Fitness and Measurement
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Measurement
an assessment or collection of information
Test
a tool used to make a particular measurement
Evaluation
an interpretation of a score. This requires a set standard.
Kinesmetrics
measurement and evaluation in kinesiology
Norm-Referenced Standards
how performance compares to others
SAT/percentile are examples of what standard?
Norm-referenced standards
Criterion-Referenced Standards
compares a performance relative to a criterion. Typically is pass/fail
Drivers test is an example of what standard?
Criterion-Referenced Standard
Formative Evaluation
an initial or intermediate evaluation. Used for tracking progress and short term goals.
Summative Evaluation
a final evaluation. Used for long term goals
Reliability
Consistency of measurement
Validity
truthfulness of measurement
Validity requires:
reliability and relevance
Selective Model
Testing is performed at the end of the unit of instruction. The purpose of the test is generally to produce grades. The test results are compared to a group of scores, hoping to identify individual differences. This is also called norm referenced.
Mastery-Based Model
Also called criterion referenced, because the individual score is evaluated in terms of a criterion measure. Those that surpass the criterion level of behavior are termed masters, and those that do not, non-masters. There is no concern about how students compare with each other.
Six general purposed for fitness and measurement
placement, diagnosis, prediction, motivation, achievement, program evaluation
Affective Domain of Human Performance
psychological or emotional attributes (krathwhol, bloom, masia)
Cognitive Domain of Human Performance
knowledge based information (Bloom)
Psychomotor Domain of Human Performance
movement, reflexive, basic motor, perceptual motor abilities, physical abilities, skilled movements (Harrow)
Domains of Human Performance are Hierarchical in nature
