ASCP: Urinalysis and Body Fluids Polansky Cards
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
2-hr postprandial urine collection is used to monitor what?
Diabetes mellitus monitoring
Needle inserted through abdomen into bladder
Suprapubic aspiration
The normal daily volume of urine produced is
600-2,000 mL (average 1,200-1,500mL)
Term: ↑ urine production
Diuresis
Term: Marked ↑ in urine flow
Polyuria
Polyuria:
Adult: >------ mL/day
Children: ------mL/kg/day
Adult: >2,500 mL/day
Children: 2.5-3 mL/kg/day
Term: Marked ↓ in urine flow
Oliguria
Oliguria:
Adult: <---- mL/day
Children: <----mL/kg/hr
Infants: <---mL/kg/hr
Adult: <400 mL/day
Children: <0.5 mL/kg/hr
Infants: <1 mL/kg/hr
Term: No urine production
Anuria
The color of urine: Normal
Yellow due to urochrome
The color of urine Dilute urine
Colorless, pale yellow
The color of urine Concentrated urine
Dark yellow, amber
The color of urine Bilirubin Amber
orange, yellow-green; yellow foam on shaking
The color of urine Urobilin Amber
orange; no yellow foam on shaking
The color of urine Homogentisic acid
Normal on voiding; brown or black on standing
The color of urine Melanin
Brown or black on standing
The color of urine Methemoglobin
Brown or black
The color of urine Myoglobin Red
brown on standing
The color of urine Blood/hemoglobin
Pink or red when fresh; brown on standing
The color of urine Porphyrin
Port-wine
The color of urine Drugs: medications: food
Green, blue, red, orange
The color of urine Pseudomonas infection
Green, blue-green
Changes in Unpreserved Urine at Room Temperature >2 hr: Turbidity
↑ Multiplication of bacteria, precipitation of amorphous crystals
Changes in Unpreserved Urine at Room Temperature >2 hr: pH
↑ Conversion of urea to ammonia by bacteria
Changes in Unpreserved Urine at Room Temperature >2 hr: Glucose
↓ Metabolism by bacteria
Changes in Unpreserved Urine at Room Temperature >2 hr: Ketones
↓ Volatilization of acetone, breakdown of acetoacetate by bacteria
Changes in Unpreserved Urine at Room Temperature >2 hr: Bilirubin
↓ Oxidation to biliverdin
Changes in Unpreserved Urine at Room Temperature >2 hr: Urobilinogen
↓ Oxidation to urobilin
Changes in Unpreserved Urine at Room Temperature >2 hr: WBCs/RBCs casts
↓ Lysis in dilute or alkaline urine
Normal pH of Urine
Random: 4.5-8.0
First Void: 5-6
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Principle: Double indicator system
pH
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Principle: Protein error of indicator
Protein
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Principle: Glucose oxidase/ peroxidase
Glucose
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Principle: Sodium nitroprusside rxn
Ketones
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Principle: Pseudoperoxidase activity of hgb
Blood
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Principle: Diazo reaction
Bilirubin
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Principle: Ehrlich's aldehyde rxn or diazo rxn
Urobilinogen
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Principle: Greiss reaction
Nitrite
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Principle: Leukocyte esterase rxn
Leukocyte esterase
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Principle: pKa change of polyelectrolyte
Specific gravity (SG)
improperly preserved specimen pH
pH 9
Most sensitive to acetoacetic acid.
Less sensitive to acetone. Doesn't
react with beta-hydroxybutyric acid.
Ketones
Urine:
Uniform color = ------
Speckled = -----
Uniform color = hgb or myoglobin.
Speckled = RBCs.
Normal renal threshold of glucose = ------ mg/dL
Normal renal threshold of glucose =
160-180 mg/dL.
POSSIBLE EFFECT: Urine Failure to mix specimen well
False-neg leukocyte, blood
Comments: WBCs, RBCs settle out.
Specific Sources of Error with Reagent Strip Testing:
pH
INCREASED OR FALSE POSITIVE:
Improperly preserved specimen
DECREASED OR FALSE NEGATIVE
acid runover from protein square
Specific Sources of Error with Reagent Strip Testing:
Protein
INCREASED OR FALSE POSITIVE:
Highly buffered alkaline urine, prolonged
dipping, contaminated container, ↑SG
DECREASED OR FALSE NEGATIVE:
Proteins other than albumin
Specific Sources of Error with Reagent Strip Testing:
Glucose
INCREASED OR FALSE POSITIVE:
Contamination with peroxide or bleach
DECREASED OR FALSE NEGATIVE:
Unpreserved specimen, ↑ascorbic acid, ↑SG, ↓temp.
Specific Sources of Error with Reagent Strip Testing:
Ketones
INCREASED OR FALSE POSITIVE:
Red pigments, dyes, some meds
DECREASED OR FALSE NEGATIVE:
Improper storage. Acetone is volatile.
Bacteria break down acetoacetic acid.
Specific Sources of Error with Reagent Strip Testing:
Blood
INCREASED OR FALSE POSITIVE:
Menstruation, oxidizing agents, bacterial
peroxidase
DECREASED OR FALSE NEGATIVE:
↑ascorbic acid, ↑nitrite, ↑SG (crenated RBCs), unmixed specimen.
Specific Sources of Error with Reagent Strip Testing:
Bilirubin
INCREASED OR FALSE POSITIVE:
Highly pigmented urine
DECREASED OR FALSE NEGATIVE:
Exposure to light, ↑ascorbic acid, ↑nitrite
Specific Sources of Error with Reagent Strip Testing:
Urobilinogen
INCREASED OR FALSE POSITIVE:
Highly pigmented urine
DECREASED OR FALSE NEGATIVE:
Improperly preserved specimen (oxidation to urobilin), formalin.
Specific Sources of Error with Reagent Strip Testing:
Nitrite
INCREASED OR FALSE POSITIVE:
Highly pigmented urine, improperly
preserved specimen (contaminating
bacteria produce nitrites)
DECREASED OR FALSE NEGATIVE:
Non-nitrate-reducing bacteria, inadequate time in bladder, reduction of nitrites to N2, ↓dietary nitrate, antibiotics, ↑ascorbic acid, ↑SG
Specific Sources of Error with Reagent Strip Testing:
Leukocyte esterase
INCREASED OR FALSE POSITIVE:
Highly pigmented urine, oxidizing agents, formalin, nitrofurantoin, vaginal discharge
DECREASED OR FALSE NEGATIVE:
↑glucose, ↑protein, ↑ascorbic acid, ↑SG; antibiotics; reading too soon
Specific Sources of Error with Reagent Strip Testing:
Specific gravity
INCREASED OR FALSE POSITIVE:
↑ protein
DECREASED OR FALSE NEGATIVE:
Alkaline urine. (Add 0.005 if pH is 6.5 or higher. Correction is made by automated readers.)
What test detect: Albumin in low concentration
Test: Microalbumin
What test detect: All proteins, including
Bence Jones proteins
Test: Sulfosalicylic acid (SSA)
What test detect: Reducing substances
Test: Clinitest
What test detect: Ketones
Test: Acetest
What test detect: Ictotest
Test: Bilirubin
Urine test method detects/Test what: Immunoassay on 24-hr urine or albumin-tocreatinine ratio (ACR) on random sample
Detects: Microalbumin
Urine test method detects/Test what: Acid precipitation
Detects: SSA
Urine test method detects/Test what: Copper reduction
Detects: Clinitest
Urine test method detects/Test what: Sodium nitroprusside reaction
Detects: Ketones & Acetest
Urine test method detects/Test what: Diazo reaction
Detects: Bilirubin & Ictotest
Acute glomerulonephritis is associated with what type of urine output?
Oliguria is associated with acute glomerulonephritis
Tamm-Horsfall protein is produced in the what?
Renal Tubules
Maltese crosses in the urine should make you think of what diagnosis?
Nephrotic Syndrome
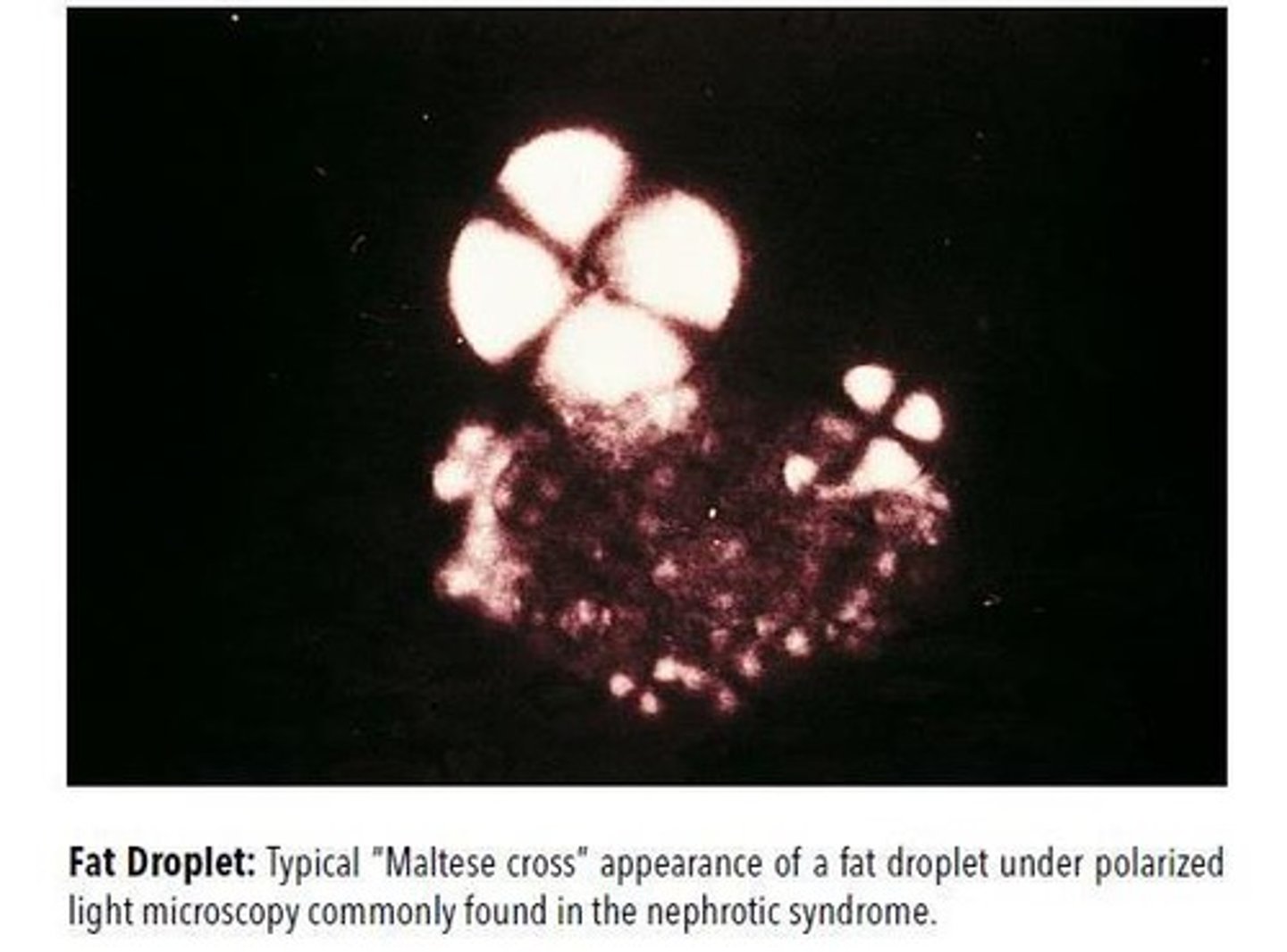
Maltese cross as a contamination is what type of crystal?
