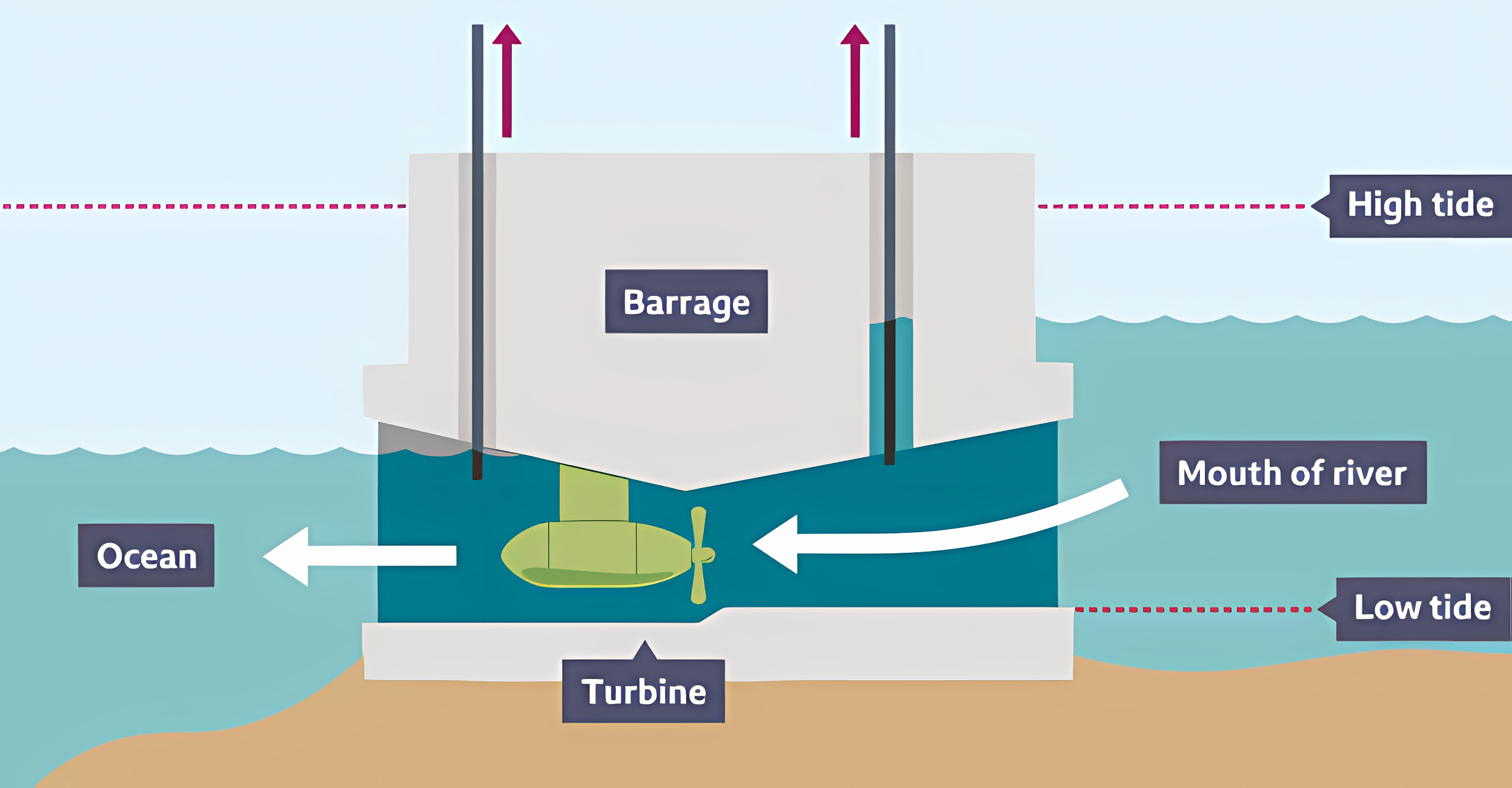
Tidal Power
Barrages generate power by turning a turbine as the tide comes in and out.
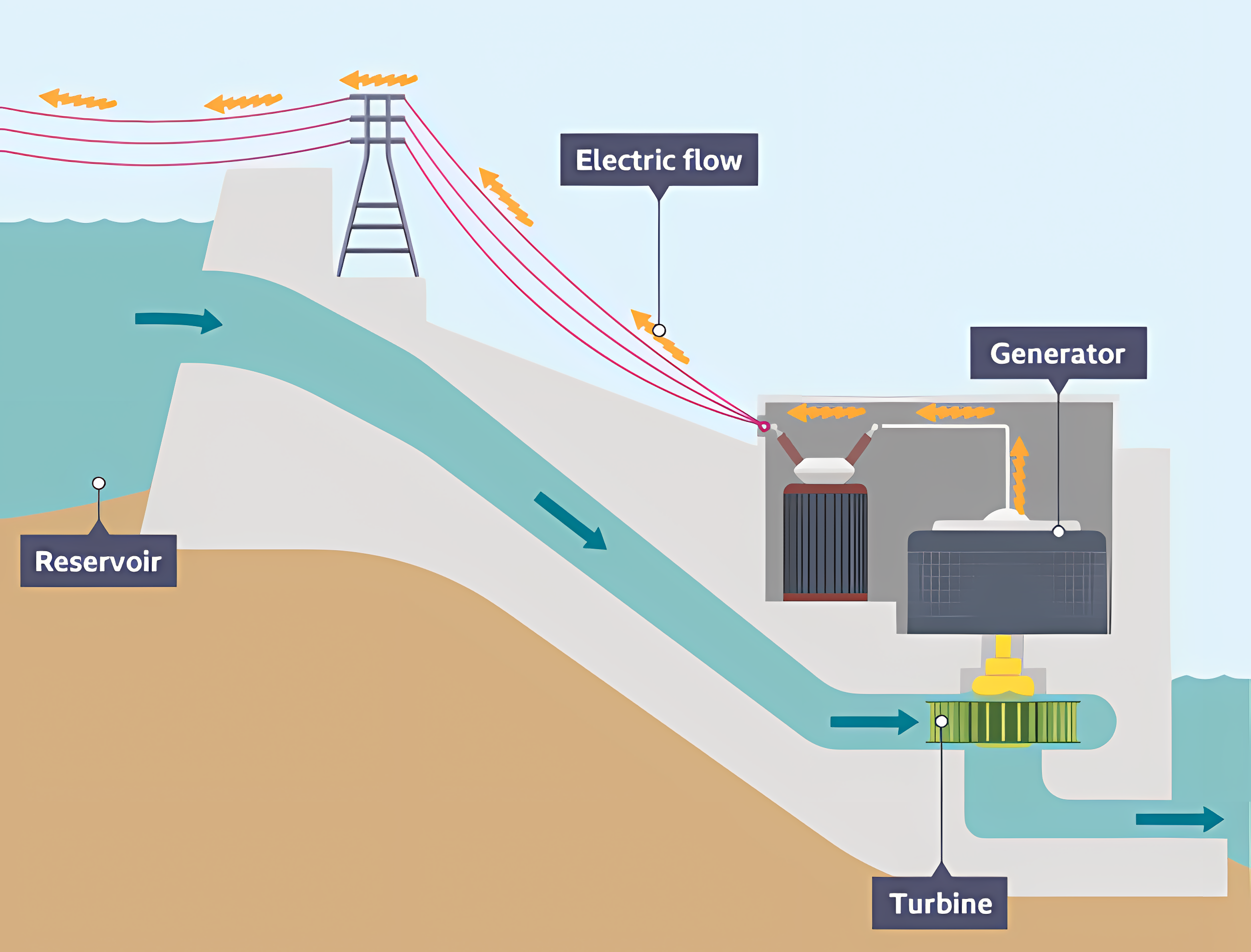
Hydro-electric Power
Generates power through water falling through a turbine, from the top of a hill to the bottom.
Biomass Power
Use waste products from wood or crops to burn creating the heat to turn the turbine.
Alkaline Batteries
Can’t be used again once the power is used, hard to dispose.
Rechargeable Batteries
They can have power put back into them, they are more expensive but also more environmentally friendly.
Traditional Materials
Materials that have been in use for centuries, such as paper, wood, stone and metals.
Modern Materials
Materials that have been engineered to have improved properties.
Smart Materials
Materials that exhibit a physical change in response to some external stimuli.
Shape-memory alloys (SMA)
Metal alloys that can remember their shape when heated.
Thermochromic Pigments
Change color when their temperature changes.
Photochromic Pigments
These pigments change their properties when exposed to Ultraviolet (UV) light.
Composite Materials
Materials made of different materials, which are combined to improve their properties.
Fiber-based composites
Mixture of 2 materials:
one part is a material in fiber strands, and the other is a resin.
Particle-based composites
Mixture of 2 materials:
one part is small particles, and the other is a liquid that sets.
Sheet-based composites
Mixture of 2 materials:
one part is thin sheets of a material, and the other is a resin.
Technical Textiles
Modern materials developed to help make fabrics.
Kevlar
Synthetic fiber which is woven to create a super strong, lightweight fabric which has uses for protective clothing.
Fire-retardant fabrics (Nomex)
Fire resistant fabric with resistance built into the fibers (so it can’t be washed out).
Input devices
Devices which allow systems to understand changes in environments. (E.g. a sensor like a light-dependent resistor).
Switches
Devices which allow currents to flow through them, when the contacts inside are joined together.
Push-to-make Switch (PTM)
A switch that ‘makes’ a circuit when pressed.

Push-to-break Switch (PTB)
A switch that ‘breaks’ a circuit when pressed.
Toggle or Rocker switch
A Switch which has 2 conditions, on or off.
Sensors
Devices that detect changes in the environment. They are inputs.