knowledge > comprehension > application > analysis > synthesis > evaluation
Descriptive Statistics
mathematical summaries of performance (the best score) and performance characteristics (central tendency)
Inferential Statistics
concerned with determining the properties within and between sets of numbers (populations) from information gathered on a smaller portion (sample) of the numbers. (infer from a sample to a population)
Continous variable
can have a virtually infinite number of possible values
Time, distance, and weight are example of what variable
Continuous variable
Discrete Variable
variable that has specific values and that cannot have values between these specific values
number of kids/number of points in a game are examples of what variable?
Discrete variable
Nominal Scale
Categorical data without a specific order.
Gender is an example of what scale?
Nominal Scale
Ordinal Scale
A scale of measurement using ranks rather than actual numbers.
Finishing in first place at a race is an example of what scale
ordinal scale
Scale or Continuous Scale
have a distinct place on a number line. can be interval or ratio.
Interval
zero is arbitrarily chose. (zero is just a number not the lowest you can go)
Temperature or IQ is an example of (interval/ratio)
interval
Ratio
has a true zero. Meaning the total absence of a quality.
The order of scales goes
(lowest) nominal < ordinal < interval < ration (highest)
Frequency Distribution
A method of organizing data that involves noting how often each of the various scores occur
Measurements of Central Tendency
Mean, Median, Mode
Mean
the most stable and reliable measure. Does not represent skewed data.
Median
the middle score in a distribution; works well for skewed data
Mode
the most unstable measure of central tendancy
Kurtosis
the peakedness of a curve
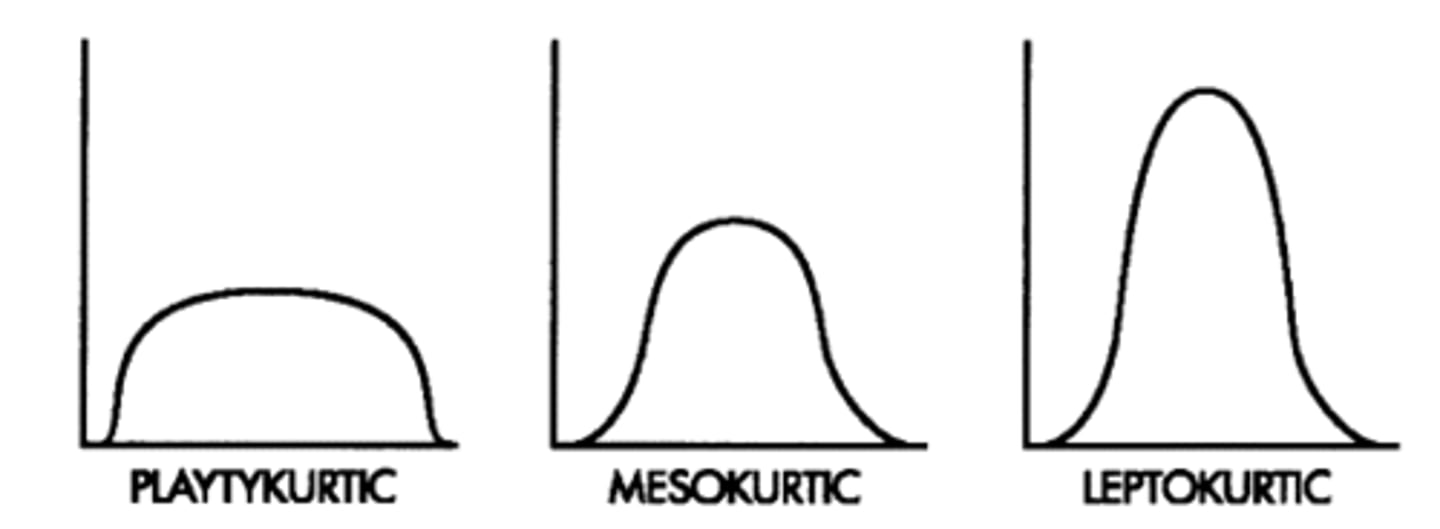
Mesokurtic
(meh) normal curve; average peak
Platykurtic
(plateau) flat curve; low peak
Leptokurtic
(leap) steep curve; high peak