Starch Crystals
Epithelial Cells in the Urine Sediment: Origin
Lower urethra, vagina
Squamous Epithelial Cells
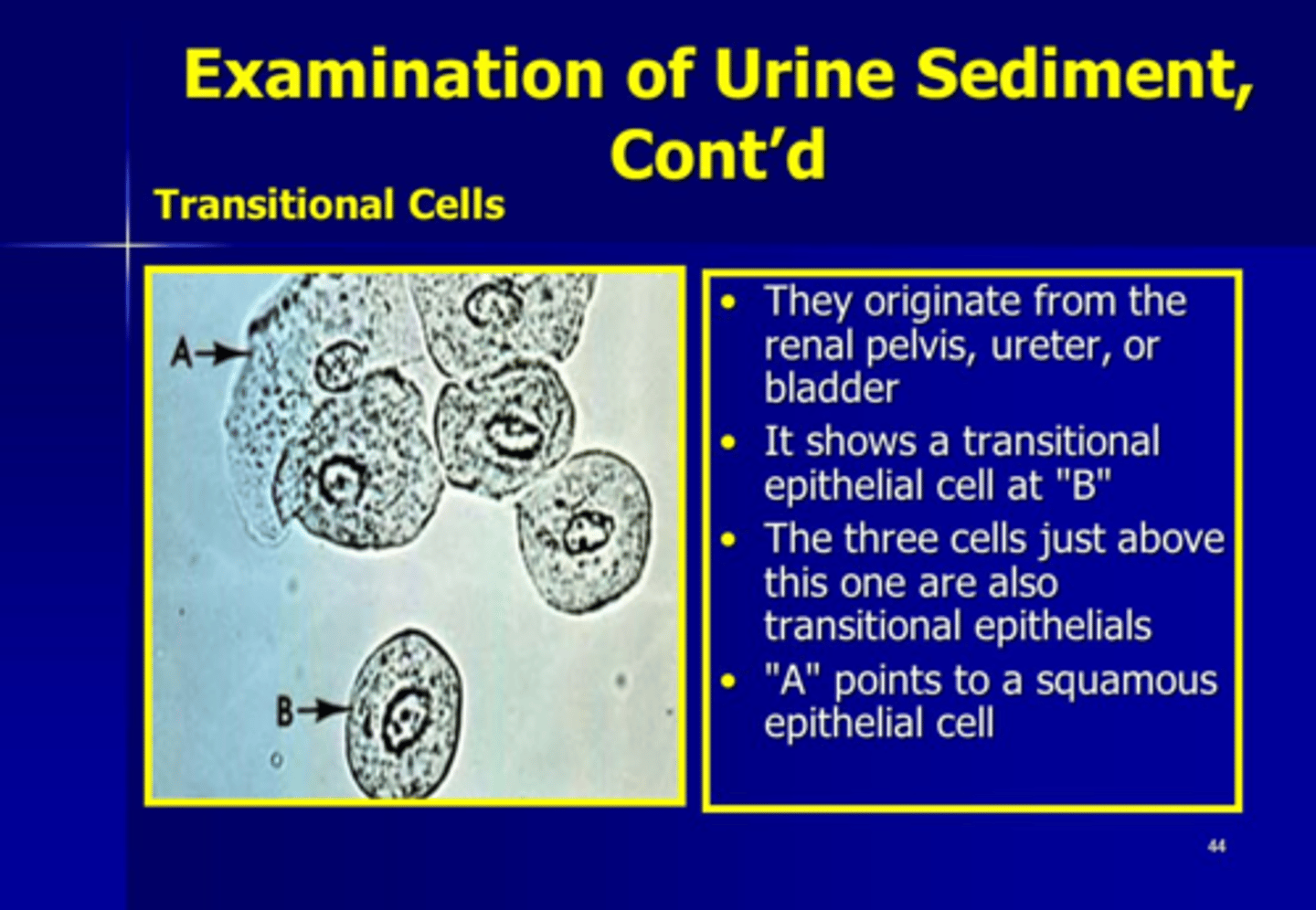
Epithelial Cells in the Urine Sediment: Origin
Renal pelvis, ureters, bladder, upper urethra
Transitional Epithelial Cells
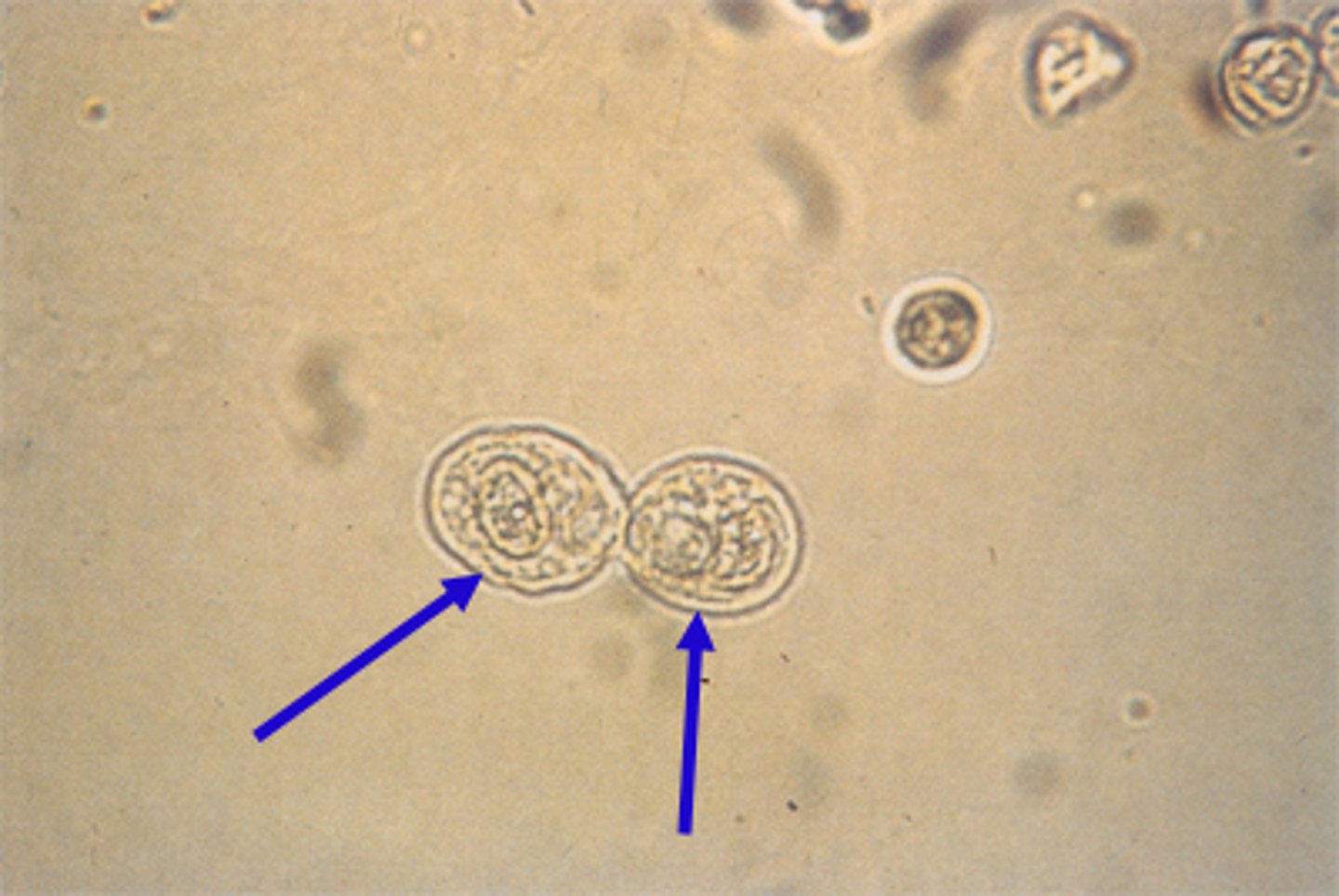
Epithelial Cells in the Urine Sediment: Origin
Renal tubular epithelial cell
Renal Tubules
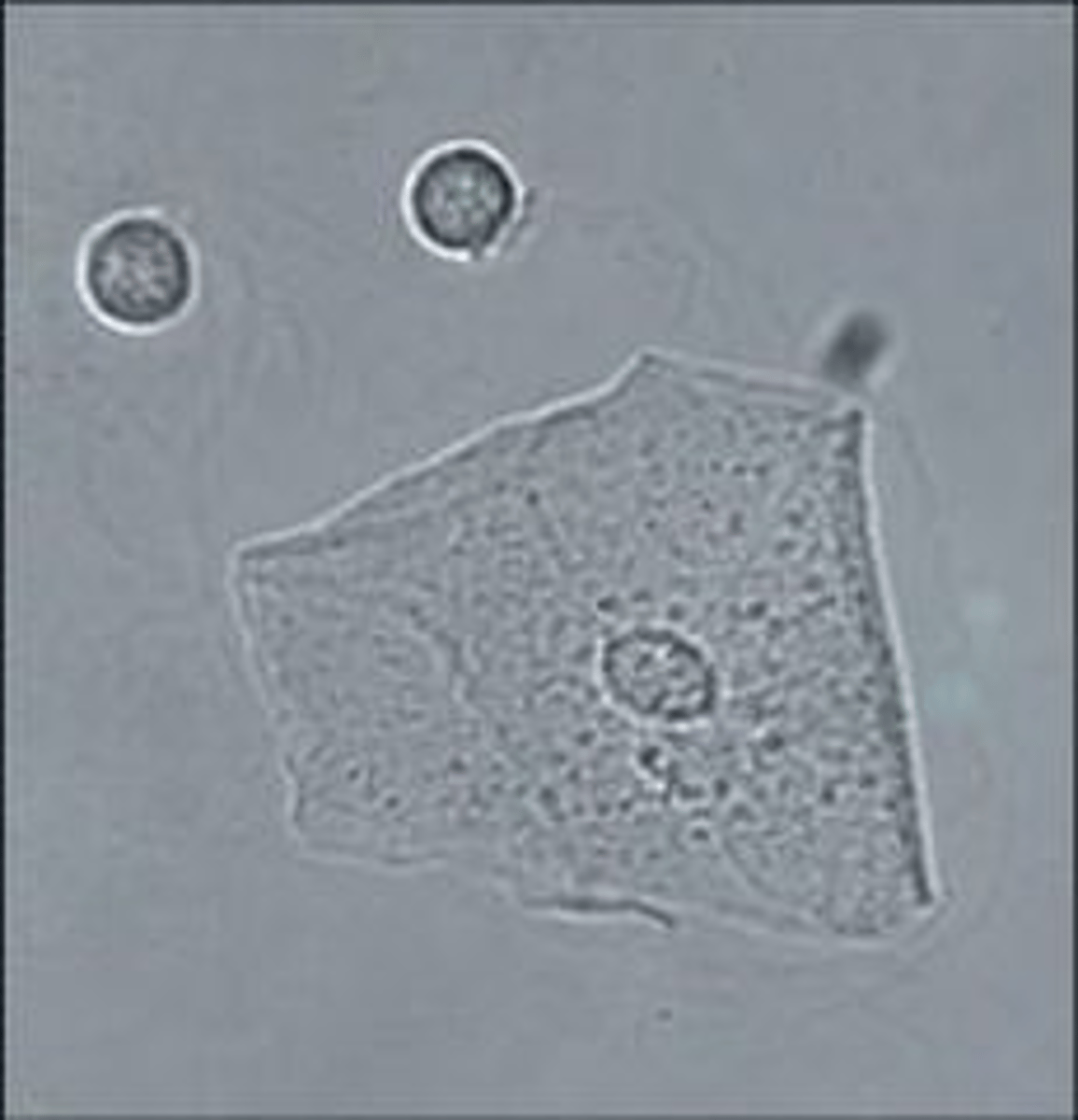
Epithelial Cells in the Urine Sediment: Origin
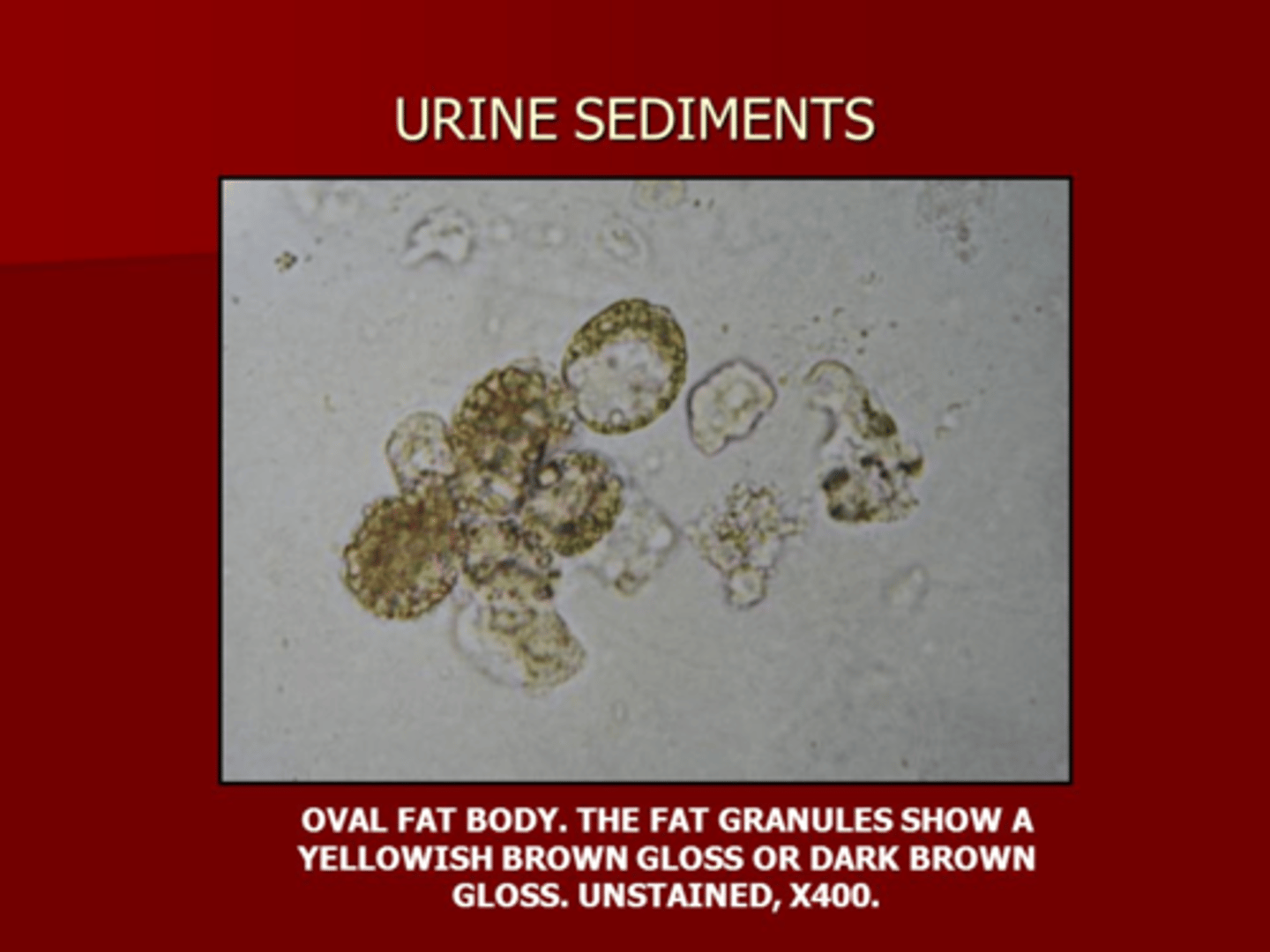
Oval fat body
Renal Tubules
-Maltese Cross with polarized light