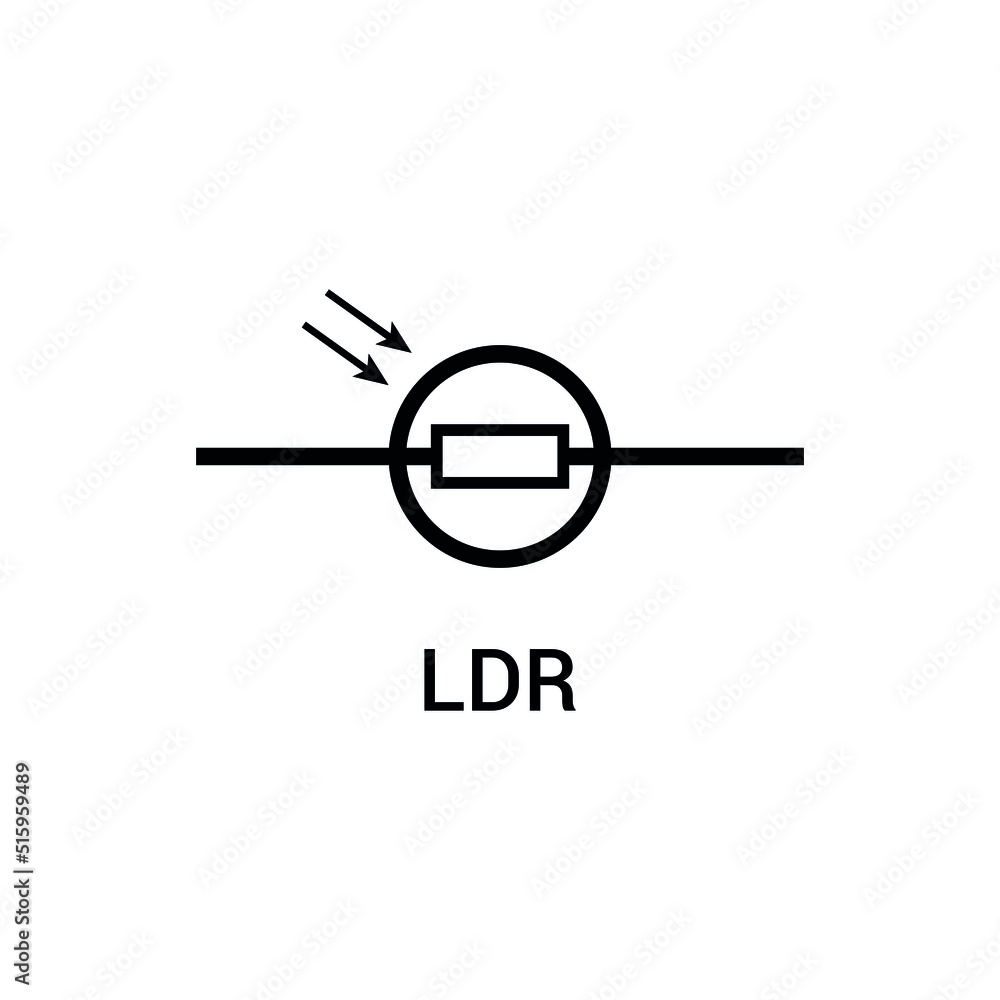
Light-dependent resistor (LDR)
Special type of resistor whose resistance changes with light levels. (Brighter light = Less resistance)
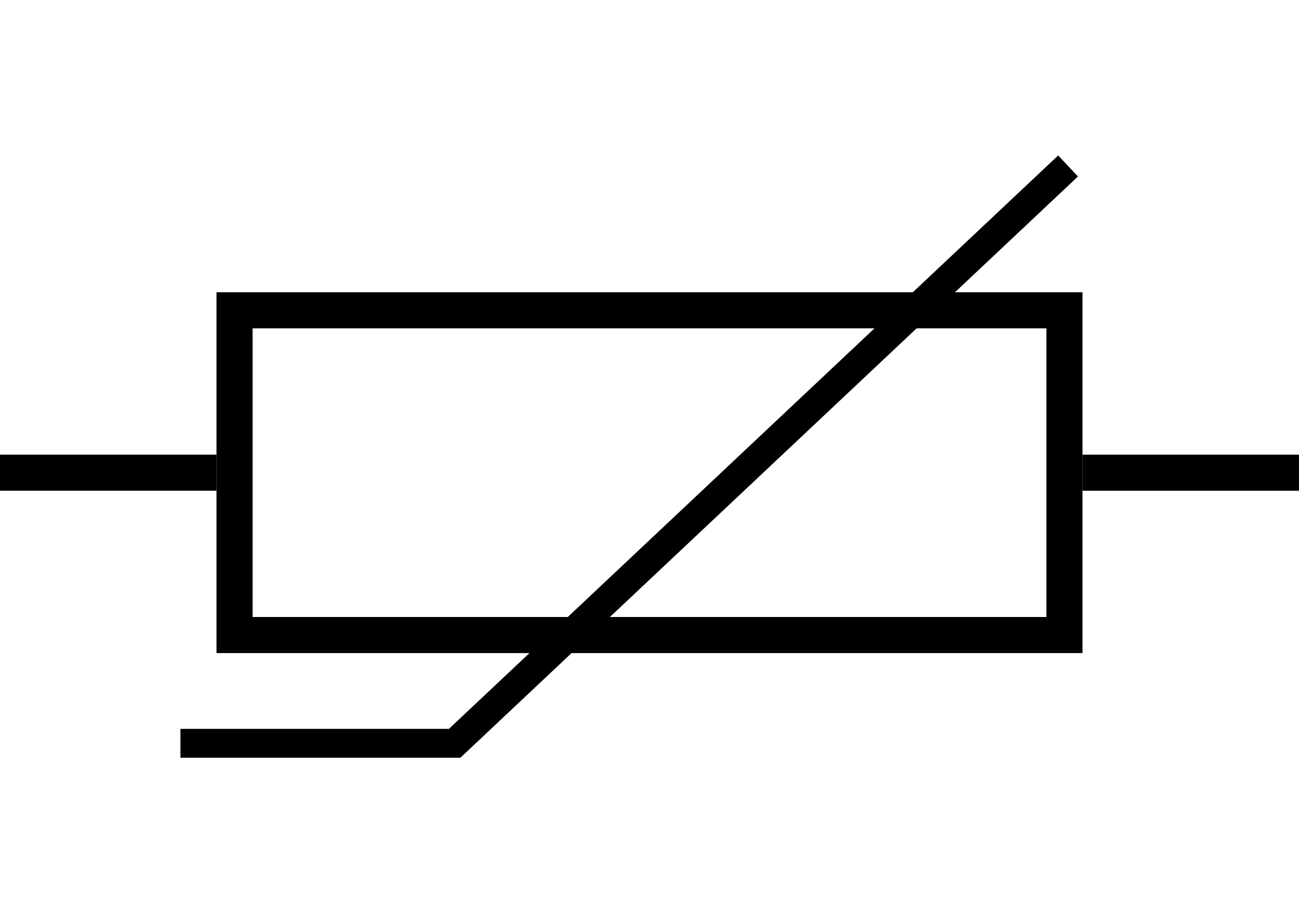
Thermistor
Special type of resistor whose resistance changes with temperature levels.
Name a suitable input device for a greenhouse cooling system
A Thermistor
Microcontrollers
A small computer chip used instead of a CPU that contains a processor, memory and inputs/outputs.
Advantages of Microcontrollers
The size of a circuit can be significantly reduced. This is because programming replaces physical components.
They can be reprogrammed many times. This allows changes to be made without replacing actual components.
They have pins for connecting several input and output devices, adding to flexibility.
Disadvantages of Microcontrollers
They often cost more than traditional integrated circuits. They are therefore not always the best option for simple systems.
Programming software and hardware is required. This can be expensive to buy.
The language of the system must be learned and this adds to training costs.
Process devices
Device that takes the signal from the input stage, and changes it in some way.
Output devices
Device which allows a system to present information back to the real world.
Name a suitable output device for an MP3 amplifier system
A Speaker
Lamp
Current flows through a filament, heating it up, creating light. It is an output.
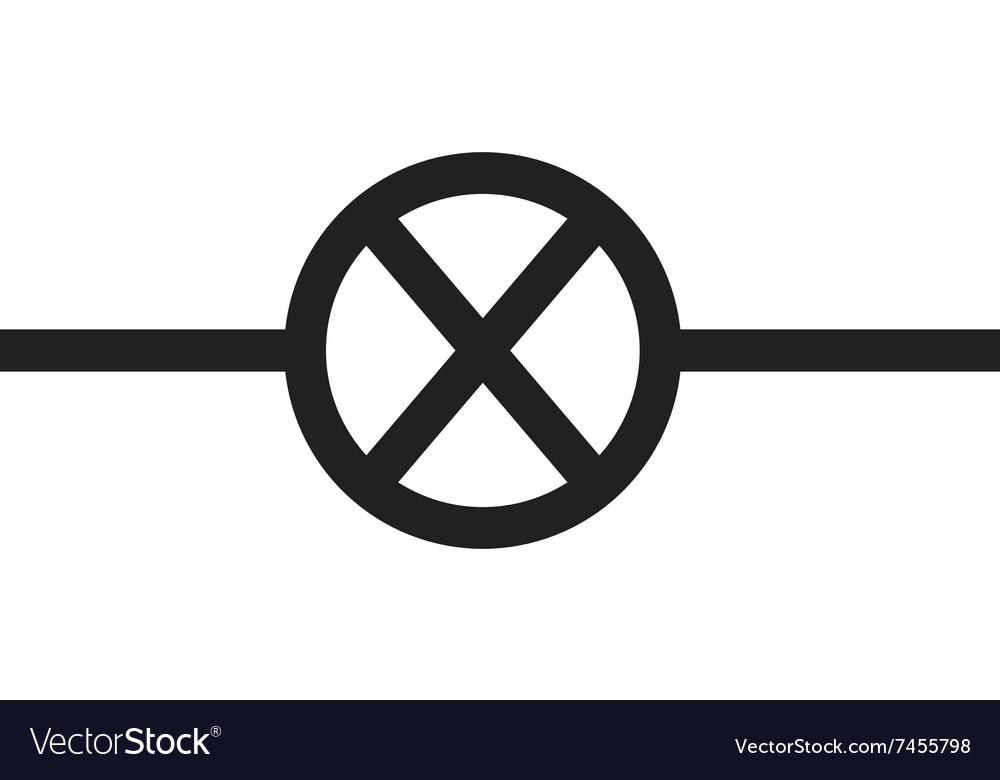
Buzzer
Current flows through the oscillator, producing a buzzing sound.
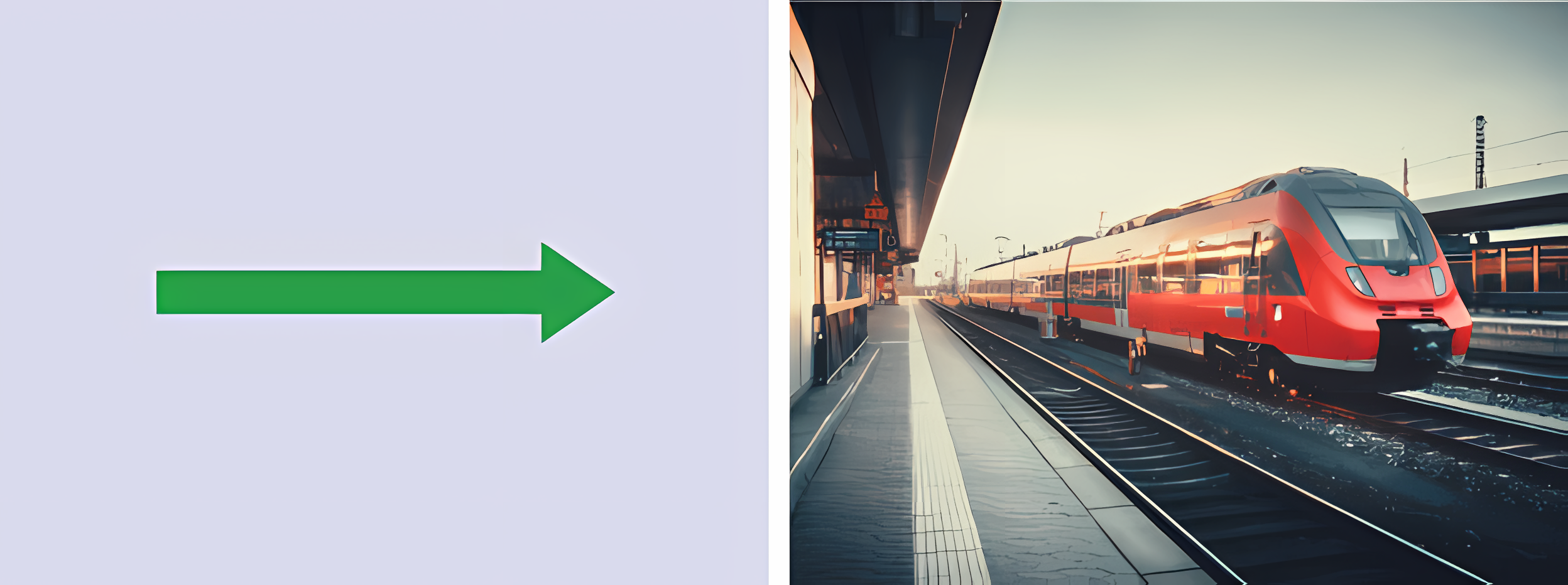
Linear Motion
Moving something in a straight line (E.g. Train moving)

Rotary Motion
Something moves around an axis or pivot point (E.g. a wheel)

Reciprocating Motion
Repeated up & down motion or back-and-forth motion (E.g. Piston or Pump)

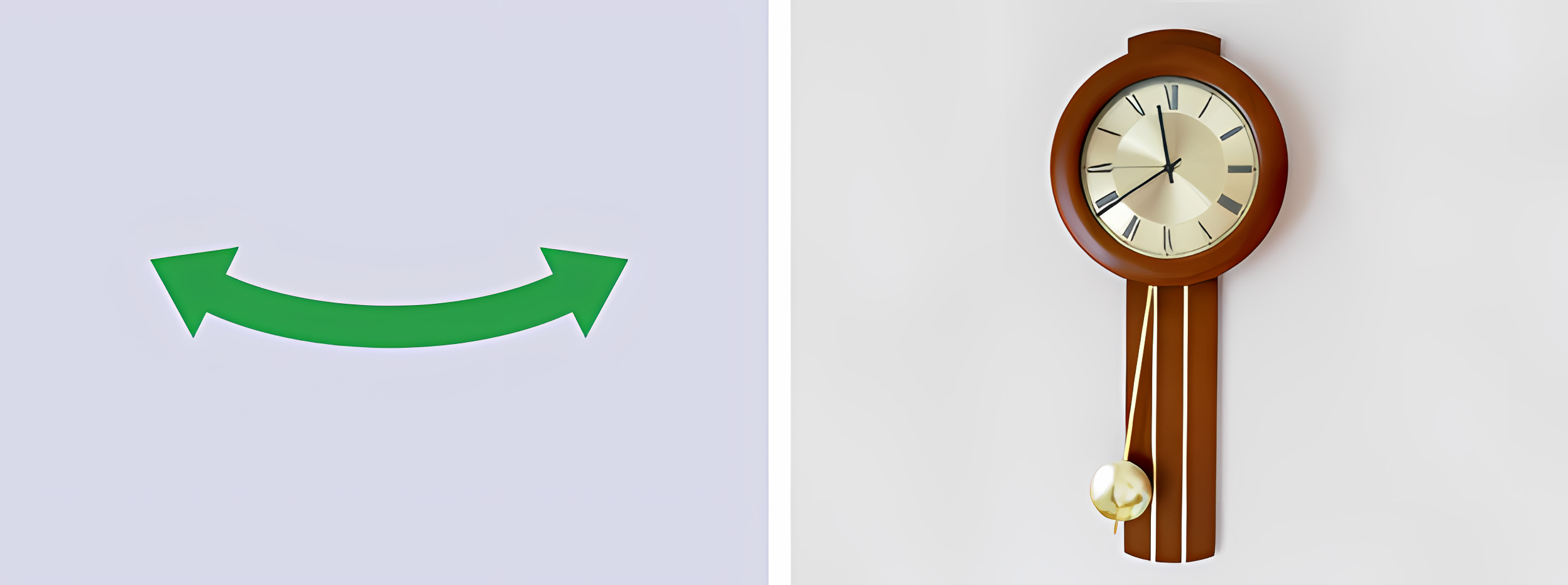
Oscillating Motion
Curved backwards & forwards movement, swinging on an axis or pivot point.