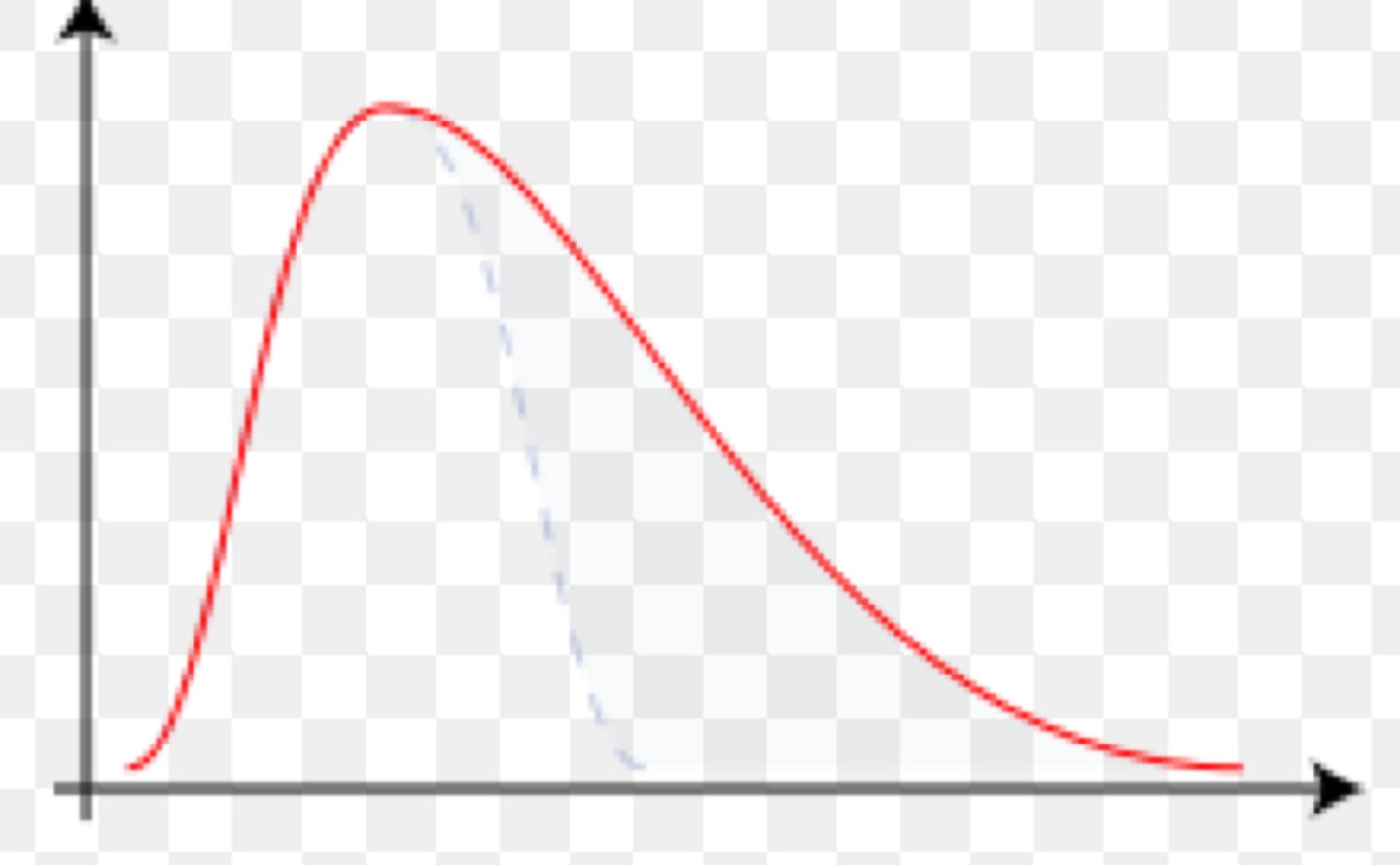
Negatively Skewed
-1 outliers to the left
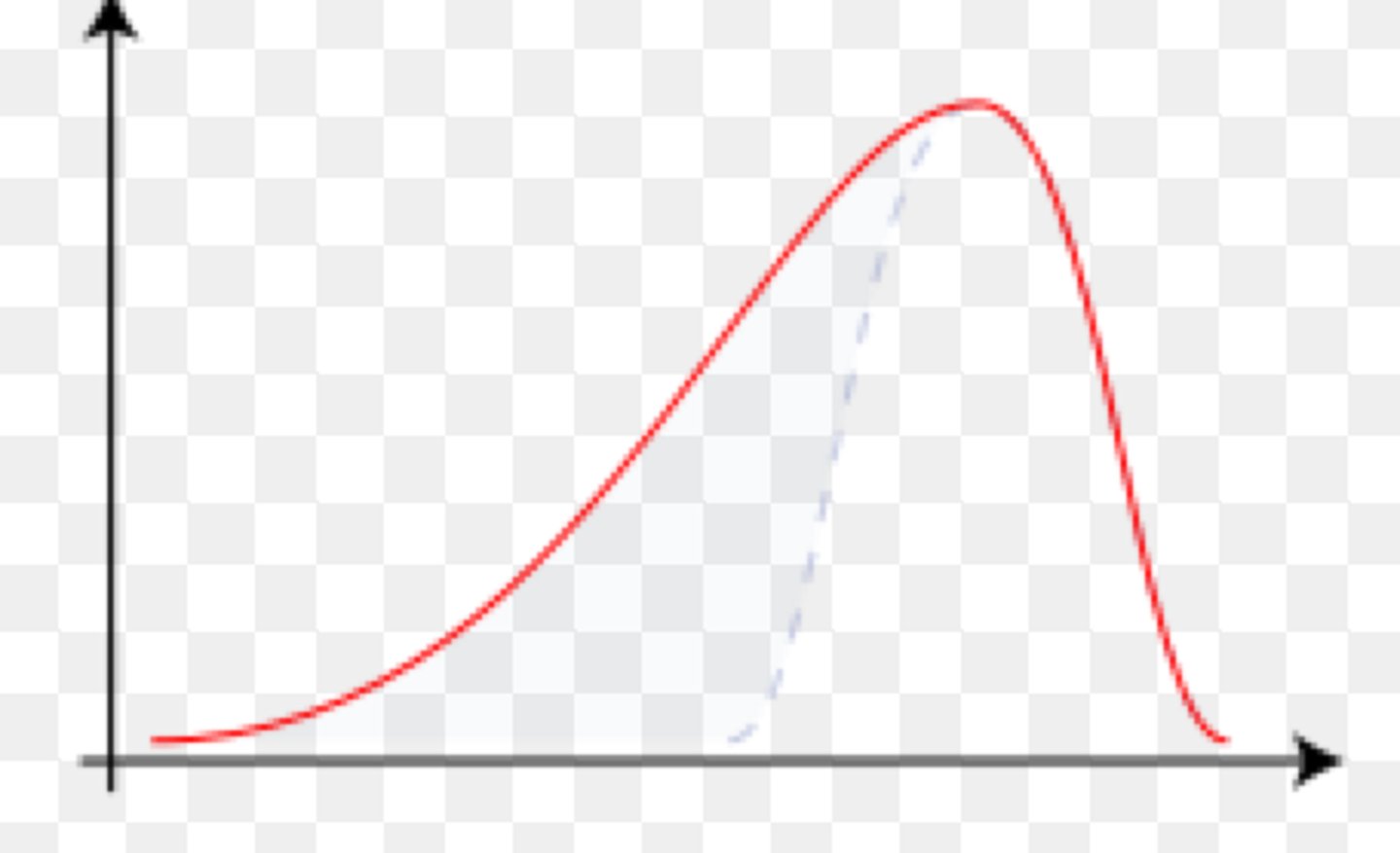
Positively Skewed
+1 outliers to the right
Measures of Variability
Range, Inter-percentile Range, Variance, standard deviation
Range
least stable measure of variability,
Inter percentile Range
Used with median; how the scores vary about the median.
Interquartile range
(X.75 - X.25) the most common
Variance
measure the spread of a set of scores based on the average of the squared deviation of each score from the mean. most stable measure of variability
Standard Deviation
square root of the variance. linear measure of variability
Standard scores
a set of observations that have been standardized around a given M (mean) and stdev.
Z-score
most fundament score; have a mean score of 0 and a stdev of 1 (X - M) / S ---- (score-mean)/stdev
T-score
has a mean of 50 and Stdev of 10; T = 50 + 10(X - M) / S
Correlation Coefficient (r)
-1 to +1 ; zero indicates no relationship
Correlation Coefficient (does/doesn't) indicate cause-and-effect relationship?
does not
Alpha level
0.05 ; the chance of results happening only by random chance
Type 1 Error
Rejecting null hypothesis when it is true (significant when its not)
Type 2 Error
Accepting null hypothesis when you should have rejected it (not signifiant when it is)
Chi-Square
examines differences in nominal data
Independent t-test
examines differences in a continuous variable between two independent groups (differences between girls and boys)
Dependent t-test
examines differences in two related groups on a continuous variable (pre and post measurement)
One-way ANOVA (f value)
examines differences in two related groups on a continuous variable
Two-way ANOVA test
examines one dependent value with two or more independent values
Post-Hoc test
performed if the one-way ANOVA results are significant. (use SCHEFFE)
Still learning (8)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!