What is seen in the urine:
Tubular necrosis, toxins, viral infections, renal rejection
Renal Tubular epithelial cells and Oval fat bodies
What blood cell in the urine is seen with Cystitis, pyelonephritis, tumors, renal calculi.
WBC and Glitter Cells
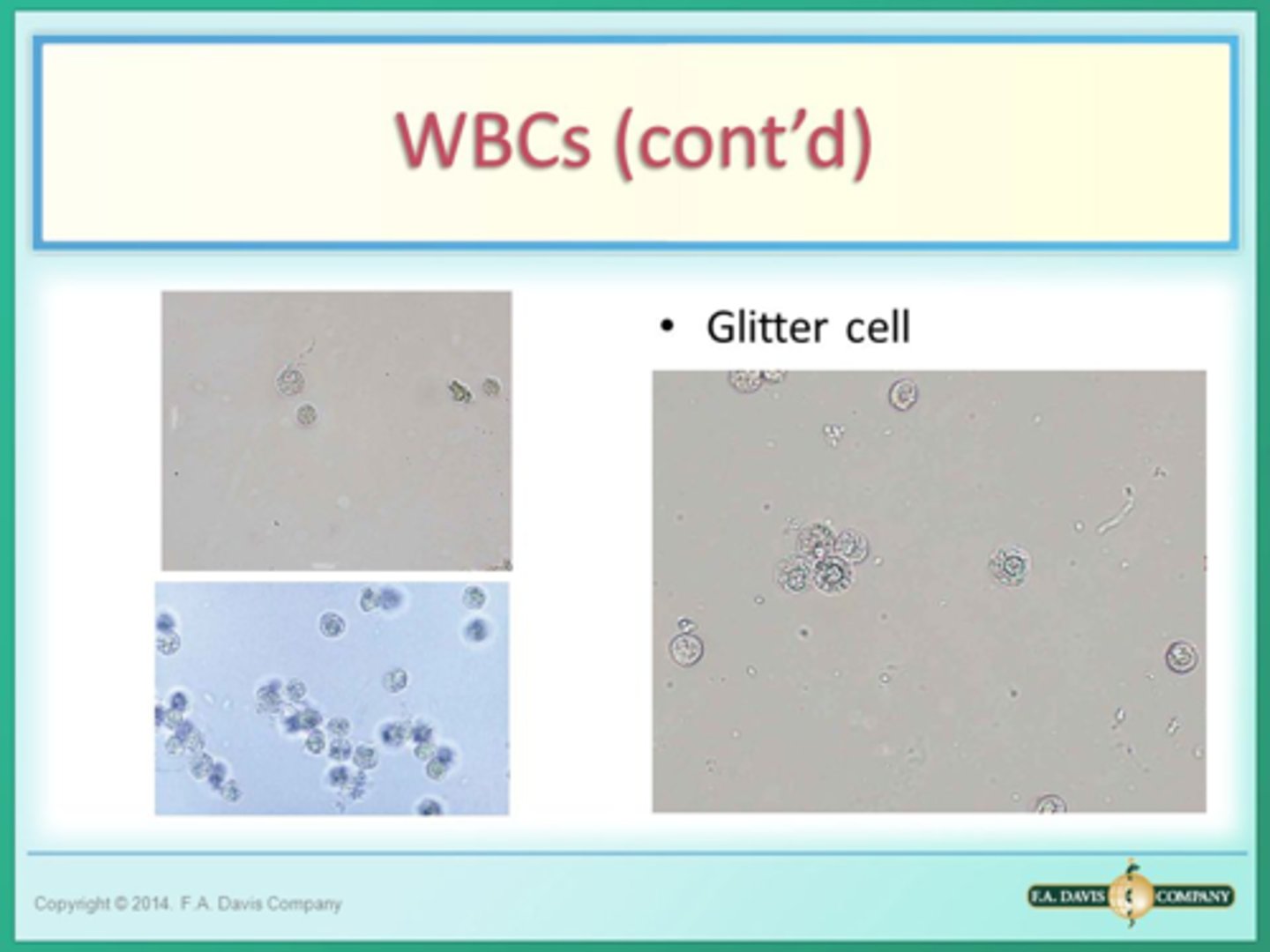
Glitter cells are seen in ----- solution and ----- urine
Glitter cells are seen in hypotonic solutions and alkaline urine
Irregular Granules:
Form pink precipitate in bottom of tube. May
obscure significant sediment. Dissolve by
warming to 60ºC.
Amorphous Urates
Normal Crystals Found in Acid or Neutral Urine:
1.
2.
3.