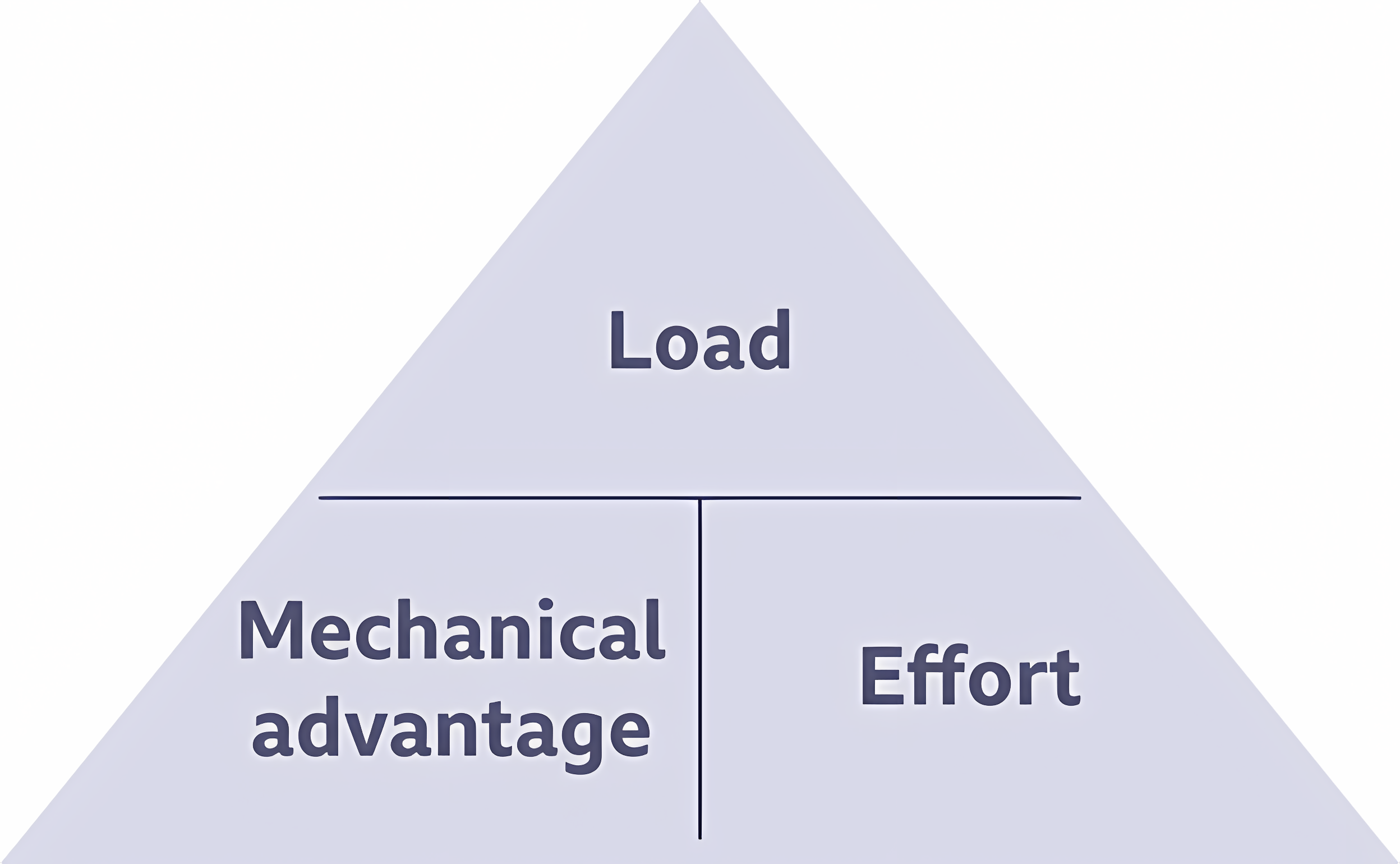
Effort
Amount of force applied by the user (Input)
Fulcrum
Where the lever pivots
Load
The weight that needs to be moved
Mechanical Advantage (Formula)
= Load (N) ÷ Effort (N)
A person is using a lever to lift a rock with a 50 N load. The mechanical advantage is 5:1. How much effort is the person having to give?
effort = 50 N ÷ 5 = 10 N
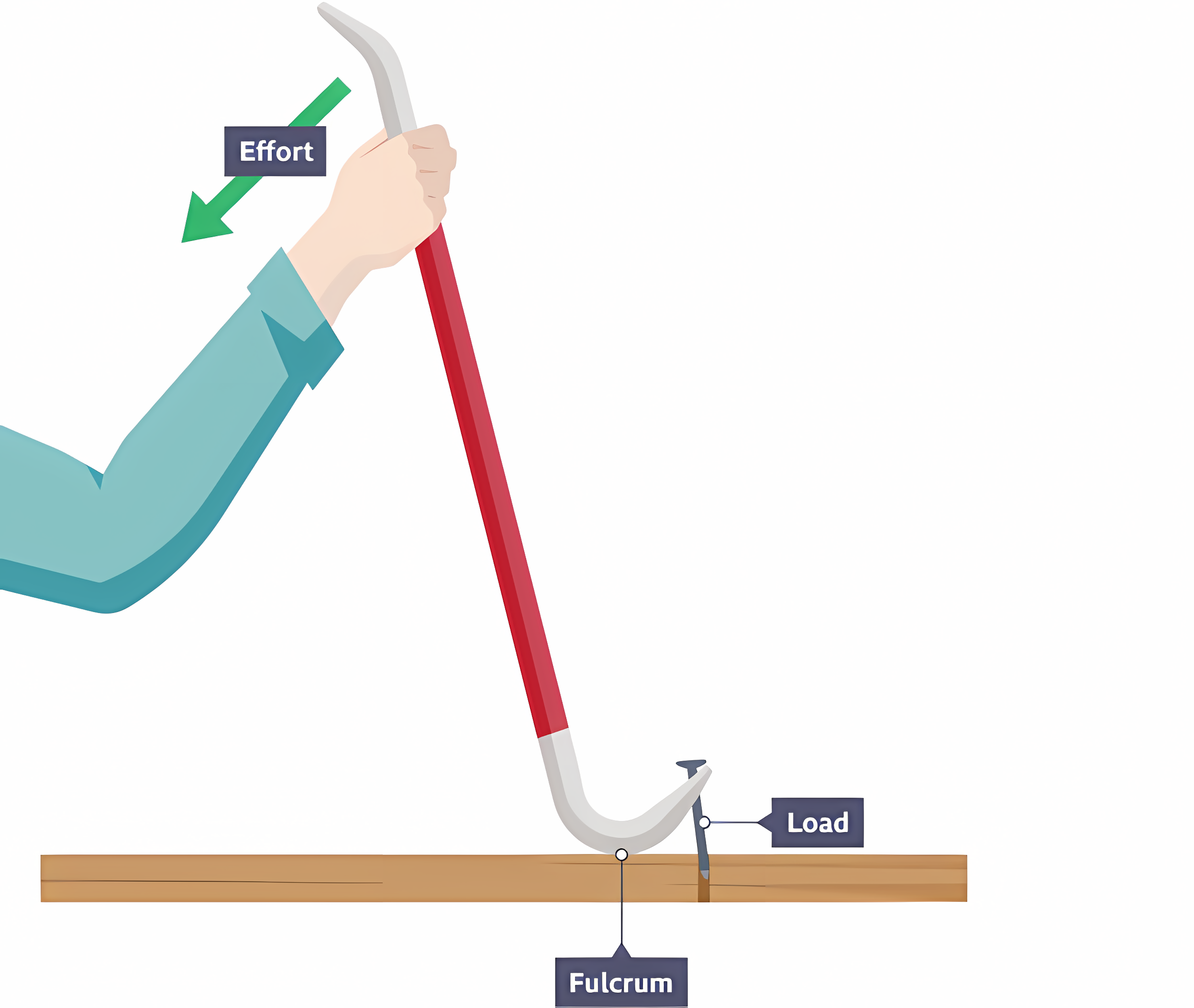
First order levers (Class #1)
The pivot (fulcrum) is between the effort and the load. (E.g. Seesaws or crowbars)
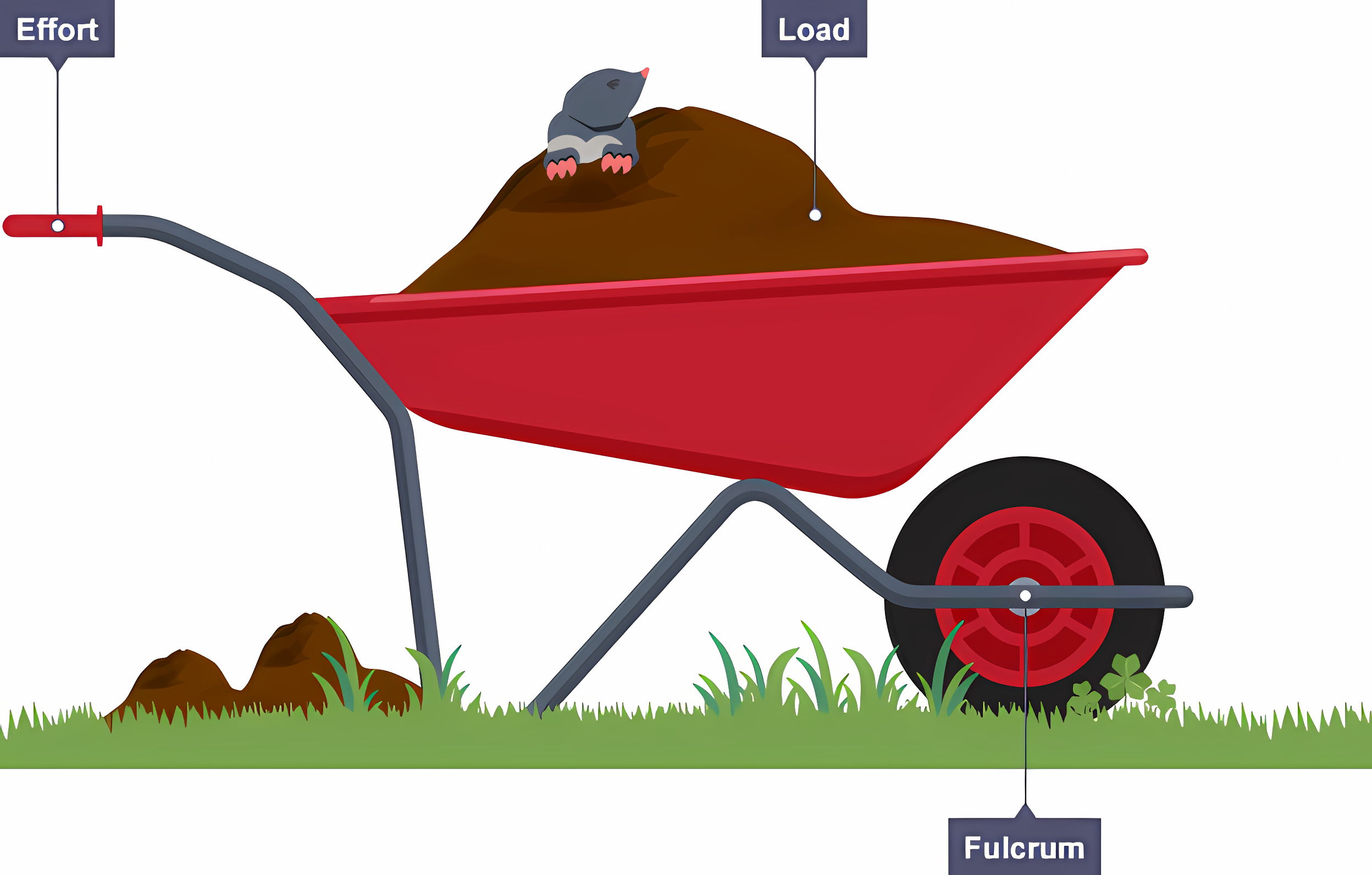
Second order levers (Class #2)