Normal Crystals Found in Acid or Neutral Urine:
1. Amorphous Urates
2. Uric Acid Crystals
3. Calcium Oxalate
Normal crystals found in alkaline urine include:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Normal crystals found in alkaline urine include:
1. Amorphous Phosphates
2. Triple Phosphates
3. Ammonium Biurate
4. Calcium Phosphates
5. Calcium Carbonate
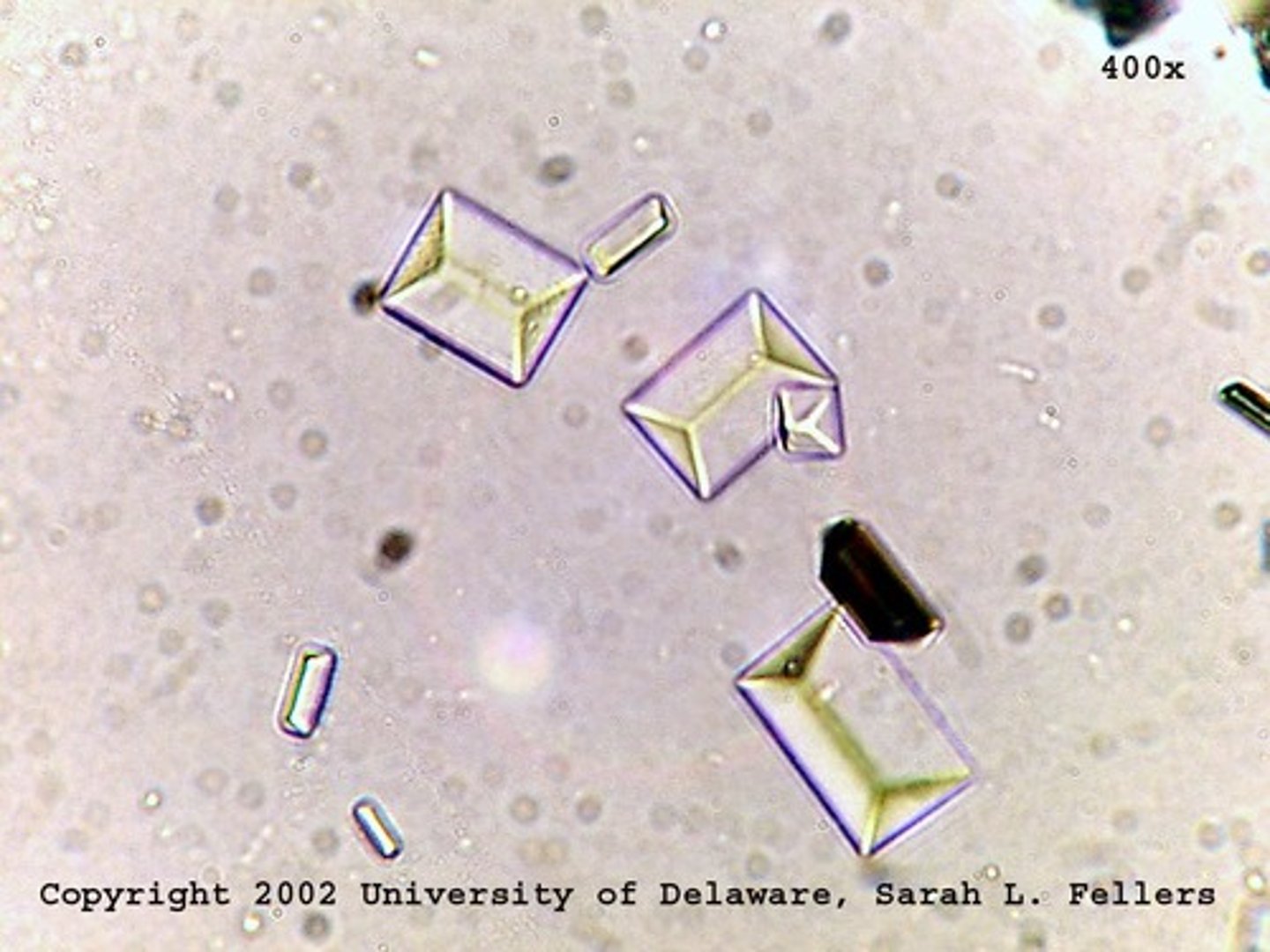
"Coffin-lid" crystal
Triple Phosphate
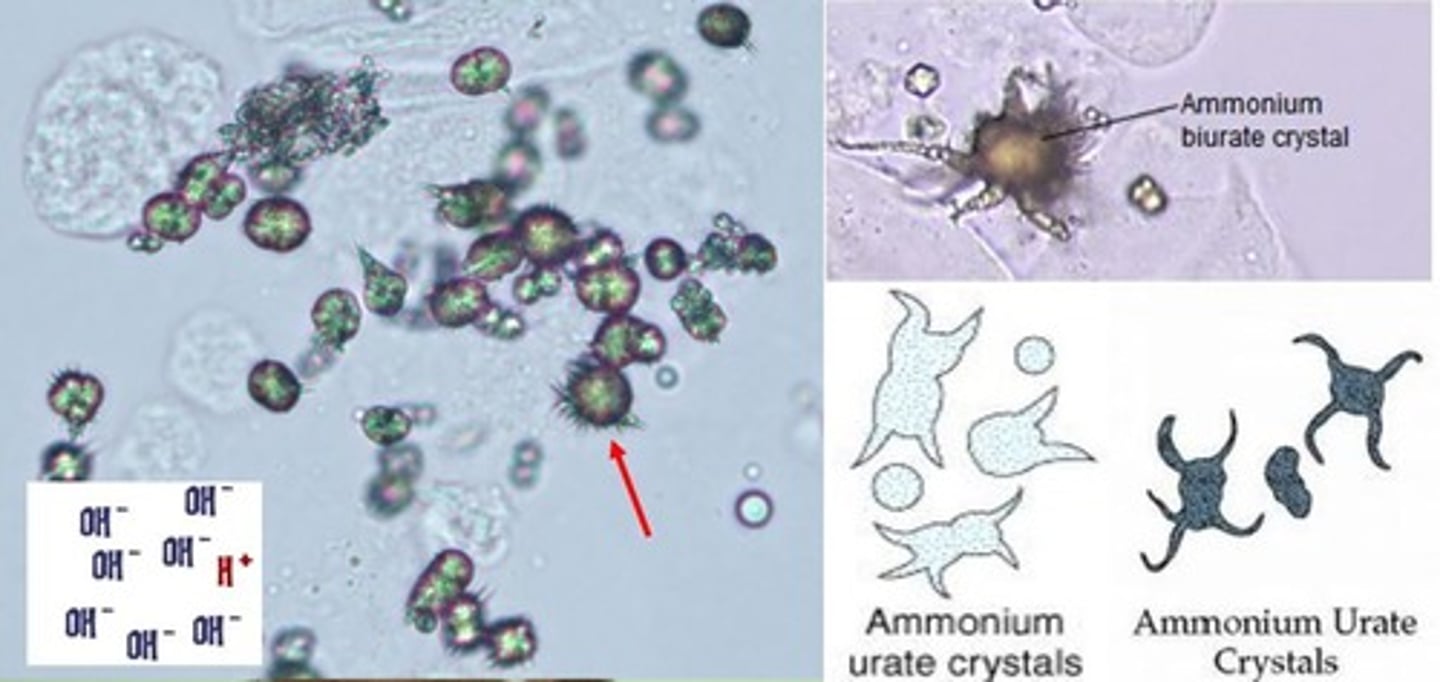
Yellow-brown "thorn apples" & spheres
Ammonium biurate
-Seen in old specimen
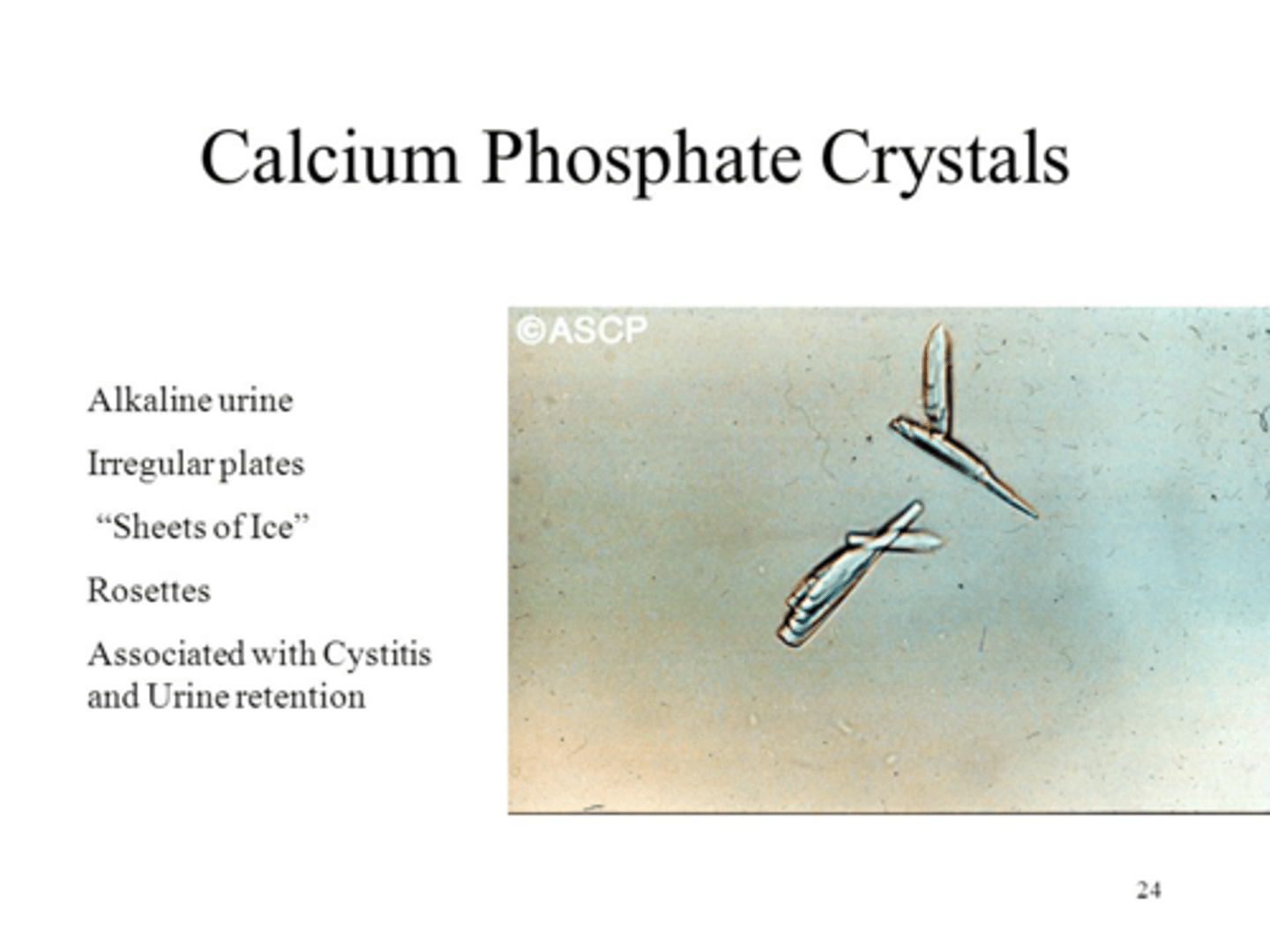
Needles, rosettes, "pointing finger"
Calcium Phosphate
-Only form seen in alkaline urine-
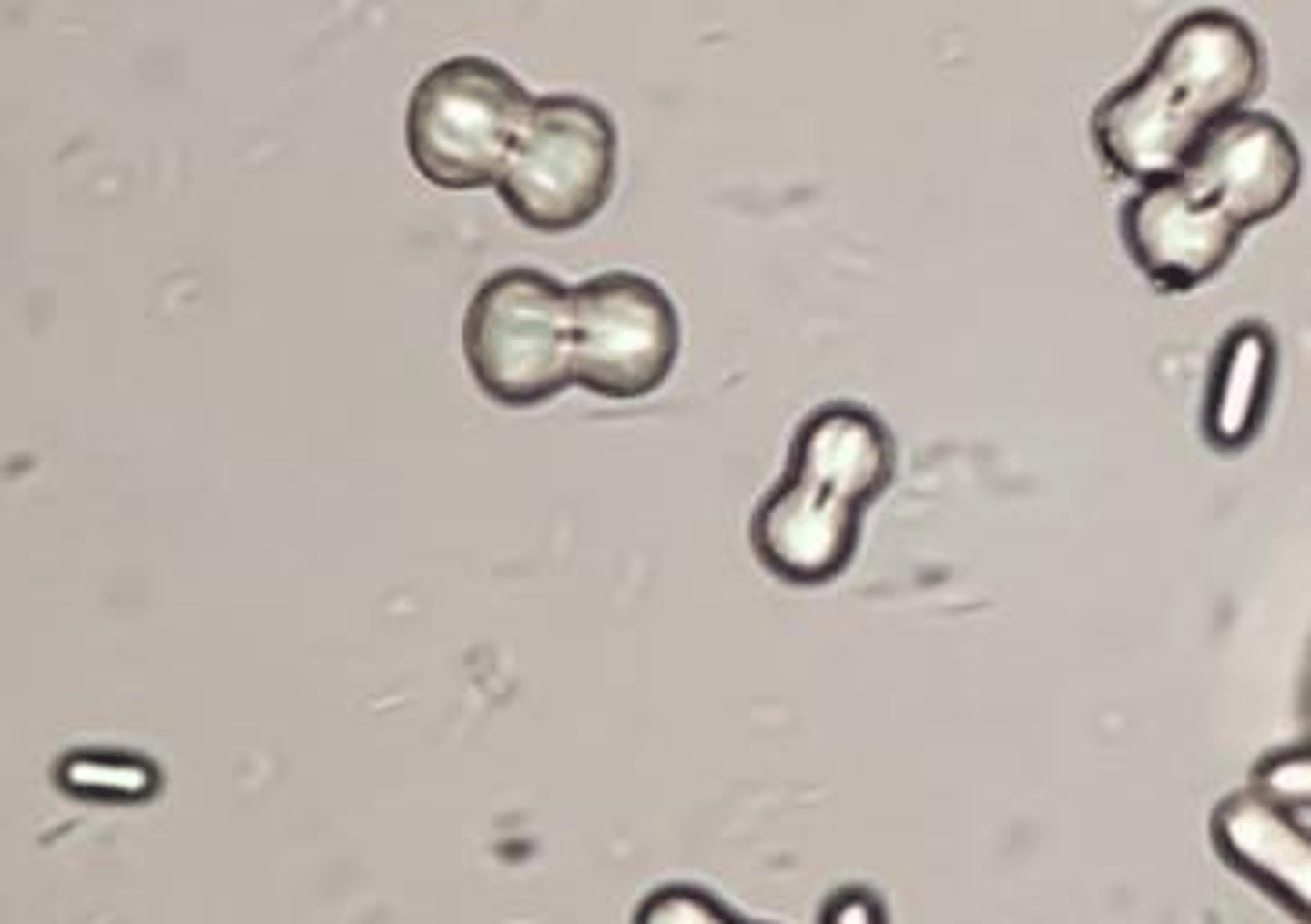
Colorless dumbbells or aggregates
Calcium Carbonate
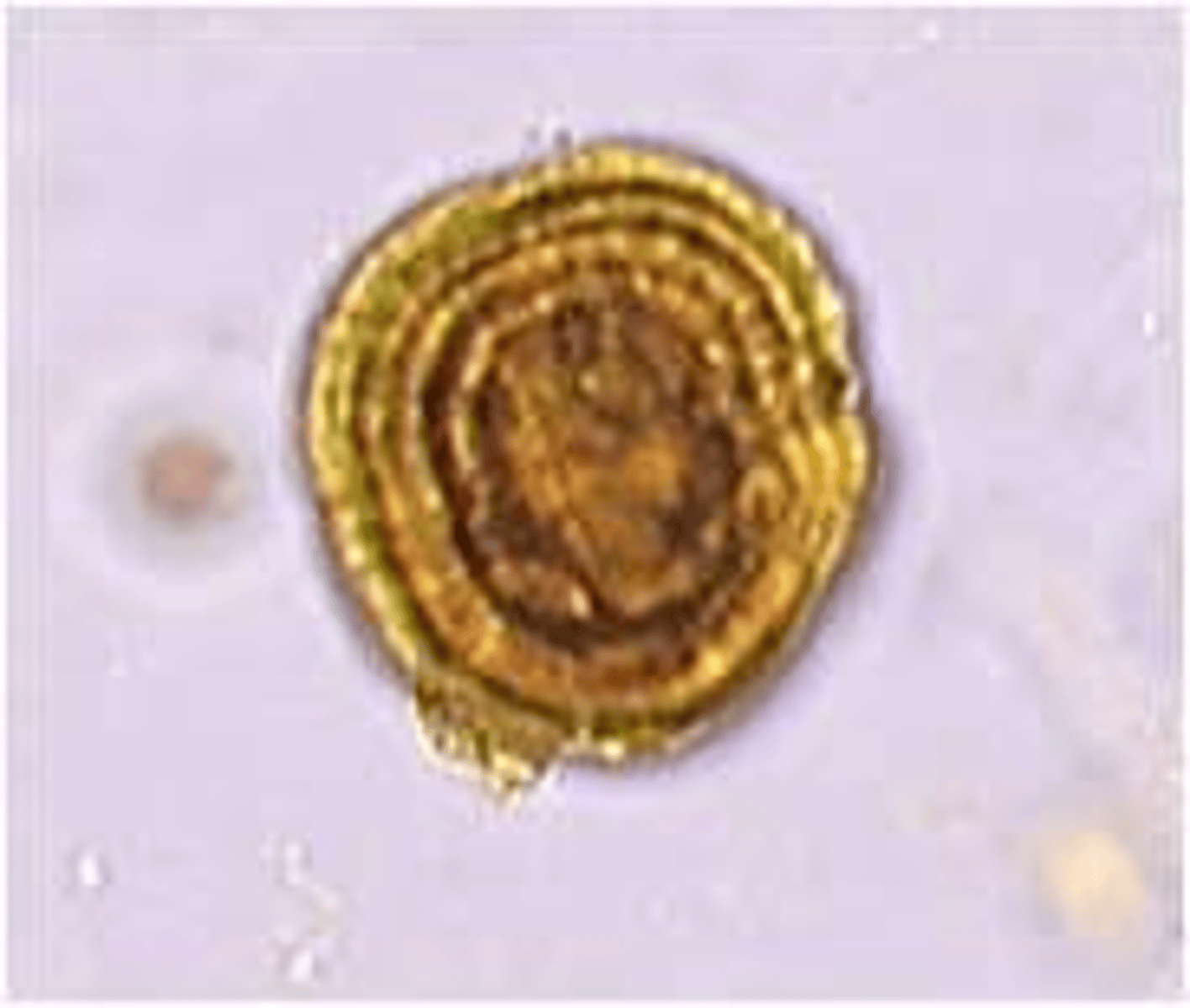
Abnormal Crystal: Seen in severe liver disease
Yellow, oily-looking spheres. Radial & concentric striations.
Leucine Crystals
-Often seen with tyrosine
Abnormal Crystal: Severe Liver Disease
Fine yellow needles in sheaves or rosettes.
Tyrosine Crystals
-Often seen with leucine
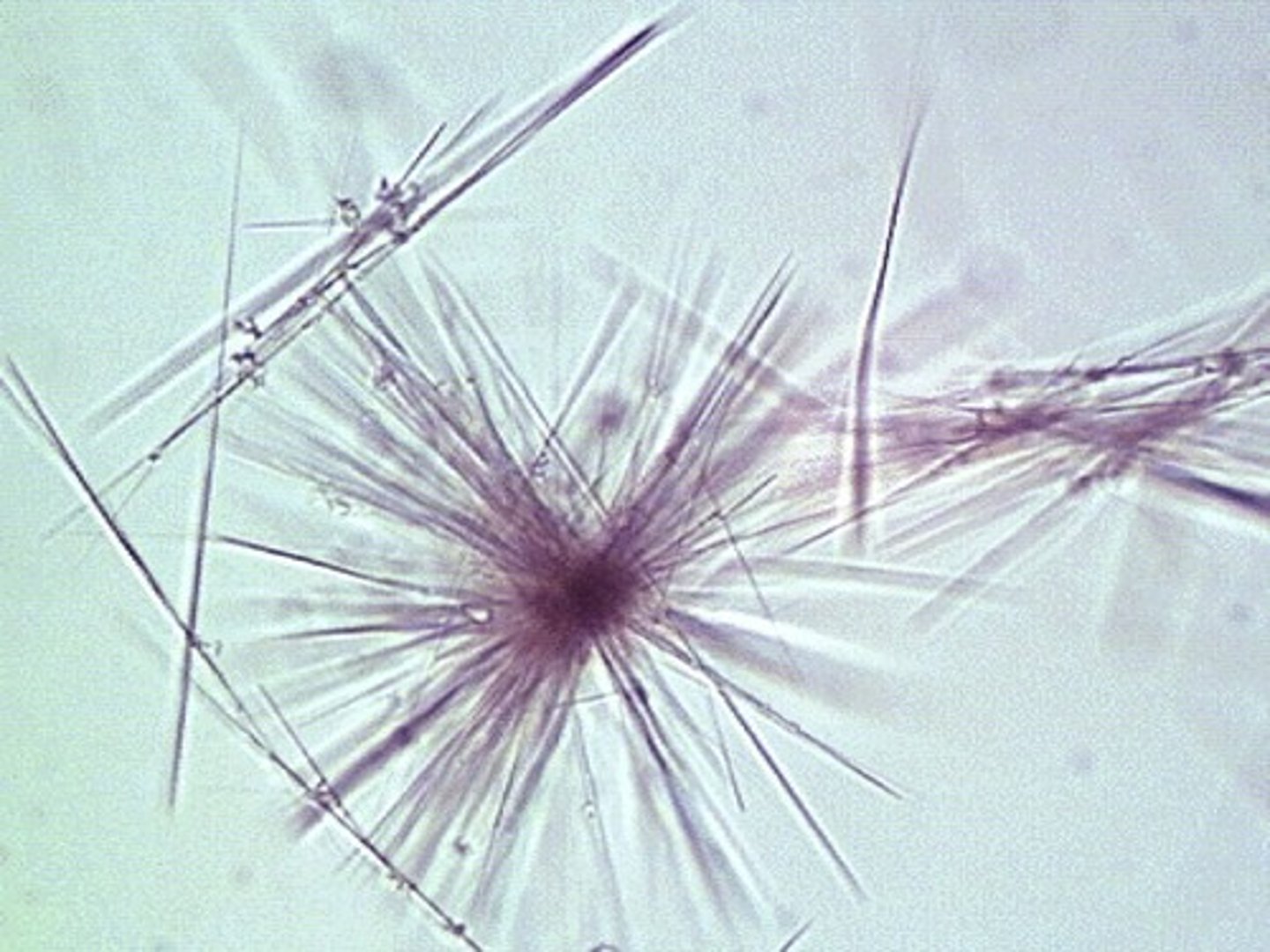