The pivot (fulcrum) is at the end of the lever, away from the user. The load is in the middle, and the effort is near the user. (E.g. Nutcrackers, Wheelbarrows, or bottle openers)
Third order levers (Class #3)
The pivot (fulcrum) is at one end, and the load is at the opposite end. The effort is in the middle. (E.g. Tweezers or fishing rods)
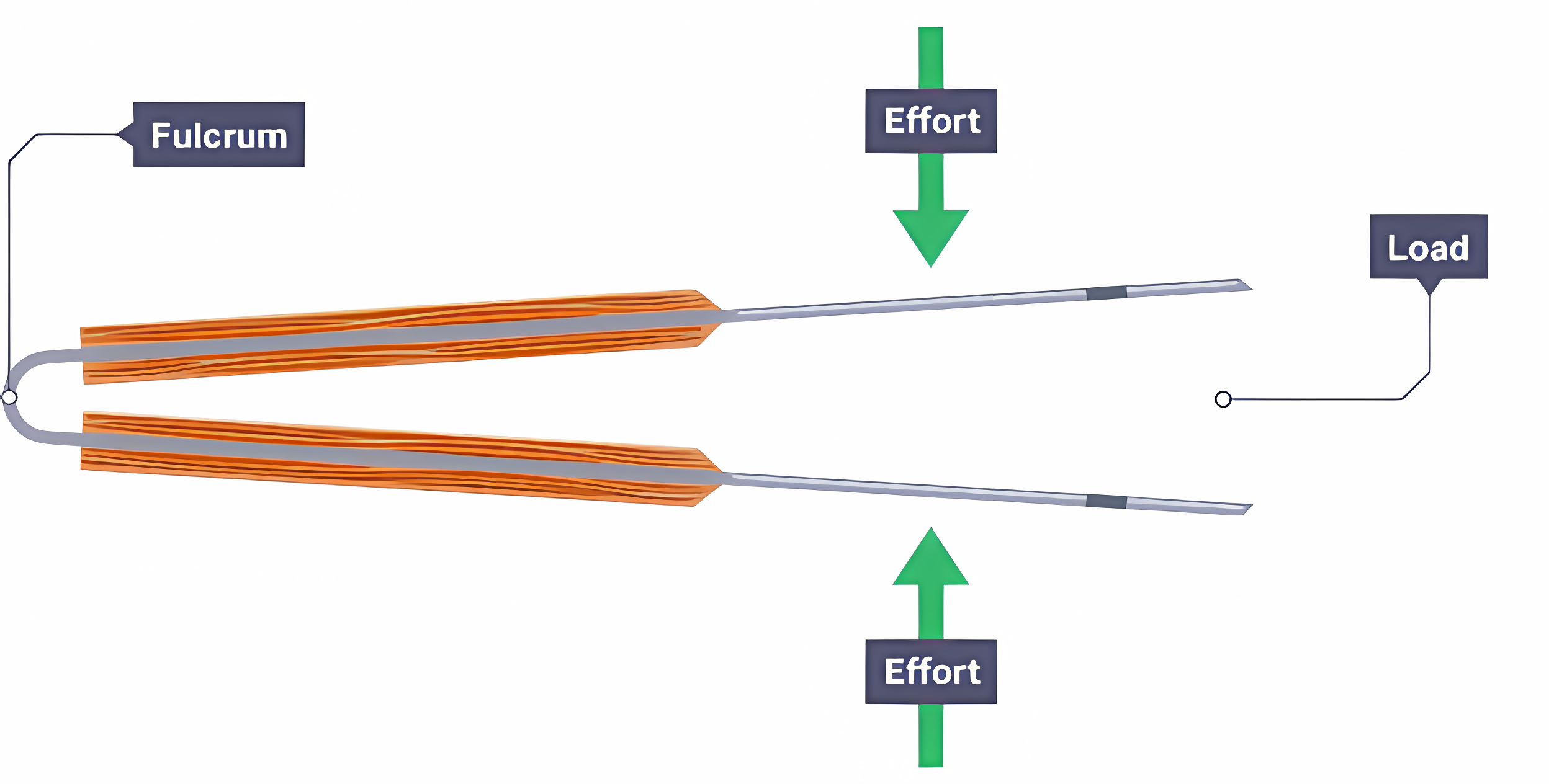
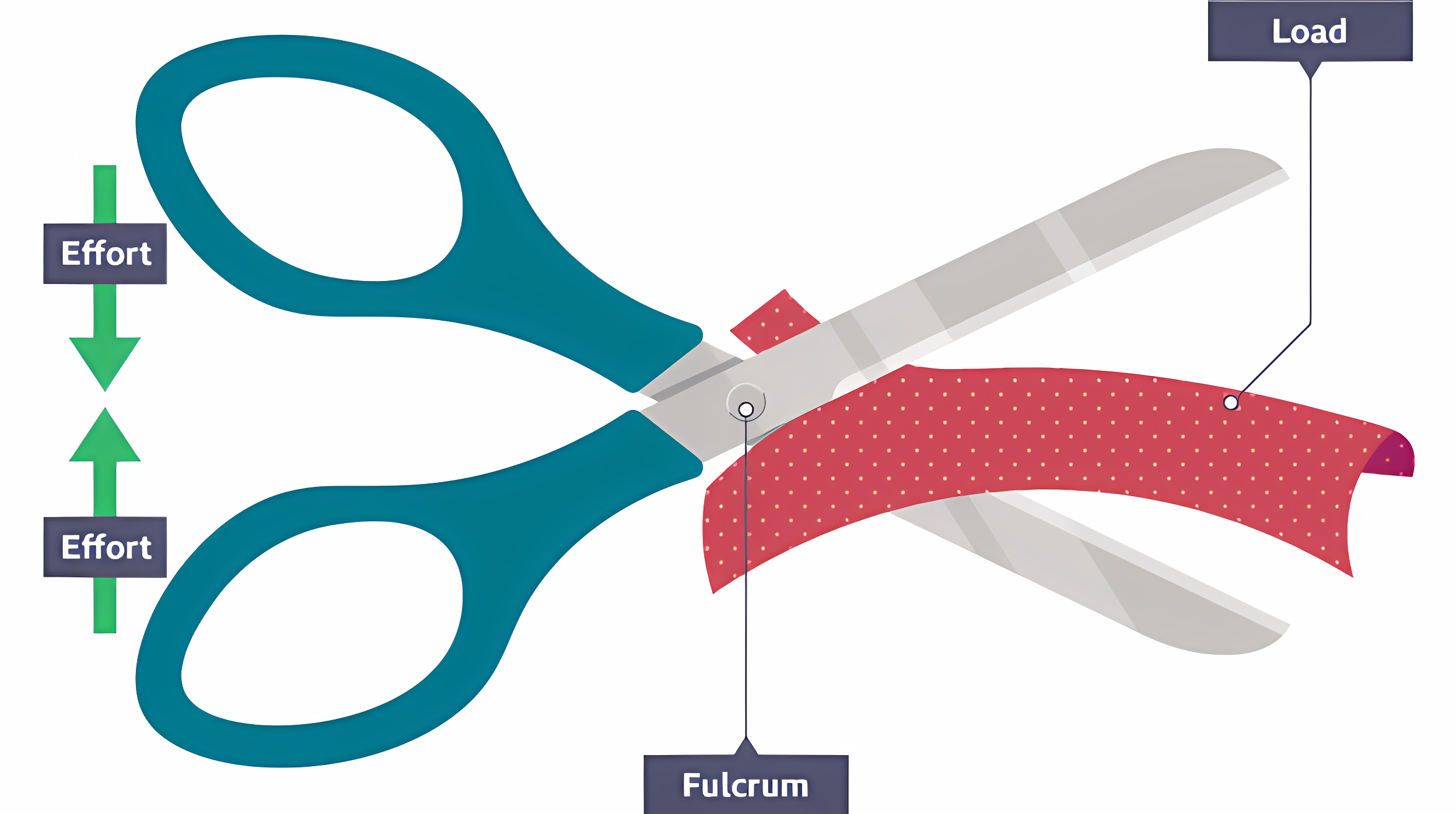
The blade on a pair of scissors is an example of which type of lever?
First order - the hand’s grip is the applied force, the fulcrum is the pin at the center of the scissors and the blade applies force to the load.
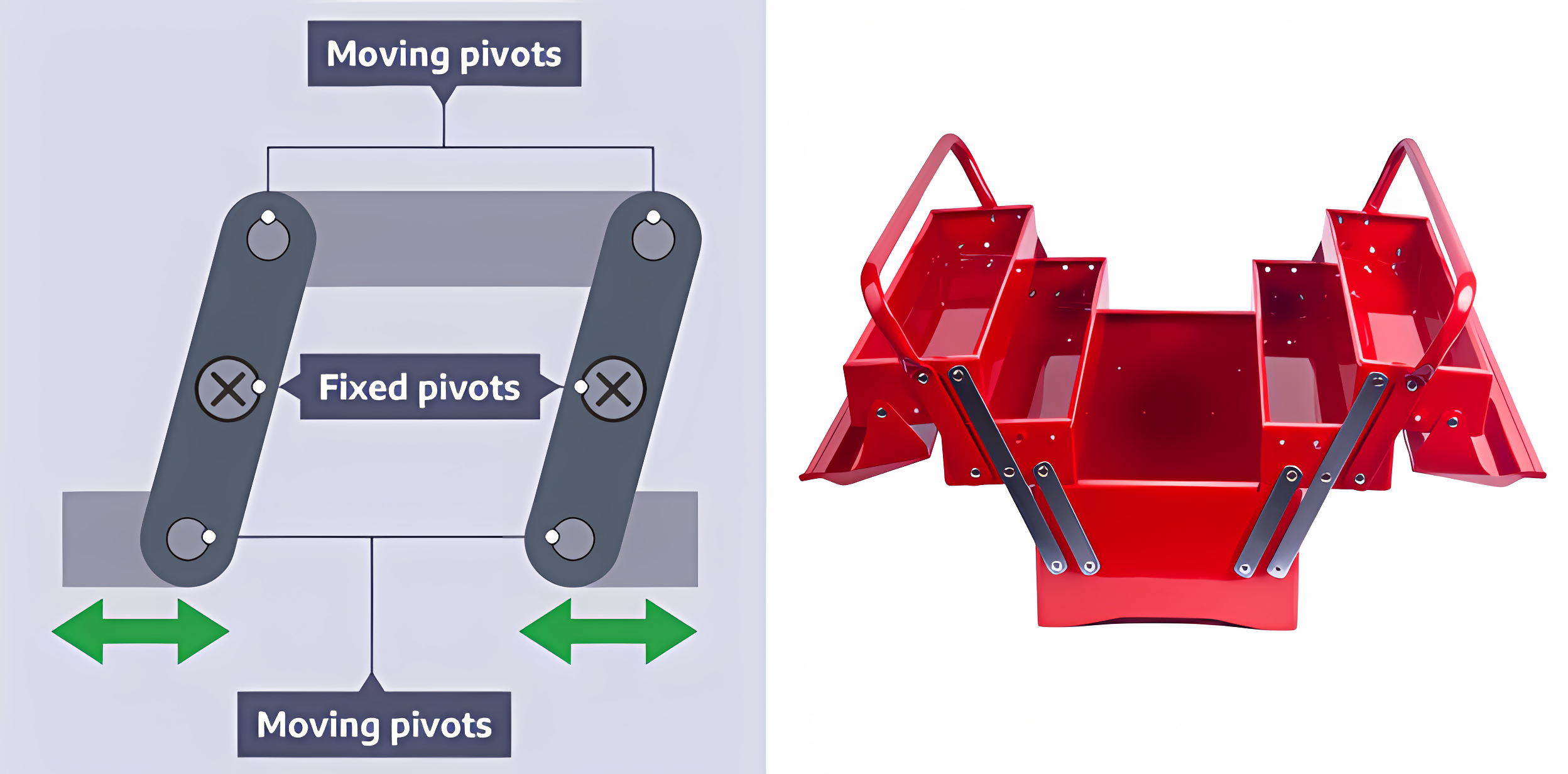
Linkages
Levers joined together, to change the direction or amount of force.