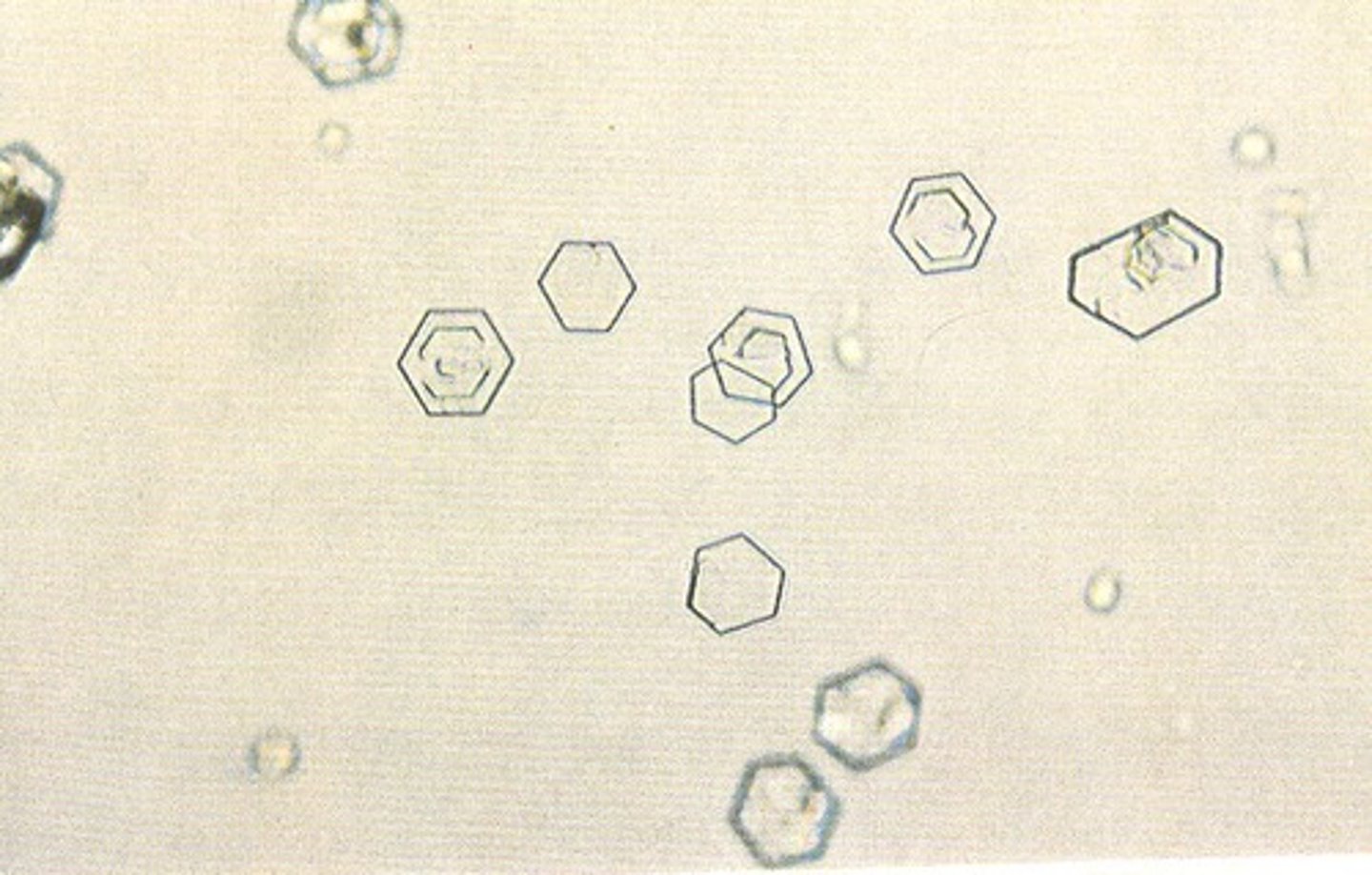
Abnormal Crystal: Cystinuria
Hexagonal (6-sided)
Cystine Crystals
-Must differentiate from uric acid. Doesn't polarize light. Confirm by cyanide-nitroprusside test
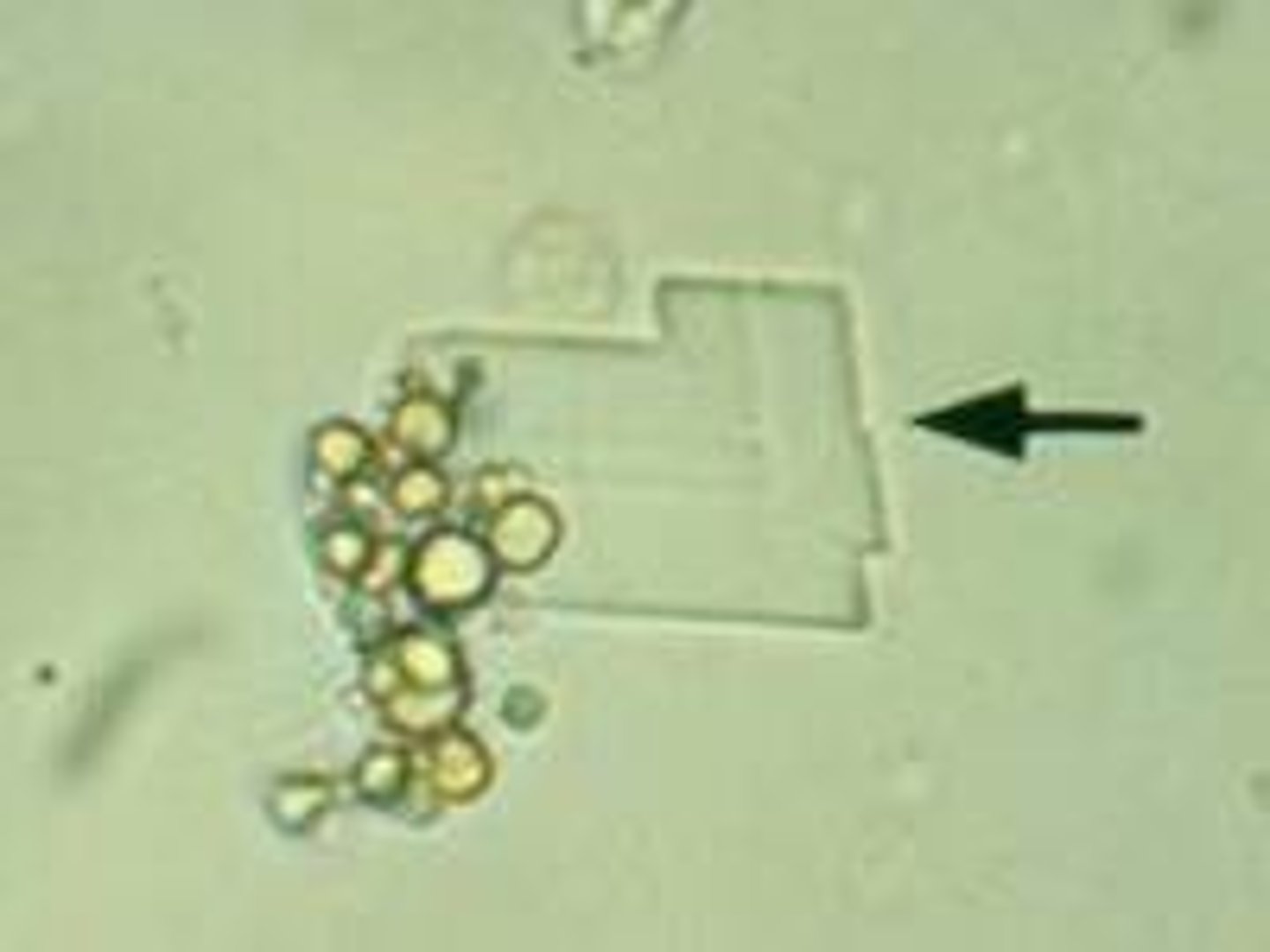
Abnormal Crystals: Nephrotic syndrome
-Flat plates. Notched out corners. "Stair-steps"
Cholesterol Crystals
-Birefringent
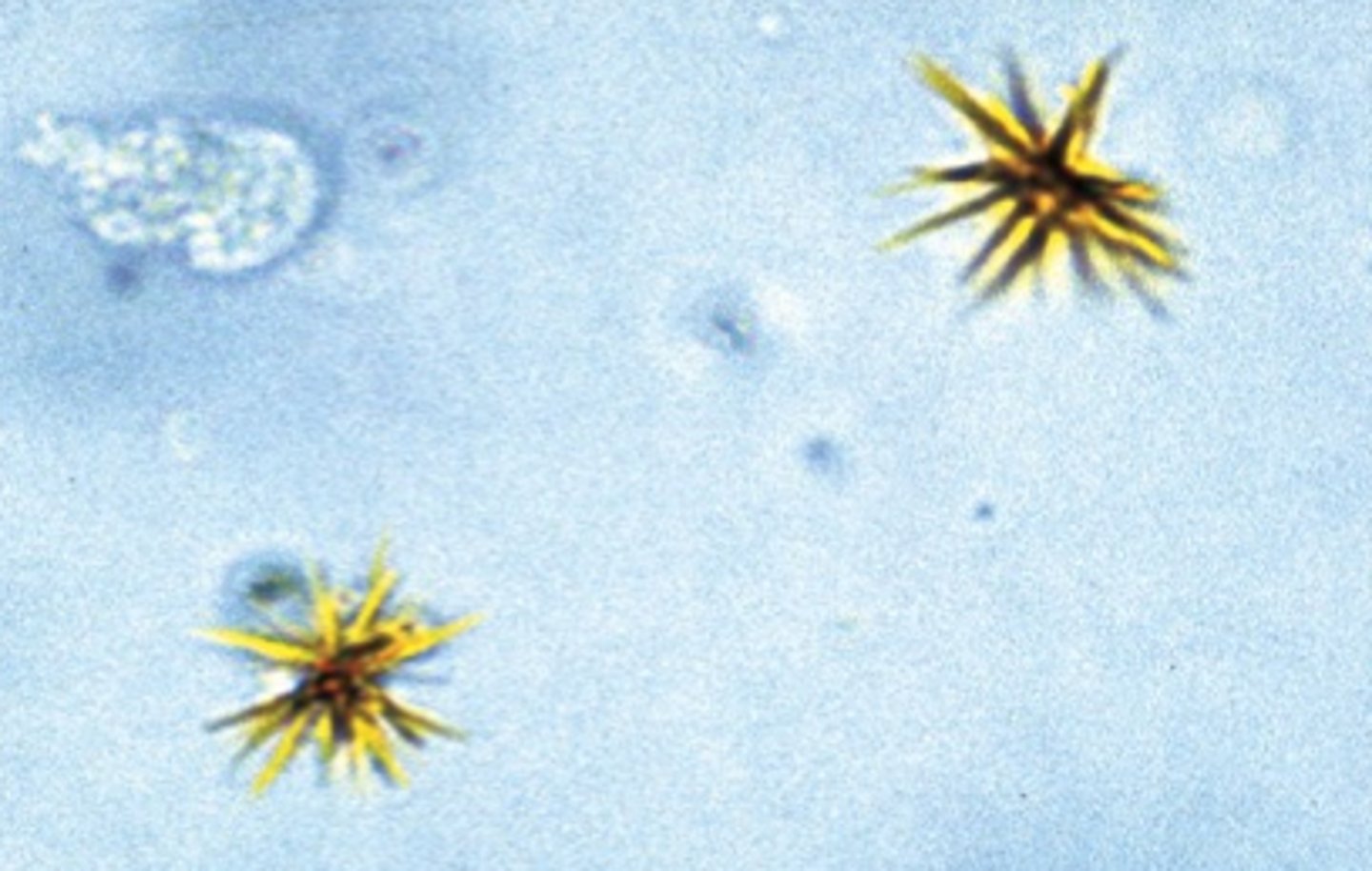
Abnormal Crystals: Liver disease
-Yellowish brown needles, plates, granules.
Bilirubin Crystals
-Chemical tests for bilirubin should
be pos.