Reverse motion linkage
A linkage that changes the direction of an input to make it go the opposite way. A fixed pivot forces the change in direction.

Parallel motion linkage (Push or Pull)
A linkage that uses 2 fixed pivots to make the input & output travel in the same direction. Each fixed pivot has a moving pivot on either side.
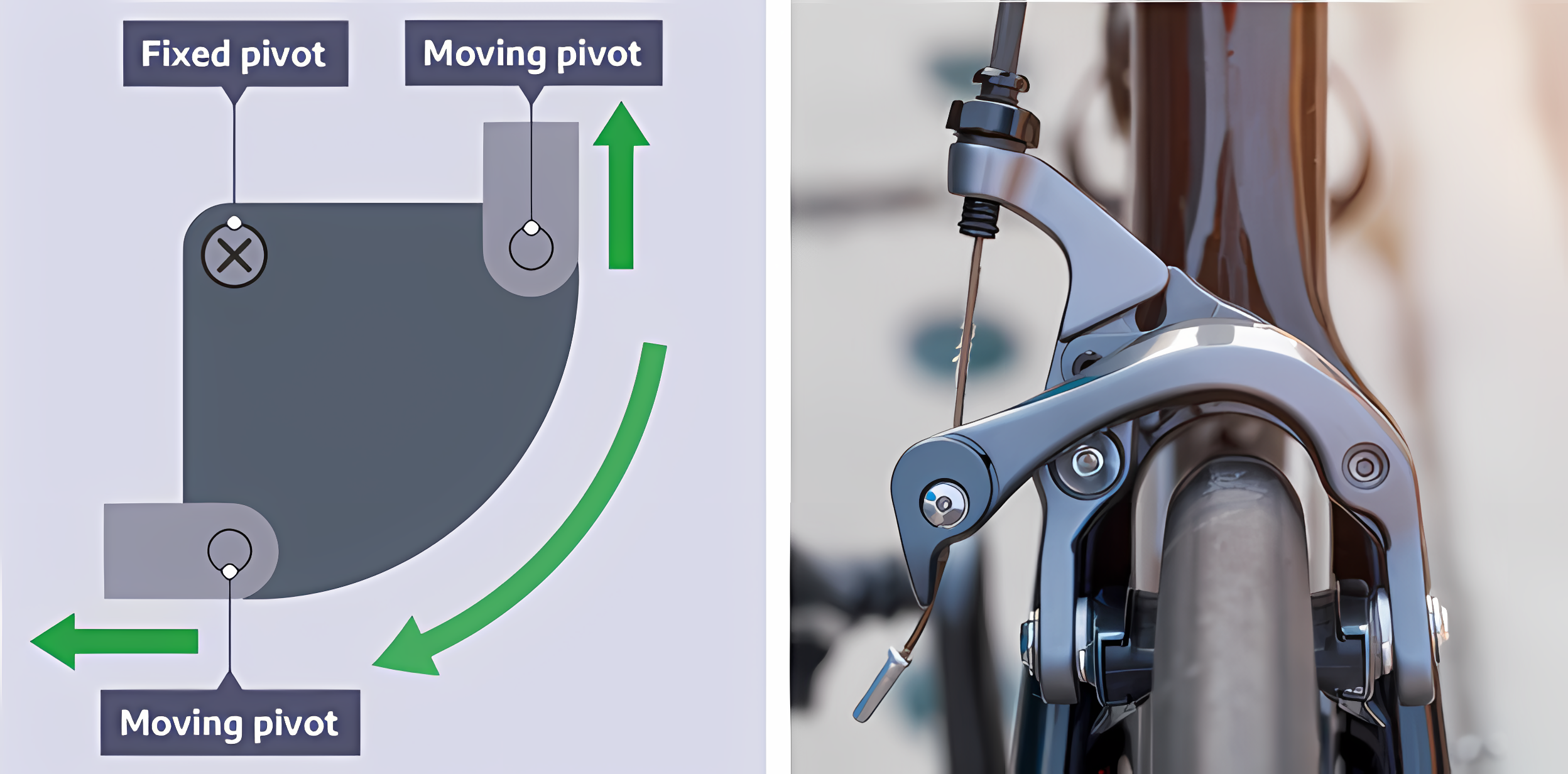
Bell crank linkage
A linkage that changes the direction of the force by 90 degrees. The amount of output force can be changed by moving the fixed pivot.
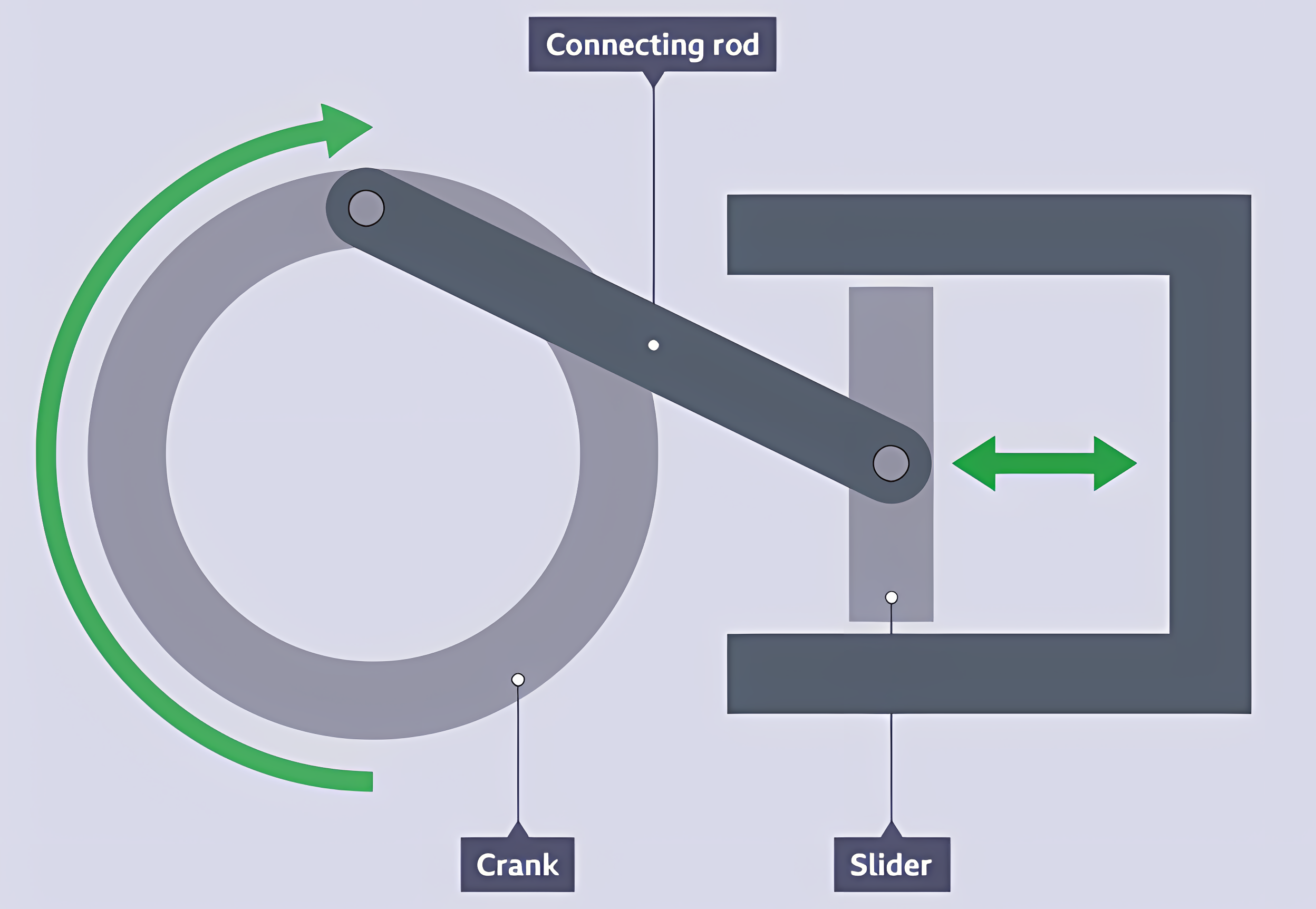
Crank & slider linkage
A linkage that changes rotary motion into reciprocating motion. A fixed pivot is attached to a crank, which turns around and pushes and pulls a slider.
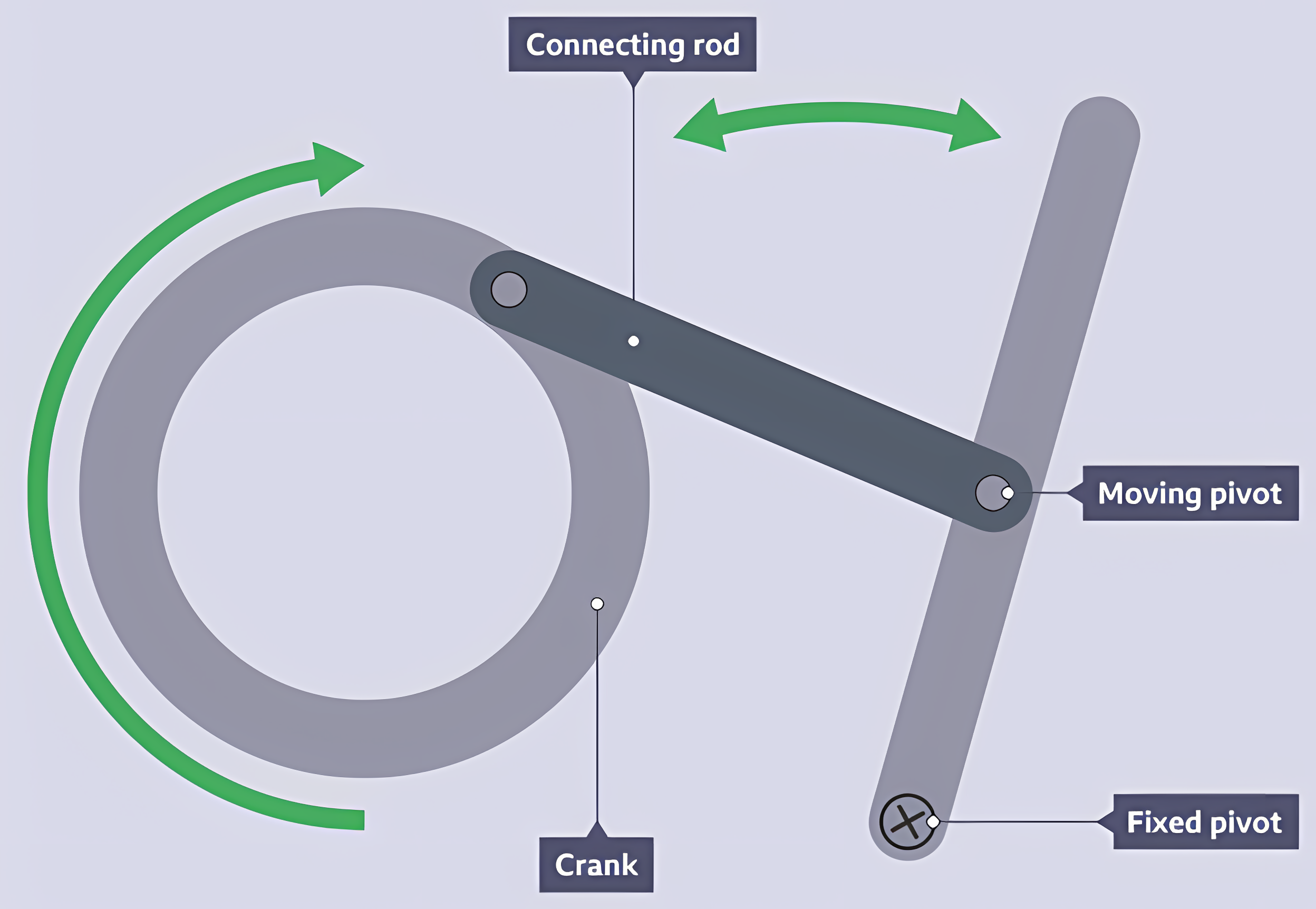
Treadle linkage
A linkage that uses a rotary input to turn a crank on a fixed pivot. A connecting rod joins two moving pivots to another fixed pivot.
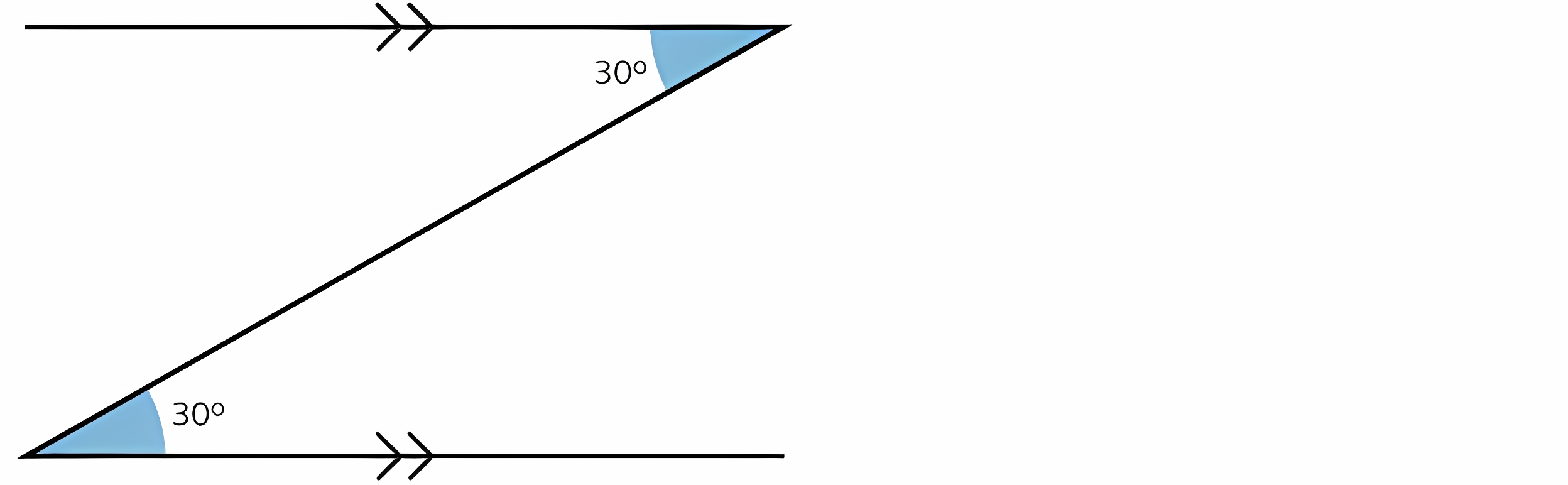
Reverse motion linkage (Angles)
Replicates a 'Z' angle. Z angles feature two internal angles, which will both be the same as long the input and output linkages remain parallel.
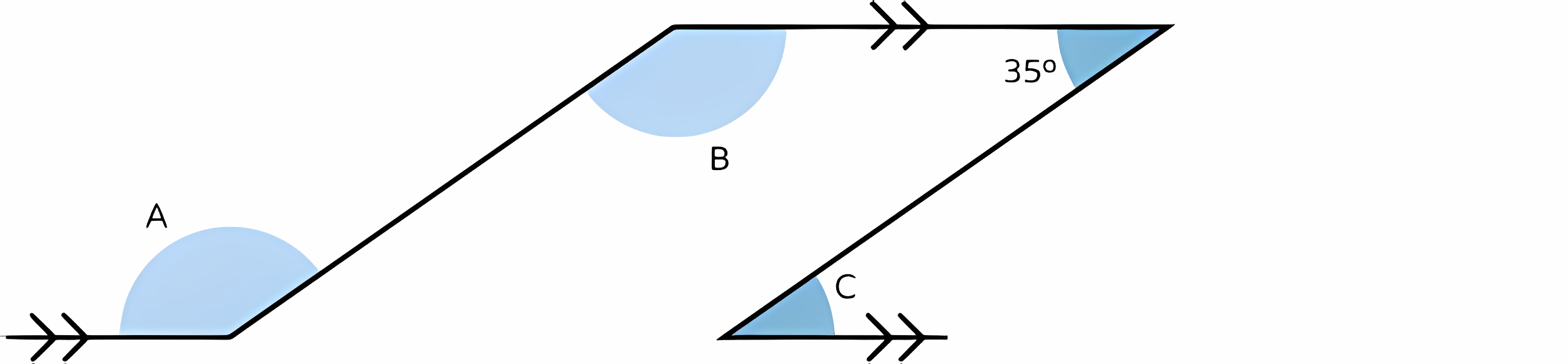
Calculate angles A, B and C in the parallel linkage:
A and B = 145°
C = 35°
Cam
A wheel attached to a crankshaft
Follower
A bar that follows a cam around its circumference
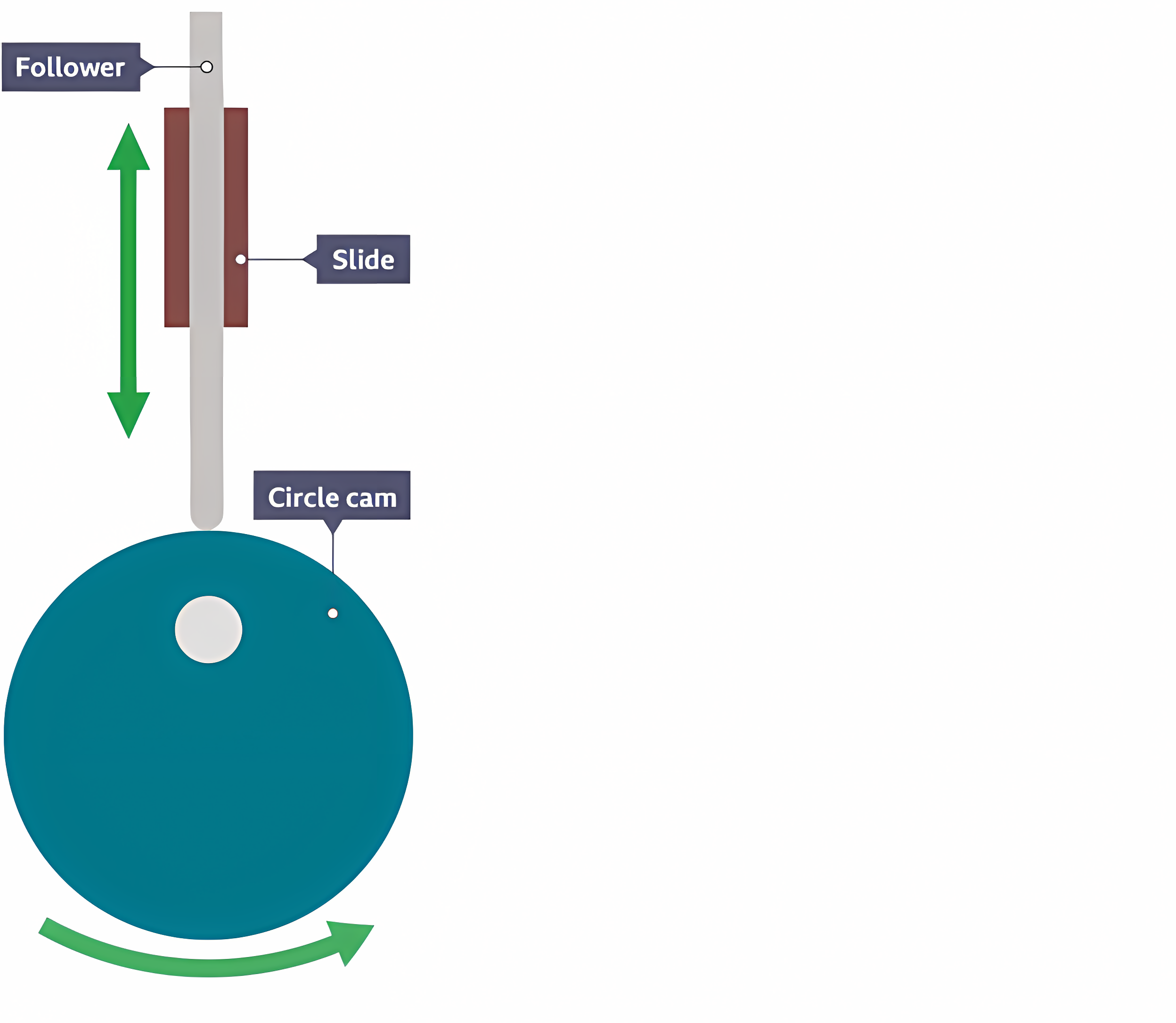
Circular (cam)
Off-centered pivot causes the follower to move up & down.
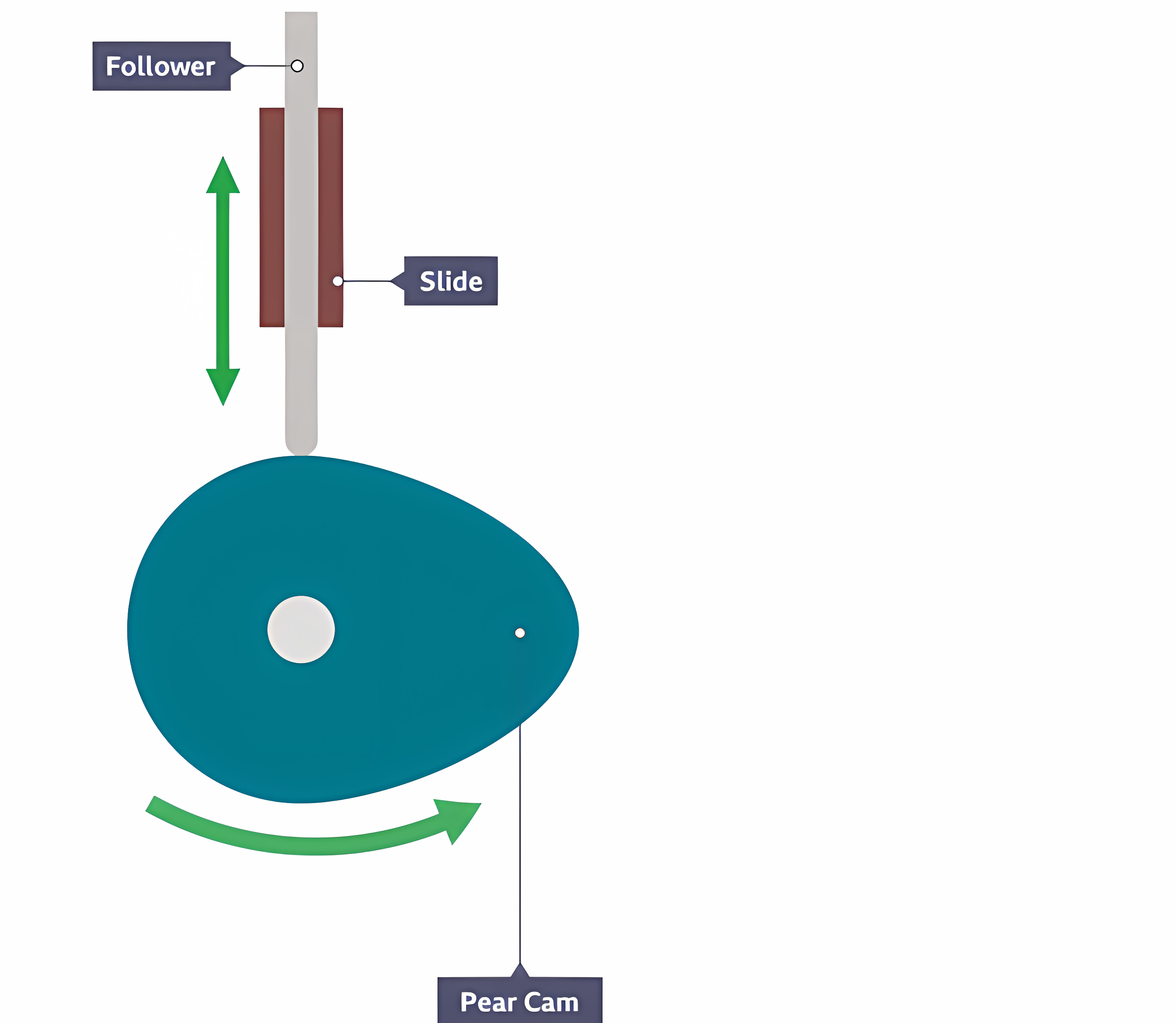
Pear (cam)
Remains stationary for half a turn, then gently rises and falls.