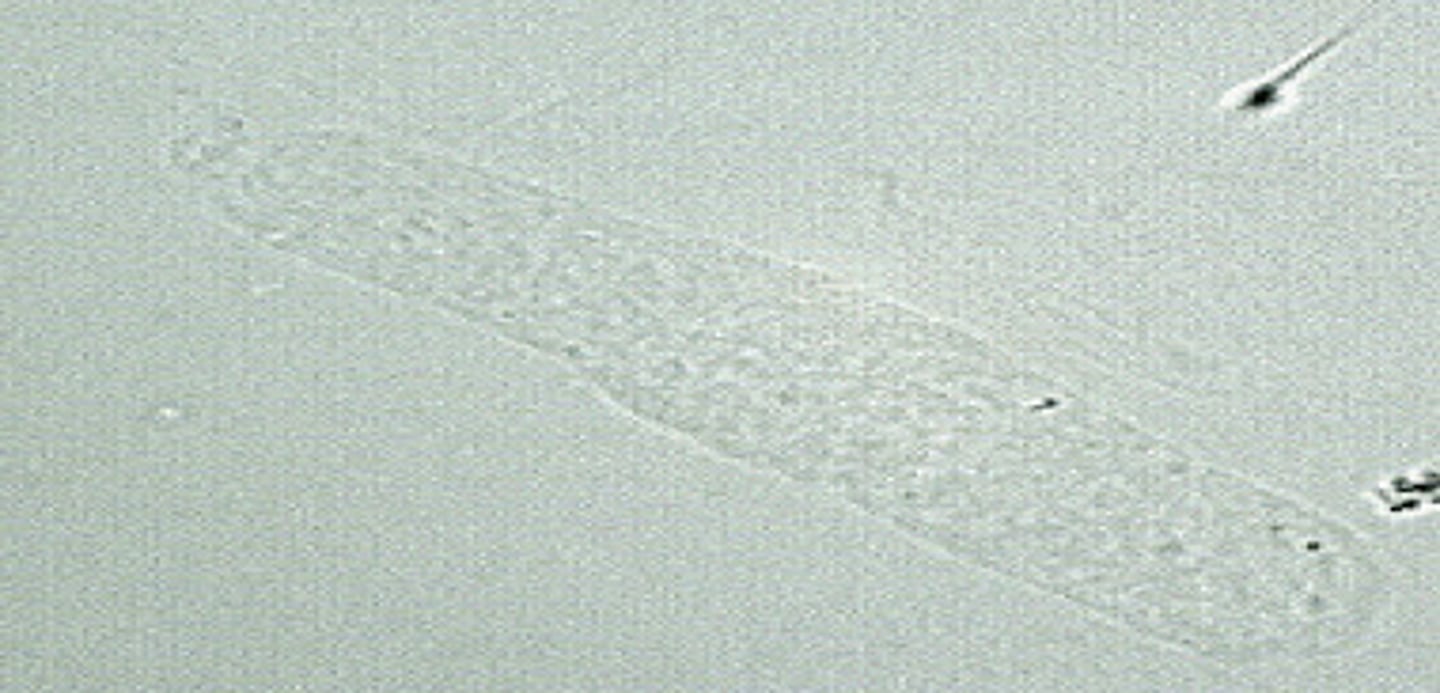
What type of Cast?
Normal: 0-2/LPF.
↑ with stress, fever, trauma, exercise, renal disease
Hyaline Cast
Most common type. Least significant.
Tamm-Horsfall protein only.
Dissolve in alk urine. Same refractive index as urine; may be overlooked with bright light

What type of Cast?
Normal: 0-1/LPF.
↑ with stress, exercise, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis
Granular Cast
-From disintegration of cellular casts.
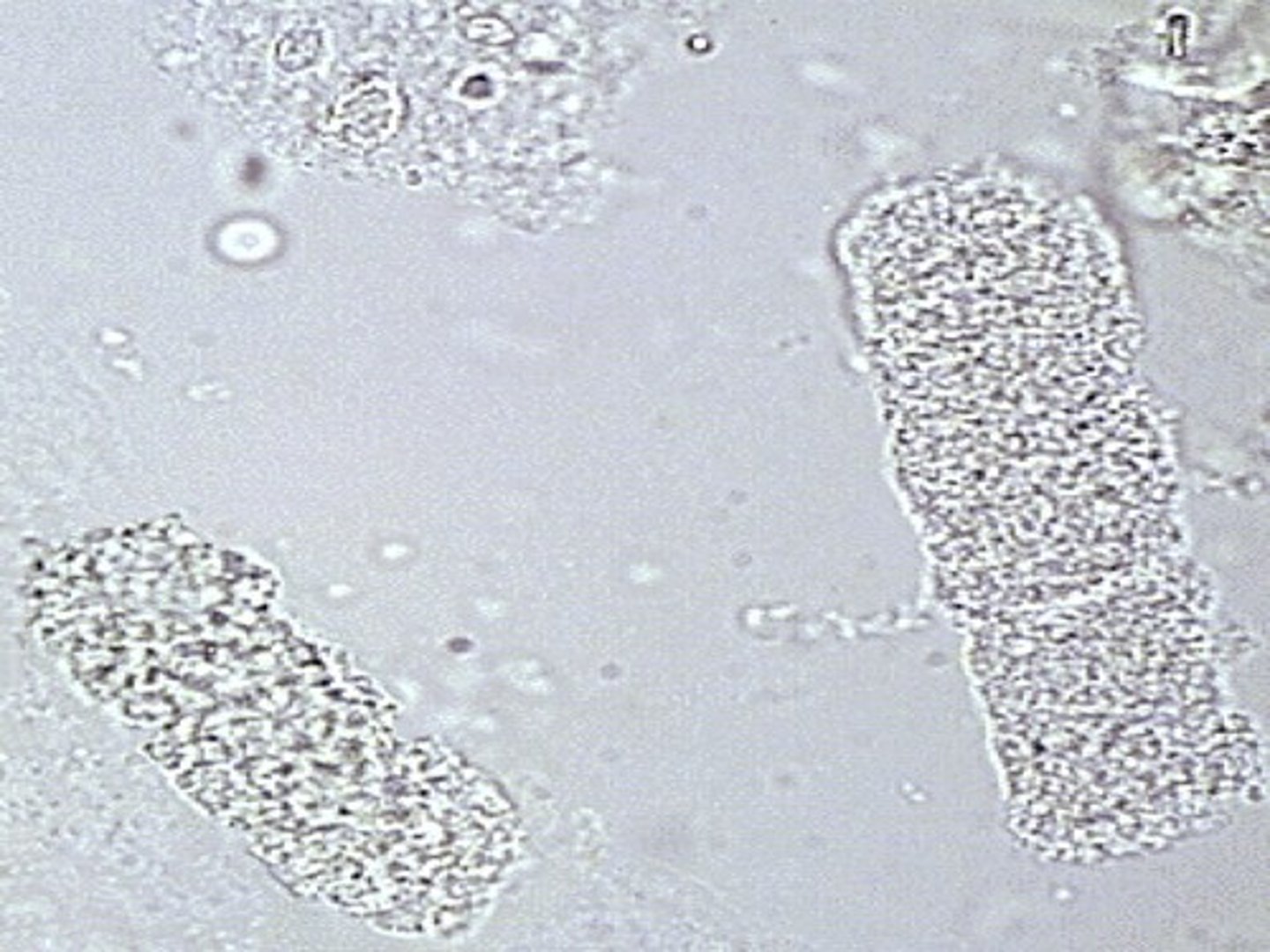
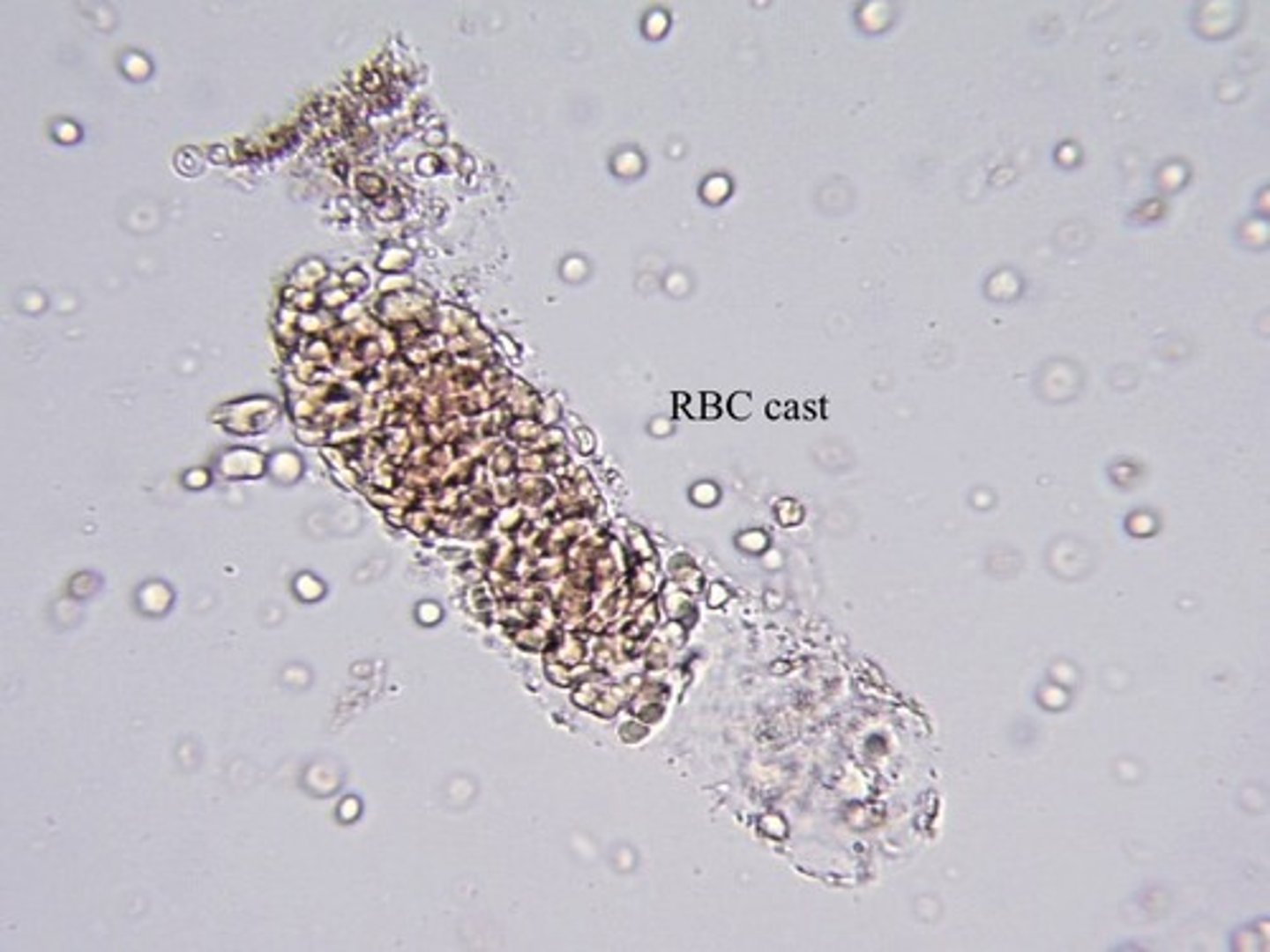
What type of Cast?
Acute glomerulonephritis, strenuous exercise.
RBC Cast
-IDs kidneys as a source of bleeding.
Most fragile cast.
Often in fragments.