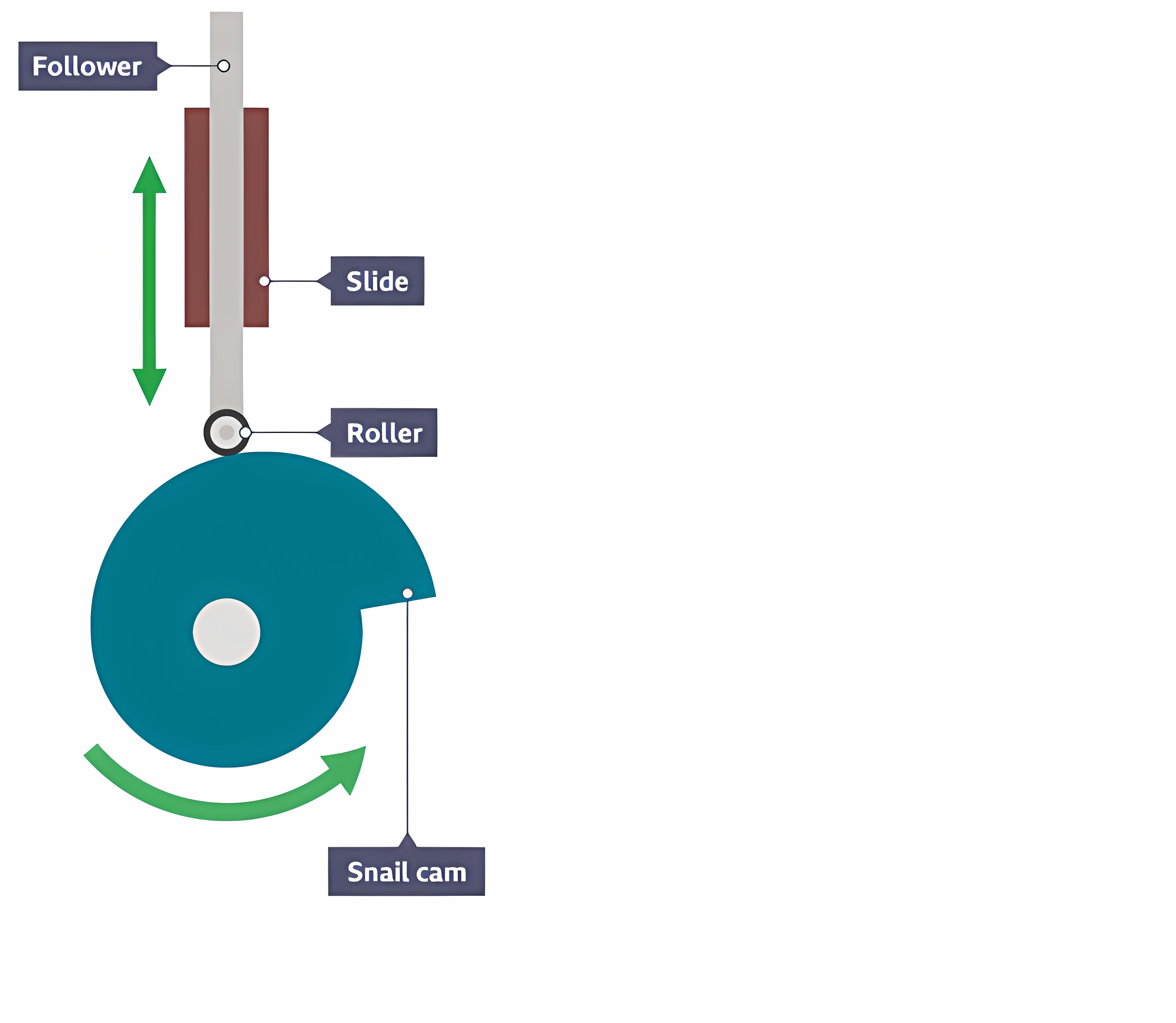
Snail or drop (cam)
Causes the follower to remain stationary for half a turn before gently rising and suddenly falling. They only work in one direction.
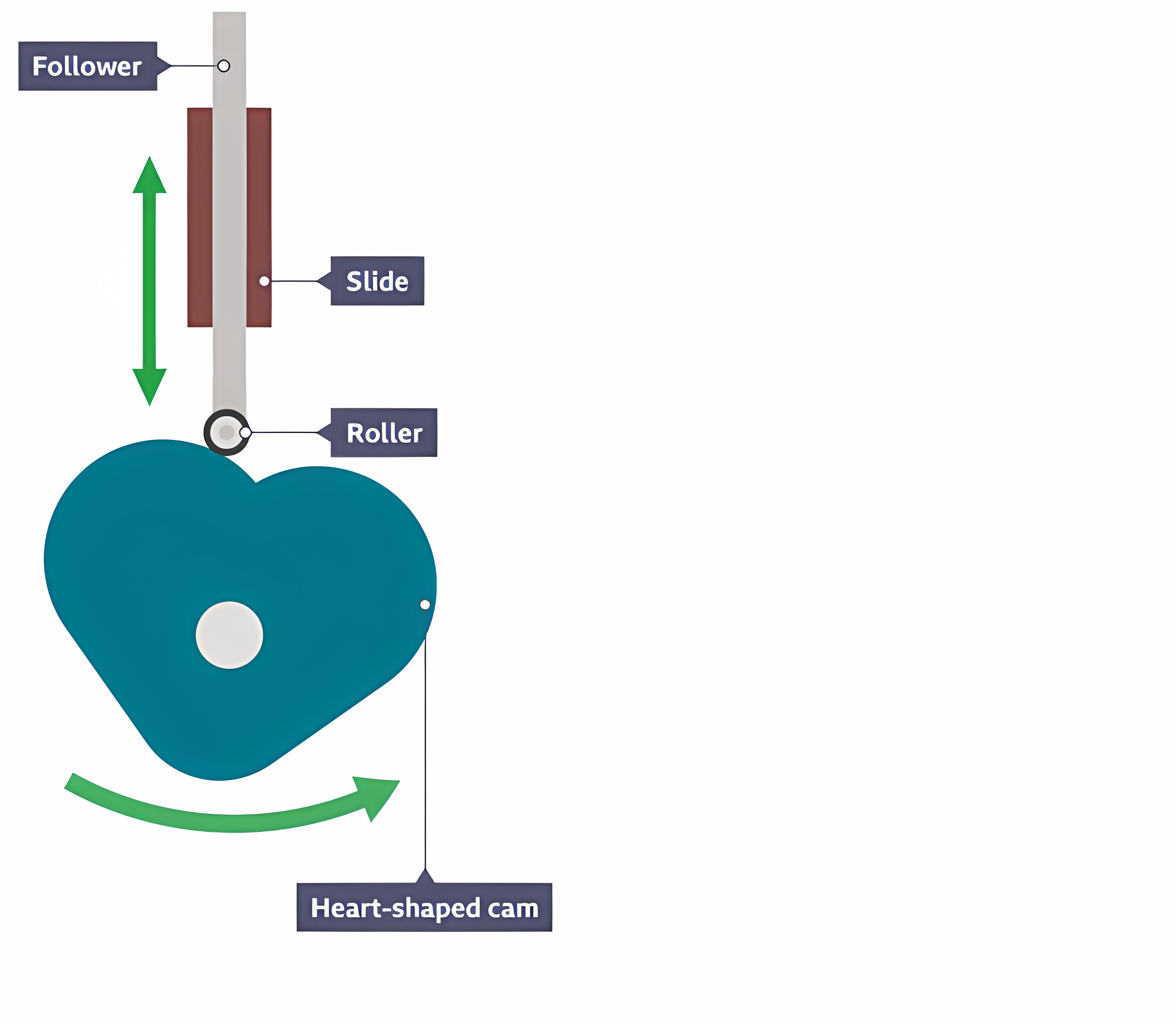
Heart-shaped (cam)
The follower rises and falls steadily with uniform velocity.
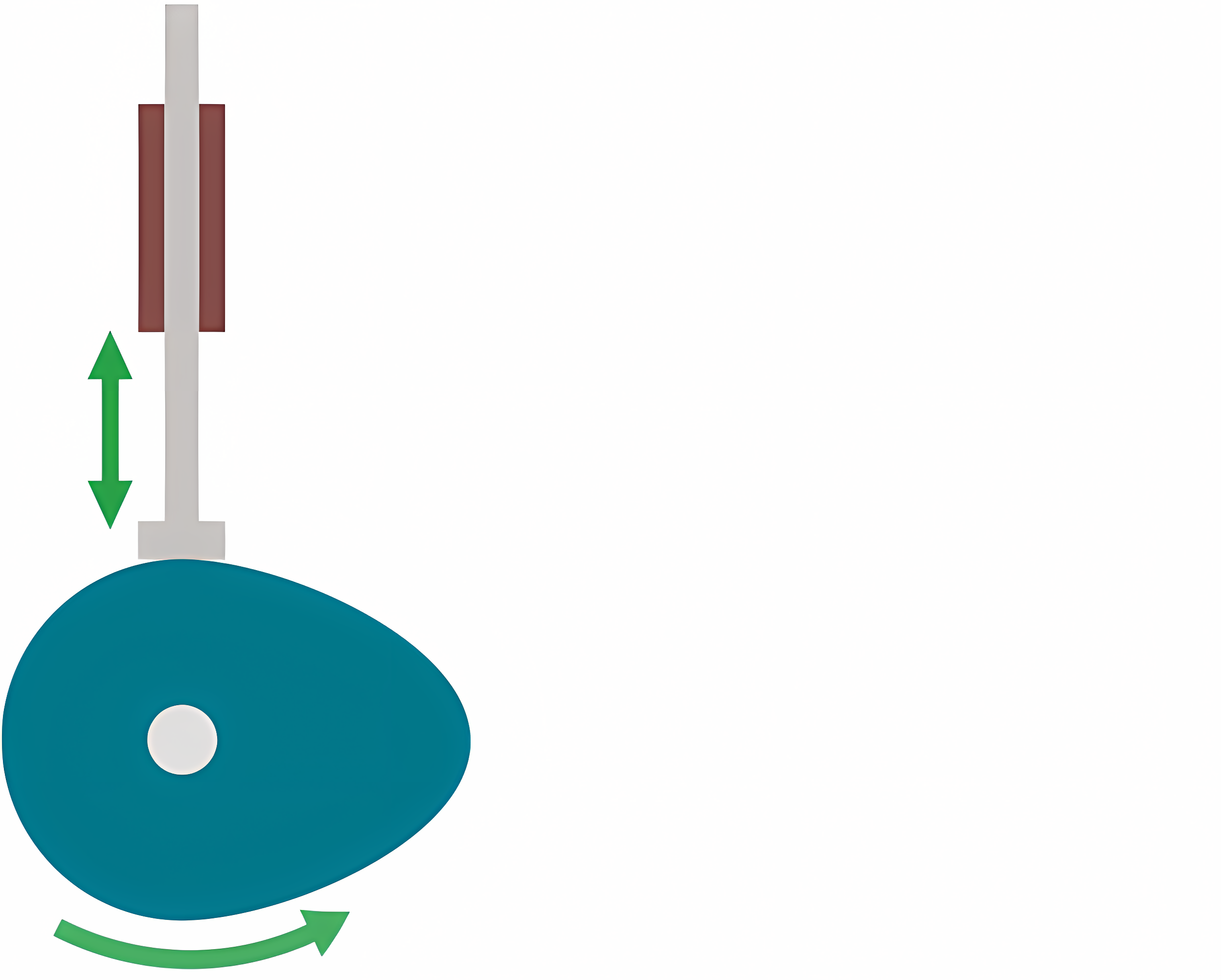
Flat (Follower)
Flat bottom that sits on the cam. Cope well under load, but aren’t very accurate, and have a lot of friction.