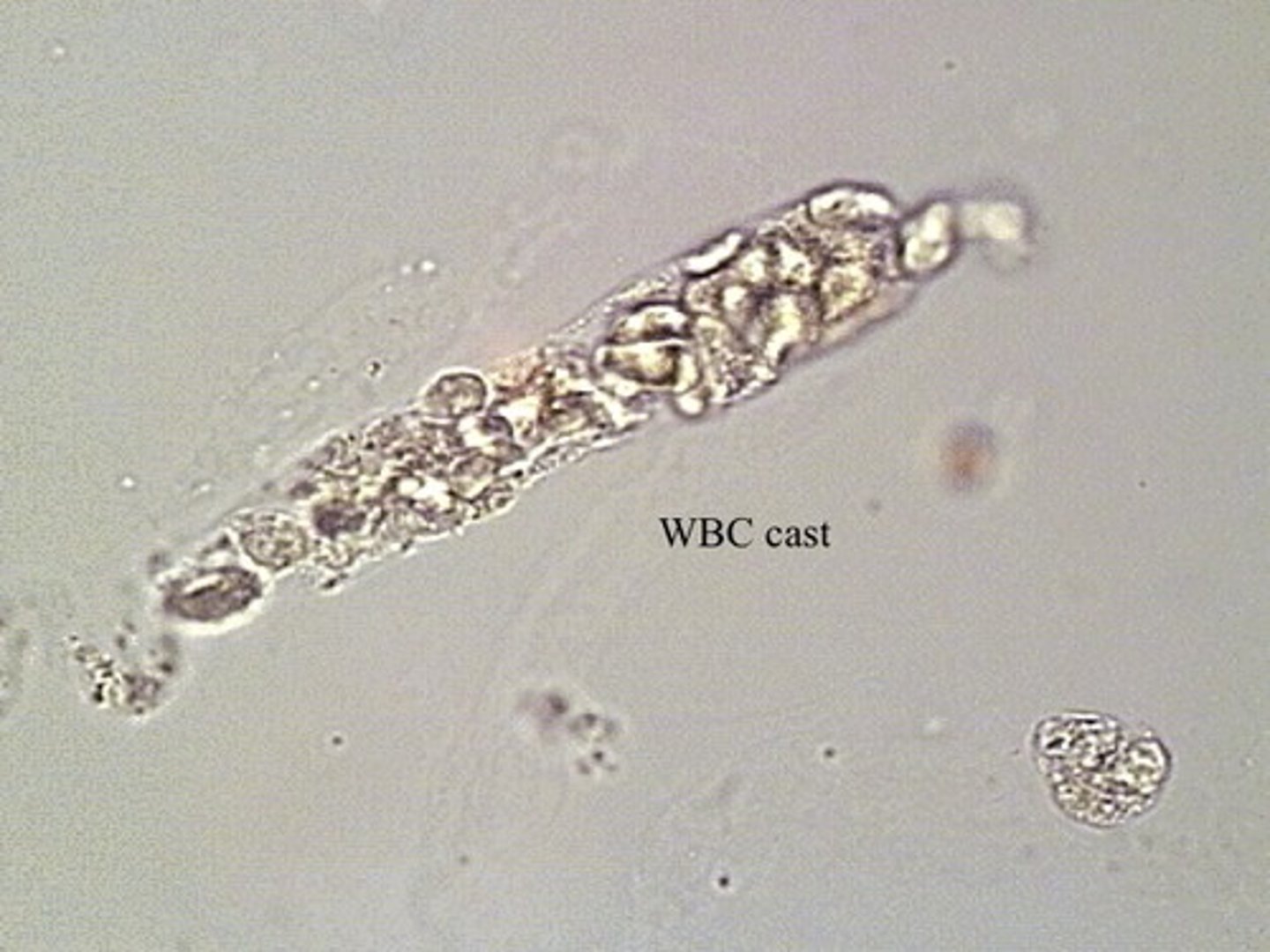
What type of Cast?
Pyelonephritis.
WBC Cast
-IDs kidneys as site of infection-
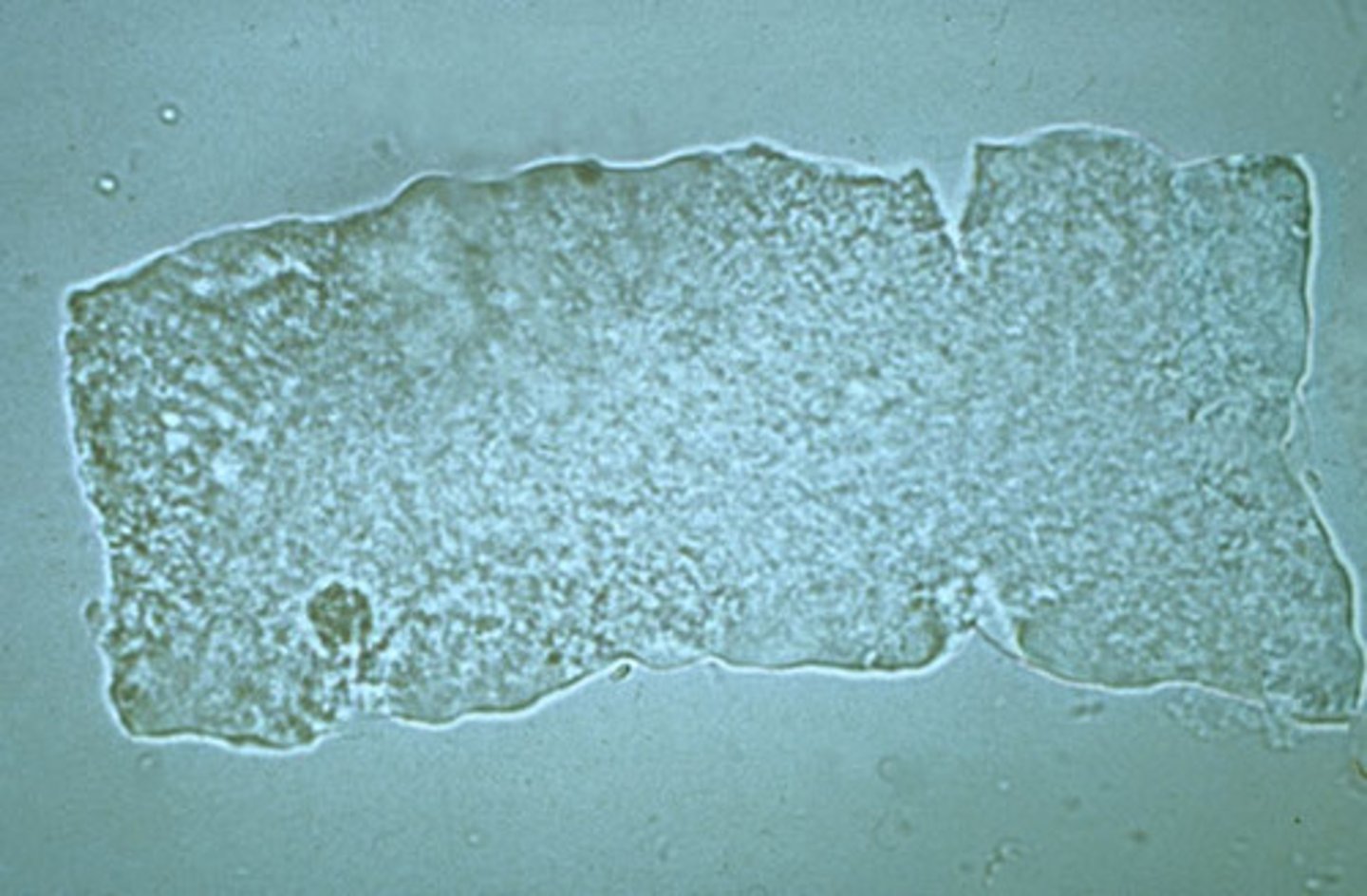
What type of Cast?
Urinary stasis
Waxy Cast
-From degeneration of cellular & granular casts.
Unfavorable sign.
What type of Cast?
Nephrotic syndrome.
Fatty Cast
-Maltese crosses with polarized light if
lipid is cholesterol.
-Sudan III & Oil Red O stain triglycerides & neutral fats
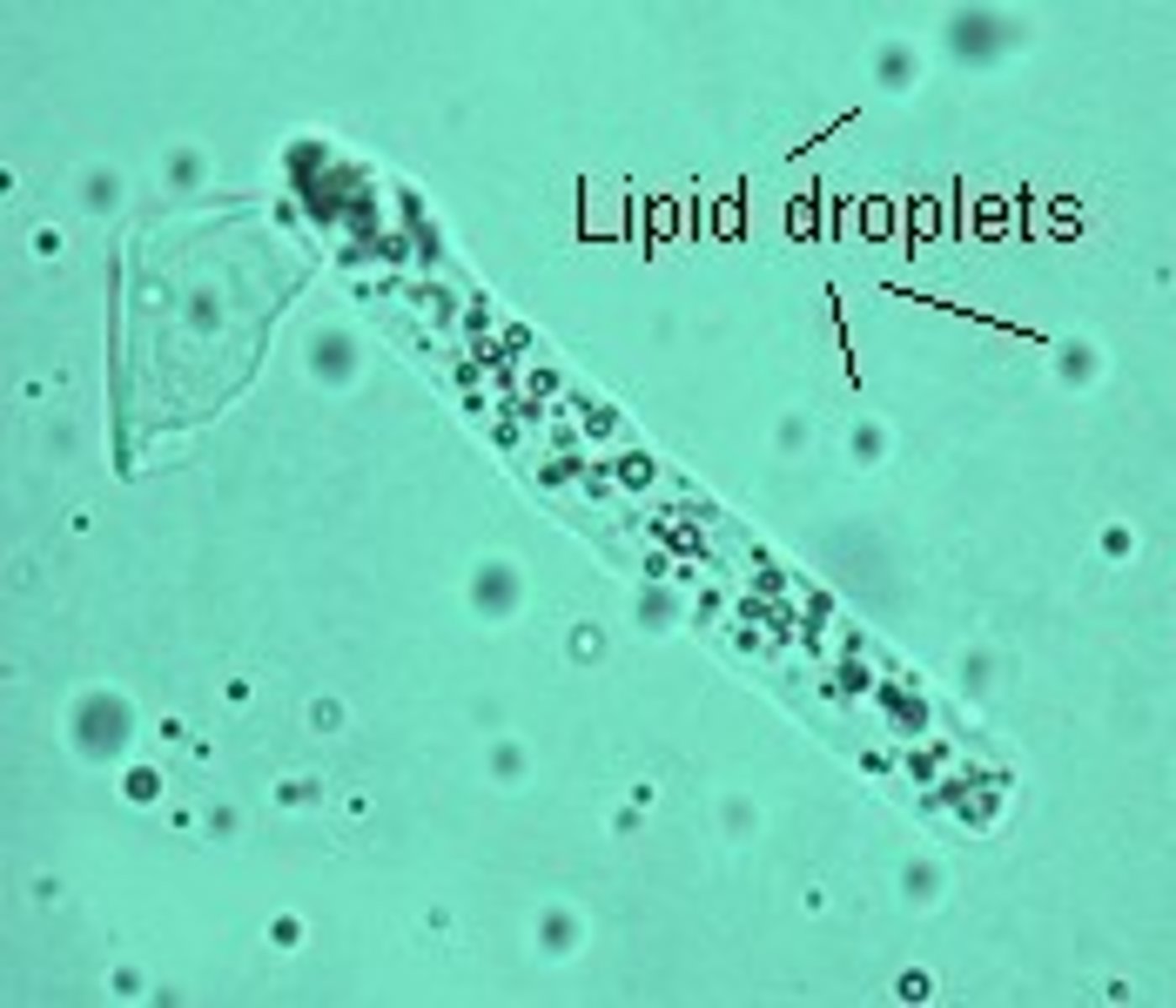
What type of Cast?
Advanced renal disease
Broad Cast
-Formed in dilated distal tubules & collecting
ducts. "Renal failure casts."
Renal Disorder:
-Inflammation & damage to glomeruli
-Frequently follows untreated group A strep infection
Acute glomerulonephritis
Renal Disorder:
Increased glomerular permeability
-Hypoproteinemia, hyperlipidemia
Nephrotic Syndrome
Renal Disorder:
Kidney infection
Pyelonephritis
Renal Disorder:
Bladder infection
Cystitis
CSF Color:
slight pink, orange, or yellow due to oxyhemoglobin or bilirubin.
Seen with subarachnoidhemorrhage
Xanthochromia