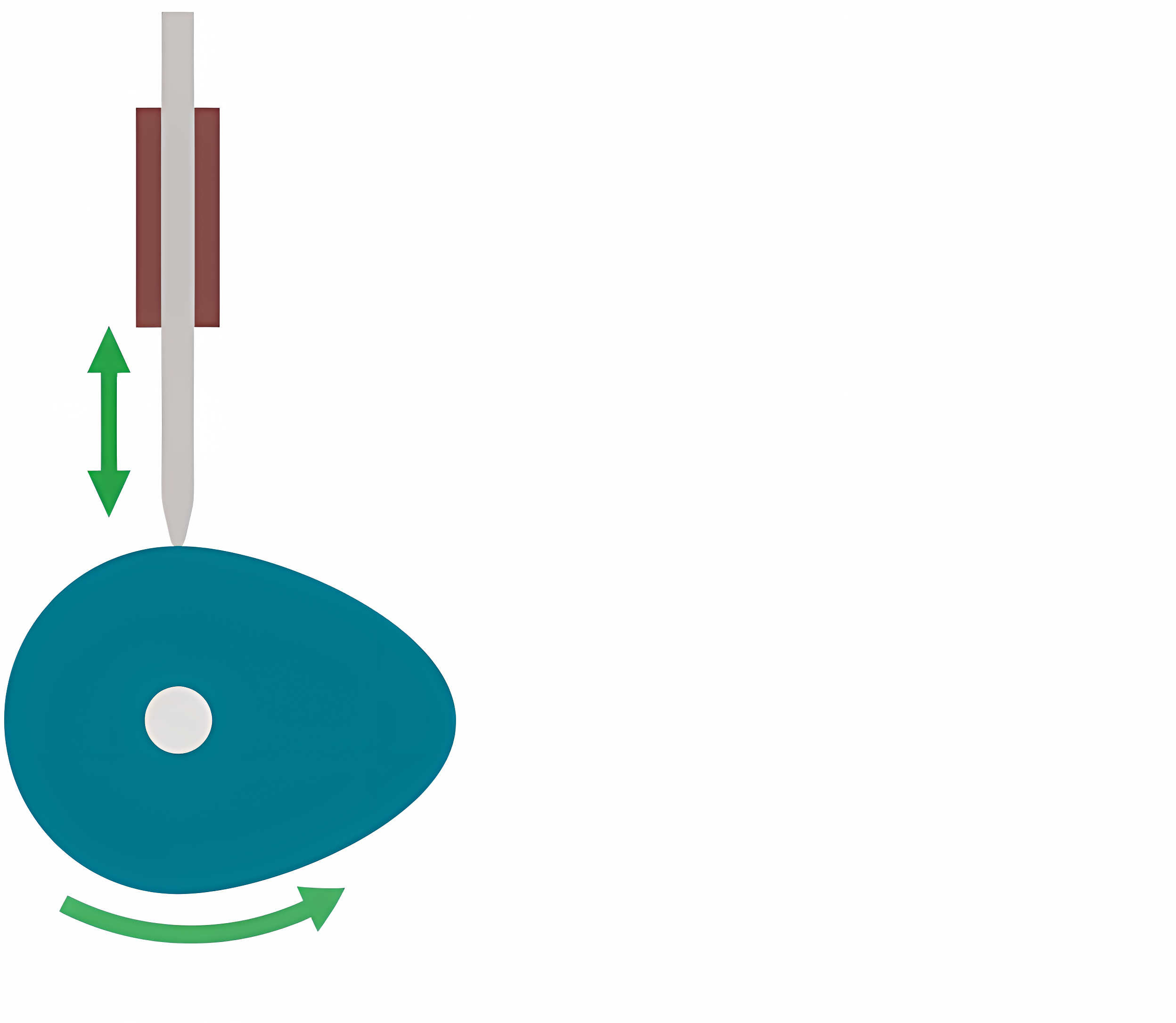
Point or knife (Follower)
Narrow point that sits on the cam. Very accurate and low friction but are quick to wear away the pointed edge.
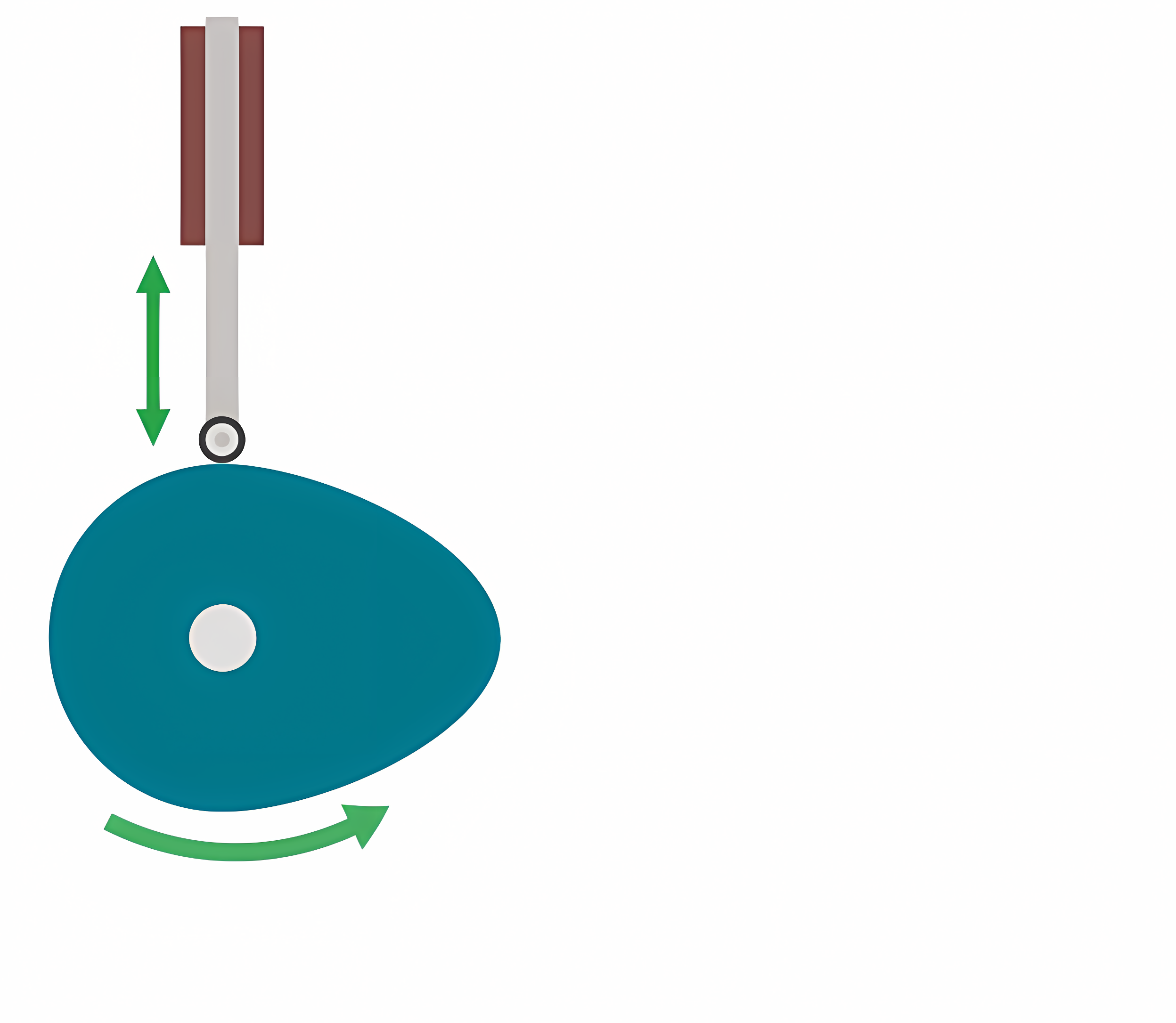
Roller (Follower)
Roller (E.g. ball bearing) attached to the bottom of the follower. Accurate, low friction and can withstand load, but are more costly to produce.
Gears
A wheel with teeth that can change the speed or direction in a mechanism.
Gear trains
2 or more gears are joined together. The drive gear causes the driven gear to turn in the opposite direction.
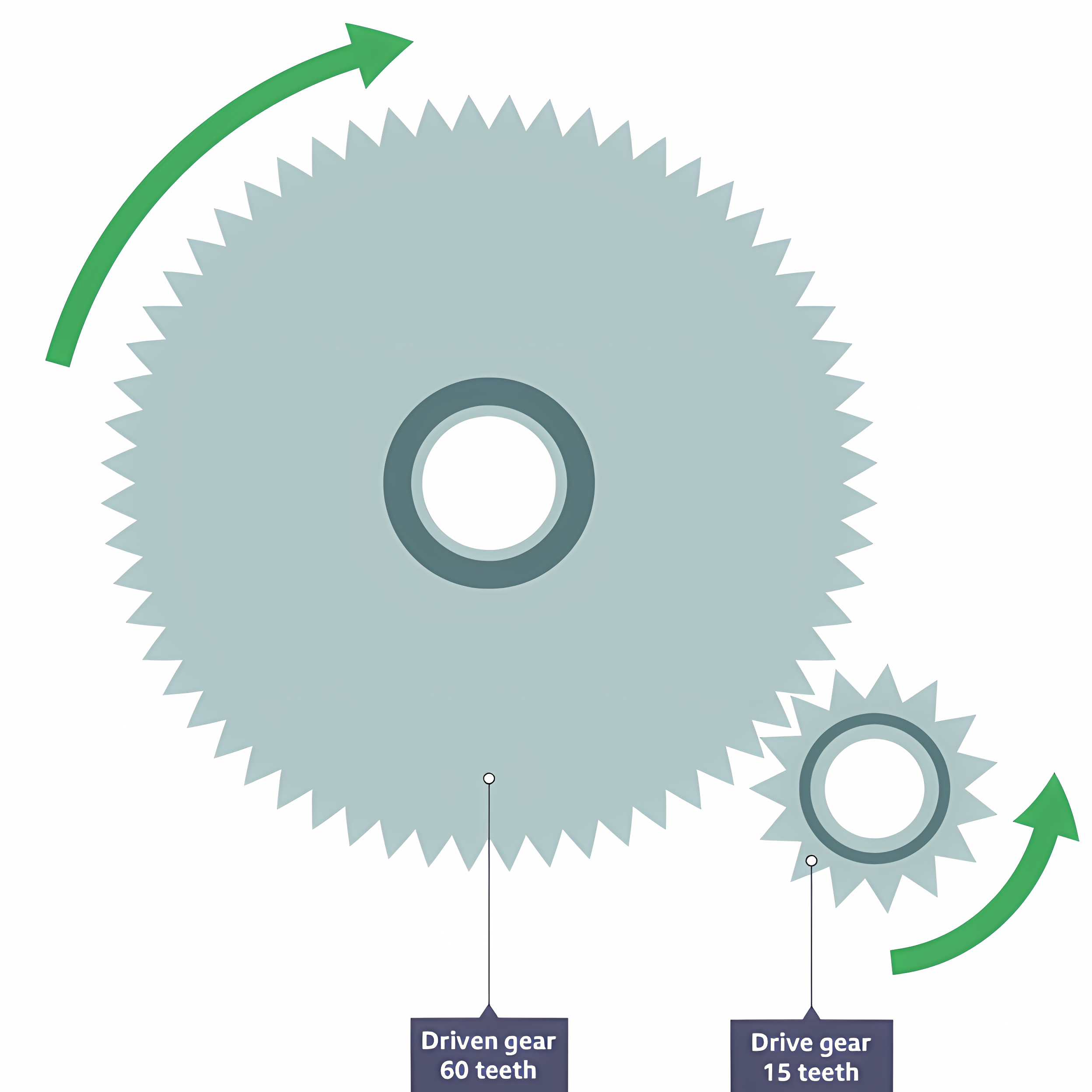
Gear Ratio
Driven (num of teeth) ÷ Driver (num of teeth)